The global injectable hydrogels market size was valued at USD 500.52 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 2022.78 million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
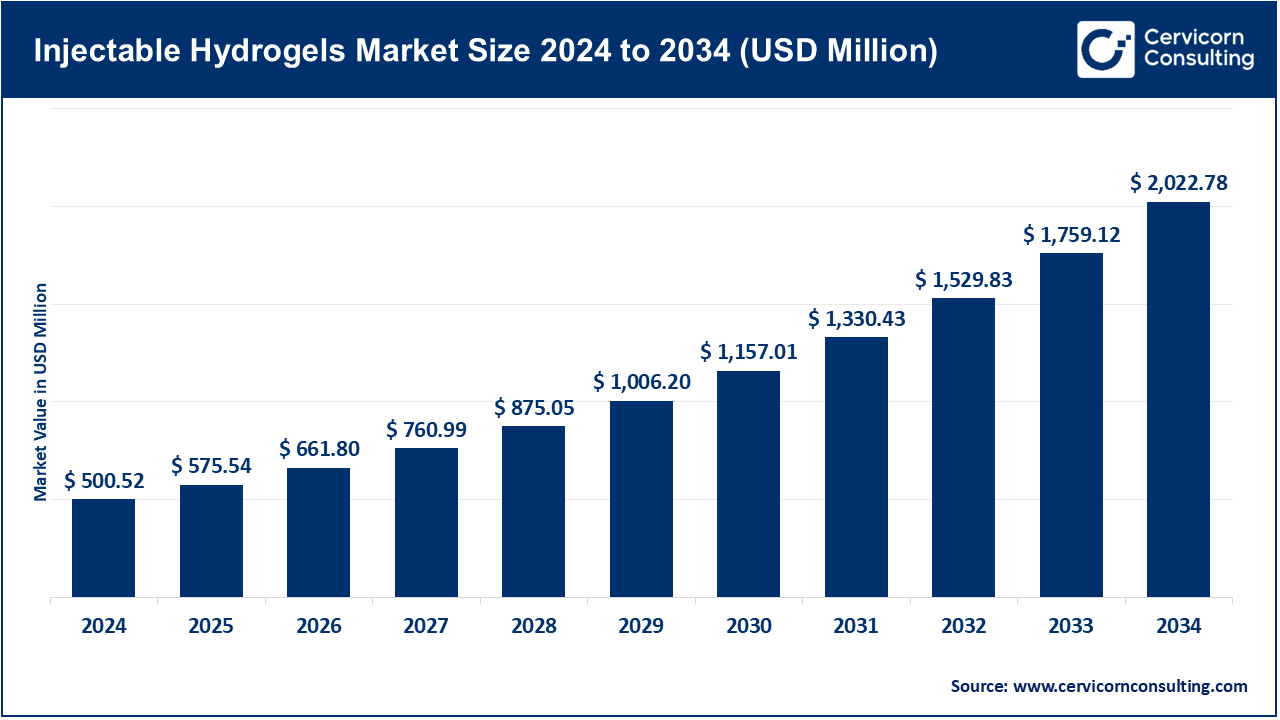
The injectable hydrogels market growth is driven by an increasing prevalence rate of chronic as well as degenerative diseases such as osteoarthritis and cardiovascular ailments, besides cancers and other related conditions. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), osteoarthritis affects over 528 million people globally (2023), with incidence rates increasing sharply in individuals over 60 years of age. This creates an urgent requirement for novel therapeutic delivery systems. Injectable hydrogels represent available site-specific drug delivery sustaining release maintaining localized treatment. As they are biocompatible and biodegradable; safe application directly injected into target tissues this reduces systemic side effects increasing efficiency of treatments. Increasing aging population across the globe leading to rising incidences of chronic diseases especially in developed countries is changing demographics thereby creating a higher demand for efficient as well as patient friendly treatment options where these products have shown great potential. Data from the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) show that biodegradable hydrogels used in localized drug delivery can reduce hospital stays and recovery times by 15–30%, contributing to overall treatment cost efficiency.
What are injectable hydrogels?
Injectable hydrogels are currently one of the fastest-growing segments in the hydrogels market. The growing need for minimally invasive therapies, targeted drug delivery, and the expanding field of regenerative medicine are all playing a key role in driving the market for injectable hydrogels forward. These are hydrogels made of natural, synthetic, or hybrid polymers. They are used in wound healing, oncology, orthopedics, and even aesthetic medicine. Because they are administered through injection and often gel in situ and can be made to be responsive to physiological triggers, they have some benefits for patient compliance and therapeutic targeting as well.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 575.54 Million |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 2,022.78 Million |
| Projected Market CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 15% |
| Dominant Region | North America |
| Accelerating Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Material Type, Application, End User, Region |
| Key Companies | 3M Company, Johnson & Johnson, Smith & Nephew plc, Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD), B. Braun Melsungen AG, Anika Therapeutics, Inc., Zimmer Biomet Holdings, Inc., Pfizer Inc., AstraZeneca plc, Biogelx Ltd., Regentis Biomaterials Ltd., T&R Biofab Co., Ltd. |
Natural Hydrogels: Natural hydrogels come from biological sources such as alginate, hyaluronic acid, chitosan, collagen, and gelatin. They hold a large market share because they are biocompatible, biodegradable, and have low immunogenicity. These hydrogels closely mimic the extracellular matrix (ECM), which makes them ideal for use in tissue engineering, wound healing, and cell delivery. For example, hydrogels based on hyaluronic acid are commonly utilized in orthopedic therapies and aesthetic procedures, such as dermal fillers. Alginate and chitosan hydrogels are also becoming more popular for drug delivery systems, thanks to their gel-forming abilities and responsiveness to physiological pH. However, some limitations still exist with natural hydrogels, including poor mechanical strength and variability between batches, which can affect their effectiveness in high-stress scenarios like cartilage repair.
Hybrid Hydrogels: Hybrid hydrogels merge both natural and synthetic polymers, aiming to harness the advantages of each material type. These innovative systems are designed to provide the biocompatibility of natural polymers while also delivering the structural integrity and functionality of synthetic materials. Hybrid hydrogels show great promise in advanced fields like regenerative medicine, 3D bioprinting, and personalized medicine, where balancing biological performance with mechanical robustness is crucial.
Synthetic Hydrogels: Natural hydrogels come from biological sources such as alginate, hyaluronic acid, chitosan, collagen, and gelatin. They hold a large market share because they are biocompatible, biodegradable, and have low immunogenicity. These hydrogels closely mimic the extracellular matrix (ECM), which makes them ideal for use in tissue engineering, wound healing, and cell delivery. Synthetic hydrogels are particularly prominent in areas like controlled drug delivery, cancer therapeutics, and biosensing. Their capability to incorporate stimuli-responsive elements—such as temperature, pH, or enzymatic triggers—makes them well-suited for smart hydrogel systems that release therapeutics according to local environmental conditions.
Drug Delivery Systems: One of the most applications of injectable hydrogels is as drug delivery system. Hydrogels are listed as promising carriers for small and large molecular drugs, owing to their high water percentage, controllable porosity, and the potential to be triggered publication responses (such as pH, temperature and enzymes). These features allow for targeted and sustained drug release, which is especially important for treating chronic diseases, cancer, and neurological disorders. For example, in cancer treatment, injectable hydrogels are used to deliver chemotherapy drugs straight to tumor sites. This approach reduces systemic toxicity and improves treatment effectiveness. Additionally, their capacity to protect sensitive drugs, such as proteins or peptides, strengthens their role in drug formulations.
Tissue Engineering: The tissue engineering/regenerative medicine market is the most rapidly evolving segment of this market. Hydrogels can simulate the extracellular matrix (ECM) to provide a supportive spatial environment for cell encapsulation, proliferation, and differentiation. They are a hot topic of research for uses in healing cartilage, treating spinal cord injuries and regrowing heart tissue and organs. Their properties such as injectable and in situ gelling ability render them ideal for minimally invasive regenerative disease therapies. They contribute to both form and function.
Wound Care: In wound care, hydrogels are important because they keep the healing area moist, reduce pain, and help tissue regenerate. Hydrogel dressings are especially useful for burns and diabetic ulcers. They provide controlled drug release, prevent infection, and speed up healing.
Cosmetic and Aesthetic Medicine: In cosmetic and aesthetic practices, injectable hydrogels—especially those based on hyaluronic acid—are widely used in dermal fillers for restoring facial volume, reducing wrinkles, and rejuvenating skin. The rising demand for non-surgical cosmetic procedures globally has turned this into a rapidly growing niche.
Hospitals: Hospitals pose as the leading end users owing to the extensive use of injectable hydrogels in drug delivery, wound care, pain management, and orthopedic applications in clinical centers. These could take advantage of the simplicity of the hydrogel application and its minimally invasive character, and this contributes to a faster postoperative recovery and hospital stay of the patient. Injectable hydrogels are widely used in osteoarthritis, chronic wounds, post-operative pain, and for esthetic purposes such as dermal fillers.
Ambulatory surgical centers (ASCs): The adoption of injectable hydrogels is rapidly increasing at ASCs due to injectable hydrogels’ lower cost and reduced length of hospital stay. With greater acceptance of outpatient cosmetic surgeries and faster recovery times, the use of hydrogels is increasing in these areas.
Research and Academic Institutes: This particular segment is expanding due to the extensive R&D efforts focused on developing advanced hydrogel systems for controlled and sustained release in targeted delivery, oncology, and regenerative medicine. The increasing government grant allocation along with the collaboration of pharmaceutical companies with research institutions helps in the advancement of this segment. In total, the hospital and clinic segment is the largest in hydrogel sales, while ASCs and research institutes are expected to have a growing share of the market with rapid technological changes and increasing areas of application.
The APAC region is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 13% between 2025 and 2034, outpacing North America and Europe. The APAC region is soon going to be the most promising and fastest growing market. China’s biopharmaceutical sector produced over 30% of the world’s medical-grade hyaluronic acid in 2023 (China Chamber of Commerce for Import & Export of Medicines), making it a key hydrogel raw material hub. Emerging markets such as China, Japan, South Korea and India are witnessing high demand on account of rising healthcare expenditure, growth in healthcare infrastructure and rising incidences of chronic diseases. And in part because of cost factors and a burgeoning number of homegrown biotech startups, China and India are turning into attractive hubs for hydrogel manufacturing. There is also a significant need in the field of injectable hydrogels for aesthetic purposes.
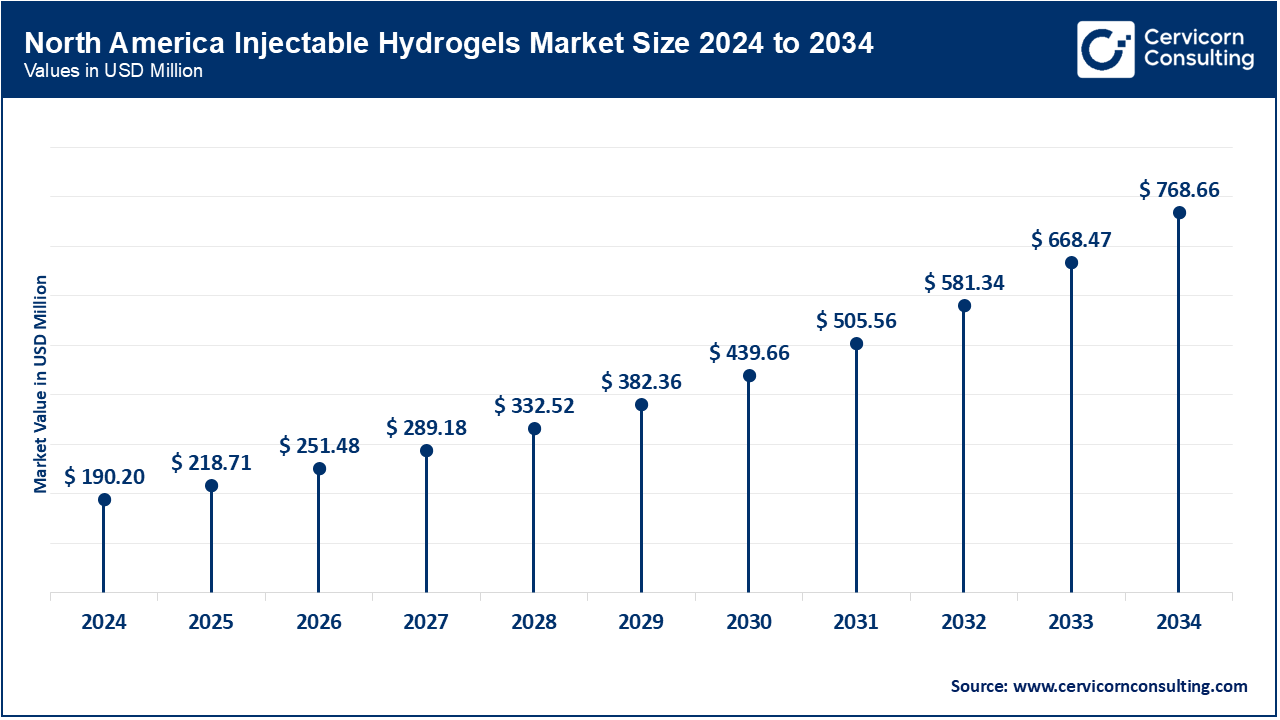
Currently, North America holds the largest share of the global market, largely because of its well-established healthcare system, early adoption of cutting-edge biomedical technologies, and substantial investments in research and development. The United States is leading the way, supported by a strong presence of biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies, favorable regulatory approvals from the FDA, and a rising number of clinical trials that focus on hydrogel-based therapies for chronic diseases, wound healing, and regenerative medicine. As of 2024, the U.S. hosts 200+ active clinical trials involving hydrogel-based therapies, focusing on areas like osteoarthritis, wound healing, and targeted cancer drug delivery. Canada also plays a significant role, especially in areas like cartilage repair and cancer drug delivery.
Important countries like Germany, the UK, France, and the Netherlands are playing a big role in market growth. The EU’s Horizon Europe program allocates €95.5 billion (2021-2027) for research and innovation, with dedicated funding for personalized medicine, regenerative therapies, and sustainable biomaterials. The region gains from government-funded research projects, increased demand for minimally invasive procedures, and a better understanding of modern drug delivery systems. Healthcare providers in Europe are using injectable hydrogels more in wound care and orthopedic treatments. Also, the European Union focuses on promoting innovation in personalized medicine and sustainable biomaterials. This is driving new product development and commercialization in this sector. France and the Netherlands are leading European clinical trials for cartilage regeneration using injectable hydrogels, supported by collaborations between universities and medtech companies. The EU’s Green Deal and Circular Economy Action Plan encourage the use of biodegradable and bio-based polymers, boosting adoption of eco-friendly hydrogel formulations.
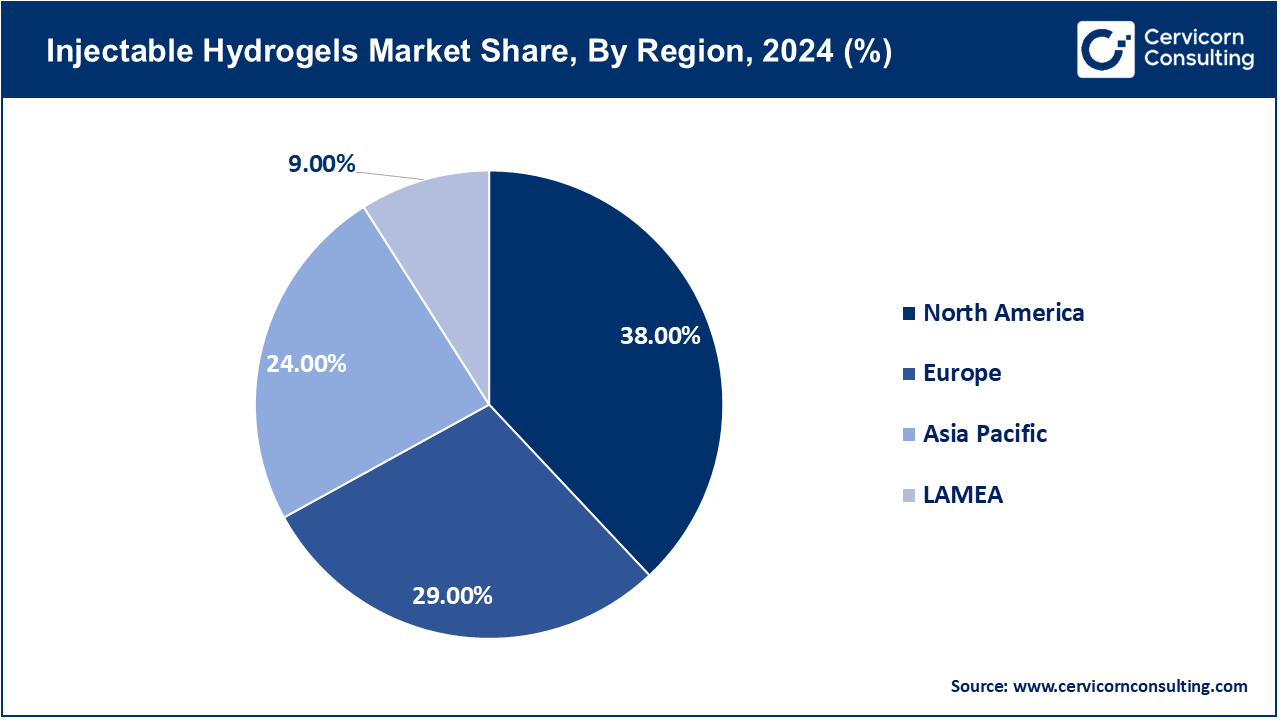
In Latin America and the Middle East & Africa, the market is experiencing moderate growth. Key contributors such as Brazil, Mexico, and the UAE are making progress, largely due to increased investments in healthcare modernization and improved access to advanced therapies. The UAE allocated AED 5.3 billion (USD 1.44 billion) to healthcare in its 2024 federal budget, prioritizing adoption of advanced biomedicine, including injectable hydrogels for orthopedics and cosmetics. However, barriers such as lack of awareness, regulatory lag and higher cost of treatment are hampering quicker entry to the market in these areas. Latin American markets face longer approval timelines (often 18-24 months compared to 9-12 months in the US/EU), slowing product launches.
Market Segmentation
By Material Type
By Application
By End User
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Injectable Hydrogels
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Material Type Overview
2.2.2 By Application Overview
2.2.3 By End User Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.2 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Rising preference for minimally invasive medical procedures
4.1.1.2 Advancement of targeted and sustained drug delivery systems
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 High development and production cost
4.1.2.2 Regulatory complexities
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 Limited Mechanical Strength
4.1.3.2 Scalability and Reproducibility
4.1.4 Market Opportunities
4.1.4.1 Integration of Nanotechnology and Advanced Bioengineering
4.1.4.2 Growing Demand for Cosmetic and Aesthetic Applications
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Injectable Hydrogels Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Injectable Hydrogels Market, By Material Type
6.1 Global Injectable Hydrogels Market Snapshot, By Material Type
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Natural Hydrogels
6.1.1.2 Synthetic Hydrogels
6.1.1.3 Hybrid Hydrogels
Chapter 7. Injectable Hydrogels Market, By Application
7.1 Global Injectable Hydrogels Market Snapshot, By Application
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Drug Delivery Systems
7.1.1.2 Tissue Engineering
7.1.1.3 Wound Care
7.1.1.4 Cosmetic & Aesthetic Medicine
Chapter 8. Injectable Hydrogels Market, By End-User
8.1 Global Injectable Hydrogels Market Snapshot, By End-User
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Hospitals
8.1.1.2 Ambulatory Surgical Centers (ASCs)
8.1.1.3 Research Institutes
Chapter 9. Injectable Hydrogels Market, By Region
9.1 Overview
9.2 Injectable Hydrogels Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
9.3 Global Injectable Hydrogels Market, By Region
9.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
9.4 North America
9.4.1 North America Injectable Hydrogels Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.3 North America Injectable Hydrogels Market, By Country
9.4.4 U.S.
9.4.4.1 U.S. Injectable Hydrogels Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
9.4.5 Canada
9.4.5.1 Canada Injectable Hydrogels Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
9.4.6 Mexico
9.4.6.1 Mexico Injectable Hydrogels Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
9.5 Europe
9.5.1 Europe Injectable Hydrogels Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.3 Europe Injectable Hydrogels Market, By Country
9.5.4 UK
9.5.4.1 UK Injectable Hydrogels Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
9.5.5 France
9.5.5.1 France Injectable Hydrogels Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
9.5.6 Germany
9.5.6.1 Germany Injectable Hydrogels Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
9.5.7 Rest of Europe
9.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Injectable Hydrogels Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6 Asia Pacific
9.6.1 Asia Pacific Injectable Hydrogels Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.3 Asia Pacific Injectable Hydrogels Market, By Country
9.6.4 China
9.6.4.1 China Injectable Hydrogels Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6.5 Japan
9.6.5.1 Japan Injectable Hydrogels Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6.6 India
9.6.6.1 India Injectable Hydrogels Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6.7 Australia
9.6.7.1 Australia Injectable Hydrogels Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
9.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Injectable Hydrogels Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
9.7 LAMEA
9.7.1 LAMEA Injectable Hydrogels Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.3 LAMEA Injectable Hydrogels Market, By Country
9.7.4 GCC
9.7.4.1 GCC Injectable Hydrogels Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
9.7.5 Africa
9.7.5.1 Africa Injectable Hydrogels Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
9.7.6 Brazil
9.7.6.1 Brazil Injectable Hydrogels Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
9.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
9.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Injectable Hydrogels Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 10. Competitive Landscape
10.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
10.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
10.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
10.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
10.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 11. Company Profiles
11.1 3M Company
11.1.1 Company Snapshot
11.1.2 Company and Business Overview
11.1.3 Financial KPIs
11.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
11.1.5 Strategic Growth
11.1.6 Global Footprints
11.1.7 Recent Development
11.1.8 SWOT Analysis
11.2 Johnson & Johnson
11.3 Smith & Nephew plc
11.4 Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD)
11.5 B. Braun Melsungen AG
11.6 Anika Therapeutics, Inc.
11.7 Zimmer Biomet Holdings, Inc.
11.8 Pfizer Inc.
11.9 AstraZeneca plc
11.10 Biogelx Ltd.
11.11 Regentis Biomaterials Ltd.
11.12 T&R Biofab Co., Ltd.