The global hydrogen buses market size was valued at USD 1.81 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 48.52 billion by 2034, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 49.10% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The hydrogen buses market is expanding significantly owing to increasing government mandates for zero-emission transportation, rising investment in green hydrogen infrastructure, and growing urban air pollution concerns. Advancements in fuel cell technology and long-range, fast-refueling capabilities also make hydrogen buses an attractive alternative to battery-electric models for heavy-duty and long-route operations.
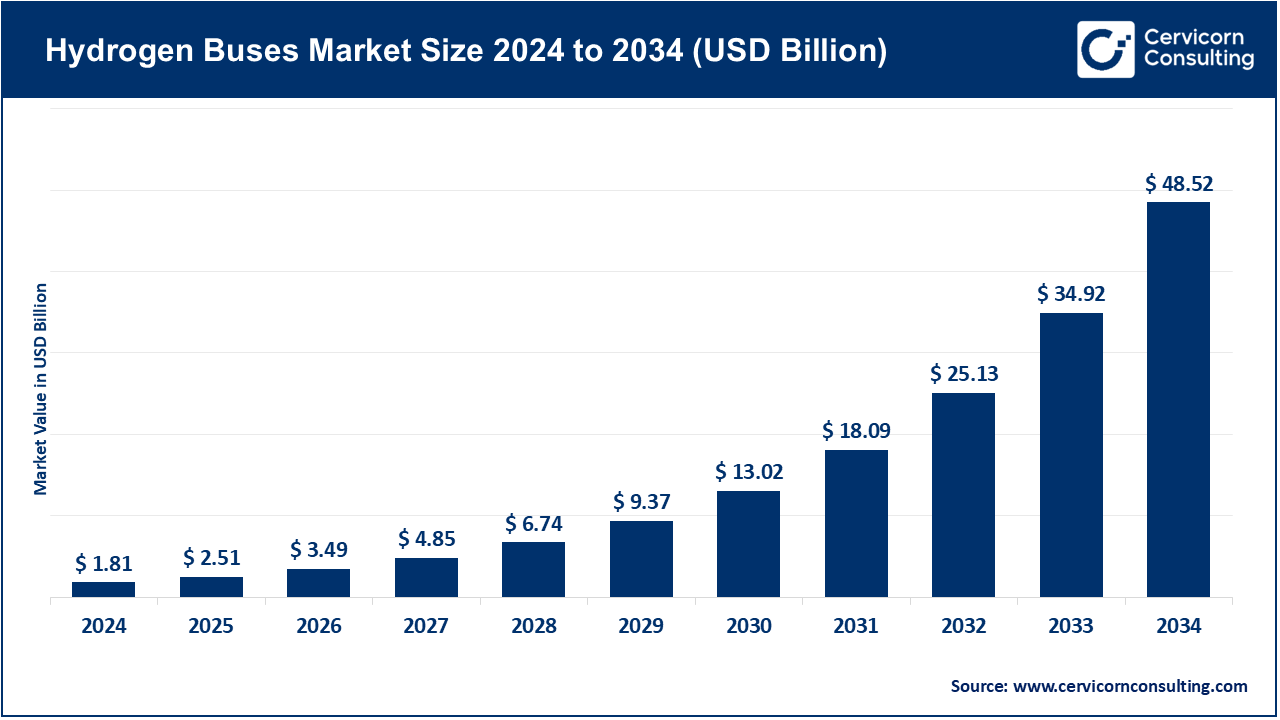
The hydrogen buses market is expected to grow significantly owing to advancements in hydrogen fuel cell technology, and rising demand for sustainable public mobility solutions. Countries are investing heavily in green hydrogen infrastructure and offering subsidies to transit agencies adopting fuel cell buses. Moreover, reduced refueling time and extended driving range compared to battery-electric alternatives make hydrogen buses ideal for long-haul and high-frequency urban routes, accelerating their adoption globally.
Currently, hydrogen buses are utilized for both commercial and travel purposes. These buses operate both within and between cities and offer numerous environmental advantages due to their quick refueling system, high energy efficiency, zero emissions, and non-polluting nature. Furthermore, compared to diesel buses, it offers greater safety and less reliance on oil. These buses offer a smoother ride and more amenities for the comfort of the driver and passengers.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 2.51 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 48.52 Billion |
| Estimated CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 49.10% |
| Leading Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Fuel Type, Bus Type, Propulsion Type, Manufacturing Type, Application, Power Output, Technology, Region |
| Key Companies | Hyundai Motor Company, Wrightbus, ITM Power, Chart Industries, Shell, Van Hool, Nel Hydrogen, Plug Power, Proton Motor Power System, Toyota Motor Corporation, Daimler Truck AG, Cummins, AFC Energy, Ballard Power Systems, Air Liquide |
The hydrogen buses market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region.
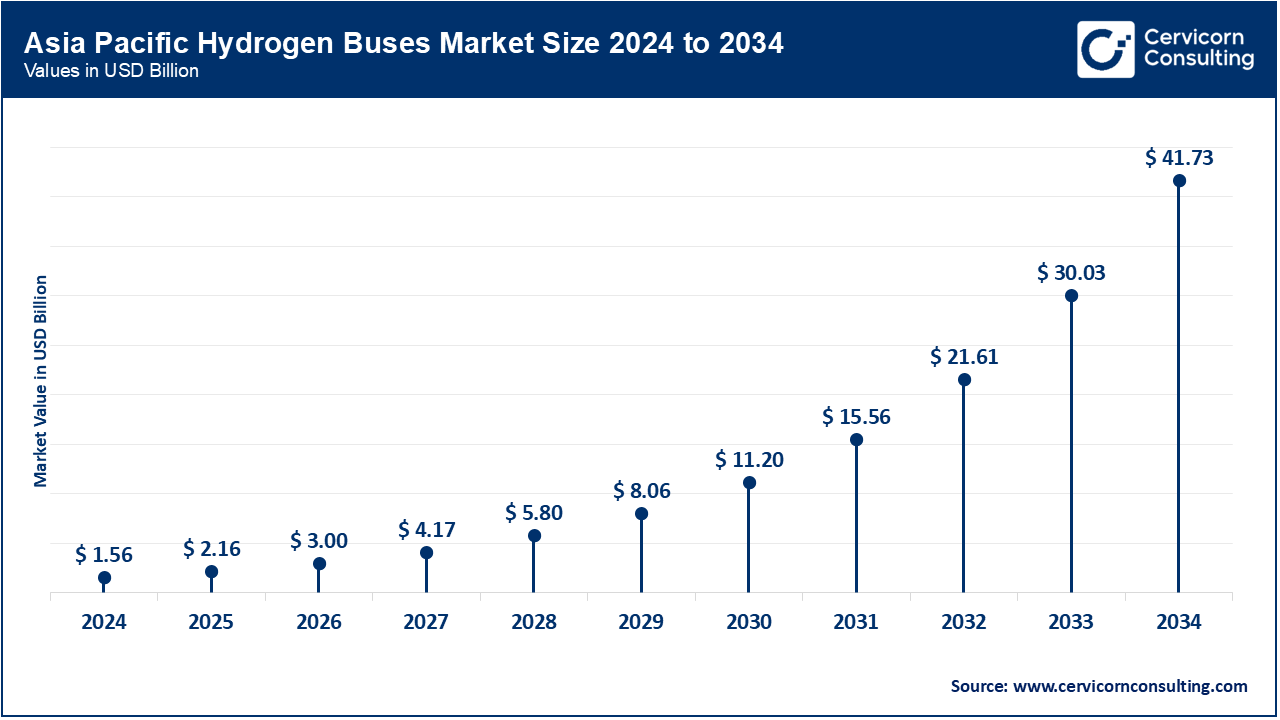
The Asia-Pacific hydrogen buses market size was estimated at USD 1.56 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 41.73 billion by 2034. The Asia-Pacific region leads in the adoption of hydrogen-powered buses, with China, Japan, and South Korea as dominant players. China alone has implemented thousands of units with government incentives and “Hydrogen City” pilot programs, with Foton, Yutong, and CRRC leading FCEV bus production. Both Japan and South Korea are southward on an FCEV roadmap through 2040, endorsing clean transport through manufacturers like Toyota and Hyundai. Governments in these countries strongly support local hydrogen production, which, paired with rising urbanization, is accelerating market maturation.
The adoption of hydrogen buses is being accelerated in North America due to California’s Zero-Emission Bus Mandate, as well as the fostering of green hydrogen infrastructure. New Flyer and Ballard Power’s partnerships with the FTA continue to bolster U.S. deployments, which are already leading the way. There is also increasing investment in hydrogen mobility pilots in Canada, most notably in British Columbia and Alberta, which seek to utilize homegrown hydrogen and transition to clean fleets.
Europe and other parts of the world such as Germany, France, Netherlands, and the UK remain leaders for the implementation of hydrogen fueled buses into service after aggressive decarbonization targets, receiving funding from the European Union under JIVE & H2Bus to further support the objectives. The region is also benefitted by the expansion of hydrogen supply chains and the availability of green hydrogen subsidies along with cross-border collaborations. These advancements are made possible by OEMs such as Solaris, Van Hool, and Wrightbus, who on are focused on product innovation across city transit networks.
In the LAMEA, the latter regions are characterized by more advanced stages with ‘pilot’ projects for hydrogen fuel cell buses in Brazil, and South Africa. Other countries in Latin America are also investigating green hydrogen as a potential export and the use of eco-friendly transportation with foreign partnerships. The Middle East utilizes inexpensive hydrogen, while Africa focuses on rudimentary infrastructure. These regions may lack appeal as a small, currently less developed area, but they are poised for great advantage later, due to abundant renewable resources.
Green Hydrogen: Green hydrogen is produced via electrolysis using renewable sources like wind and solar. As the cleanest variant, it emits no carbon during production. In the hydrogen bus market, green hydrogen is being adopted more quickly due to alignment with climate mandates and net-zero goals. Governments and fleet operators want to procure green hydrogen to enable the sustainable decarbonization of public transport fleets. Green hydrogen’s large-scale adoption is hindered by high production costs and a limited electrolyzer capacity.
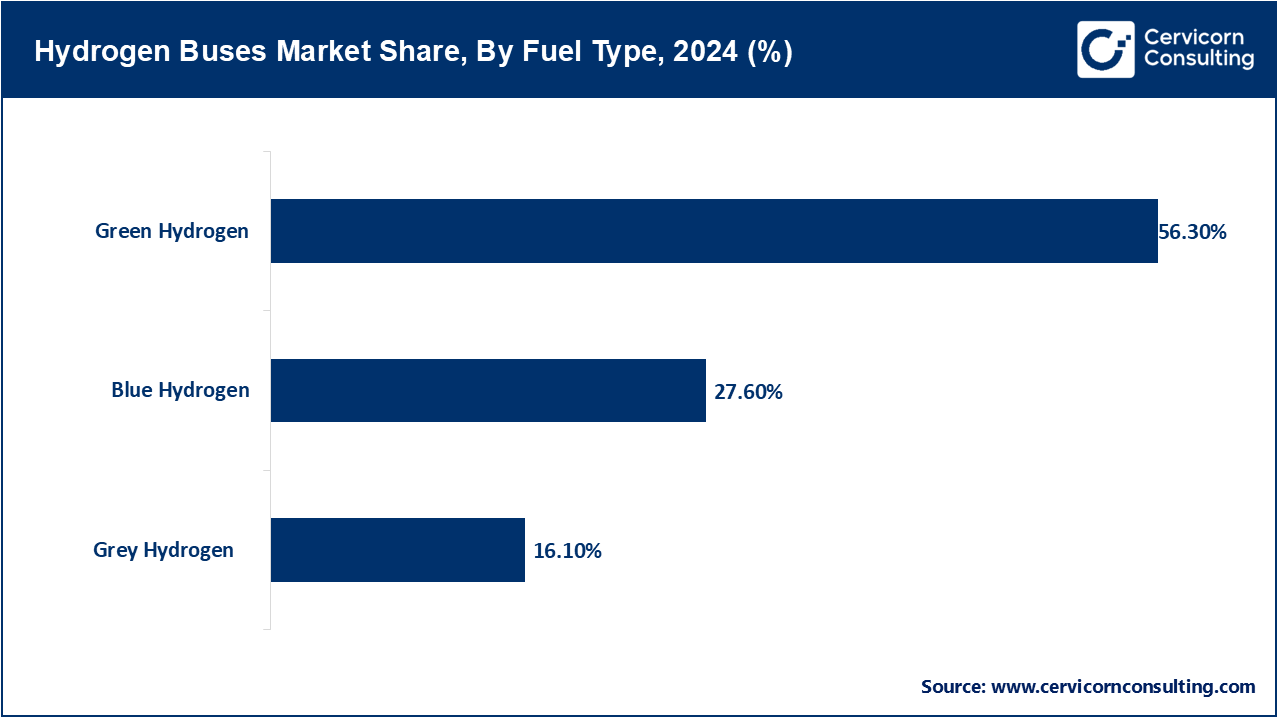
Blue Hydrogen: Produced from natural gas, blue hydrogen is created using steam methane reforming with CCS applied to reduce emissions. Where natural gas infrastructure is established, it serves as a transitional hydrogen source. Blue hydrogen will, in the near future, allow scaling up operations of hydrogen-powered buses while green hydrogen infrastructure is still in development. Blue hydrogen’s sustainability credentials are adversely impacted by methane leakage and concerns of incomplete carbon capture.
Grey Hydrogen: Hydrogen produced from fossil fuels without integrating carbon capture technology is known as grey hydrogen. It is also the most prevalent and least environmentally friendly form of hydrogen. In pilot programs for hydrogen fueled buses, grey hydrogen is often used as a stop-gap fuel where green or blue hydrogen is unavailable. While it lowers the upfront economic barrier to hydrogen adoption in transportation, it utterly negates long-term emissions reduction strategies baked into environmental transport policy.
Single-Decker Hydrogen Buses: The buses are fully low-floor buses widely used in intercity and intracity travel. They form the majority of fleets in hydrogen fuel cell bus systems in London, Cologne, and Tokyo. Single decker hydrogen buses are optimal in terms of cost effectiveness, passenger supply and demand, and routing flexibility. From an operational perspective, both the passengers and the bus stand to gain from improved efficiency. The lighter construction of these buses improves fuel efficiency and increases operational range.
Double Decker Hydrogen Buses: These buses have higher passenger capacity and serve high density and congested routes. They are common in space constrained cities like London and Seoul which are accustomed to vertical seating. Compared to single deckers, they are more expensive, but they offer higher fuel economy per passenger and reduce the required number of buses for a single route, thus improving the fleet economics of megacities.
Hydrogen Buses Market Share, By Bus Type, 2024 (%)
| Bus Type | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Single-Decker Hydrogen Buses | 37.20% |
| Double-Decker Hydrogen Buses | 15.30% |
| Fuel Cell Hybrid Buses | 26.10% |
| Battery Electric Hydrogen Buses | 21.40% |
Fuel Cell Hybrid Buses: The synergy achieved from implementing fuel cells and batteries together improves energy utilization on these buses. Fuel cells generate power, while batteries both store energy from regenerative braking and discharge during periods of peak demand. This configuration is particularly advantageous in mountainous regions or areas with undulating power demand as the energy efficiency, fuel economy, travel ranges, and power-to-fuel consumption ratios are significantly enhanced.
Battery Electric Hydrogen Buses: These buses operate mainly on electric batteries, but can use hydrogen systems to expand range or recharge during service. There is notable interest in combining both technologies due to the high requirement and low-emission downtime of some routes. While currently limited to pilot programs, clean hybrid transit systems hold promise.
Internal Combustion Engine (ICE): Hydrogen Internal Combustion Engine (HICE) buses make changes to burn hydrogen instead of diesel. While not as clean or efficient as fuel cells, hydrogen ICE buses maintain a more conventional drivetrain structure, offering transitional solutions. Their servicing complements established frameworks, aligning with existing systems, thus proving useful in budget-limited markets lacking fuel cell technology expertise.
Hydrogen Buses Market Share, By Propulsion Type, 2024 (%)
| Propulsion Type | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) | 62.30% |
| Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV) | 37.70% |
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV): FCEV buses have established a remarkable foothold in the market as they fully utilize hydrogen for electricity generation through a fuel cell which drives the electric motor. Their flawless operations allow them to be integrated into urban fleets: they have superb efficiency with no tailpipe emissions, operate quietly, and can be refueled in a matter of minutes. Continuous advancements in fuel cell technology and ongoing decreases in lifecycle costs further strengthen fuel cell electric buses as the best long-term supported as hydrogen mobility elevates.
Public Transportation: Hydrogen buses are especially suited for public transportation in large metropolitan areas seeking to eliminate carbon emissions. Their adoption is being piloted by municipalities in Europe, North America, and Asia as part of national clean mobility programs. As in most cases, public transportation receives the most generous government funding and regulatory assistance for the adoption of zero-emission vehicles.
Private Transportation: Private fleet operators, including shuttle services and private intercity carriers, are exploring hydrogen buses for their operational range and low environmental impact. Though adoption is slower due to high upfront costs, rising ESG mandates and client preferences for sustainable travel are creating new demand in corporate and commercial transit sectors.
Hydrogen Buses Market Share, By Application, 2024 (%)
| Application | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Public Transportation | 43.10% |
| Private Transportation | 19.20% |
| School Transportation | 10.40% |
| Tourism and Airport Transportation | 27.30% |
School Transportation: Hydrogen-powered buses provide an environmentally friendly alternative to diesel-powered school buses, especially in places deeply concerned with children's health from pollutant exposure. In the U.S., California is testing hydrogen-fueled buses in schools where a dedicated refueling facility is available. Even though this area is developing, it could advance rapidly because of the increased adoption resulting from government funding. This segment is still nascent; however, the availability of government funding could enhance adoption.
Transportation for Tourism and Airports: For their sightseeing and terminal shuttle services, airport and tourism operators are now using hydrogen buses which are silent and have quick refueling with no emissions. Some countries like Japan and Netherlands have included hydrogen buses with airport shuttle services as part of wider sustainable airport programs. The promotional public relations advantages also aid in increasing public acceptance of hydrogen technology.
Below 100 kW: Hydrogen buses with power output below 100 kW serve light-duty or short-distance intra-city shuttles and campus transit buses. Their lower passenger capacity and lighter build improves energy usage. While cost-efficient and easier to maintain, their limited range and power makes them poorly suited for longer, heavier routes. Such vehicles are used in small towns and airports, or in areas where hydrogen infrastructure is insufficient, such as in the pilot projects for low emission zones.
100-200 kW: The majority of commercially available hydrogen-powered buses have their systems set to a power range of 100-200 kW. This range maximizes fuel economy alongside line-haul capability. These buses operate within the metropolitan and suburban public transport systems. This category includes most 12-meter hydrogen buses from Hyundai, Toyota, Van Hool and many others. Buses operating within this power range are able to cover a daily distance of 300-400 km, which suits densely populated urban areas that require moderate speed and acceleration.
Hydrogen Buses Market Share, By Power Output, 2024 (%)
| Power Output | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Below 100kW | 23.60% |
| 100-200kW | 44.30% |
| Above 200kW | 32.10% |
Above 200kW: Hydrogen-powered articulated and double-decker buses are employed on intercity routes and in megacities that require more than 200 kW of power. These buses maintain excellent available power, ensuring reliable performance in mountainous terrain and extreme weather conditions, as well as under full load, heavy stress, and harsh conditions. However, articulated and double-decker buses have higher consumption due to extra fuel cell system costs, complex hydrogen storage requirements, and advanced storage systems which limits their use to well-funded ecosystems.
Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC): Within the hydrogen fuel cell industry, PEMFCs stand out as the most commonly adopted technology for buses due to their small size, ability to quickly start, and high power output. PEMFCs are also quite effective at lower temperatures, working efficiently at approximately 80°C. Moreover, they are ideal for urban buses that operate in stop-and-go cycles. Major hydrogen bus original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) such as Toyota and Hyundai have integrated PEMFCs into their fleets. Its scalability, responsiveness, and commercial maturity make it the backbone of the hydrogen mobility sector.
Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC): Operating at extremely high temperatures, 600–1000°C, SOFCs have an advantage over PEMFCs with higher electrical efficiency. Their historical use in stationary power systems is being challenged by R&D for long-range transport applications due to their flexible fuel use. SOFCs might be useful for long-haul and intercity hydrogen fuel cell busses that have high energy requirements. However, due to the public facing “inactive” fleet operational issues like lengthy warm-up periods, high expenditures, and system overheating wear and tear, SOFCs are not useful for active public bus fleets.
Hydrogen Buses Market Share, By Technology, 2024 (%)
| Technology | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) | 48.50% |
| Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC) | 20.30% |
| Alkaline Fuel Cell (AFC) | 31.20% |
Alkaline Fuel Cells (AFC): Traditionally employed in aerospace applications, AFCs are one of the earliest types of fuel cells. They offer good economic efficiency “in certain controlled situations” but are very sensitive to CO2 pollution, making them impractical for use in vehicles such as hydrogen buses. Although research is focused on increasing CO2 tolerance and durability, they are still not commercially available for public hydrogen transport use and remain confined to niche or experimental applications.
Market Segmentation
By Fuel Type
By Bus Type
By Propulsion Type
By Manufacturing Type
By Application
By Power Output
By Technology
By Region