On-Demand Healthcare Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
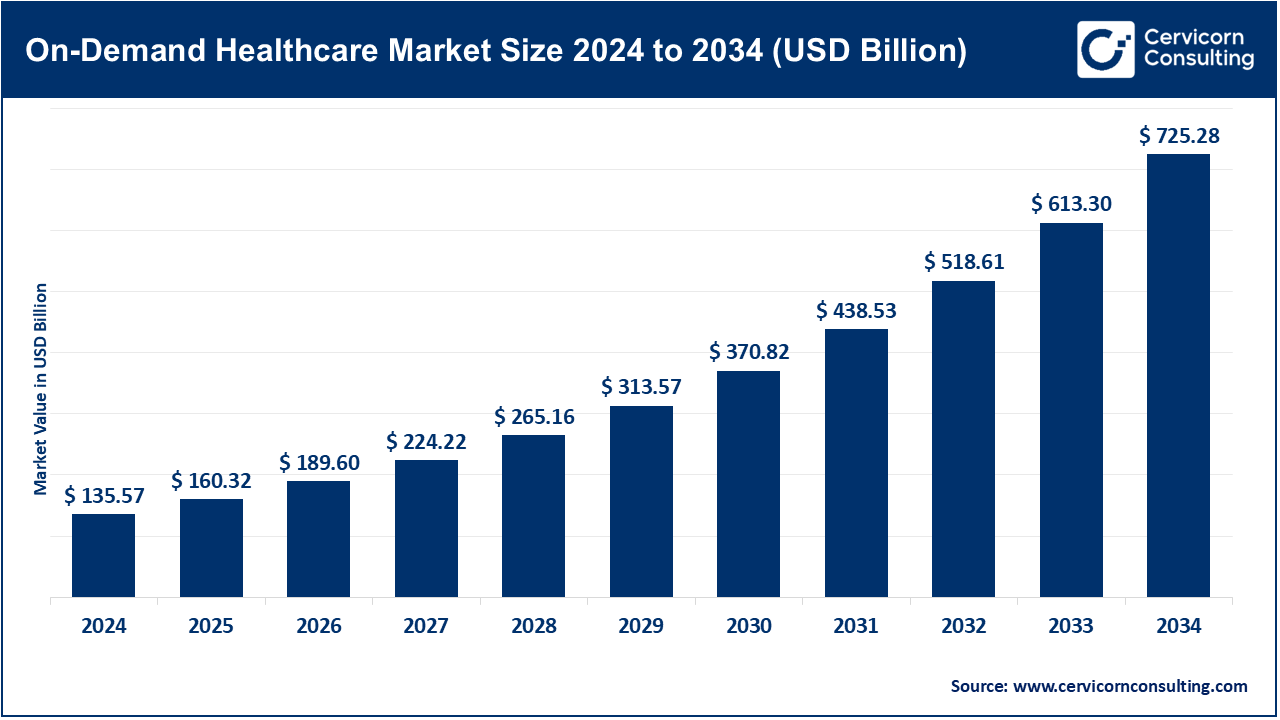
The global on-demand healthcare market was valued at approximately USD 135.57 billion in 2024 and is projected to climb to roughly USD 725.28 billion by 2034, translating into a compound annual growth rate of 18.5% across the period from 2025 to 2034.
The rapid digital transformation now reshaping healthcare is driven by telemedicine, mHealth apps, wearables, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing, each delivering real-time care beyond clinic walls. Together, these tools let doctors hold virtual visits, track patients at home, and rely on cloud-hosted algorithms to guide clinical choices, so assistance reaches people whenever and wherever it is needed. AI is rapidly becoming a clinical partner: 90% of healthcare organizations are allocating resources toward AI in diagnostics and patient care, with 69% of hospitals having adopted or planning to adopt AI-based diagnostic tools. For instance, smart wristbands paired with a mobile phone send heart rates and step counts straight to a physician, allowing steady oversight of long-term issues such as diabetes or high blood pressure. Complementing this, algorithm-backed screening bots and virtual triage line managers speed up diagnosis, keep patients involved, and in turn ease overcrowding in emergency rooms and inpatient wards. A marked shift toward on-demand, consumer-oriented care is driving rapid growth in the healthcare market. Patients now expect the same ease and immediacy in receiving care that they enjoy from retail, banking, or travel applications.
What is on-demand healthcare?
This persistent upward trend illustrates a clear consumer shift toward swift, user-friendly healthcare interactions that seamlessly integrate into hectic routines. Smartphone ubiquity and high-speed connectivity make on-demand paradigms possible, enabling virtual visits, ongoing remote surveillance, digital pharmacies, and at-home diagnostics, all orchestrated through mobile applications or web-based gateways. Rising smartphone adoption, growing willingness to engage with telehealth, and the escalating prevalence of chronic diseases jointly accelerate the momentum. Stakeholders—patients, providers, insurers, and employers—are all indispensable, yet the framework reorients the patient-provider dynamic to favor ongoing, instantaneous dialogue. By bringing care to remote and historically underserved locales, the model trims costs, reduces appointment backlogs, and expands the health system’s overall throughput.
On-Demand Healthcare Market Report Highlights
- North America still sets the standard at the regional level, yet Asia-Pacific is poised to overtake with annual gains between 20-22%, driven by sheer population size, deeper broadband penetration, and policies that push healthcare into the digital fold.
- The mobile-expert segment should post the steadiest acceleration, climbing above 18% yearly, a shift tied to wider smartphone ownership, clearer app designs, and the simple, immediate help they offer people on the move.
- Teleconsultation still holds the biggest revenue slice, but remote patient monitoring is catching up, with some analysts projecting around 20% annual growth as more patients watch long-term conditions and as the older demographic needs steady, unobtrusive support.
- Individuals already account for the broadest audience and should keep growing near 18% a year, buoyed by better medical literacy, high comfort with mobile tools, and an upsurge in requests for tailored, ongoing guidance.
- Niche services such as online therapy, home-testing kits, and virtual wellness coaching are printing above-average numbers, often exceeding 18% a year, a sign that the market is broadening well beyond walk-in clinics and emergency care.
On-Demand Healthcare Market Trends
- The expansion of virtual care ecosystems: Virtual care is no longer limited to phone or video calls; it has evolved into a cohesive digital health ecosystem that covers remote testing, mental health counseling, chronic disease supervision, e-pharmacy, and follow-up after hospitalization. What started as a pandemic stopgap is now accepted as a permanent channel in many health systems. To expand reach, governments and private firms are pouring resources into telemedicine platforms, mobile clinics, and app-based services aimed at rural and underserved communities. By shifting some services away from crowded hospitals, this approach eases pressure on urban facilities while still delivering high-quality care. In 2023, 38% of patients in the U.S. utilized telehealth services, a sharp increase from 11% in 2019. Further, the global market for virtual care is anticipated to surpass $137 billion by 2029. In India, the government’s eSanjeevani platform has recorded more than 160 million consultations, with adoption in rural districts increasing by more than 200% from 2021 to 2024. AI-powered chat agents, and remote diagnostic tools designed for people who lack time or live far from clinics. Combining expanded technical capability with these evolving consumer attitudes is transforming the global on-demand sector into a faster, more open, and patient-led system.
- Growing use of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and data analytics: AI is now common in triage platforms, virtual assistants, symptom checkers, and risk calculators, all aimed at steering patients to the right care and sharpening clinical judgement. In 2024, around 320 million wearable health devices are estimated to be shipped globally, marking a 21% increase from the previous year. Many of these devices include advanced features like heart rhythm analysis, glucose monitoring, and sleep tracking. Moreover, IoT-enabled smart monitors and wearables continuously stream patient data to AI located in the cloud. Predictive analytics then lets providers spot high-risk patients early and step in sooner, cutting both hospital stays and costs. Together, these tools are reshaping on-demand care into a smarter, more connected, and patient-focused system that offers the scalability and sustainability health systems will need in the future.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 160.32 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 |
USD 725.28 Billion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 |
18.50% |
| Dominant Region |
North America |
| Fastest Growing Region |
Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segment |
Mode of Service, Platform, Component, Technology, Deployment, Mode, End User, Region |
| Key Companies |
Teladoc Health, Inc., Amwell (American Well Corporation), MDLIVE, Inc., Doctor on Demand, Inc., HealthTap, Inc., Babylon Health, PlushCare, Inc., Ping An Good Doctor, Practo Technologies Pvt. Ltd., 1mg Technologies Pvt. Ltd. (Tata 1mg), Zocdoc, Inc, Oscar Health, Inc., Medici Technologies, LLC |
On-Demand Healthcare Market Dynamics
Market Drivers
- The rising burden of chronic diseases coupled with aging populations: Chronic illnesses like diabetes, heart disease, lung conditions, and mood disorders are rising steadily, and they keep pushing the need for long-lasting, easy-to-reach care. The World Health Organization notes that non-communicable diseases now cause almost 74% of deaths worldwide, and most of these cases demand regular check-ups and guidance. Because of that persistent demand, traditional hospitals and clinics-those already stretched for staff, equipment, and time-struggle to offer help when and where patients actually need it, especially in rural or low-income areas. On-demand health platforms begin to fill that void by linking smartphones and smart bands to remote monitoring, video visits, and AI alerts, making it possible to oversee chronic conditions from home instead of the emergency room. Such a model matters even more for older adults, who often have limited mobility yet still require frequent, non-urgent attention from a nurse or doctor.
- Strong investments and policy support from governments: Favourable government policies, dedicated funding, and streamlined regulations are jointly accelerating the digital health transformation in many countries. trong investments and policy support from governments are accelerating digital health adoption across the globe. In the U.S., telehealth services received a boost with the CARES Act funding $200 million via the FCC. In addition, the HITECH Act incentives helped increase electronic health record (EHR) adoption, with 9% of hospitals using EHRs in 2008 and the number rising to over 96% by 2023. With this infusion, companies are scaling telepsychiatry, at-home laboratory diagnostics, and AI-aided interpretive services, even as telecommunications providers enhance bandwidth coast to coast. When aligned with favorable regulatory environments, this infusion of financial, technical, and policy support creates a digital health framework resilient enough to embed affordable, accessible care as a durable pillar of global health infrastructure.
Market Restraints
- Regulatory and data privacy challenges: The tangled patchwork of health-care rules across states and nations still stands in the way of smooth expansion. Telehealth programs routinely cross borders, yet each region brings its own demands for physician licenses, remote visits, digital prescriptions, billing codes, and reimbursement procedures. Because of this, many clinics hesitate to grow or even test a new geography. Handling sensitive health data adds another layer of risk; U.S. providers must obey HIPAA while those in Europe follow GDPR, and the two sets of rules do not match. As with any technology, there are concerns that come with the adoption of AI, in this case, around data security. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services reported 725 healthcare data breaches in 2023, impacting over 133 million people. The majority of these breaches, over 77%, were linked to cyberattacks.
- Limited digital infrastructure in emerging and rural regions: Across large sections of Africa, South Asia, and parts of Latin America, a notable share of people still cannot access stable internet or own basic digital tools. Limited digital infrastructure in emerging and rural regions remains one of the most persistent barriers to equitable on-demand healthcare. Access to mobile internet services remains low in, where only 36% of the population had mobile internet access in 2023, And in some rural areas, network coverage can drop to below 20%. Even in wealthier countries, older residents and those in remote villages run into tech barriers like shaky language options and low confidence with online services. When reliable digital networks are absent, on-demand health services roll out unevenly and end up deepening, not closing, the gaps already found in care.
Market Opportunities
- Fully integrated digital care platforms: Healthcare delivery is evolving from isolated video calls to cohesive digital care platforms that unite telehealth, online pharmacies, AI-powered diagnostics, electronic health records, wearables, and remote monitoring within a single, intuitive interface. Patients now move through the process-from setting an appointment to receiving treatment and follow-up-care at home with minimal interruption. This connected flow allows providers to view and act on data in real time, boosting coordination, compliance, and clinical outcomes. In the UK, the NHS app allows users to book appointments, view their medical records, order prescriptions, as well as track data from wearables. The app has more than 33 million active monthly users in 2025, up from 22 million in 2023.
- Targeting specialized and underserved segments: Health technology firms are increasingly pursuing narrow, underserved segments-such as on-demand mental-health therapy, pediatric care, womens health, geriatric support, and post-surgical oversight. Although these verticals carry heavy patient demand, access is regularly blocked by stigma, cost, and distance in conventional offices. Platform-based services offer discreet, affordable, and location-neutral care through smartphones, thereby removing many of those barriers. App-driven therapy for anxiety or postpartum depression, for instance, has attracted millions of users worldwide in less than four years. Remote maternity-monitoring tools, virtual fertility clinics, and geriatric telehealth rounds are displaying parallel rates of adoption. In women's health, virtual fertility clinics like Maven Clinic have grown to serve 15 million members around the globe, and remote prenatal care programs like Babyscripts have demonstrated a 25% reduction in emergency room visits during pregnancy for emerging pre- birth care. The simultaneous expansion of platform-based care delivery and the focused attention on discrete population segments are converging to generate substantial and scalable growth pathways for on-demand health enterprises.
Market Challenges
- Maintaining the quality, safety, and accuracy of remote healthcare services: Unlike face-to-face visits, most virtual consultations depend heavily on what patients report themselves, leaving room for incomplete histories, overlooked signs, and even misdiagnoses. At the same time, the rise of AI tools in triage, diagnosis, and treatment guidance introduces both technical puzzles and ethical debates that cannot be ignored. The increasing application of artificial intelligence in triage, diagnostics, and therapy monitoring adds another layer of difficulty. Algorithms built on sparse and unrepresentative data tend to perpetuate bias, such as the Stanford study from 2023 in which an AI detector of skin cancer trained on images of lighter skin rendered 25% less accurate diagnoses on darker skin. Algorithms trained on narrow datasets may echo existing biases, and even experts admit it is often hard to see exactly how they arrive at a recommendation. Routes to care are also uneven because telehealth platforms lack standard operating procedures and because some providers weigh many years of experience while others are just starting out. Around the world, regulators are still updating laws and rules to match these fast-moving tools, creating a rules-free patch in which malpractice claims may wander.
- Sustainability of the business models and operational strain on healthcare professionals: Although countless startups and health systems have rushed into on-demand care, turning these services into a reliable revenue stream is still a heavy lift. Many organizations lean on fresh venture funding, grapple with steep patient-acquisition costs, or rely on payment from insurers that arrives late or is never paid in full. In the US, a 2024 Rock Health survey found only 27% of digital health companies reported being EBITDA-positive, with the majority of companies still dependent on venture capital funding. In the same period, 24/7 virtual care offered remote access to services and placed a major workload on the providers. Medscape reported that 49% of physicians and 54% of nurses reported burnout in 2024, with “screen fatigue” and “always being on” as major factors. Taken together, the fragmentation of patient records and the struggling workforce form a twin threat to the future health and stability of on-demand systems around the globe.
On-Demand Healthcare Market Segmental Analysis
Platform type Analysis
Mobile-based Platforms: Mobile apps propel this convergence because smartphones are ubiquitous, intuitive interfaces keep users engaged, and push features drive daily interaction. Through a single dashboard, patients can launch video visits, book clinics, retrieve e-prescriptions, log workouts, and settle bills. As Teladoc stated, 62% of its consultations in 2024 stemmed from mobile devices. In India and Southeast Asia, Practo serves more than 100 million users every year. Flexible, real-time access, supplemented by alerts and adherence nudges, explains why urban consumers worldwide are rapidly embracing the mobile health paradigm.
Web-based platforms: Despite the rise of mobile apps, web-based platforms continue to play an indispensable role, particularly for large organizations and users who prefer a desktop setup. Hospitals, outpatient clinics, and managed-care systems typically choose browser-based portals to coordinate virtual visits, link electronic health records, and settle insurance claims. In the US, 82% of hospitals reported using web-based patient portals for the exchange of health information and care coordination, based on a report from the ONC for Health IT. The larger display accommodates complex information, making it easier to conduct lengthy examinations or switch between multiple patient files without losing context.
Mode of Service Analysis
Real-time: Real-time services-meaning live video, voice, or chat sessions-represent the signature on-demand model, allowing patients and clinicians to exchange information in real time. This immediacy suits a wide range of scenarios, including urgent-care visits, routine primary checks, mental-health assessments, and post-procedure follow-ups.
Store-and-forward services: The store-and-forward model permits regional clinics or individual patients to transmit images, laboratory results, and textual summaries to a remote specialist, who subsequently reviews the uploaded material at a convenient time. Specialties such as dermatology, radiology, pathology, and ophthalmology have integrated the architecture, recognising its capacity to improve workflow. In the US, over 40 states have store and forward systems reimbursed for at least one specialty, while in Australia’s national telehealth program, store and forward makes up nearly 30% of the dermatology consultations, shortening the waiting period from weeks to days. By removing the synchronous requirement of patient and specialist presence, the model enables consultations scheduled during evenings, facilitates international referral pathways, and permits careful, non-urgent second opinions, thus smoothing demand across time zones.
Remote monitoring: Remote patient monitoring (RPM) has emerged as a vital tool in managing chronic disease, allowing clinicians to track heart rate, oxygen levels, glucose, or blood pressure from afar. Wearable gadgets and Internet-linked sensors gather this information, sending it to care teams for immediate review. In the U.S., Medicare data indicates that RPM programs have decreased hospital readmission rates for heart failure patients by as much as 25%. In addition, diabetes management programs that utilize continuous glucose monitoring systems have reduced hypoglycemia by as much as 60%. Major implementations, like the RPM network of the Veterans Health Administration, which monitors over seventy thousand patients each year, have reduced hospital costs by $1,600 per patient annually.
End-user Analysis
Individuals: Individuals represent the largest and fastest-growing group using RPM, a shift fueled by the quest for low-cost, convenient care. Many people want health services that work around-the-clock, whether they are seeking help for a chronic illness, a sudden anxiety episode, or a routine check-up. To illustrate, Livongo reports that over 80% of patients using their diabetes control platform improve glucose control within six months. Not only do these tools empower patients to take charge of their health, but they also make a tangible difference—for example, a 15–20% drop in ER visits for chronic disease patients on RPM tools. It is clear why this segment is expected to dominate the market in coming years.
Providers: Hospitals, primary-care clinics, and private practitioners are now using on-demand digital services to reach more patients, conserve staff time, and provide care from home. When telehealth is stitched into room-scheduling, EHRs, and lab networks, clinics cut wait queues, keep treatment plans in one flow, and boost care quality, especially in rural and low-resource zip codes. Virtual consultations that are integrated into NHS hospital IT systems have, to this date, saved approximately 1.2 million staff hours per year in the UK. Meanwhile, eSanjeevani, India’s national telemedicine service, has enabled over 150 million consultations.
Payers: Insurers, or payers, back on-demand care as a way to ease claims costs, steer low-acuity cases away from crowded ERs, and lift member loyalty. A growing number of health plans sponsor virtual-visit apps, paired remote monitoring kits, and year-round wellness nudges as part of the benefits wallet.
Employers: Employers have become a key, and strategic, buyer in the on-demand picture. To keep workers healthy and curb sick days, many firms fold virtual mental-health portals and urgent-care chat lines into broader wellness menus. The trend is strongest in mid-sized to large employers, with rapid adoption seen in tech, financial services, and life-science sectors.
On-Demand Healthcare Market Regional Analysis
Asia-Pacific experiencing the strongest and fastest growth in the on-demand healthcare market
Smartphones are becoming prevalent throughout the Asia-Pacific region, which is experiencing the strongest and fastest growth for on-demand healthcare services, expanding at a compound annual growth rate of over 18% from 2025 to 2034. This growth is aided by a flooding middle class as well as government digitization efforts toward health initiatives. In India, services such as Practo, Tata Health, and 1mg are broadening teleconsultations and at-home lab tests, while the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) creates the national infrastructure to further digitize care. China s market is equally robust, propelled by Ping An Good Doctor, WeDoctor, and similar platforms, all backed by strong public-private funding and a dynamic regulatory landscape.
North America region dominates the on-demand healthcare market
The global on-demand healthcare market is led by North America, and more specifically, the United States which generated more than 40% of revenues worldwide in 2024. This is driven by a well-established healthcare system, a smartphone and high-speed internet penetration rate beyond 95%, and healthcare market leaders, Teladoc Health, Amwell and MDLIVE, which together account for over 25 million virtual visits in a year, and are used by more than 75 million people. Major federal policies-HITECH, the telehealth expansions of the CARES Act-have carried virtual care from pilot to mainstream in a few years. Canada is also moving forward, with provincial authorities rolling out virtual-health programs that reach both urban centers and remote regions.
Europe On-Demand Healthcare Market Trends
Europe has entered a consolidation phase, driven by an ageing population and a mounting prevalence of chronic conditions. Due to Europe’s population aging, with more than a 20% share of population aged 65 and over, coupled with the rise in the prevalence of chronic conditions such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease, Europe is moving into a consolidation phase for on-demand healthcare. The United Kingdom, Germany, France, and the Nordic nations lead eHealth uptake, each pursuing tailored national programmes. These local efforts receive backing from the European Commission’s Digital Health Strategy and the General Data Protection Regulation, which jointly offer a secure and interoperable environment. Nevertheless, divergent regulatory frameworks among member states continue to obstruct the widescale, cross-border deployment of telehealth services throughout the continent.
LAMEA On-Demand Healthcare Market Trends
Consumption of on-demand healthcare in Latin America is still patchy but is evolving swiftly, with Brazil and Mexico leading the charge. They accounted for over 60% of the region’s telemedicine revenue in 2024. Virtual consultations are accessible to millions of citizens due to Brazil’s Conecte SUS platform and Mexico’s Salud Digital initiative. Moreover, chronic disease management is becoming much more affordable thanks to startups like Doctoralia and Clivi. In response, neighbourhood startups and public-sector programs are accelerating projects meant to broaden access to virtual appointments. The Middle East and Africa sit at an earlier stage overall, though urban hubs reveal considerable latent demand. In the Gulf Cooperation Council, for instance, the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia allocate sizable resources to digital-health infrastructure within larger national transformation blueprints. By contrast, many sub-Saharan communities confront limited internet access and high-service costs, yet simple mobile-based models are being tested as cost-effective bridges.
On-Demand Healthcare Market Top Companies
Recent Developments
- June 2025: Amazon India has rolled out Amazon Diagnostics, enabling sample collection at home in under sixty minutes and digital results within six hours. The service launches in six cities-Bengaluru, Delhi, Gurugram, Noida, Mumbai, and Hyderabad-and covers over 450 pin codes, offering more than eight hundred routine tests through a partnership with Orange Health Labs. With this addition, Amazon rounds out its medical ecosystem, linking teleconsultation, medicine delivery, and now diagnostics under one platform.
- June 2025: Hims & Hers Health has announced an all-cash deal to purchase Zava, a European digital care provider. Zava serves more than 1.3 million active users and recorded roughly 2.3 million consultations in the UK, France, Germany, and Ireland during 2024. Closing in the second half of 2025, the transaction is projected to swell Hims customer numbers by nearly 50% and strengthen its presence in key European markets. The deal highlights continued consolidation as telehealth firms seek bigger scale and broader geographic reach.
Market Segmentation
By Mode of Service
- Real-time Services
- Store-and-Forward
- Remote Monitoring
By Platform
- Mobile Applications
- Web-based Platforms
By Component
- Hardware
- Software
- Services
By Technology
- Blockchain
- Artificial Intelligence
- Machine Learning
- Internet of Things
- Cloud Computing
- Big Data Analytics
By Deployment
- On-Premise
- Cloud-Based
- Hybrid
By Mode
By End User
- Individuals
- Providers
- Payers
- Employers
By Region
- North America
- APAC
- Europe
- LAMEA
