Automotive Telematics Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
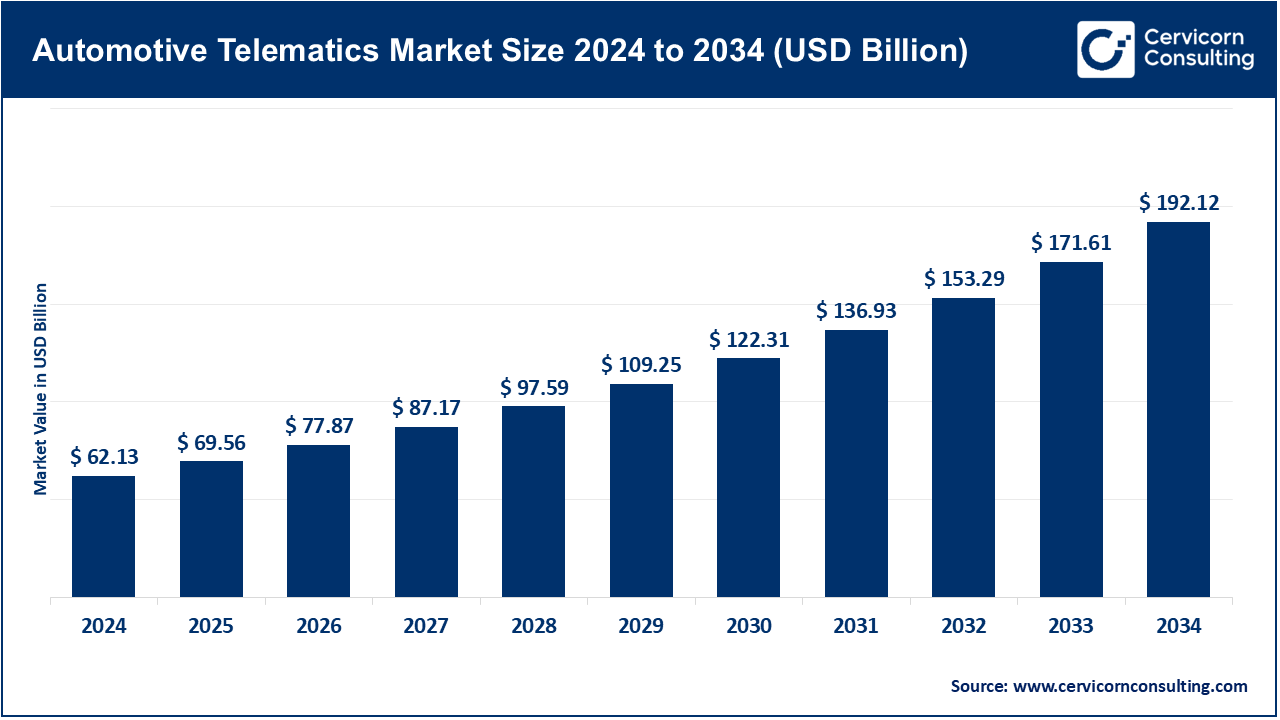
The global automotive telematics market size was valued at USD 62.13 billion in 2024 and is expected to surpass around USD 192.12 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.2% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The automotive telematics market is expected to grow significantly owing to the rising demand for connected vehicles, enhanced fleet management solutions, and increasing emphasis on vehicle safety and regulatory compliance. Growing integration of GPS, real-time tracking, remote diagnostics, and V2X communication in both passenger and commercial vehicles is driving adoption. Additionally, government mandates for eCall systems and insurance telematics, along with advancements in 5G and cloud platforms, are further fueling market expansion across mobility ecosystems, smart transpo00rtation networks, and autonomous driving infrastructure.
Automotive telematics is the combined application of telecommunications and informatics to share, recoup, and keep matters with respect to vehicles and vehicle residents. It incorporates the use of onboard diagnostics, GPS, and wireless connectivity, which allows real-time monitoring, real-time navigation, diagnostic management, and remote and fleet diagnostics. Telematics systems have become common in vehicle tracking and driver behavior analysis, emergency, and predictive maintenance, and infotainment. The technology can improve the safety of vehicles, their efficiency and the user experience. Both consumer and commercial vehicles are incorporating automotive telematics because of the increase in the demand of the connected mobility as an option to receive information, regulatory drivers, and the development of wireless communication infrastructure.
Report Highlights
- By Region, the Asia Pacific has accounted highest revenue share of around 42.7% in 2024.
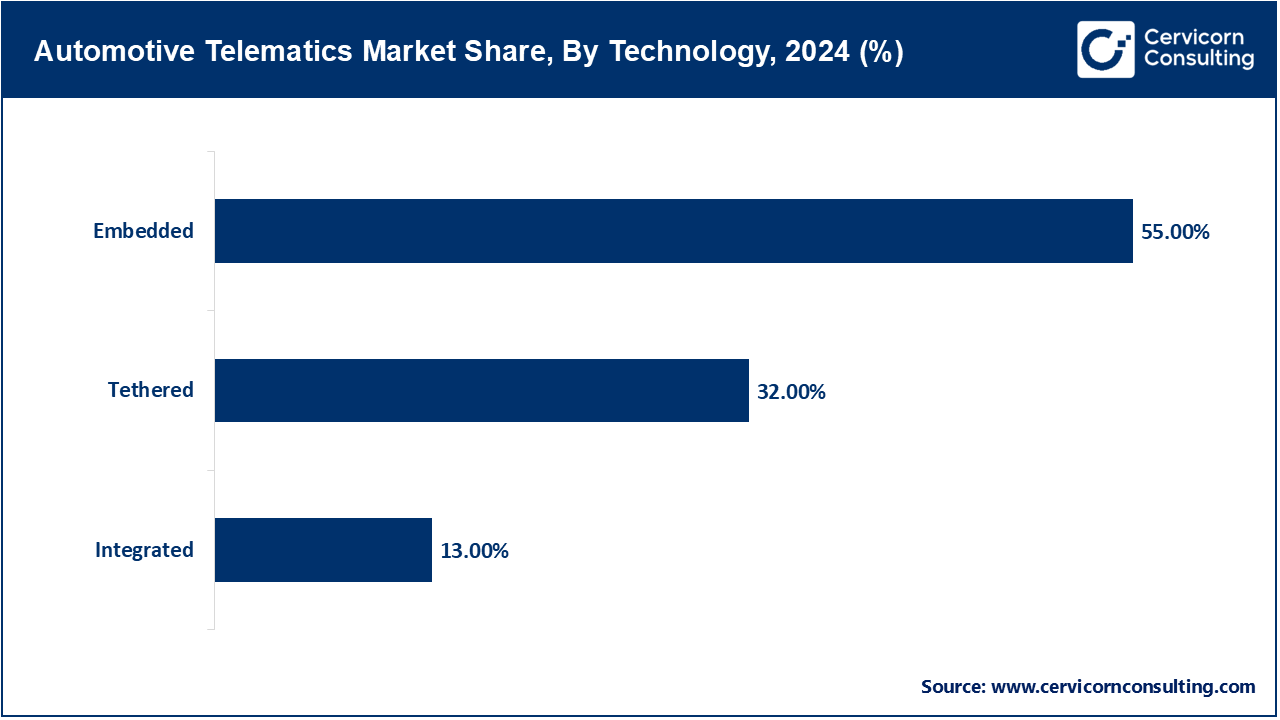
- By Technology, the embedded segment holds a significant market share of more than 55% of the global market in 2024 owing to its seamless integration, regulatory compliance, and growing OEM preference for factory-fitted, always-connected telematics systems.
- By Solution, the component segment holds a major share of more than 57% in the market in 2024 owing to its essential role in hardware-based telematics infrastructure, enabling core functionalities like GPS, diagnostics, and real-time data exchange.
- By Vehicle, the passenger vehicle segment held a significant market share of more than 73% in 2024 owing to rising demand for connected services, high production volumes, and stringent safety and emission regulations driving OEM adoption of telematics.
- By Sales Channel, the OEM segment held a significant market share of more than 65% in 2024 owing to increasing factory-level integration of telematics solutions that ensure warranty compliance, cost-efficiency, and built-in connectivity features.
- By Application, the fleet management segment held a significant market share of more than 45% in 2024 owing to its critical role in optimizing logistics operations, reducing fuel costs, enhancing vehicle tracking, and improving driver performance analytics.
- By Service, the on-road assistance segment held a significant market share of around 30% in 2024.
- By Connectivity, the 4G/3G segment has captured revenue share of 45% in 2024.
Market Growth Factors
- Connected vehicles are a rapidly expanding area in automotive telematics: Consumers are expecting more infotainment, connectivity, and navigation services along with real-time diagnostics. To enhance the user experience and productivity, manufacturers are employing telematics systems like embedded SIMs and GPS with V2X communications. This is essential for performing remote diagnostics and over-the-air (OTA) updates. In Europe and North America, the use of telematics for vehicle safety and insurance purposes is mandatory. Urbanization together with smart mobility telematics create the backbone of connected vehicle infrastructure services, which include advanced diagnostics and dynamic vehicle-to-traffic communication.
- Legal Aspects Concerning Safety and E-Call Systems: An example of safety telematics is the eCall system, which is mandatory in all new cars sold within the EU as it automatically notifies the relevant authorities in case of severe accidents. Similar policies are being adopted in South Korea, Russia, and Brazil. These policies increase the rate at which original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) implement telematics solutions and fuel further growth in the market. Safety telematics enable monitoring of driver behavior in real-time, as well as predictive maintenance, remote shutdown of vehicles, and other measures that improve safety and reduce fatalities. The support of large companies combined with insurance company benefits (e.g., usage based insurance) make telematics a compelling solution driven by compliance needs for all stakeholders including fleet operators, end-users, and automotive manufacturers.
- Fleet Management and Logistics Optimization: The advent of e-commerce and last-mile delivery services has created an urgent need for real-time fleet management systems. Telematics in automotive technology enables monitoring and control of asset tracking, driver performance, vehicle and route scheduling, as well as preemptive maintenance which considerably lowers operational costs while improving delivery efficiencies. With data-driven approaches becoming the norm for most large logistics companies and fleet operators, telematics now supports smart mobility services. The adoption of fleet telematics software as a service (SaaS) is growing in both developed and developing regions. Telecommunication companies turned leaders in the industry such as Verizon Connect, Geotab, and Trimble, have incorporated automation of complex logistics and fuel expenditure as well as real-time alerts using AI and cloud technologies which makes telematics indispensable in transportation.
- The Growing Importance of Cellular and Satellite Connectivity: Cellular 4G LTE and 5G as well as satellite technology are extending the capabilities of automobile telematics. These powerful networks enable real-time communication of all necessary information between the vehicles, users, drifting clouds, and other systems. 5G not only supports data transfer but also enables real time HD navigation, video surveillance as well as other cloud based diagnostics due to its low latency and high bandwidth capabilities. Furthermore, satellite telematics is now utilized for long-haul this in remote and rural areas, as well as for heavy goods vehicles. Upgrades to these networks assist in other telematics innovations such as edge computing, where processing data withinikhail the car improves responsiveness in autonomous systems and accelerates decision making. especially in responsive systems.
Market Trends
- Telematics-as-a-Service (TaaS): TaaS is changing how OEM's and fleet operators are going to learn to extract value from telematics. Due to the high hardware and software costs, telematics systems are offered through subscriptions. These services offer real-time diagnostics, locating, fleet and driver behavior assessment, and reporting. Moreover, the subscription model comes with automated integration with ERPs and CRMs, scalability, continuous updates, and uninterrupted enhancements. Agile startups and first-tier suppliers are utilizing modular APIs to create telematics systems across various sectors. TaaS allows automakers to enrich data ecosystems and diversify monetization strategies which enhances customer loyalty and retention through automated service-based features tailored to autonomous systems and AI. This supports the development of advanced predictive maintenance.
- Role of Edge Computing in Telematics Systems: The Impact of Edge Computing on Telemetric Technologies Because data processing can now occur within vehicles, edge computing is fundamentally transforming the telematics industry. Telemetric units equipped with edge technologies perform real-time evaluations on data streams which greatly improves latency and bandwidth consumption. This is essential for mission critical tasks like Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), predictive maintenance, and AI-driven analytics and decision making. Now, automotive original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) are enhancing TCUs (Telemetry Control Units) by adding edge processing chips and co-processors which boosts the reliability and response time for automobile systems. This is essential for autonomous vehicles and fleet operators in remote regions with scant connectivity where operations need to be real-time, continuous, and responsive.
- In-vehicle Cybersecurity Systems: The growing digitization of vehicles is intensifying focus on cybersecurity within automotive telematics systems. Telematics systems now act as interfaces for numerous vehicular systems like navigation,” engine diagnostics, or even infotainment systems. As such, they are especially vulnerable to cyberattacks. To counter these threats, OEMs and telematics service suppliers are adopting protective measures such as end-to-end data encryption, secure booting, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and even remote patching of firmware updates (OTA). Regulatory policies like UNECE WP.29 impose mandatory cyber risk assessment for telematics in hardware and software systems. Industry players like Harman, Continental, or Blackberry QNX are developing secure TCU architecture frameworks. As vehicles become centralized data hubs for advanced services, telematics cybersecurity is crucial to establish trust, restrict access to sensitive data, and ensure the vehicle functions as intended.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 69.56 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 |
USD 192.12 Billion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 |
15.20% |
| Dominant Region |
Asia-Pacific |
| Fastest Growing Region |
Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments |
Technology, Solution, Vehicle, Sales Channel, Service, Connectivity, Application, Region |
| Key Companies |
Ford Motor Company, Toyota Motor Corporation, Mercedes-Benz AG, Volkswagen AG, General Motors Company, BMW Motors, AB Volvo, Hyundai Motor Company, Tata Motors, Nissan Motor Co., Ltd |
Market Dynamics
Market Drivers
- The Growth of Electric Vehicles in Parallel with Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) Platforms: Due to the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) frameworks, Telema-tics is increasingly being integrated for EV power management, charging station navigation and predictive analytics functions by OEMs and IT companies. Telematics in shared mobility and ride-hailing services supports monitoring fleet utilization, instantaneous location tracking, and virtual health tracking. Lifecycle data, warranty, and subscription services are actively utilized by OEMs who are embedding telematics systems. Real-time analytics, route optimization, and OTA firmware updates are fundamental for telecomm EV startups and mobility service providers who rely on telematics. Cost management, asset security, and fleet uptime within urban transport models will heavily depend on telematics as transport model electrification expand.
- Insurance Telematics (UBI – Usage-Based Insurance): Under insurance telematics, driving behavior with systems such as Pay-As-You-Drive (PAYD) and Pay-How-You-Drive (PHYD) is assessed. These models monitor driving actions in real time using acceleration, braking, speed, and distance. Safe driving encourages adoption by lowering premiums, thus encouraging adoption of these systems. Smartphone data and telematics devices improve risk assessment fraud, thus lowering costs tied to insurance fraud. This mutual benefit increase adoption in the US, UK, and Italy. Though still expanding from personal passenger vehicles to commercial fleets, telematics driven insurance offers dynamic pricing, real time incident alerts, and automated claims processing. Thus, enabling better revenue generation for the insurers while driving value-added services for the drivers.
- AI and Predictive Analytics Integration: The use of AI and predictive analytics is enhancing telematics analytic, enabling real-time vehicle data analysis for failure forecasting, driving behavior optimization, and maintenance schedule automation. Predictive analytics not only minimizes unexpected breakdowns but also enhances safety by identifying patterns associated with fatigue and aggressive driving. AI is also being used by telematics providers for predictive fuel analytics, automated service alerts, and route optimization. OEMs and fleet operators are adopting these features to improve operational efficiency and optimize vehicle lifespan. Autonomous driving, preventive diagnostics, and telematics-based intelligent management of vehicle lifecycle fusion form the boundaries where AI and telematics intersect.
Market Restraints
- The Cost of Integration of Advanced Telematics Features: Implementation of advanced telematics systems which include Artificial Intelligence, V2X communication, and 5G technologies, incurs immense financial costs in terms of capital, operations, and software. This poses tremendous difficulty for small to mid-sized fleet operators and original equipment manufacturers in South East Asia and Latin America. Additionally, the integration of telematics into differing vehicle architectures leads to incurring extra costs of customization, engineering resources, compliance verification, and test case analysis which adds to the implementation costs. Moreover, premium tier telematics services offer real-time monitoring which includes perpetual subscription fees, further preventing adoption from budget-constrained purchasers. This strengthens the hypothesis that affordability remains the primary hindering factor to the global adoption of telematics systems in commercial and entry-level vehicles.
- Compliance Issues and Data Privacy: Because telematics systems provide the ability to track and collect vast amounts of information on vehicles and their users in real-time, they have gained popularity and widespread adoption. However, innovation within the telematics field as led to increasing worries related to privacy, data ownership, and compliance frameworks. Policies like GDPR or CCPA exemplify strict telematics compliance requirements regarding the collection, storage, sharing, and even deletion of data. Automotive companies face challenges regarding pre-requisites that need to be fulfilled to gain user trust, consent, and achieve data portability. These legal obligations incur additional costs associated with IT systems, legal compliance frameworks, and enhanced cybersecurity/infrastructure spending. Moreover, user resistance—especially for fleet telematics and insurance—creates additional barriers to data sharing that could limit the potential usefulness of telematics. There remains an unmoving and significant challenge for global use regarding cross-border policy deployment.
Market Opportunities
- Integration with Electric Vehicle (EV) Ecosystems: As the adoption of electric vehicles increases, telematics is becoming increasingly important for maintenance of the batteries, charging analytics, and energy optimization. As result original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and EV makers are integrating telematics into their systems to offer accurate range estimations, automated charge scheduling, and automated locator for charging stations. In addition, fleet telematics is being used by fleet managers for EV fleet performance monitoring and energy cost analytics, enabling them to optimize fleet performance. This convergence enables new service models, including predictive maintenance for batteries, charging infrastructure planning telematics, and utility grid load balancing. Startups, along with energy companies, are forming partnerships to integrate telematics into home and commercial EV charging stations, aiming to shape the future of intelligent and connected electric mobility.
- Development of Autonomous Driving Features: The basics of telematics systems provides the necessary infrastructure for autonomous driving capabilities through vehicle-to-infrastructure information exchange, integration of various sensors, as well as real-time route assessment. With the advent and commercialization of Level 3–5 autonomous cars, the role of telematics in maintaining real-time communication between vehicles, infrastructure, and cloud systems will be essential. Both automotive manufacturers and information technology companies are focusing on telematics to manage sensor data, perform over-the-air software changes, and provide autonomous systems with the capability to continuously learn. In addition, cities that are rolling out smart mobility projects are partnering with vehicle manufacturers to test autonomous shuttles and delivery vans that are telematics-enabled. This offers telematics providers the chance to deliver solutions that guarantee safety, compliance, and functional intelligence.
- Telematics Expansion for Insurance Purposes in Emerging Markets: Countries like India, Brazil, and those in Southeast Asia are showing increasing adoption of telematics based insurance models. As the digital infrastructure and mobile phone usage improves, insurance companies are adopting “pay as you go" and behavior based premium models. Telematics aids insurers by providing tailored premiums, giving driving feedback, and sending alerts for crashes. Insurance telematics are being bundled with in-car subscriptions by original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and telecom companies, hence opening a new distribution channel. Due to high urban traffic and accident rates in emerging countries, the use of telematics in insurance stands to greatly aid in mitigating risks and improving safety on the roads.
- Use in Aerospace and Defense Applications: The adoption of advanced reinforced plastics in aerospace and defense industries is growing because of the materials’ weight, heat tolerance, and structural resilience. For such critical mission materials, the precision with which AI drives the compounding processes is imperative. A UK based aerospace supplier partnered with a compounding firm to design thermoplastics for the next generation drone fuselages employing AI driven compounding. These materials allow for a 25% reduction in weight of the component while still achieving the necessary strength thresholds. The defense industry has shown a marked interest in replacing metal materials with plastic composites due to their lightweight nature. This impactful growth is creating investment opportunities for AI targeted at intricate formulation design. The forecast of aerospace-grade Automotive Telematics is 4.6 billion USD by 2027.
Market Challenges
- Lack of International Regulations and Standards: The absence of a singular global benchmark poses the most significant challenge concerning telematics hardware, software, and communication infrastructures. Different original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and service operators work within closed proprietary ecosystems which complicates system upgrades, vehicle recalls, or fleet integrations due to interoperability gaps. Cooperative gaps of systems slow seamless data integration from disparate fleets and impede Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communications. Efforts for open standards are being developed from regulatory and industry consortia such as ISO, AUTOSAR, and UNECE Regulations, but the adoption is multifaceted. The telematics and smart mobility frameworks are nourished by system-wide acceptance of telematics and smart mobility frameworks.
- Developing Areas Boundaries of Telemetric Technologies: Meticulous telematic technology can only be deployed in areas that have sufficiently developed digital and transportation infrastructure. Weak mobile internet infrastructure, lack of reliable cloud computing infrastructure, geo-spatial coverage gaps, along with other constraints reduce the efficiency of real-time vehicle monitoring, navigation, and diagnostics. This impacts the dissemination of services into low-density sparsely populated and hard-to-reach areas that would benefit the most from telematics in logistics and emergency services. In addition, the geographically driven delays associated with telematics-based routing and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) further aggravate the situation. Bridging the digital divide in these regions through public-private partnerships and targeted subsidized network expansion investment is needed in order to fully capitalize on automotive telematics.
Regional Analysis
The automotive telematics market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region.
Why is Asia-Pacific dominating the automotive telematics market?
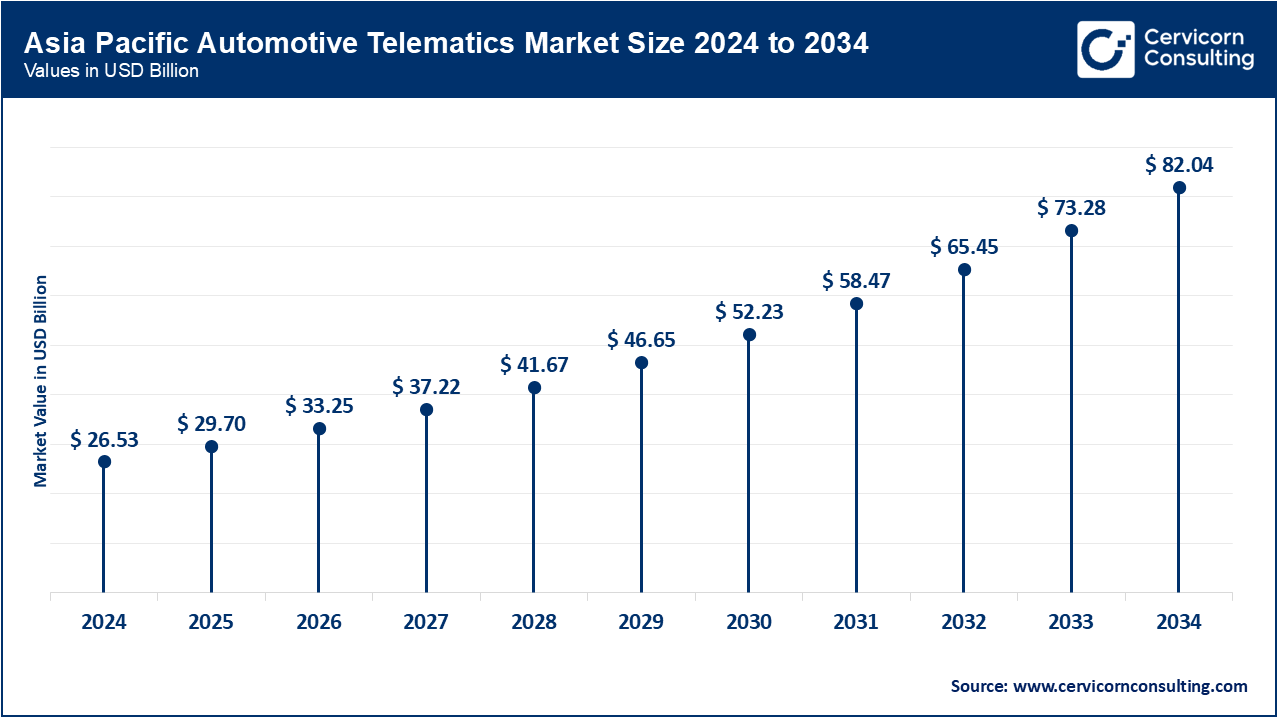
- The Asia-Pacific automotive telematics market size was valued at USD 26.53 billion in 2024 and is expected to surpass around USD 82.04 billion by 2034.
In China, Japan, South Korea, and India: These countries are leaders in the automobile market. The region has a growing rate of automobile production along with a developing middle class population and government support for the smart transport systems which drives adoption. In China, domestic OEMs have accelerated telematics with AI integration, while in India, fleet telematics are growing with the expanding logistics industry. The deployment of integrated and tethered vehicle systems continues to be supported within the region by the adoption of low-cost smartphones, as well as the proliferation of 4G and 5G networks.
What are the key drivers of the North America automotive telematics market?
- The North America automotive telematics market size was estimated at USD 13.85 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 42.84 billion by 2034.
In North America, the connected vehicle ecosystem, safety regulations, and multiple collaborations with telematics OEMs enables telematics adoption to spets fron other regional for North America. Advanced telematics systems in logistics and insurance serve considerable commercial fleets in the USA and Canada. In addition, the region leads in driving smart mobility, real-time diagnostics, and deep consumer analytics alongside significant growth in electric vehicle (EV) adoption.
Automotive Telematics Market Revenue Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region |
Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America |
22.30% |
| Europe |
26.50% |
| Asia-Pacific |
42.70% |
| LAMEA |
8.50% |
Europe Market Trends
- The Europe automotive telematics market size was reached at USD 16.46 billion in 2024 and is forecasted to grpw around USD 50.91 billion by 2034.
The Europe region is driven by eCall and other safety regulation compliance as well as the green environment policy objectives. Leading automotive countries Germany, France, and the UK are proactive in telematics and fleet management as well as in ADAS innovation, focusing on embedded telematics, fleet surveillance, and ADAS integration. Other supporting factors include telematics-based insurances, adoption of EVs, and investments into smart infrastructures driven by the EU’s connected mobility agenda.
LAMEA Market Trends
- The LAMEA automotive telematics market was valued at USD 5.28 billion in 2024 and is expected to surpass around USD 16.33 billion by 2034.
The adoption of telematics in LAMEA is taking place through fleet management, insurance, and security systems. Brazil and Mexico are leading this trend in Latin America due to increased urbanization and the growing commercial fleets. The Middle East, particularly Saudi Arabia and UAE, concentrates on smart city projects coupled with mobility-as-a-service. While there are still gaps in infrastructure and high cost concerns, telematics driven logistics alongside government digitization initiatives are creating fresh opportunities for growth.
Segmental Analysis
Technology Analysis
Embedded: The embedded segment has accounted highest revenue share in the market. Within-vehicle embedded systems link to telematics systems which are integrated and installed by a vehicle's manufacturer. They support advanced mobility functions like remote diagnostics and emergency calls, real-time crash notification, and navigation integration. These systems are becoming more desirable due to their lower cost and increased accuracy. OEM-generated data serves as the basis for subscription services, which now require compliance with safety mandates issued by governing bodies. The integral embedded telematics systems are vital for advancing mobility solutions – the growing desire for connected and autonomous vehicles, more sophisticated telematics systems, and fleet management systems fulfills that need.
Tethered: Connectivity of vehicles via dongles or other peripheral devices marks the emergence of tethered telematics systems. With this advancement, smartphones can now be viewed as the main instruments for the receiving and sending of information. Such telematics systems are utilized in lower-tier automobiles, where they can be purchased as aftermarket enhancements, thus offering a greater accessibility relative to embedded systems. Through tethered telematics, owners can access basic vehicle diagnostics alongside emergency and navigation services; however, these functions are dependent on the mobile device's data connection and battery life. Although tethered telematics are less advanced than embedded telematics, they are popular among budget-conscious customers and regions with limited OEM availability.
Integrated: Integrated telematics combines embedded and tethered functions and permits users to make use of onboard modules while connecting with external devices or cloud services. It facilitates the provision of sophisticated services such as smart infotainment, V2X communication, OTA updates, real time data streaming and analytics. These systems are used by automobile manufacturers and service providers in order to enhance the drivers’ experience by merging hardware-driven systems with software systems. This solution is becoming increasingly popular as vehicles shift towards being connected and software-define.
Solution Analysis
Component: The component segment has generated highest revenue share in the market. Component-based telematics includes hardware elements like control units, sensors, GPS modules, antennas, and connectivity chips. These are critical for enabling communication between the vehicle and external systems. As vehicles become more complex and interconnected, the demand for efficient, lightweight, and high-performance components has grown. OEMs are now more dependent on developments in telematics components to streamline latency, bolster cybersecurity measures, and facilitate 5G for the transmission of data in real-time.
Automotive Telematics Market Revenue Share, By Solution, 2024 (%)
| Solution |
Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Component |
57% |
| Service |
43% |
Service: service-based telematics includes the software components’ cloud service systems, portals for fleet management, and advanced analytics systems serving the telematics data. This segment is critical in the management of driver behavior, routing, predictive maintenance, and emergency management response. With the emergence of subscription-based models and smart mobility platforms, services are turning into the center of value for telematics. OEMs, Tier 1 suppliers, and telematics service providers gain enhanced functionality alongside recurring revenue streams through integration with CRM systems, estimation insurance, and Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS).
Vehicle Analysis
Passenger: The passenger cars segment has captured maximum revenue share in the market. The telematics market integrates technology and vehicles mainly for passenger cars mostly for tracking and navigation entertainment due to increased consumer interest. Telemetry is integrated by OEMs to meet compliance (e.g., eCall in Europe), strengthen brand perception, maintain customer loyalty, and foster brand loyalty by providing remote diagnostics and concierge services. The implementation of electric and connected vehicles telematics into this sector for real-time active connectivity is a necessity with regard to the passenger car experience.
Automotive Telematics Market Revenue Share, By Vehicle, 2024 (%)
| Vehicle |
Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Passenger |
73% |
| Commercial |
27% |
Commercial: Telematics is utilized for productivity and fuel management in commercial vehicles for the fleet management of logistics operations. Telemetry includes GPS-based tracking, real-time driver evaluation, and scheduled maintenance. Regulatory requirements for vehicle monitoring such as ELD mandate in USA have expedited telematics uptake. In sectors like delivery, construction, or logistics, telematics improves compliance with regulatory mandates, reduces system downtimes, and enhances overall asset utilization. With increasing fleet electrification, commercial telematics will need to evolve to include data on charging, battery status, and emissions.
Sales Channel Analysis
OEM: The OEM segment has recorded major revenue share in the market. Telematics manufactured OEM are combined with infotainment systems and ADAS during the telematics unit’s production. OEM telematics are leveraged by automakers for gated access to customer information, data security, and paying with information-preserved gated access. In addition to Tesla’s Autopilot and GM’s OnStar, proprietary platforms these ecosystems serve alongside ecosystem-agnostic telematics-enabled services and infrastructure frameworks. Telemetry systems from the manufacturers are integrated with the vehicle's architecture which guarantees their proper operation and maintenance of usability, especially in luxury and connected vehicles.
Automotive Telematics Market Revenue Share, By Sales Channel, 2024 (%)
| Sales Channel |
Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| OEM |
65% |
| Aftermarket |
35% |
Aftermarket: Aftermarket telematics systems are implemented on older vehicles and are preferred by fleet managers and individual car drivers looking for budget-friendly ways to enhance telematics connectivity. These systems are offered as plug-and-play units, as well as smartphone applications featuring tracking, fuel usage, and driver safety evaluation. The aftermarket segment focuses on older and budget cars alongside commercial fleets. There is an increasing number of aftermarket providers addressing fleets of small and medium-sized enterprises as subscription services expand, offering cloud-based systems and mobile applications.
Application Analysis
Information & Navigation: This consists of location-based services, location tracking, real-time navigation updating, and turn-by-turn guidance. With the rise of AI, telematics systems have begun to include voice command navigational assistants, weather information, and AI-based route optimizing. These features, along with other information-based options, are fundamental to the experiences offered by connected vehicles, which aim at convenience and safety for the drivers, while also supporting larger goals of smart city integration.
Safety & Security: eCall services, vehicle theft recovery, crash notification, and geofencing enhance vehicle safety through telematics. Real-time monitoring as well as unauthorized access using predictive analytics ensure safety. Telemetry safety has become important to Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and insurance companies due to compliance laws requiring telematics safety features, vehicle safety systems, coupled with liability fraud safeguards.
Fleet Management: The fleet management segment has recorded leading position in the market. Telemetry aids in diagnosing problems with commercial fleet vehicles and in their maintenance, route optimization, as well as driver and fuel management. Enhanced fleet and fuel management systems improve compliance with industry standards, control costs, reduce vehicle maintenance, achieve functional improvement, and operational efficiency. Companies today have the ability to reduce operational costs while driving compliance and improving maintenance with these systems. Advanced systems today offer AI-driven analytics, integration with ERP systems, and real-time mobile dashboards for decision-making.
Insurance Telematics: Insurance telematics, or telematics based insurance (UBI), allows insurers to track and monitor client’s driving habits in real-time. Metrics like acceleration, speed, braking, and even geolocation are captured to adjust premiums to the insurer's actual risk exposure. Telematics supports discounts for safe drivers but also fosters improved driving behaviors. Insurers apply the data also for claims validation and fraud prevention.
Others: This category features new use cases like vehicle-to-infrastructure communication, remote vehicle diagnostics, over-the-air software updates, driver wellness monitoring, and infotainment customization. Such use cases further the development of connected and autonomous vehicles for niche and experimental purposes as the automotive industry shifts toward increased digitalization.
Automotive Telematics Market Top Companies
Recent Developments
Key players in the automotive telematics industry—such as Verizon Connect, Continental AG, Geotab, and Trimble Inc.—are redefining intelligent mobility through the integration of AI, IoT, and cloud connectivity into telematics platforms. In March 2024, Verizon Connect enhanced its fleet management software with AI-powered driver behavior analytics and predictive maintenance modules. Continental AG unveiled its next-gen OTA (over-the-air) architecture in September 2023 to support remote diagnostics and feature updates. Geotab introduced cross-OEM telematics data harmonization tools in May 2024 to support interoperability in large mixed fleets. Trimble, in June 2025, integrated real-time route optimization and energy monitoring tools specifically for electric vehicle fleets. These advancements underscore how telematics is evolving into a central pillar of data-driven, connected, and sustainable transportation ecosystems.
- In September 2024, Cummins, Bosch, and KPIT Technologies jointly launched Eclipse CANought, an open-source telematics software platform designed specifically for commercial vehicles. The solution provides standardized, secure access to vehicle ECUs (Electronic Control Units), enabling seamless integration of telematics applications and enhancing interoperability across multi-brand fleets
- In October 2023, Nauto unveiled advanced telematics capabilities that offer real-time insights into vehicle tracking, usage patterns, misuse, and predictive maintenance. This solution integrates AI-powered driver and vehicle safety features, streamlining in-cab hardware requirements and helping fleet operators reduce costs, improve safety outcomes, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Market Segmentation
By Technology
- Embedded
- Tethered
- Integrated
By Solution
By Vehicle
By Sales Channel
By Service
- Emergency Calling
- On-Road Assistance
- Remote Diagnostics
- Insurance Risk Assistance
- Stolen Vehicle Assistance
By Connectivity
- Satellite
- Cellular
- 4G/3G
- 5G
By Application
- Information & Navigation
- Safety & Security
- Fleet Management
- Insurance Telematics
- Others
By Region
- North America
- APAC
- Europe
- LAMEA


