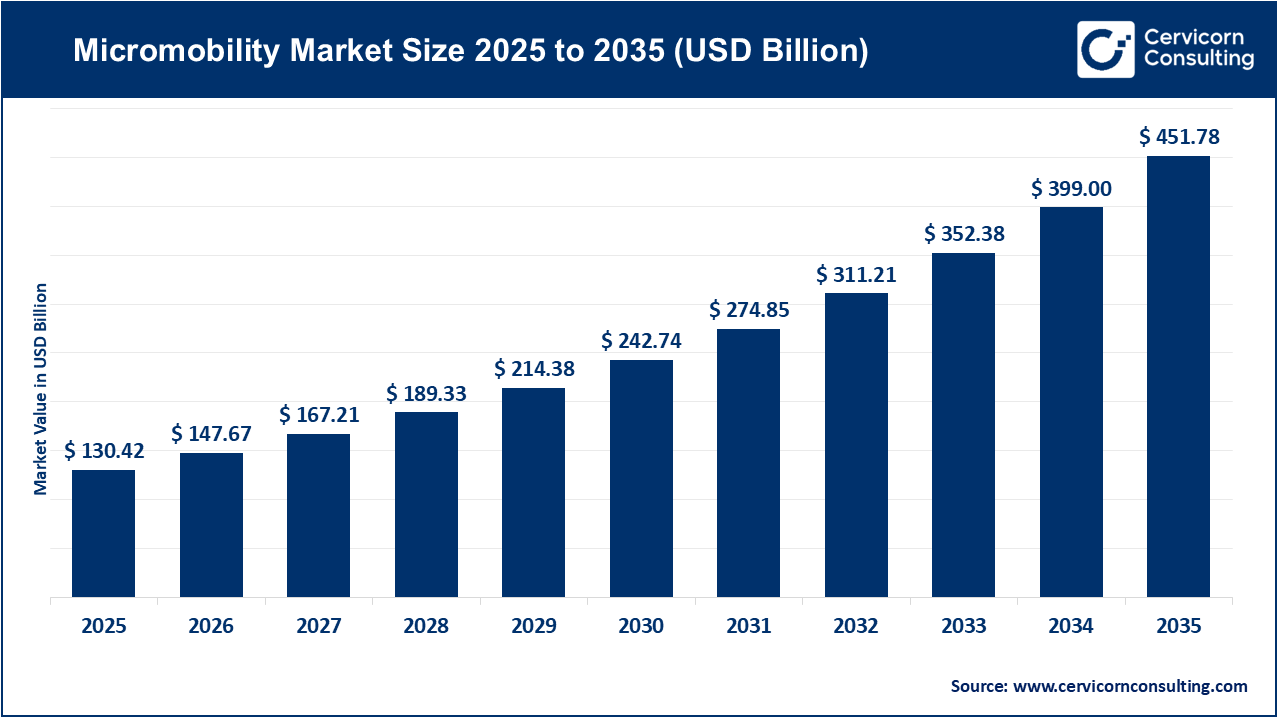
The global micromobility market size was valued at USD 130.42 billion in 2025 and is expected to hit around USD 451.78 billion by 2035, exhibiting at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.2% over the forecast period from 2026 to 2035. The micromobility market is expanding rapidly because more people want fast, cheap, and eco-friendly ways to travel short distances in cities. Rapid urbanization, rising traffic congestion, and growing environmental awareness are pushing commuters to choose e-scooters and e-bikes over cars, helping reduce emissions and road crowding. Governments in many regions are also supporting micromobility through infrastructure improvements like bike lanes and charging stations, and by promoting shared mobility services that make it easy to rent vehicles with a smartphone. Rising fuel prices and a growing middle class with higher disposable income further encourage people to adopt micromobility options instead of traditional transport.
Recent developments show the micromobility market evolving with new vehicle models and expanded services that attract broader user groups. For example, Lime launched LimeGliders, seated electric scooters in Seattle, to make micromobility accessible to more riders and meet diverse commuting needs. Companies like Rivian have even created new micromobility ventures focused on e-bikes and scooters to tap into growing demand. Meanwhile, cities and regions are updating laws to integrate micromobility safely into transport systems, such as planned legalisation of e-scooters on roads and paths in New South Wales with speed limits and age rules. These innovations and policy changes help the micromobility market grow by expanding use cases and addressing regulatory challenges.
How On-Demand Public Transportation in Smart Cities Drives the Micromobility Market
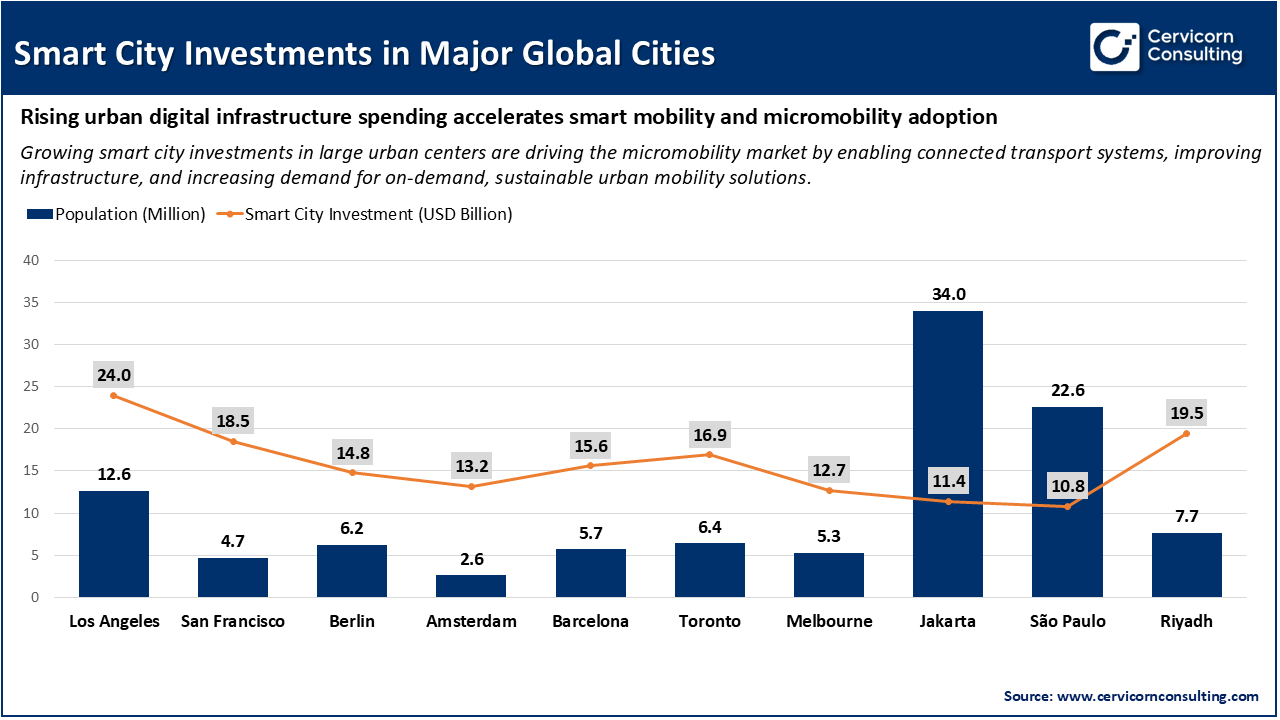
The growing demand for on-demand public transportation in smart cities is a key driver for the micromobility market because people want fast, flexible, and integrated ways to travel short distances within urban areas. Smart cities are building digital, app-based systems that let users easily access transport options like e-scooters and e-bikes whenever needed, often connected to public transit hubs for seamless travel. This increases the use of micromobility services as commuters look for efficient first- and last-mile solutions that reduce time, cost, and traffic congestion while supporting sustainability goals. Cities are also investing in infrastructure such as dedicated lanes, sensors, and shared mobility platforms that make it easier for operators to deliver on-demand services and for users to choose micromobility as part of their daily travel. This integration of micromobility with broader smart transport networks strengthens the overall appeal and adoption of the market.
Recent Developments in the Micromobility Market
| Development | Description |
| LimeGliders Launched in Seattle | Lime introduced 3,000 seated electric scooters (LimeGliders) to expand accessible micromobility choices. |
| New Bike and Scooter Integration | NYC’s Citi Bike expands e-bike docks and charging stations, linking more micromobility with public transit. |
| AI Sensors for Active Travel | SmartCitiesWorld reports deployment of AI sensors in Brighton & Hove to better manage micromobility flows. |
| Smart City Last-Mile Gaps Noted | Bhopal metro’s rollout highlights the need for improved e-bike and bike sharing for effective last-mile connectivity. |
1. Rivian Spins Off Micromobility Unit “Also” (2025)
In 2025, electric vehicle maker Rivian launched a dedicated micromobility business named Also focused on small, lightweight electric vehicles. This strategic move signals that major automakers see micromobility as a growth opportunity beyond traditional cars and trucks. By tapping into micromobility with dedicated products, Rivian helps expand customer awareness and adoption of alternative urban transport options, pushing the micromobility market toward broader acceptance and diversified offerings.
2. New York Commits USD 21 Million to Zero-Emission Mobility (2025)
The State of New York announced plans to invest over USD 21 million in zero-emission mobility infrastructure and solutions. Such public funding boosts micromobility deployment by supporting vehicle infrastructure, charging facilities, and incentives for e-bike and e-scooter use. This kind of government backing accelerates adoption and reduces barriers to entry for operators, strengthening the micromobility market by making it easier for cities and users to choose clean, flexible transport solutions.
3. E-Bike Market Growth Projection (2024–2034)
Recent industry projections show the global e-bike market growing from about USD 60.94 billion in 2024 to USD 149.23 billion by 2034, driven by subsidies, technology improvements, and rising urban cycling demand. Because e-bikes are a core segment of micromobility, this growth forecast reflects stronger consumer and operator confidence in electric two-wheelers, contributing to increased production, investment, and deployment. These trends help expand the micromobility market by attracting both consumers and businesses to invest in e-based transport alternatives.
4. NSW E-Micromobility Action Plan (2025)
The New South Wales (Australia) government released its E-Micromobility Action Plan 2025 to promote e-bikes, e-scooters, and related devices as sustainable and accessible transport options. The plan includes safety standards, coordination among agencies, and policies to integrate micromobility into broader transport networks. Government frameworks like this reduce regulatory uncertainty and create a supportive environment for operators, thereby accelerating adoption and usage — a direct boost to the micromobility market by clarifying rules and enabling safer expansion.
The micromobility market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. Here is a brief overview of each region:
The North America micromobility market size was valued at USD 28.56 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach around USD 98.94 billion by 2035. North America is a mature and innovation-driven region in the market, supported by high smartphone penetration and strong shared mobility adoption. Large urban populations rely on e-scooters and e-bikes for short trips and first- and last-mile connectivity. Cities are actively promoting sustainable transport to reduce emissions and traffic congestion, which benefits micromobility operators. Strong venture funding and partnerships between cities and private companies help scale fleets and improve service quality. Consumer preference for convenience and flexible travel options continues to support steady market growth.
Recent Developments:
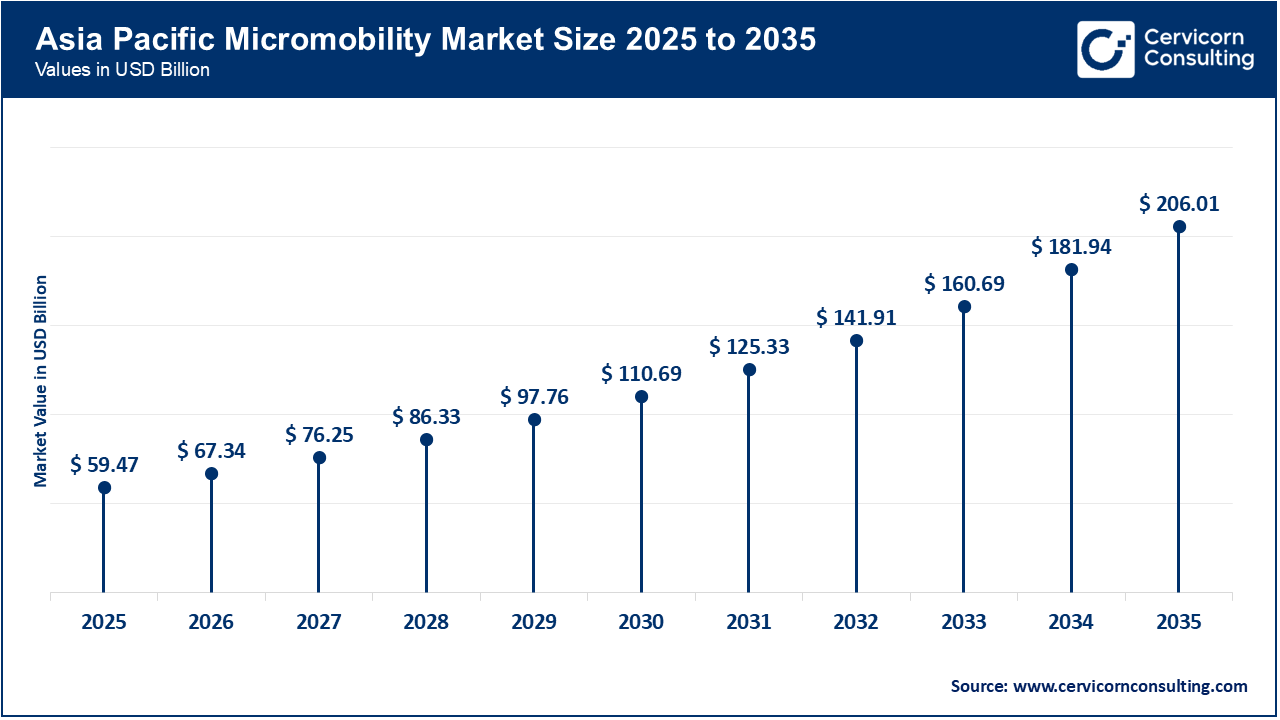
The Asia-Pacific micromobility market size was estimated at USD 59.47 billion in 2025 and is forecasted to surpass around USD 206.01 billion by 2035. Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region in the market due to high population density and heavy reliance on two-wheelers. Governments in countries such as China, India, and Southeast Asian nations promote electric mobility through subsidies and favorable policies. Micromobility offers an affordable solution for daily commuting in crowded cities. Rapid urbanization and growing middle-class income further increase demand. The region also benefits from strong local manufacturing capabilities, which lower vehicle costs and support large-scale adoption.
Recent Developments:
The Europe micromobility market size was reached at USD 36.26 billion in 2025 and is projected to expand around USD 125.59 billion by 2035. Europe market is driven by well-defined regulations and a strong focus on road safety and environmental goals. Governments across the region actively support cycling and low-emission transport as part of climate action plans. Extensive bike lane networks and urban planning policies favor micromobility usage. While regulations can be strict, they provide long-term stability and build user confidence. This structured environment encourages responsible operator expansion and steady adoption across major European cities.
Recent Developments
Micromobility Market Share, By Region, 2025 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2025 (%) |
| Asia-Pacific | 45.60% |
| Europe | 27.80% |
| North America | 21.90% |
| LAMEA | 4.70% |
The LAMEA micromobility market was valued at USD 6.13 billion in 2025 and is anticipated to reach around USD 21.23 billion by 2035. The LAMEA is emerging and driven by rapid urban growth and limited public transport infrastructure. Many cities face congestion and high transportation costs, making micromobility an attractive alternative. Shared e-scooters and e-bikes provide affordable and flexible mobility options, especially in tourist-heavy and densely populated areas. Increasing awareness of electric mobility and sustainability is also supporting adoption. Although infrastructure is still developing, growing interest from global operators is accelerating market entry.
Recent Developments:
The micromobility market is segmented into vehicle type, propulsion type, business model, speed, and region.
E-scooters dominate the micromobility market due to their wide adoption in shared mobility services and strong presence in urban areas. They are easy to deploy, require low upfront cost, and are well suited for short-distance travel and last-mile connectivity. Many cities allow e-scooters under existing transport rules, which supports large-scale deployment. Their high daily usage and strong operator preference make them the leading vehicle type. This dominance is further supported by strong investments from global shared mobility operators.
Micromobility Market Share, By Vehicle Type, 2025 (%)
| Vehicle Type | Revenue Share, 2025 (%) |
| E-scooters | 41.80% |
| E-bikes | 34.60% |
| E-mopeds | 12.30% |
| Kick scooters (non-electric) | 7.10% |
| Others | 4.20% |
E-bikes are the fastest-growing segment in the market because they offer longer range, higher comfort, and better suitability for daily commuting. They attract a wider user base, including older riders and delivery workers. Government incentives for e-bikes and expanding cycling infrastructure further support growth. Their ability to replace short car trips drives rapid adoption. Increasing use of e-bikes for cargo and delivery applications also accelerates growth.
Electric propulsion dominates the market as most modern micromobility vehicles use battery power. Electric vehicles provide higher efficiency, reduced physical effort, and better speed control compared to human-powered options. Shared mobility operators mainly deploy electric fleets due to higher utilization rates. Growing demand for low-emission transport strengthens this segment. Advances in battery technology further improve vehicle performance and reliability.
Micromobility Market Share, By Propulsion Type, 2025 (%)
| Propulsion Type | Revenue Share, 2025 (%) |
| Electric | 72.90% |
| Human-powered | 16.40% |
| Hybrid | 10.70% |
Hybrid propulsion is the fastest-growing segment in the market, mainly driven by pedal-assist e-bikes. These vehicles combine electric support with human power, offering flexibility and extended battery life. They are popular among commuters who want both exercise and convenience. This balance supports strong growth in urban and suburban areas. Hybrid systems also help reduce charging frequency and operating costs.
Shared and dockless mobility dominates the market because it offers easy, app-based access without ownership costs. High adoption in major cities and tourist locations supports this segment. Operators benefit from recurring usage and fleet scalability. This model plays a key role in first- and last-mile transportation. Continuous app improvements and user incentives further strengthen this segment.
Micromobility Market Share, By Business Model, 2025 (%)
| Business Model | Revenue Share, 2025 (%) |
| Shared / Dockless mobility | 38.50% |
| Private ownership | 33.70% |
| B2B fleet services | 14.20% |
| Docked / Station-based mobility | 8.10% |
| Subscription-based mobility | 5.50% |
B2B fleet services are the fastest-growing segment, due to rising demand from delivery companies, campuses, and enterprises. Businesses use e-bikes and e-scooters to reduce fuel costs and emissions. Growth in e-commerce and urban logistics strongly supports this segment. Long-term contracts provide stable revenue for operators. Corporate sustainability goals are also driving adoption.
Low-speed vehicles dominate the market because they comply with regulations in most countries. These vehicles are widely approved for bike lanes and shared services. They are safer for urban use and require fewer licensing requirements. This makes them the preferred choice for operators and city authorities. Regulatory support continues to favor this speed category.
Micromobility Market Share, By Speed, 2025 (%)
| Speed | Revenue Share, 2025 (%) |
| Low speed (up to 25 km/h) | 61.30% |
| Medium speed (25–45 km/h) | 31.60% |
| High speed (above 45 km/h) | 7.10% |
Medium-speed vehicles are the fastest-growing segment in the market as users seek faster commuting options. E-bikes and e-mopeds in this range support longer trips and suburban travel. Improved battery technology and better safety features enable growth. This segment benefits from increasing demand for alternatives to cars. Expansion of suburban micromobility infrastructure further supports adoption.
By Vehicle Type
By Propulsion Type
By Business Model
By Speed
By Data Service
By Travel Range
By Battery Type
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Micromobility
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Vehicle Type Overview
2.2.2 By Propulsion Type Overview
2.2.3 By Business Model Overview
2.2.4 By Speed Overview
2.2.5 By Data Service Overview
2.2.6 By Travel Range Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.2 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Rising urban congestion and last-mile demand
4.1.1.2 Government support for sustainable transport
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 Safety concerns and accident risks
4.1.2.2 Regulatory uncertainty across cities
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 High operational and maintenance costs
4.1.3.2 Infrastructure limitations in many cities
4.1.4 Market Opportunities
4.1.4.1 Integration with smart cities and public transport
4.1.4.2 Growth of delivery and commercial use cases
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Micromobility Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Micromobility Market, By Vehicle Type
6.1 Global Micromobility Market Snapshot, By Vehicle Type
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 E-scooters
6.1.1.2 E-bikes
6.1.1.3 E-mopeds
6.1.1.4 Kick scooters (non-electric)
6.1.1.5 Others
Chapter 7. Micromobility Market, By Propulsion Type
7.1 Global Micromobility Market Snapshot, By Propulsion Type
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Electric
7.1.1.2 Human-powered
7.1.1.3 Hybrid
Chapter 8. Micromobility Market, By Battery Type
8.1 Global Micromobility Market Snapshot, By Battery Type
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Lithium-Ion
8.1.1.2 Lithium-Ion Polymer
8.1.1.3 Lead Acid
8.1.1.4 Others
Chapter 9. Micromobility Market, By Business Model
9.1 Global Micromobility Market Snapshot, By Business Model
9.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
9.1.1.1 Shared / Dockless mobility
9.1.1.2 Docked / Station-based mobility
9.1.1.3 Private ownership
9.1.1.4 Subscription-based mobility
9.1.1.5 B2B fleet services
Chapter 10. Micromobility Market, By Speed
10.1 Global Micromobility Market Snapshot, By Speed
10.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
10.1.1.1 Low speed (up to 25 km/h)
10.1.1.2 Medium speed (25–45 km/h)
10.1.1.3 High speed (above 45 km/h)
Chapter 11. Micromobility Market, By Data Service
11.1 Global Micromobility Market Snapshot, By Data Service
11.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
11.1.1.1 Navigation
11.1.1.2 Payment
11.1.1.3 Others
Chapter 12. Micromobility Market, By Travel Range
12.1 Global Micromobility Market Snapshot, By Travel Range
12.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
12.1.1.1 Up to 3 miles
12.1.1.2 3-6 miles
Chapter 13. Micromobility Market, By Region
13.1 Overview
13.2 Micromobility Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
13.3 Global Micromobility Market, By Region
13.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
13.4 North America
13.4.1 North America Micromobility Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.4.3 North America Micromobility Market, By Country
13.4.4 U.S.
13.4.4.1 U.S. Micromobility Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
13.4.5 Canada
13.4.5.1 Canada Micromobility Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
13.4.6 Mexico
13.4.6.1 Mexico Micromobility Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
13.5 Europe
13.5.1 Europe Micromobility Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.5.3 Europe Micromobility Market, By Country
13.5.4 UK
13.5.4.1 UK Micromobility Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
13.5.5 France
13.5.5.1 France Micromobility Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
13.5.6 Germany
13.5.6.1 Germany Micromobility Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
13.5.7 Rest of Europe
13.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Micromobility Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
13.6 Asia Pacific
13.6.1 Asia Pacific Micromobility Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.6.3 Asia Pacific Micromobility Market, By Country
13.6.4 China
13.6.4.1 China Micromobility Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
13.6.5 Japan
13.6.5.1 Japan Micromobility Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
13.6.6 India
13.6.6.1 India Micromobility Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
13.6.7 Australia
13.6.7.1 Australia Micromobility Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
13.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
13.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Micromobility Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
13.7 LAMEA
13.7.1 LAMEA Micromobility Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.7.3 LAMEA Micromobility Market, By Country
13.7.4 GCC
13.7.4.1 GCC Micromobility Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
13.7.5 Africa
13.7.5.1 Africa Micromobility Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
13.7.6 Brazil
13.7.6.1 Brazil Micromobility Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
13.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
13.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Micromobility Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 14. Competitive Landscape
14.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
14.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
14.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
14.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
14.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 15. Company Profiles
15.1 Bird Global, Inc.
15.1.1 Company Snapshot
15.1.2 Company and Business Overview
15.1.3 Financial KPIs
15.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
15.1.5 Strategic Growth
15.1.6 Global Footprints
15.1.7 Recent Development
15.1.8 SWOT Analysis
15.2 Neutron Holdings, Inc. (Lime)
15.3 TIER Mobility SE
15.4 Voi Technology AB
15.5 Bolt Technology OÜ
15.6 Helbiz, Inc.
15.7 Beam Mobility Holdings Pte. Ltd.
15.8 Wind Mobility S.r.l.
15.9 Cityscoot SAS
15.10 Cooltra Motosharing, S.L.U.
15.11 Yulu Bikes Pvt. Ltd.
15.12 Vogo Automotive Pvt. Ltd.
15.13 GO Sharing B.V.
15.14 Motivate, LLC
15.15 Micro Mobility Systems AG