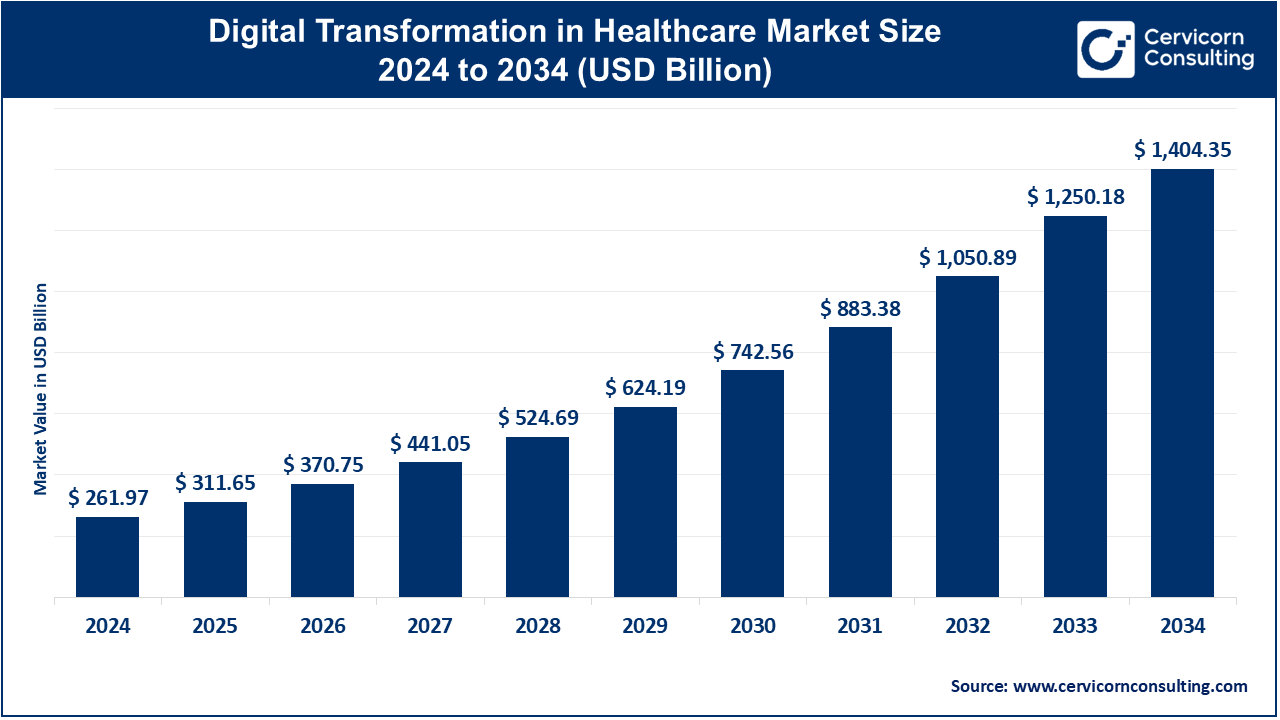
The global digital transformation in healthcare market size was valued at USD 261.97 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 1,404.35 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 30.20% from 2025 to 2034.
The digital transformation of healthcare market is expanding rapidly as the demand for efficient, accessible, and patient-centered care increases. Healthcare organizations are increasingly adopting technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, telemedicine, and electronic health records (EHR) to enhance patient care, reduce costs, and improve operational efficiency. Telemedicine, in particular, has gained widespread acceptance due to its convenience, allowing patients to access healthcare remotely, reducing the need for in-person visits. This shift has been further accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, which highlighted the importance of digital health solutions for both patients and healthcare providers. As more healthcare organizations embrace these technologies, the demand for digital health solutions continues to rise. Moreover, advancements in AI and machine learning are improving clinical decision-making by offering predictive analytics, automating administrative tasks, and enhancing diagnostics. In 2024, investment in AI medical note-taking apps surged, with startups like Nabla, Heidi, Corti, and Tortus collectively raising USD 800 million. Major corporations such as Microsoft, Amazon, and Oracle have also introduced AI co-pilots to auto-generate clinical notes, aiming to save physicians significant time.
Digital transformation in healthcare refers to the integration of digital technologies into all aspects of healthcare services, including patient care, medical records, communication, and administration. This transformation enhances the efficiency, accuracy, and accessibility of healthcare services. Key technologies driving this change include electronic health records (EHR), telemedicine, artificial intelligence (AI), big data analytics, wearables, and mobile health apps. These innovations allow for more personalized care, faster diagnoses, improved patient outcomes, and reduced costs. For instance, telemedicine allows patients to consult with doctors remotely, while AI-powered tools assist in diagnosing medical conditions with greater precision.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 261.97 Billion |
| Projected Market Size (2034) | USD 1,404.35 Billion |
| Growth Rate (2025 to 2034) | 30.20% |
| Dominating Region | North America |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Technology, Application, Organization Size, End-User, Region |
| Key Companies | Epic Systems Corporation, Cerner Corporation, Allscripts Healthcare Solutions, McKesson Corporation, Philips Healthcare, Siemens Healthineers, IBM Watson Health, Medtronic, GE Healthcare, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Health, Microsoft Health, Zebra Medical Vision, Deloitte Healthcare, Oracle Health Sciences |
The digital transformation in healthcare market is segmented into technology, application, organization size, end-user and region. Based on technology, the market is classified into telemedicine, artificial intelligence, cloud computing, big data and analytics, internet of things (IoT), robotics, wearable devices, mobile health (mHealth), virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR). Based on application, the market is classified into clinical data management, remote monitoring, telehealth services, diagnostics, robotic surgeries, medical training and education. Based on organization size, the market is classified into small and medium size enterprises, large enterprises. Based on end-user, the market is classified into hospitals and clinics, pharma companies, life science & biotech companies, healthcare insurance providers.
Telemedicine: Telemedicine platforms transform the delivery of health care at consultation, diagnosis, and treatment that can be made from remote places. Video conferencing, safe messages, and health record web portals allow patients to view their medical care from the comfort of their homes. This helps to reduce physical visits that have to be made, saves time, and gives more convenience to patients, especially those residing in a place that is rural or underserved.
Artificial Intelligence: AI is transforming the health care industry by using applications like machine learning and predictive analytics, natural language processing. These technologies are further utilized to track large datasets of huge proportions related to the diagnosis of diseases, discovering new drugs, and developing personalized treatment options. AI system pattern identification in patient data can then predict possible health issues before they turn critical.
Cloud Computing: It helps enable secure storage and handling of such enormous and immense volumes of patient data. Thus, healthcare providers have the convenience of accessing and sharing data more easily, improving collaboration, and care coordination. The cloud platforms are scalable; this means healthcare organizations can store data at lower costs, yet ensure it is secured and privy. The requirement for easy access to patient records and healthcare applications from anywhere is making workflows in hospitals efficient.
Big Data and Analytics: Big data analytics tools in health are transforming the face of healthcare since it collects, processes, and analyses patient data to deliver improvements in clinical results as well as operational efficiencies. Such insights can be used by hospital and healthcare providers to identify trends, predict outbreaks, and optimize treatment plans.
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT defines the interconnection of healthcare machinery, wearables, and sensors with the ability to monitor patients persistently, continuously, and remotely. Real-time data is gathered through smartwatches, heart monitors, or glucose meters, enabling healthcare professionals to monitor and give appropriate action in real time. IoT encourages better chronic disease care and quality of care through continuous remote monitoring outside of hospital or clinical settings.
Robotics: Robots are increasingly used in surgery, care for patients, and elderly assistance. Surgical robots perform more precisely than human surgery, which makes surgeries minimally invasive, thus making the patient recover faster and reducing cases of infection. In general, apart from surgery, robots are used for elderly care in carrying out daily activities at home to make lifestyle more independent. In general, this integration of robotics also reduces the physical stress experienced by the medical workers while increasing the procedural accuracy.
Wearable Devices: Wearable health-monitoring devices, such as fitness trackers and heart rate monitors, allow patients to monitor their vital signs and general health. These devices track the following key metrics-physical activity, heart rate, sleep patterns-far more frequently than any human ever could, making it much easier for the user to make appropriate health choices. Wearable devices can alert in abnormal reads, and the healthcare providers will quickly intervene to either prevent or effectively manage chronic diseases.
Mobile Health (mHealth): mHealth involves the application of mobile apps in healthcare services such as monitoring fitness activities, reminding patients when to take medicines, or having telehealth consults. mHealth empowers patients because it offers them access anywhere, anytime to information related to their health and self-management tools. This can be linked at any time to healthcare providers, thereby granting patients direct access for immediate advice from their providers and monitoring adherence to treatment plans for better health outcomes.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR and AR change the game in medical training, surgery, and rehabilitation. It can provide fully immersive simulations wherein complex surgeries that may not cause harm without the fear of causing damage can be executed. AR technology lets the surgeon have real-time information during surgeries; it gives the key information to the surgeon directly in his or her line of vision.
Clinical Data Management: It involves clinical data management using electronic health records (EHRs), HIEs, and other systems for the storage and management of patient data. These provide platforms that centralize patient information while allowing the use of such information by authorized healthcare providers, hence enhancing decision-making as well as minimizing mistakes. With digital clinical data management, an up-to-date patients' record available at all times is ensured, which makes the follow-through healthcare easier in different health care facilities.
Remote Monitoring: The remote monitoring systems track patients' vital signs and health conditions in real time through IoT devices. This kind of close follow-up, especially for chronic diseases such as diabetes or heart disease, enables healthcare providers to keep an eye on the patient without having to keep a constant check on them. Remote monitoring brings increased safety for the patient as any problem can be detected early and effective action is taken to minimize hospital readmissions.
Telehealth Services: Telehealth services vary from video consultations and online prescriptions to more enhanced virtual health care services that do not necessarily require a patient to visit a hospital or clinic. It is considerably beneficial for people who are ill and live in areas far from large towns, as well as others who may have immobility issues. It gives patient-orientated convenient, real-time access to health through minimizing or fully eradicating waiting time and improving accessibility to health.
Diagnostics: Diagnostic tools include AI diagnosis, with imaging technologies and lab testing solutions, which provide better and faster diagnostic capabilities for diseases. These systems analyse medical images, laboratory results and patient information to help doctors detect health conditions much earlier and more accurately. With AI diagnostics, the occurrence of diagnostic mistakes is reduced, proper treatment planning is enhanced, and this leads to better health outcomes.
Robotic Surgeries: Robotic surgeries offer greater accuracy and dexterity during surgical procedures, hence becoming more appropriate for minimal invasiveness. These robots can aid in surgery or even perform surgery unaided, performing surgeries much more accurately than human hands can.
Medical Training and Education: With VR and AR platforms, doctors and other medical professionals are trained with great effectiveness to treat patients in the real-world medical settings and conditions. Both of these kinds of immersive technologies provide experience that can be tried hands-on within a controlled environment and thus improve medical education and equip the healthcare workers to tackle various complex situations. VR/AR tools enhance the process of learning and developing skills that are procedural without the danger of actual patients.
Hospitals and Clinics: Hospitals and clinics are the biggest end-users of digital healthcare technologies. These accept EHR systems, telemedicine platforms, AI-driven diagnostics, and robotic surgeries for improving patient care, increasing the efficiency of their operations, and putting a site on more patient values.
Healthcare Providers: Health care technologies are making care more efficient and effective by reducing errors, leading to better patient outcomes and also bettering administrative workflows. General practitioners, specialists, and other healthcare providers rely on digital tools for managing patients. AI-based diagnosis, remote monitoring, and telehealth services help facilitate more effective care, especially in outpatients. These technologies help healthcare providers make better decisions regarding the patient, handle the record, and teach the patient about self-management.
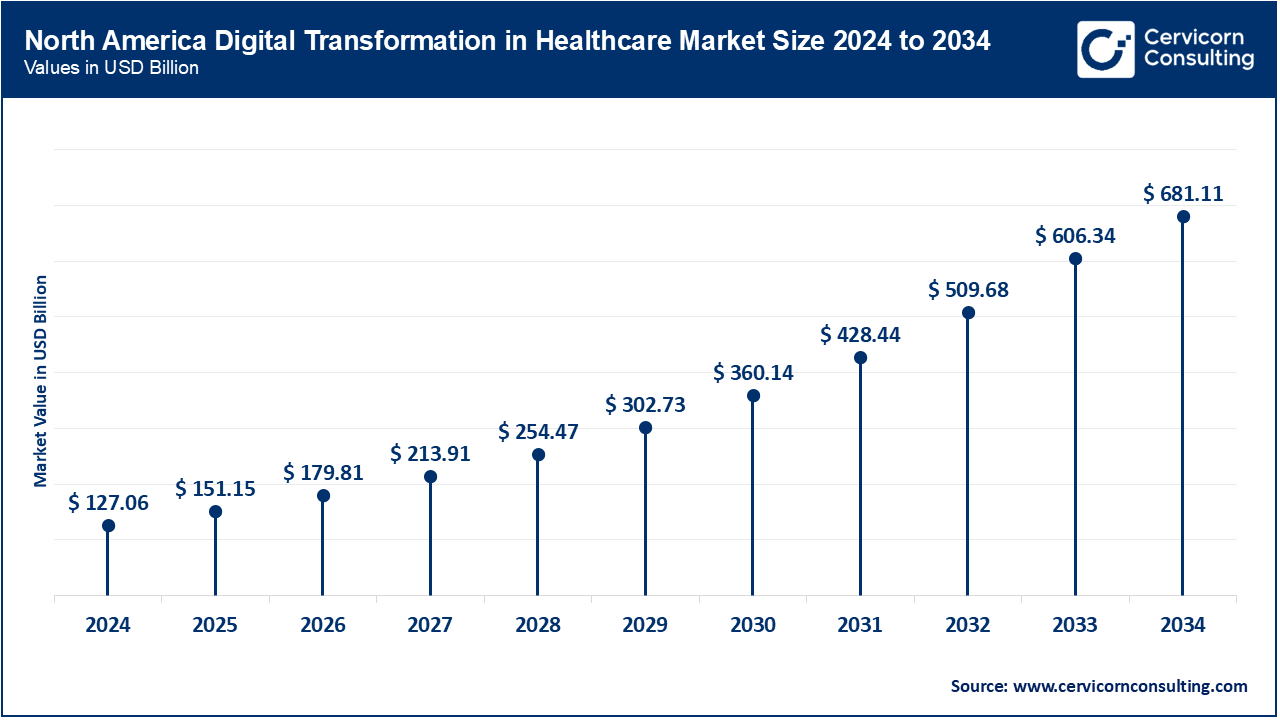
The North America digital transformation in healthcare market size was estimated at USD 127.06 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 681.11 billion by 2034. The market in the North America is booming, primarily due to huge health IT infrastructure spending and adoption of the latest technologies. Both the U.S. and Canada are pioneers in telemedicine, EHRs, and AI applications in healthcare. Government policies, such as the U.S. Further, the HITECH Act has taken off to boost efforts in improving patient data security and health interoperability among other systems. Data analytics is further advanced, improving remote patient monitoring and personalized medicine through IoT-enabled devices across the region.
The Europe digital transformation in healthcare market was valued at USD 64.71 billion in 2024 and is expected to hit around USD 346.87 billion by 2034. Europe is growing with notable pace in the market primarily due to the deep concern of the European Union towards its efforts of achieving healthcare sustainability and an improvement of the standards of patients' care. There has been a positive approach towards healthcare digital transformation among governments of Europe, especially in Germany, France, and UK, as they have been implementing aggressive digital health strategies to modernize healthcare infrastructure and enhance interoperability of data.
One such example is the European Health Data Space initiative, which aims to enhance cross-border exchange of health data for improved treatment and research outcomes. Telemedicine, AI diagnostics, and digital therapeutics are being adopted fast across Europe, but a region like Europe-the place of its origin-enforces the care that has been taken with privacy in GDPR, thereby ensuring that handling patient data is safe.
The Asia-Pacific digital transformation in healthcare market size was estimated at USD 51.08 billion in 2024 and is projected to surpass around USD 273.85 billion by 2034. The Asia-Pacific region is witnessing a high growth in market, with countries such as China, Japan, and South Korea taking front-stage roles in telemedicine, AI-driven diagnostics, and healthcare robotics. Rising healthcare costs in the region are weighed against an aging population; therefore, governments are spending heavily on healthcare IT infrastructure. In China, AI in healthcare is widely being taken up, especially in diagnostics and drug discovery. Japan Aims at using robotics in this region in support of its aged population and AI to facilitate healthcare delivery as well as support elderly care.
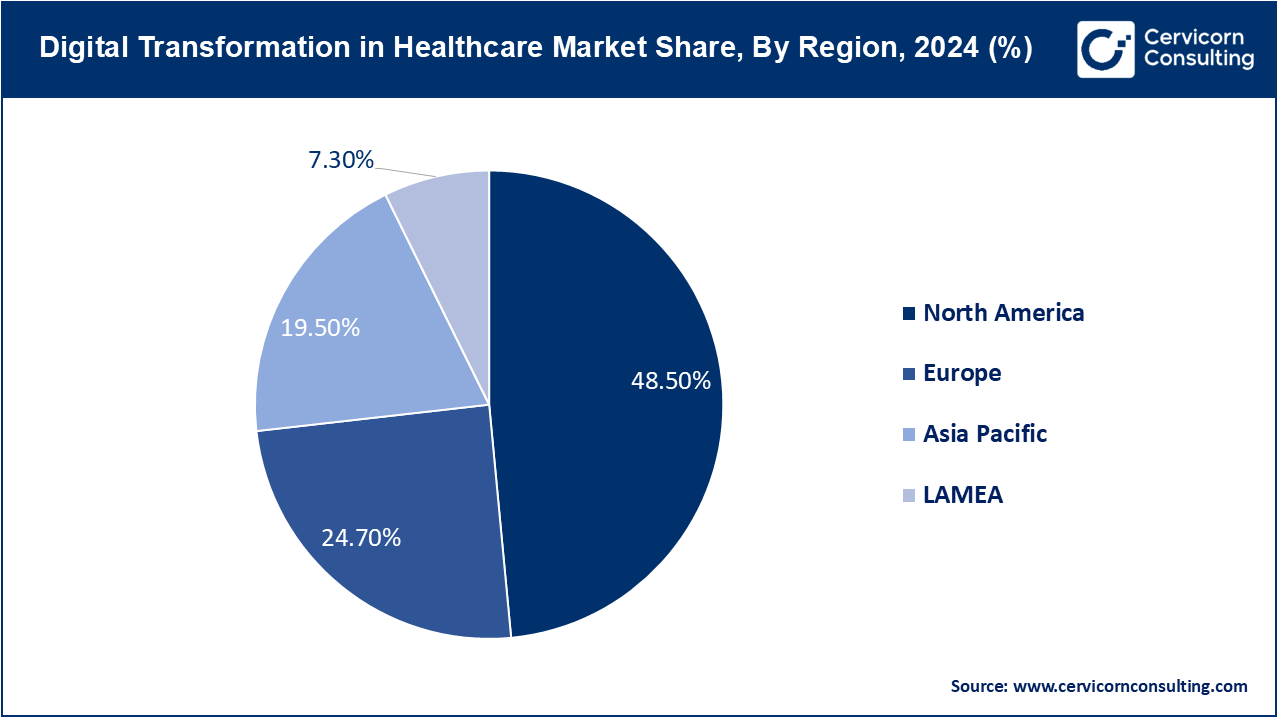
The LAMEA digital transformation in healthcare market size was accounted for USD 19.12 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 102.52 billion by 2034. The LAMEA region is rising regarding the digital transformation of healthcare; here again, variations exist with degrees of adoption and growth of different countries. Brazil and Mexico are headlining this push from Latin America to benefit from the digital health movement, through the improvement of access to health care through telemedicine and mobile health platforms. The countries are solving challenges within regional health infrastructures, including shortages of healthcare workers, through improving access to care through digital solutions in remote patient care.
The Middle East, UAE, and Saudi Arabia, in particular, has been pumping a lot into smart hospitals, AI-based health services, digital health platforms, and wearable technology/telehealth services, which are all part of a larger vision pertaining to future healthcare systems. Governments here are trying to diversify healthcare delivery models and reduce dependence on traditional ways.
Emerging companies in the digital transformation in healthcare sector, such as Epic Systems Corporation and GE Healthcare, are making progress with cutting-edge technology, focussing on advanced AI, data analytics and IoT integration to improve healthcare technology efficiency.
Organizations like Tempus and Owlet are also growing and finding their place in the digital transformation in practice, which involves creative solutions in the scope of the data analytics and IoT Technologies for the improvement of patient support and health care management. At the same time, global players such as Epic Systems and Cerner Corporation occupy the relevant market and domain thanks to sufficient international coverage and understanding of the healthcare IT systems. Not only does Epic Systems provide the market with advanced electronic health records and solutions for the data exchange, but integration between various health systems as well, while Cerner Corporation focuses on innovational processes through collaborative activities and active R&D.
Emerging and, what is perhaps more important, more established players in the market are key to the further development of the transition of the healthcare system to digital and practical immersion of such innovations into the existing variety of medical and health services.
CEO Statements
Epic Systems Corporation | Judy Faulkner, CEO
"Our commitment to advancing healthcare through innovative EHR solutions is unwavering. We empower providers with tools that enhance patient care, improve efficiency, and facilitate seamless data exchange across the healthcare ecosystem."
Philips Healthcare | Frans van Houten, CEO
"At Philips, our mission is to improve lives through meaningful innovation. By leveraging advanced imaging technology and data analytics, we empower healthcare professionals to deliver better, more personalized care to patients worldwide."
GE Healthcare | Kieran Murphy, CEO
"At GE Healthcare, we believe in a future where data-driven insights transform patient care. Our digital solutions enable healthcare providers to make informed decisions that enhance efficiency and improve patient outcomes."
Strategic Launches and Expansions highlight the rapid advancements and collaborative efforts in the digital transformation in healthcare industry. Industry players are involved in various aspects of digital transformation in healthcare, including technology, component, and AI, play a significant role in advancing the market. Some notable examples of key developments in the market include:
These developments underscore significant strides in advancing digital infrastructure and technology, reflecting growing launches and strategic investments aimed at expanding the global healthcare economy.
Market Segmentation
By Technology
By Application
By Organization Size
By End-User
By Region