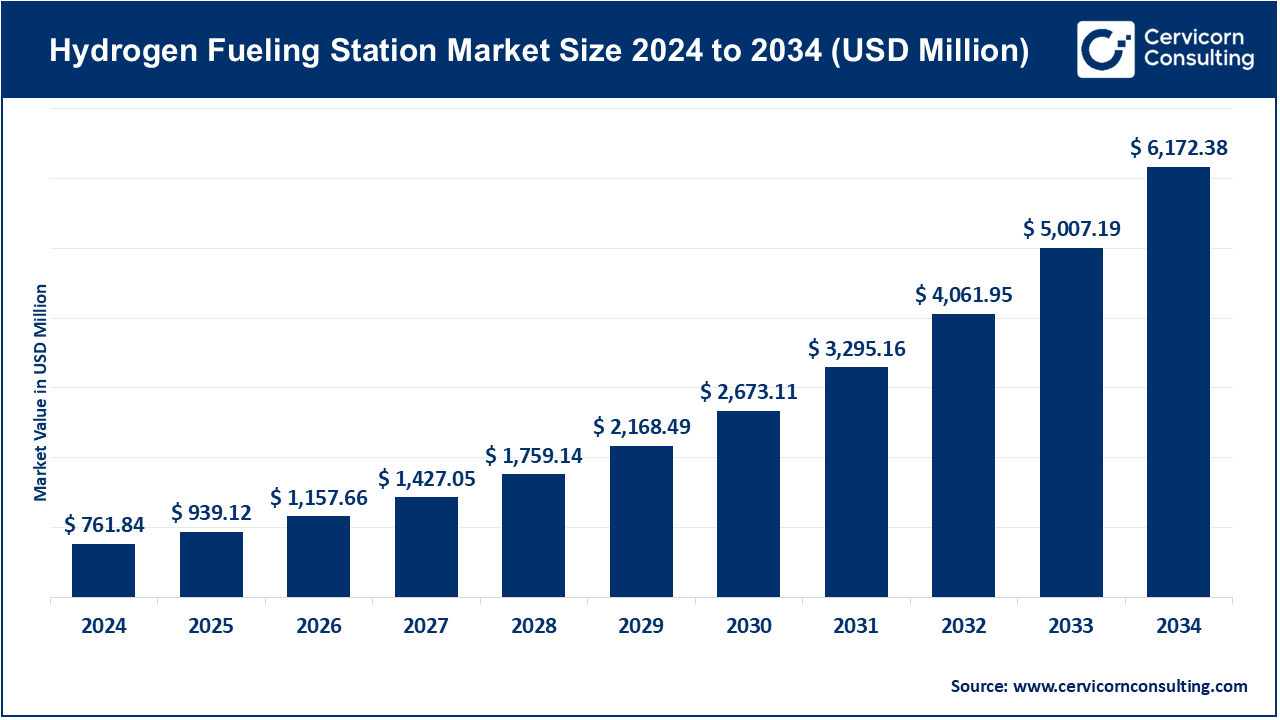
The global hydrogen fueling station market size was reached USD 761.84 million in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 6,172.38 million by 2034, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23.27% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
The hydrogen fueling station market is driven by a combination of government support, technological advancements, and rising demand for zero-emission vehicles. Across the globe, governments are setting tough emission standards and offering incentives for clean energy technology. The European Union, for instance, has committed to becoming carbon neutral by 2050 and has already made substantial investments in hydrogen technology. The U.S. government has also invested significantly in hydrogen infrastructure as part of its energy policy. All these efforts reduce cost barriers and stimulate private sector investment in constructing hydrogen fueling stations.
Technological advancements are also playing a crucial role in market expansion. Improvements in hydrogen production, storage, and dispensing technologies are making it more cost-effective and affordable, thus enhancing the competitiveness of hydrogen fuel. The increased adoption of fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) by major automakers such as Toyota, Hyundai, and Honda is also driving demand for hydrogen fueling infrastructure. As more people become aware of hydrogen's sustainability and cleanliness, consumer demand for FCEVs will grow, necessitating the expansion of hydrogen fueling stations to meet this new demand.
What is a Hydrogen Fueling Station?
Hydrogen fueling stations are set up to provide hydrogen gas for fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) and promote the use of clean energy in transportation. There are three types of hydrogen fueling stations: on-site production stations, where hydrogen is generated on-site at the station through processes such as electrolysis; off-site delivery stations, which are refilled with hydrogen produced elsewhere via pipelines or delivery trucks; and mobile stations, which are portable units that can be transported to various regions in need. In practical applications, hydrogen fueling stations provide fuel for a wide range of vehicles, including passenger cars, buses, trucks, forklifts, and even ships, serving industries such as public transportation, logistics, and industrial processes.
Key Insights and Developments in the Hydrogen Fueling Station Market
| Aspect | Insight |
| Station Types |
|
| Applications |
|
| Regional Developments |
|
| Technological Advancements |
|
| Challenges |
|
Shift Toward Heavy-Duty and Industrial Applications
While hydrogen-powered passenger vehicles have struggled due to limited infrastructure and high costs, there is a noticeable shift toward heavy-duty and industrial applications. Hydrogen fuel cells are increasingly utilized in trucks, ocean vessels, and heavy machinery, where centralized refueling infrastructure is more practical. For example, General Motors is investing in hydrogen fuel cells for heavy-duty trucks, and the Energy Observer, a hydrogen-powered ship, showcases renewable hydrogen power in decarbonizing shipping.
Development of Regional Hydrogen Hubs
Governments are investing in regional hydrogen hubs that consolidate production, storage, and distribution to support local economies and reduce emissions. In January 2025, the Port of Houston Authority received a USD 25 million grant from the U.S. Department of Transportation to create a hydrogen fueling station at Bayport, Texas. The project will introduce pipeline-based truck fueling and facilitate supply chain development in Texas and the Gulf Coast.
Technological Advancements in Hydrogen Infrastructure
Technological advancements in hydrogen production, storage, and dispensing technologies are enhancing efficiency and lowering costs. For instance, Air Liquide launched the SmartFuel® H70 hydrogen dispenser in 2024, capable of dispensing hydrogen at 700 bar pressure, which reduces refueling time for fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs). Additionally, Nel Hydrogen introduced the Nel Proton PEM electrolyzer series in 2023, achieving efficiencies above 80%, significantly decreasing the energy required for hydrogen production from renewable sources.
Collaborations Between Automakers to Advance Hydrogen Technology
Automakers are forming partnerships to tackle challenges in hydrogen technology. In September 2024, Toyota and BMW strengthened their collaboration on hydrogen fuel cell vehicles with a new memorandum of understanding to expedite the development of next-generation, zero-emission cars. BMW plans to introduce its first hydrogen-powered model in 2028. Their partnership aims to standardize components, reduce costs, and develop shared powertrains, along with establishing hydrogen fueling infrastructure.
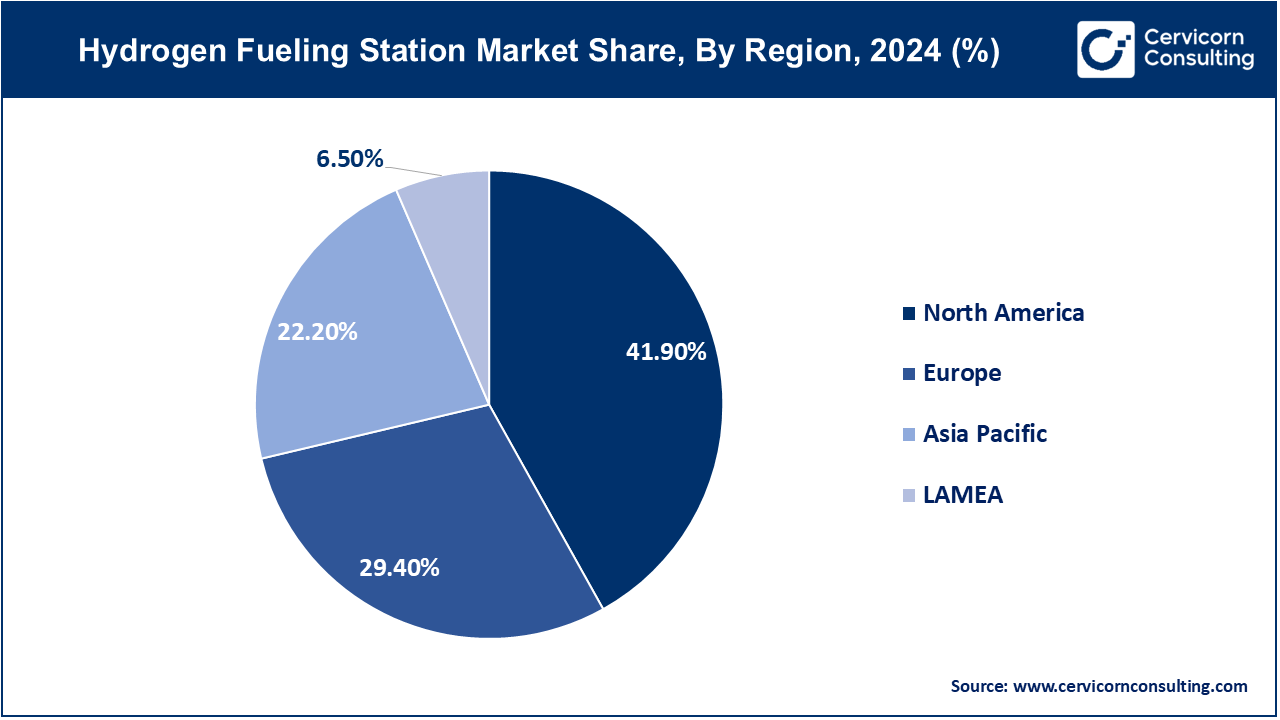
The hydrogen fueling station market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA.
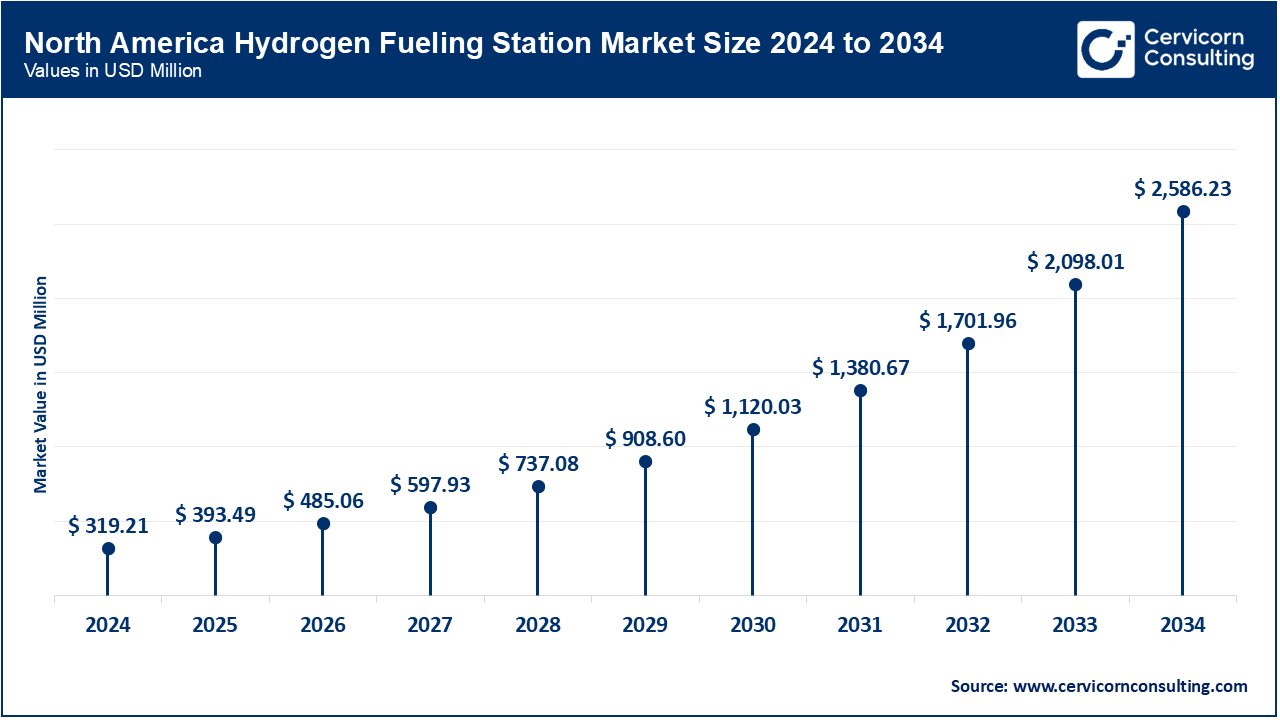
The North America hydrogen fueling station market size reached USD 319.21 million in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 2,586.23 million by 2034. North America is the leading region in the market, driven by strong government initiatives and increasing investments in clean energy infrastructure. The United States and Canada are focusing on hydrogen infrastructure development, with California leading the charge through a highly dense network of hydrogen stations for fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs). The region benefits from robust funding programs and public-private partnerships aimed at decarbonizing transportation, particularly for heavy-duty trucks and public transit fleets. Technological innovation and collaboration between automakers and energy companies are also propelling market growth.
The Asia-Pacific hydrogen fueling station market size reached USD 169.13 million in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 1,370.27 million by 2034. APAC is experiencing steady growth, mainly driven by the aggressive policies and substantial investments f countries like Japan, South Korea, China, and Australia. Japan's shift to hydrogen fuel cell cars and government-backed infrastructure plans have established a global benchmark. China is rapidly expanding its hydrogen fueling infrastructure to meet its ambitious carbon neutrality goals and the electrification of transportation, including buses and commercial vehicles. The region's strong government policies, combined with industrial and technological advancements, continue to solidify APAC's position as the world's fastest-growing market.
The Europe lobal hydrogen fueling station market size reached USD 223.98 million in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 1,814.68 million by 2034. Europe is witnessing significant momentum in hydrogen fueling infrastructure, driven by stringent emissions regulations and a strong commitment to green hydrogen production. Germany, France, and the Netherlands are making substantial investments in fixed hydrogen stations and hydrogen mobility to reduce carbon footprints in industry and transportation. The European Union's hydrogen strategy, based on renewable energy derived hydrogen, promotes the integration of electrolysis and refueling networks among member states. Cross-border collaboration is envisioned to develop a pan-European hydrogen corridor, facilitating cross-border transport and market development.
The LAMEA hydrogen fueling station market size reached USD 49.52 million in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 401.20 million by 2034. The Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (LAMEA) region is an emerging market, characterized by gradual adoption and pilot projects targeting public transport and industrial applications. Although infrastructure is in its infancy, countries such as Brazil, UAE, and South Africa are looking to hydrogen as a key element in their transition to clean energy strategies. The abundance of renewable energy resources, such as solar and wind, in the region presents a tremendous opportunity for the production of green hydrogen. Growing global investments and strategic partnerships are expected to foster growth in LAMEA over the next several years.
The hydrogen fueling station market is segmented into station size, supply type, pressure, station type, solution, and regions. Based on station size, the market is classified into large stations, mid-size stations, and small stations. Based on the supply type, the market is categorised into off-site (gas, and liquid) and on-site (electrolysis, and steam methane reforming (SMR)). Based on pressure, the market is categorised into high pressure and low pressure. Based on station type, the market is classified into mobile hydrogen stations and fixed hydrogen stations. Based on solution, the market is categorised into engineering procurement and construction (EPC) and components (dispensers, compressors, storage units, dispensing chiller systems, hydrogen inlets, hydraulic power units and controls, and others.
Small stations continue to dominate the market, largely due to cost efficiency, compact size, and suitability for early-phase deployment in urban and suburban areas. They are ideally suited for medium-traffic locations or where hydrogen infrastructure is being developed. Their lower installation and operation costs make them a preferred choice for governments and private investors experimenting with hydrogen refueling infrastructure. They also serve as proving grounds for new technology and are typically used to supply fleets of passenger fuel cell vehicles.
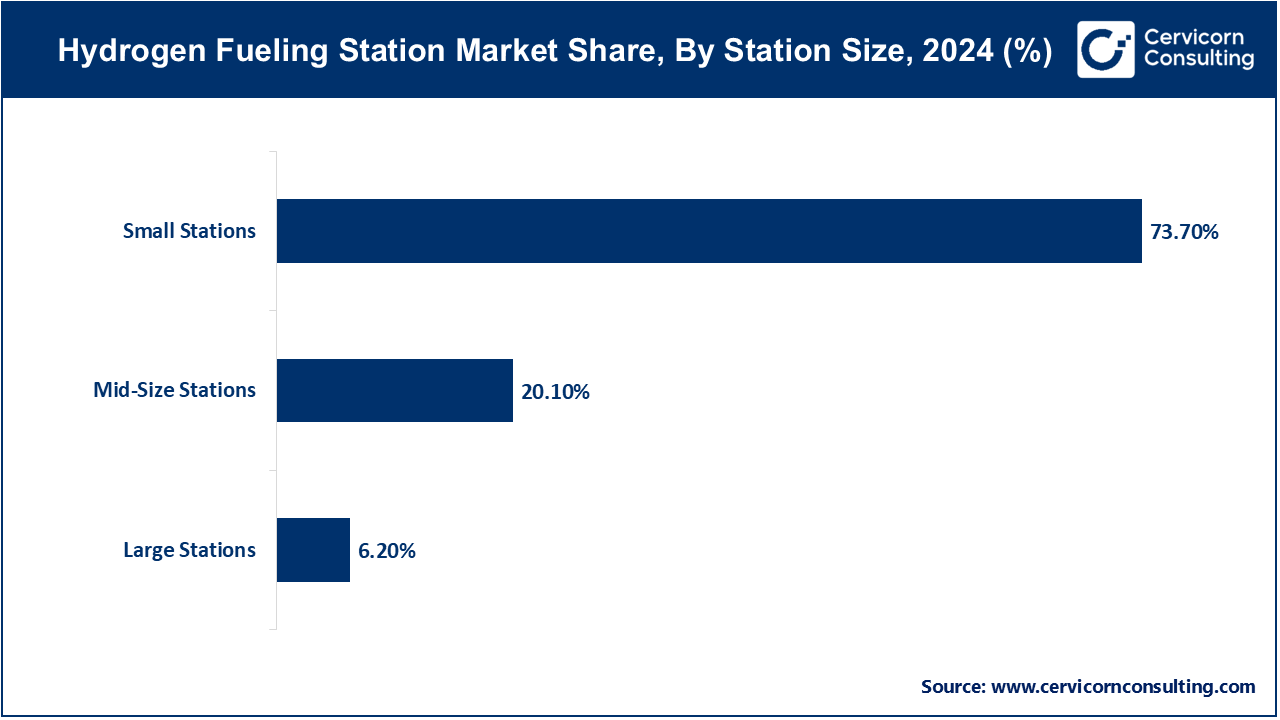
Large stations represent the fastest-growing segment, driven by increasing investment in heavy-duty transport and industrial applications. As hydrogen is increasingly utilized as a decarbonization solution for buses, trucks, and commercial fleets, the demand for high-capacity refueling stations has grown exponentially. Large stations are typically located in highway corridors and logistics hubs, where they refuel substantial quantities of fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) daily. Their capability to support rapid, high-throughput fueling makes them essential enablers of scaling hydrogen mobility solutions.
On-site supply methods currently dominate the market, particularly electrolysis and steam methane reforming (SMR), as these allow for in-place hydrogen production, eliminating the need for external supply chains. This arrangement is particularly attractive in regions with abundant renewable electricity or natural gas. In-situ stations also enable real-time hydrogen production, which is more flexible to operate and results in reduced transport emissions.
Off-site supply is emerging as the fastest-growing supply type, especially with the establishment of centralized hydrogen production plants and distribution networks. Gas and liquid hydrogen supplied from off-site facilities fuel filling stations in densely populated urban areas or intercity routes, where space limitations make on-site production challenging. These supply contracts rely on economies of scale and are particularly significant for rapidly expanding hydrogen supply in broader regions.
High-pressure stations remain the dominant standard in the industry due to their compatibility with 700-bar systems used in most commercial hydrogen vehicles. High-pressure stations facilitate the same speedy refueling as gasoline, which is critical for fleet management and customer convenience. High-pressure system technology and infrastructure are advanced and represent the best solution for both new and existing hydrogen vehicles.
Low-pressure stations are experiencing steady growth, particularly in specialized industrial or material handling applications where lower pressure is sufficient. These stations are easier and more cost-effective to install and are gaining interest in niche applications such as forklifts, stationary backup power, and warehouse operations. Their development is also supported by companies wishing to explore hydrogen's potential at a lower operational level.
Fixed hydrogen stations dominate the market as they provide permanent, scalable infrastructure essential for the long-term deployment of hydrogen vehicles. These stations are typically included in national and regional plans to establish a reliable refueling network. Their consistent presence and reliability are critical for building public confidence in hydrogen transportation.
Mobile hydrogen stations are expanding rapidly, offering flexible, temporary solutions for hydrogen refueling in remote or underserved locations. They are particularly useful during pilot programs or when assessing hydrogen vehicle viability in new regions. Their relocatable nature also makes them valuable during special events or for fleet operators that operate across different locations.
Hydrogen Fueling Station Market Revenue Share, By Station Type, 2024 (%)
| Station Type | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Fixed Hydrogen Stations | 60.2% |
| Mobile Hydrogen Stations | 39.8% |
Engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) services form the backbone of the hydrogen station market by providing turnkey solutions from design to execution. EPCs ensure that stations meet strict regulatory, safety, and performance standards, making them the most utilized service model, especially for public-private partnerships and major energy providers.
Component solutions, particularly dispensers, compressors, and storage units, are witnessing the fastest growth within the market. As more stations are constructed and older ones upgraded, the demand for high-quality, efficient components is on the rise. Continuous innovation in component technology—such as advanced cooling systems and smart control units—is driving this segment’s development and enhancing overall station performance.
The hydrogen fuel station market is characterized by the presence of global players, strategic partnerships, and increasing investments in research, development, and infrastructure. Industry leaders such as Air Liquide, Linde plc, Nel ASA, Plug Power Inc., and Toyota Tsusho are expanding aggressively through strategic partnerships, joint ventures, and government-sponsored projects. All participants are focusing on the development of turnkey hydrogen refueling solutions, station component upgrades, and the integration of renewable hydrogen production technologies. Competition is also intensifying with growing interest from energy companies, automakers, and new entrants looking to benefit from the global shift towards zero-emission mobility and clean fuel solutions.
Chart Industries
Air Liquide
Linde Engineering
FuelCell Energy, Inc.
Air Products and Chemicals, Inc.
Market Segmentation
By Station Size
By Supply Type
By Pressure
By Station Type
By Solution
By Region