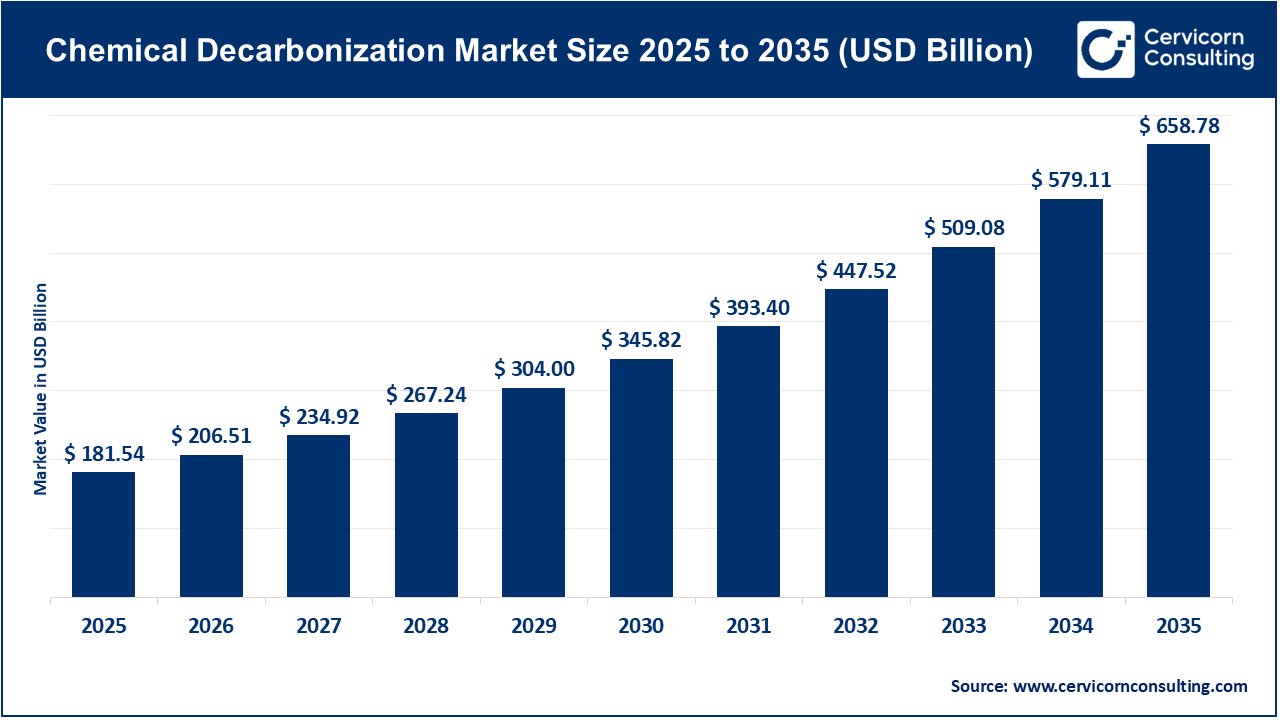
The global chemical decarbonization market size was valued at USD 181.54 billion in 2025 and is expected to be worth around USD 658.78 billion by 2035, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.8% over the forecast period from 2026 to 2035. The chemical decarbonization market is currently being driven primarily by solid regulatory pressure and climate commitments to decarbonize. Approximately 5 to 7% of global CO2 emissions originate from the chemical sector (the chemical industry), making the chemical industry one of the world's largest emitters of CO2 from industry. Regulatory bodies in the EU, the U.S., and Asia are implementing stricter carbon-pricing mechanisms, such as carbon emission caps and carbon reporting requirements. An example of the type of regulation being mandated is the EU Emission Trading Scheme (ETS), which has created substantially tighter guidelines on free allowances of CO2 for chemical producers. Because CO2 emissions are becoming progressively more expensive to produce, more than 70% of the major chemical producers worldwide have committed to net-zero or emission-reduction targets, thus accelerating investment in low-carbon technologies.
The chemical decarbonization market has also experienced rapid growth as a result of increasing demand from downstream industry sectors such as automotive, construction, and consumer products for more sustainable products. Brand owners have pressured their suppliers to reduce Scope 3 emissions that directly impact chemical manufacturers. Green hydrogen production costs have decreased by about 60% over the last decade, which has greatly improved the feasibility of producing low-carbon ammonia and methanol. Advancements in carbon capture, electrification, and digital process optimization will enable companies to continue to operate profitably and reduce emissions. The availability of public-funding programs and subsidies, including grants and tax credits related to industrial decarbonization, will support the large-scale deployment of the above-mentioned solutions.
Decarbonizing the Chemical Industry: A Critical Lever for Achieving Global Climate Targets
One of the more difficult industries to decarbonize is chemicals due to the large proportion of CO₂ generated by the industry coming from chemical processes and fossil raw materials, rather than from the production of energy. Globally, chemicals account for approximately 5-7% of all CO₂ emissions and the increasing level of demand for chemical products related to their vital functions in manufacturing, agriculture and consumer goods will continue to rise. A rapid reduction in CO₂ emissions from the production of chemicals is required to achieve national and corporate climate targets, which is consequently driving significant growth in the market for chemical decarbonization. The resulting demand for these technologies is pushing for widespread adoption of many innovative solutions (such as carbon capture and storage, green hydrogen, electrifying the production process, and replacing fossil feedstocks with low carbon alternatives) that address the emissions produced during the manufacturing process, which cannot be eliminated through traditional means of improving efficiency.
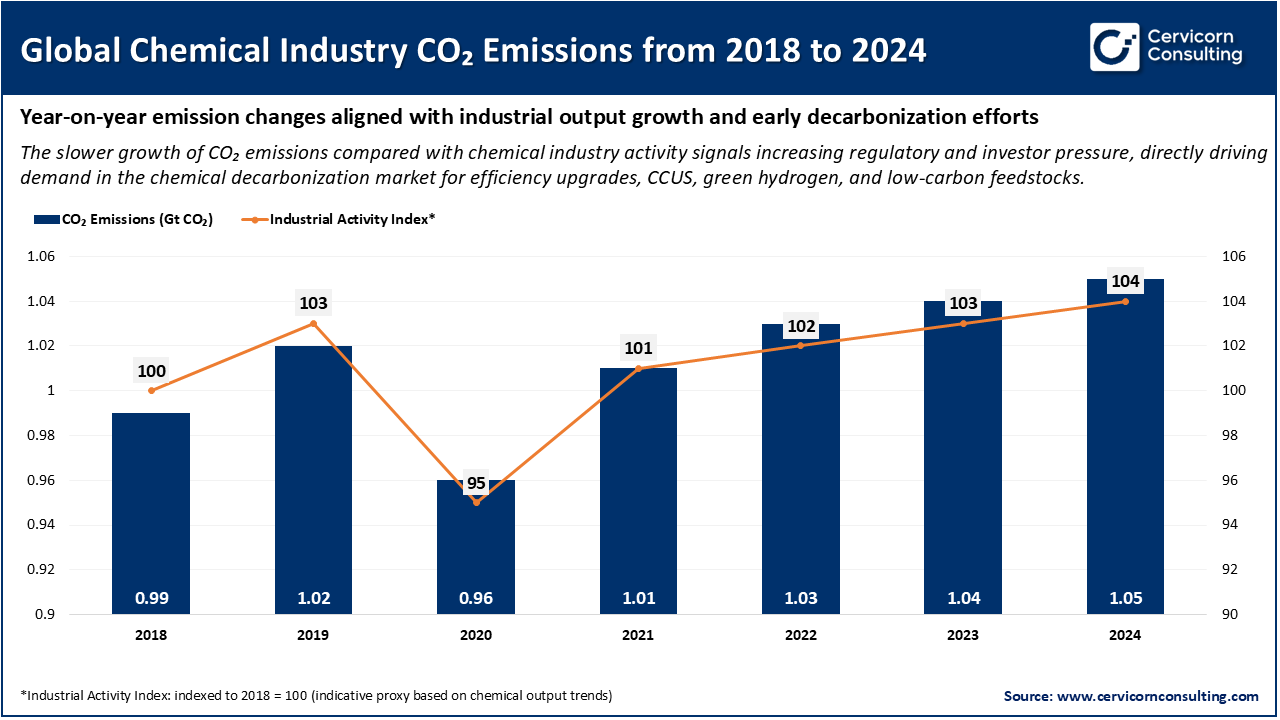
As illustrated in the graph, global CO2 emissions from chemical manufacturing fell sharply in 2020 due to COVID-19 disruptions, then rose steadily from 2021 through 2024 as industrial activity increased. CO2 emissions rose from approximately 0.96 to 1.05 Gt CO2 during this period. Over this same time frame, the industrial production index grew at a rate that exceeded CO2 emissions growth, indicating that production growth is becoming increasingly independent of emissions growth. This expanding gap signals the growing pressure on chemical manufacturers to decrease their CO2 emissions while continuing to grow their production capacity, which will ultimately fuel the chemical decarbonization market. Chemical producers are investing more in energy efficiency, carbon capture, green hydrogen and other forms of low-carbon feedstock to meet government regulations and ultimately achieve net-zero emissions while continuing to grow without proportionally increasing their CO2 emissions.
How the Chemical Industry Drives the Chemical Decarbonization Market
| Factor | Why It Matters | Impact on the Market |
| High share of global emissions | Chemical production emits 5-7% of global CO₂ | Forces targeted decarbonization investments |
| Process-based emissions | Emissions are embedded in chemistry, not just energy use | Increases demand for CCUS and alternative processes |
| Limited short-term substitutes | Core chemicals are essential to many industries | Supports long-term, stable demand for solutions |
| Net-zero commitments | Over 70% of large chemical firms have climate targets | Accelerates technology adoption and capex |
| Policy and carbon pricing | Rising cost of CO₂ in regulated markets | Improves economics of low-carbon technologies |
Germany EUR 6 billion Industrial Decarbonisation Program (2025) - includes CCS for chemicals
In October 2025, Germany announced an extensive program worth EUR 6 billion to fund industrial decarbonization and, for the very first time, to explicitly include Carbon Capture & Storage (CCS) technologies as part of this program. This includes support for heavy industries, such as chemicals, through financial subsidies and longer-term incentives to lessen the financial burden associated with the implementation of CCS and other forms of decarbonization technology for chemical producers. As a result, this lowers the barriers of entry to the market for chemical decarbonization and creates increased demand for carbon capture, utilization, and storage systems and decarbonization infrastructure, significantly increasing the size of the chemical decarbonization market.
India National CCUS R&D Roadmap 2025‑2070 - First national roadmap including chemical sector
The Indian government introduced its first dedicated CCUS Research and Development road map in December 2025. The CCUS R&D road map outlines government support (through the creation of supporting regulations and policies) for the development of CCUS technologies for hard-to-abate sectors, including chemicals. By creating a stable and supportive environment for the adoption of low-carbon technologies, India will be able to accelerate carbon decarbonization within its chemical sectors through increased research, investment, and collaboration between public and private sector organizations.
Technip Energies Wins Contract for Blue Ammonia Plant (2025)
Technip Energies received a contract to construct a low-carbon blue ammonia facility in Louisiana in April 2025. This facility will produce 1.4 million tonnes of blue ammonia annually. Blue ammonia is a fundamental building block for worldwide agricultural production and fertilizer manufacturing. The commercial success of this blue ammonia facility will serve as proof of the technical feasibility of producing low-carbon chemicals in large quantities. Other chemical producers will likely pursue similarly structured projects, thus enhancing the demand for hydrogen, the need for CCUS, and the necessity of producing the chemical industry's goods and services using low-carbon (clean) methodologies. All of these developments contribute to further development of the global chemical decarbonization market.
The chemical decarbonization market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. Here is a brief overview of each region:
The North America chemical decarbonization market size was estimated at USD 43.75 billion in 2025 and is estimated to attain around USD 158.77 billion by 2035. The North America is primarily fueled by government policies, tax breaks and extensive green hydrogen and CCUS project development. The U.S. Inflation Reduction Act provides a significant amount of tax credit for the production of clean hydrogen and carbon capture making it much easier to invest in the production of ammonia, methanol and other low-carbon chemical products. North America is leading in the deployment of blue ammonia due to the abundance of inexpensive natural gas, currently available export infrastructure and increasing demand for low-carbon fuels in Asia. Growing conferences and industry networks oriented around CCUS and industrial decarbonization allow for greater collaboration between technology developers and chemical manufacturers in accelerating the development of CCUS projects.
Recent Developments:
The Asia-Pacific chemical decarbonization market size was accounted for USD 58.82 billion in 2025 and is forecasted to hit around USD 213.44 billion by 2035. The Asia-Pacific region is being fueled by a combination of rapid industrial growth, increasing demand for fertilizers and petrochemicals, and government support for hydrogen and ammonia technologies. An increasing number of countries are positioning themselves as significant production centers for green ammonia, which offers the ability to decarbonize fertilizer production and serve as a low-carbon fuel or hydrogen carrier. In addition, the large energy needs of the Asia-Pacific Region and growing emphasis on energy security provide a significant long-term opportunity to develop low-carbon chemical production, which will be driven by government funding and partnerships with large chemical companies.
Recent Developments:
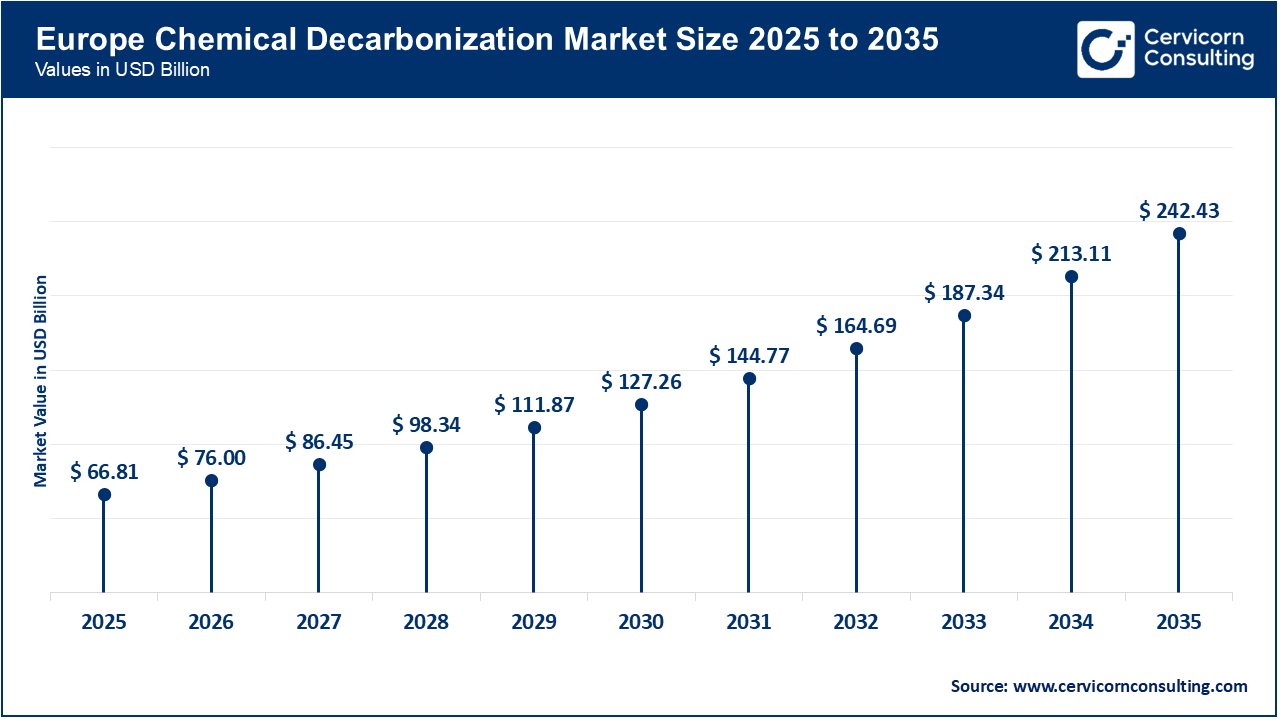
The Europe chemical decarbonization market size was reached at USD 66.81 billion in 2025 and is projected to surpass around USD 242.43 billion by 2035. The Europe is primarily influenced by the strict climate regulations and the EU Green Deal. The stringent greenhouse gas emissions prices and sustainability requirements force chemical manufacturers to make investments in low-carbon feedstocks, electric processing, and CCUS. In addition, the European Union (EU) is creating an extensive policy framework for hydrogen and other low-carbon-based fuels as well as clear greenhouse gas regulations for low-carbon hydrogen. As a result, the support of green and blue ammonia and methanol projects within the chemical value chain is expanding. European chemical manufacturers are developing innovative solutions that support green chemistry and promote circular use through the establishment of large-scale pilot facilities. Moreover, European chemical manufacturers continue to face high prices for energy inputs and global competitive pressures across the supply chain.
Recent Developments
Chemical Decarbonization Market Share, By Region, 2025 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2025 (%) |
| Europe | 36.8% |
| Asia-Pacific | 32.4% |
| North America | 24.1% |
| LAMEA | 6.7% |
The LAMEA chemical decarbonization market was valued at USD 12.16 billion in 2025 and is anticipated to reach around USD 44.14 billion by 2035. The LAMEA is driven by the continued ambitious aspirations of the Middle East to be the global hub of blue and green ammonia production with the assistance of cheap gas, solar resources, and the associated export infrastructure needed for both products. Gulf Coast nations are positioning themselves to serve as the primary supplier of low-carbon ammonia and hydrogen to Europe and Asia, thereby directly linking to the decarbonization of fertilizer and other chemical supply chains. Large-scale CCUS projects are planned or in progress in conjunction with existing petrochemical facilities. The emergence of a number of Latin American and African nations is beginning to develop green hydrogen and ammonia production facilities through the development of abundant renewable energy sources.
Recent Developments:
The chemical decarbonization market is segmented into type, application, end user, and region.
Energy efficiency solutions represent the vast majority of the chemical decarbonization market because they provide the chemical industry with significant and nearly immediate reductions in GHG emissions, as well as cost savings compared to other decarbonization alternatives. In addition, these technologies can be readily deployed by chemical manufacturers with little disruption to their existing operations and facilities. Energy efficiency solutions continue to be successfully implemented in both developed and developing countries.
Chemical Decarbonization Market Share, By Type, 2025 (%)
| Type | Revenue Share, 2025 (%) |
| Energy Efficiency Solutions | 22.6% |
| Carbon Capture, Utilization & Storage (CCUS) | 18.9% |
| Renewable Energy Integration | 14.7% |
| Green Hydrogen Solutions | 12.4% |
| Low-Carbon Feedstocks | 9.8% |
| Process Electrification | 8.3% |
| Digital Decarbonization & Energy Management | 6.1% |
| Catalyst & Process Optimization | 4.2% |
| Waste Heat Recovery Systems | 2.3% |
| Others | 0.7% |
Green hydrogen solutions are currently the fastest-growing type of technology as chemical producers attempt to transition away from using fossil fuel-based hydrogen and hydrogen derived from fossil fuels. The use of green hydrogen is essential in the development of ammonia, methanol, and other refining processes. As the cost of renewable energy continues to decline and governments around the world increase their support for large-scale hydrogen projects, many producers are entering the market and increasing the growth rate of green hydrogen solutions in the chemical industry.
The ammonia and fertilizer production segments are currently the largest in terms of emissions produced per unit quantity produced (emission intensity) and total volume of production. Ammonia currently contributes a large percentage of the total emission from the chemical industry, thus being one of the highest targets for carbon reduction strategies. Because of continued food security, manufacturers are investing significantly into producing lower carbon ammonia and developing cleaner processes for producing these products.
Chemical Decarbonization Market Share, By Application, 2025 (%)
| Application | Revenue Share, 2025 (%) |
| Ammonia & Fertilizer Production | 26.9% |
| Petrochemical & Polymer Production | 21.4% |
| Refining & Chemical Intermediates | 14.2% |
| Methanol & Synthetic Fuels | 11.6% |
| Specialty Chemicals Manufacturing | 9.7% |
| Basic Inorganic Chemicals | 7.2% |
| Chemical Recycling & Circular Chemicals | 6.1% |
| Chlor-Alkali Production | 2.1% |
| Others | 0.8% |
The chemical recycling & circular chemicals segment is projected to be the fastest-growing application segment. The primary driver for increased growth in the demand for chemical recycling (and by extension circular chemicals) comes from sectors that utilize recycled or low-carbon materials in their manufacturing processes (e.g., packaging, automotive, consumer goods). As a result, chemical manufacturers are compelled to invest in new technologies that facilitate recovery of residuals, thereby reducing emissions from feedstock use while assisting the chemical industry in achieving its goals related to the circular economy.
Integrated chemical production will be the predominant segment of the end-user market due to the significant size and the diversified operations of integrated chemical production companies with higher access to capital compared to others in the market. Due to the higher level of regulatory pressure that integrated chemical production faces compared to the other subsegments, as well as the public commitment to reach net-zero goals from various governments, these companies will be early adopters of decarbonization technologies. The scale of integrated chemical production companies allows for the ability to substitute multiple solutions that can contribute to reducing carbon emissions, such as CCUS, electrification, and using low-carbon feedstocks.
Chemical Decarbonization Market Share, By End User, 2025 (%)
| End User | Revenue Share, 2025 (%) |
| Integrated Chemical Producers | 33.5% |
| Commodity Chemical Manufacturers | 19.8% |
| Fertilizer Producers | 17.6% |
| Petrochemical Companies | 14.9% |
| Specialty & Fine Chemical Manufacturers | 9.1% |
| Contract & Toll Chemical Manufacturers | 3.6% |
| Others | 1.5% |
Fertilizer producers are the fastest-growing end user group in the chemical decarbonization industry. Changes in regulatory requirements related to both the emission of greenhouse gases and the sustainability of agriculture have prompted fertilizer manufacturers to make efforts to lower their carbon footprint. Because of the rapid implementation of green hydrogen and carbon capture technologies, fertilizer manufacturers have initiated new projects to reduce their carbon footprint.
By Type
By Application
By End User
By Region