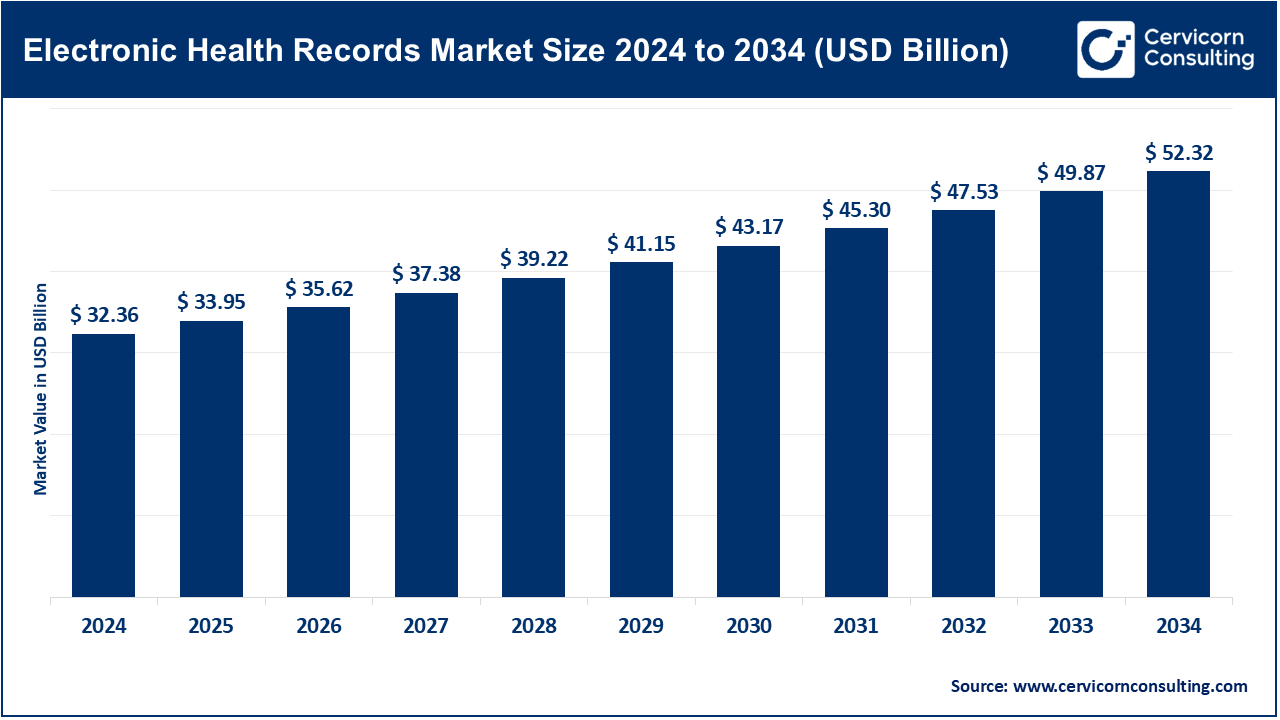
The global electronic health records market size was reached at USD 32.36 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 52.32 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.6% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The electronic health records market is expected to grow at a significant rate owing to rising digital transformation in healthcare, government mandates for EHR adoption, and increasing demand for integrated patient data management. Enhanced clinical workflows, improved patient care, and the growing use of AI and cloud-based solutions are further driving the global EHR market expansion.
The electronic health records market is focused on the design and deployment of digital platforms that can consistently collect, store, and manage patient health data in real time. These systems combine clinical workflows with administrative information and diagnostics and thus will allow providers to have access to comprehensive patient records regardless of provider or care settings. Growth in this market is being propelled by a need for healthcare digitization at all levels, a tendency of governments to mandate standardization of records, and a demand for interoperable and cloud-based solutions. EHRs are moving forward into capabilities that leverage advancements in artificial intelligence, data analytics, and natural language processing. AI utilization, for example, is advancing EHRs into smart platforms versus EHRs maintaining traditional EHR solutions that provide analytic capabilities are supporting clinical decision-making and facilitating personalized patient experiences. The convenience of EHRs on the end of the providers to be efficient, and coordinate care while promoting positive patient outcomes is will build EHRs to being a foundational building block of connected, data-driven value-based healthcare eco-systems.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 33.95 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 52.32 Billion |
| Projected Market CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 6.60% |
| Dominant Region | North America |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Component, Deployment Mode, Functionality Level, Business Model, Application, End User, Region |
| Key Companies | Epic Systems Corporation, Oracle Cerner, MEDITECH, CPSI (TruBridge) , WellSky, Cerner Corporation (Oracle), Netsmart Technologies, VistA EHR, Altera Digital Health (a Harris Company), athenahealth, MEDHOST, GE Healthcare, eClinicalWorks, Greenway Health, LLC, NextGen Healthcare, Inc. |
Software: The software segment has dominated the market in 2024. EHR software is the digital core for documentation, storage, and patient health records management and guidelines. These include clinical charting, patient portals, order entry, and analytics functionality. In 2023 the ONC required EHR vendors to create/ support FHIR-based APIs to enhance interoperability as required by U.S. Federal law. This ruling required software vendors to certify secure and modular platforms more secure that easily integrated and supported. currently EHR systems are being built out with integrated decision support tools for diagnosis and care planning. With telehealth and mobile interfaces becoming more sophisticated; the subsegment remains paramount as providers continue to push for smarter, compliant, and easy-to-use software platforms.
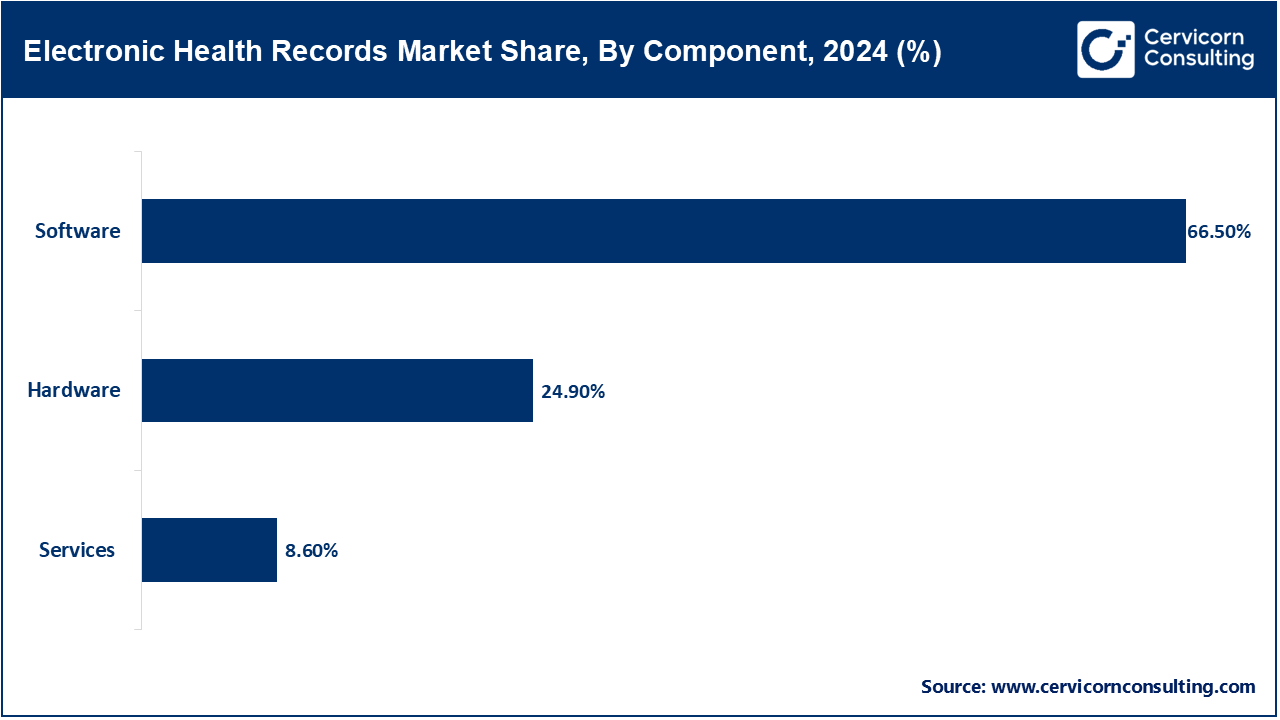
Hardware: Hardware in the EHR ecosystem includes servers, workstations, network infrastructure, biometrics, and portable diagnostic equipment. Hardware also facilitates the physical body for the delivery of digital health services and secure storage. In 2024 the U.S. Department of Defense Upgrade made changes to treatment facilities under the Joint Health Information Exchange to improve secure access to EHRs with upgraded hardware configurations. Military facilities improved their speed of processing versus reliance on older devices. Hardware continues to be particularly relevant with on-premise deployments and in rural health centers with limited access to high speed connectivity. The timeliness and accuracy of clinical care is directly dependent on the reliability of physical infrastructure. Hardware encryption will help improve cyber security.
Services: EHR-related services include system configuration, staff training, legacy data migration, maintenance, and support. These ensure that the digital platforms align with local workflows and user skills. In 2022, the U.S. General Services Administration revised procurement standards to emphasize high-quality service contracts for public EHR rollouts. Services are often crucial for transitioning older records into structured EHR systems. Providers are also relying on consultants to optimize clinical efficiency and compliance. As EHRs evolve with new federal regulations, demand for experienced service providers is growing. These services bridge the gap between advanced technology and daily healthcare delivery.
On-Premise: On-premise systems are physically housed in the IT spaces of a provider. The on-premise model allows for a greater level of customization, provider control over data, and management of in-house cybersecurity threats. Providers have to pay for capital and use their own IT people to maintain the on-premise system. In terms of the EHR controversy, the Veterans Health Administration reaffirmed their preference for the on-premise EHR model in 2024 due to increased data governance concerns. Worries about data breaches associated with cloud have been a major factor in their decision. On-premise continues to be the model for larger hospitals and healthcare systems and those associated with defense-related businesses due to compliance and continuity assumptions inherent with having the data on-premise. Although, the increased use of cloud-based systems is reducing the amount of on-premise solutions, there are still some prevailing concerns about security, so it is not surprising that there are still lots of on-premise systems in high-risk areas. Additionally, there are always backup systems in case of ransomware attacks and downtime.
Electronic Health Records Market Share, By Deployment Mode, 2024 (%)
| Deployment Mode | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| On-Premise | 39.50% |
| Cloud-Based | 60.50% |
Cloud-based: Cloud-based EHRs mean healthcare-related data exists on third-party servers at offsite locations that provide cloud services, so they are highly scalable, are priced lower because of the lack of upfront costs, and allow users to access their data easily when they are at different locations. Small and mid-size outpatient and mobile health providers are increasingly using cloud solutions. In 2023, the Department of Health and Human Services developed a way to explain to the industry that they have HIPAA compliance for cloud-based solutions, helping the industry understand cloud-based systems can legally exist when it comes to privacy regulations. As a result, small and mid-size outpatient and mobile health providers are now confidently using cloud systems. The cloud system often includes real-time system updates with remote support; therefore, the IT workload is reduced to a large extent as compared with an on-premise system. Not only can cloud-based EHR systems use telehealth seamlessly, many now have mobile capabilities. This model of health information technology is also shifting rapidly within rural health and other digital health contexts.
Basic HER: Basic EHRs include basic capabilities, such as a patient demographics, clinical notes, scheduling and basic billing. They are typically used by smaller practices or by individuals just getting into digital utillization. In 2023, CMS amended its Promoting Interoperability requirements, even for basic EHRs, so that patients could timely access their lab results and notes from their physician. As a result, many providers were forced to update older systems in order to maintain their medicare accredidation. The basic system included at least minimum standards for security and portal access. They tend to be hosted in the cloud, as they are very basic and simple to deploy. Their simplicity and low-cost model make basic HER systems ideal for use by independent practitioners.
Electronic Health Records Market Share, By Functionality Level, 2024 (%)
| Functionality Level | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Basic EHR | 34.60% |
| Advanced EHR | 65.40% |
Advanced HER: Advanced EHRs includes a number of features beyond professional record keeping, these included AI tools, instantaneous alerts, clinical decisional support, and advanced analytics, as well as, clinical pathways and protocols. Advanced EHRs are typically employed by large integrated health care organizations and specialty care. In 2025, the ONC enacted enhanced interoperability rules that required EHRs to support instantaneous notifications and automated information exchange. Consequently, advanced platforms are now integrating machine learning components that can assist with risk scoring, as well as, diagnosis support. There is also increase use of public health surveillance and genomics information exchange. Advanced HIS systems support population health goals and value-based care, and hospitals are seeking accreditation in such systems for their reporting and quality improvement metrics.
Licensed Software: Licensed EHR software is characterized by one-time payments that give users permanent rights to software in many cases, typically hosted on-premise with optional ongoing maintenance, i.e., annually. Healthcare organizations use licensed software and manage all updates, support, and data security in-house. In 2024, the U.S. IRS clarified through Section 179 that the cost for licensed software must qualify for the accelerated deduction, positively impacting hospital budgets for large EHR implementations. This regulatory update promotes the purchasing of capital items in systems that fully utilize local authority. For example, hospitals using licensed models often leverage a high degree of functionality in order to validate internal workflows. However, the hospitals are wrongfully liable for any cyber breach, regulatory compliance issues, new patch releases, etc. This hospital model is best suited for large providers that value continuous customization and management of their own IT staff.
Technology Reseller: Technology resellers provide a bundled EHR platform from a third-party developer along with hardware and implementation support services. By utilizing a technology reseller a small clinic, or public sector client, gets a complete "turnkey" product whereby outsourcing uncertainty related to vendor selection as well as any related compliance requirements. In 2023 the U.S. General Services Administration (GSA) added new health information technology bundles to its Schedule 70, thereby allowing federally approved technology resellers to include compliant systems for public health services. This new administrative infrastructure complex provided essentially a three-step-menu that allowed resellers agency's to access certified EHR systems with bundled services. Technology resellers continue to fulfill a critical role to ensure the organization made the best vendor or service, all the while preventing smaller providers from vendor lock-in to monitor standards.
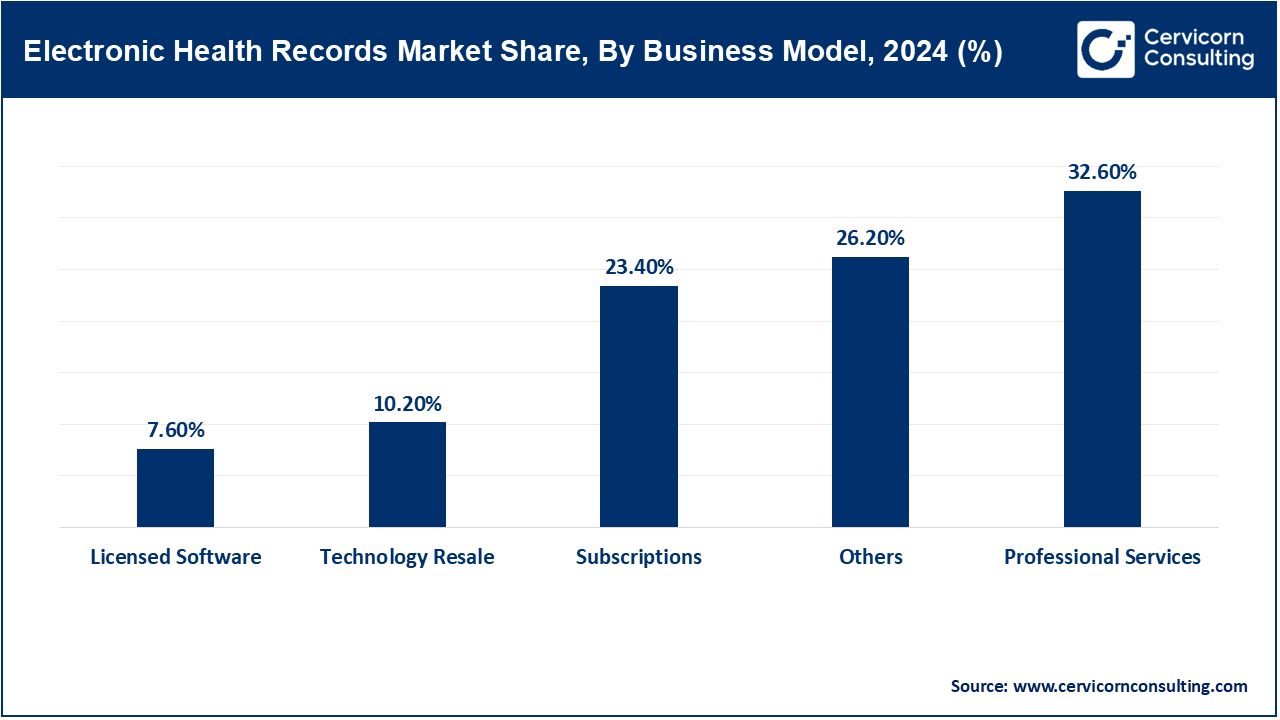
Subscriptions: Subscription-based EHRs offer software-as-a-service access via monthly or annual fees, covering hosting, upgrades, and customer support. This model reduces upfront costs and ensures ongoing compliance. In 2024, the 21st Century Cures Act clarified that subscription payments for cloud EHRs are reimbursable under Medicare as telehealth costs, easing provider budgeting. This regulatory recognition accelerated adoption among rural and community clinics. Providers benefit from managed updates and disaster recovery included in subscriptions. The model scales easily for multi-site operations. Subscription EHRs are becoming the standard for digital-first, distributed care models.
Professional Services: Professional services encompass strategic consulting, workflow redesign, analytics, compliance auditing, and integration tailored to provider needs. Firms specialize in aligning EHR technology to clinical operations. In late 2022, the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) awarded grants to support rural EHR optimization services, emphasizing professional support in underserved regions. Providers can offset consultancy costs while improving efficiency and interoperability. These services ensure regulatory compliance with HIPAA and Cures Act interoperability rules. Demand is growing as EHRs include AI modules and telehealth ecosystems. Expert guidance becomes key to unlocking system potential.
Others: Other EHR business models include hybrid on-prem/cloud setups, pay-per-use modules, mobile-first platforms, and accessibility services tailored for diverse healthcare settings. Vendors innovate with specialty add-ons and UI accessibility enhancements. In 2023, ONC mandated ADA-compliance features in certified EHRs—forcing vendors to include screen-readers and customizable interfaces. This regulatory push spurred development of hybrid EHRs combining mobile apps with secure cloud storage. Smaller providers now have more flexible, accessible options. Custom add-ons like mental health tools are also emerging. This variety reflects evolving regulatory, clinical, and patient needs.
Revenue Cycle Management (RCM): The RCM segment dominated the market in 2024. RCM modules that are built into EHRs manage billing, claims, eligibility checks and denial resolution within the clinical workflow to transform and expand the revenue creation activities and compliance agendas of healthcare provider organizations. The CMS 2024 approach to prior authorization and interoperability makes specific demands of EHRs to check patient eligibility and benefits at the point of care in real-time using application programming interfaces (APIs). The wok forced EHR vendors to build RCM functions and leverage payers into the platforms as standard functionality. Providers are using the checks to manage claim denials. RCM and EHR convergence has yielded usable financial performance information and improved patient interaction. Embedded RCM and EHR has become a well-placed expectation for system vendors for enterprise use.
Patient Engagement: The overall concept of patient engagement includes portals, secure messaging, telehealth scheduling and direct access to laboratory results all linked to the foundation of the EHR. The innovations make real-time data and information about patients' health available to patients and their designated supports. In 2023, ONC issued a regulation that directed laboratories and physicians to provide real-time access to test results and notes from their visits and share that information with patients through patient portals. This requirement also challenged EHR vendors to remap, redesign and embed the portal functionality into its applications. Following ONC's information-blocking regulation, the adoption of portals and messaging functionality for health systems increased with volume. Health systems improved their tools and the tools supported remote monitoring, healthcare satisfaction metrics, etc. The patient engagement standards are expected to meeting program compliance and regulatory requirements.
Population Health Management: These tools analyze aggregated EHR data to track population outcomes, stratify risk, and guide preventive care. They support public health initiatives and quality reporting. In late 2024, CDC mandated immunization and infectious disease reporting via certified EHR APIs to improve surveillance. Providers updated population health modules to include automated reporting triggers for notifiable diseases. This expanded functionality beyond internal analytics into public health compliance. EHR platforms now include real-time data feeds and dashboards for regulatory reporting. This integration strengthens provider contributions to surveillance and public health response.
e-Prescription Management: e-Prescription modules allow clinicians to electronically send medication orders to pharmacies, check for interactions, and manage prior authorization. These tools support medication safety and compliance. In 2023, ONC expanded e-prescribing rules to require controlled substance prescriptions be routed through EHR APIs, increasing safety protocols around opioid prescribing. This update put pressure on platforms to integrate secure e-Rx modules. Providers now send prescriptions directly through certified EHR systems to pharmacies. The automation reduces manual errors and enhances auditability. It's a key step in nationwide digital prescribing infrastructure.
Others: Additional functionalities include clinical decision support, teletriage, referral management, and imaging order entry. These modules support specialized tasks within the EHR. In 2025, ONC’s draft rule mandates EHRs support automated Care Event Notifications to third-party providers during transitions, pushing referral tools into the mainstream. EHR platforms are adapting with standardized notification engines. This improves care coordination across specialist networks. Teletriage and virtual intake modules are advancing simultaneously. EHRs are evolving into coordination hubs, not just record repositories—reflecting policy-driven expansion of functionality.
Hospitals: The hospitals segment has held leading position in 2024. Hospitals utilize fully-integrated, enterprise-wide EHRs to manage inpatient, outpatient, revenue cycle, quality and regulatory reporting requirements. EHRs are deployed across departments and care sites of service. In 2024, CMS updated its Hospital Inpatient Quality Reporting program with interoperability metrics that put pressure on hospitals to implement real-time event notifications and data exchange. These mandated regulatory changes made necessary upgrades to hospital-wide EHR capabilities. These upgrades enhanced coordination amongst departments and continuity across the patient hub. Hospitals continue to establish robust EHR ecosystems to meet compliance, quality care mandates.
Electronic Health Records Market Share, By End User, 2024 (%)
| End User | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Hospitals | 50.50% |
| Ambulatory Surgical Centers (ASCs) | 32.80% |
| Others | 16.70% |
Ambulatory Surgical Centers (ASC): ASCs have EHR solutions that have ambulatory surgical scheduling, documentation, anesthesia notes, and billing features. ASCs prefer mobile or cloud-native access. In 2023, CMS updated ambulatory payment classification revisions requiring certified EHR integration into quality reporting in ASCs. This change also accelerated EHR upgrade and adoption, as well as encouraged ASCs to source systems that were cloud-based and lightweight. In addition, procedural analytics and operative time-tracking modules began to be available to ASCs. ASCs are now reliant on certified EHRs to fulfill reporting obligations, and to manage surgical throughput.
Specialty Clinics: Specialty clinics, e.g., oncology or cardiology, use EHRs that contain domain-specific templates, integrated diagnostics, and order sets to accommodate complex workflows. As part of an expansion strategy that is recommended for specialty providers in their TEFCA guidance, ONC anticipated that APIs specific to oncology data exchange, would encourage vendor-specific module creation in 2024. Specialty registries and formalized documentation templates connected to EHR platforms were updated to improve the specificity and compliance in clinical workflows. Additional layers of integration occurred as the clinical workflows for orders and diagnostic image review would be developed. The specialization enhances clinical workflows; clinics benefit from improved data accuracy along with added reporting capabilities.
Government & Defense- These entities deploy secure, and specialized EHRs for veterans, active-duty personnel, and prospective public health purposes, often under federal standards. Simply put, security and portability are at the top of the list for consideration. For example, in 2023 the DoD released its Gen-FY24 upgrade to its MHS Genesis system to provide better direct interoperability with the VA EHRs through FHIR-based exchange protocols and directed by federal policy. MHS Genesis through this IT initiative improved the flow of civilian-military health data. Moreover, new layers of security were added with improved authentication and encryption protocols. MHS offers public health reporting, and interoperable care for service members and reflects the level of consideration given to deploying EHR products as large or enterprise level implementation.
Others: Other users include long-term care, behavioral health providers, home health agencies, and telehealth startups—each requiring specialized EHR tools. Flexibility, usability, and mobility are key. In 2025, HHS proposed expanding CMS’s Home Health Value-Based Purchasing Program to include interoperability and EHR-driven quality metrics—encouraging broader EHR use in community care. Vendors introduced mobile-friendly interfaces and caregiver communication portals. Compliance with telehealth and data privacy laws became essential. Specialized modules for behavioral health triage emerged. These tools support holistic, continuity-focused care across varied healthcare contexts.
The EHR market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region.
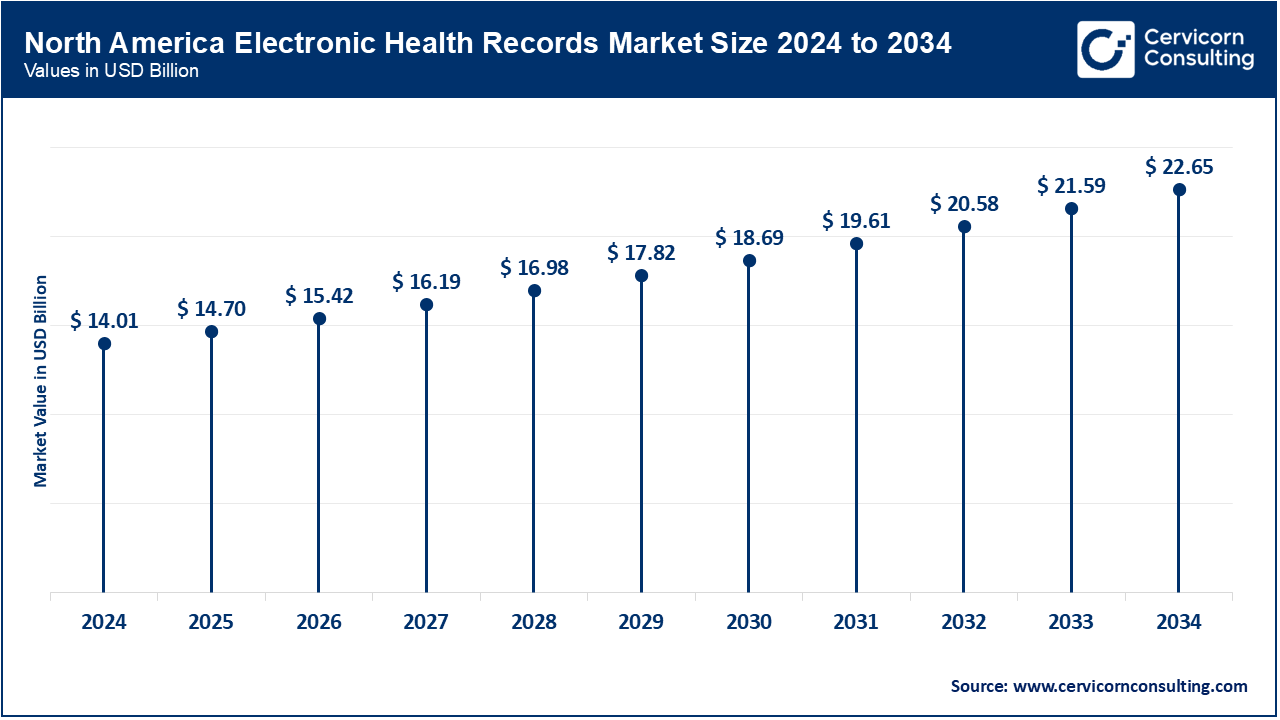
North America is the most developed EHR market because of strong policy support and digital infrastructure. In the United States, over 96 percent of non-federal acute care hospitals utilize certified electronic health records, benefitting from interoperability mandates from the ONC and from CMS. Canada has reached 95 percent utilization of EHRs by clinicians by 2023, aided by national investments in virtual care and sharing of patient data. Most recently, Mexico is advancing on its digital journey through IMSS and its electronic centralized health data system, which is home to over 1 billion medical records. There are federal requirements in each of the three countries that emphasize how patients can access their data, as well as interoperability and sharing of patient data securely. A more recent initiative in the United States 2024, was that many stakeholders were working in conjunction to integrate the advantages of AI-assistive technology into EHRs to address clinician burden. North America is at the forefront of integrating EHRs with real-time analytics and telemedicine systems, assisted by AI-enabled triage.
The EHR market in Europe is influenced by universal healthcare systems, rigid data privacy laws, and government use of digital strategies. According to the UK, 97 percent of general practices are using EHRs, and nearly universal use of digital prescriptions. Germany amended its legal eHealth Act to improve EHR accessibility through its ePA platform with an opt-out data sharing in place for 2025. France is embedding predictive AI-enabled diagnostic systems into its national EHR systems under the programme “Ma Santé 2022.”
Electronic Health Records Market Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America | 43.30% |
| Europe | 25.80% |
| Asia-Pacific | 22.40% |
| LAMEA | 8.50% |
Asia-Pacific’s EHR market is expanding rapidly through government-backed digital health missions and reforms. China implemented a nationwide health data system as part of its Healthy China 2030 initiative, mandating EHR use in all tertiary hospitals. India’s Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission linked EHRs to digital health IDs across over 500 million citizens. Japan expanded hospital information systems with cloud-based sharing under METI guidelines. Australia reached over 97% general practice EHR use, driven by its My Health Record platform and telehealth policies. South Korea introduced regional health data hubs and electronic prescribing mandates under its Smart Hospital expansion. Countries across this region prioritize national digital identity, mobile access, and real-time data sharing within public health networks.
In Latin America, Brazil leads EHR adoption through federal SUS programs, mandating digital prescriptions and integrating health records across public hospitals. Rural telehealth initiatives have extended EHR access to remote Amazon areas. By 2024, digital prenatal and chronic care modules will be expanded to 3,000+ municipalities. In MEA, UAE’s Riayati system enforces unified EHR use across all Emirates, supported by 2023 digital documentation laws. Saudi Arabia’s SEHA platform now links public and private records, with AI modules deployed in 2024 to streamline care. South Africa is scaling EHR pilots under its National Health Insurance plan, with growing focus on system-wide data exchange. These regions emphasize digitization, standardization, and national-level health data platforms.
Recent partnerships in the EHR market highlight cross-platform collaboration and digital healthcare transformation. Epic Systems partnered with Microsoft Azure to expand secure cloud-based EHR services for large hospital networks. Oracle Cerner is working with the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs to modernize federal health records with AI-enabled, cloud-integrated platforms. MEDITECH deepened its alliance with Google Cloud to scale its Expanse platform for faster, mobile-first clinician workflows. CPSI (TruBridge) partnered with American TelePhysicians to extend EHR access across rural care settings via telehealth tools. WellSky acquired multiple specialty software providers to unify care coordination and EHR data in post-acute settings. Oracle continues advancing Cerner’s global EHR reach through cloud infrastructure enhancements. These strategic moves enhance interoperability, cloud scalability, and sector-specific digital health innovation.
Market Segmentation
By Component
By Deployment Mode
By Functionality Level
By Business Model
By Application
By End User
By Region