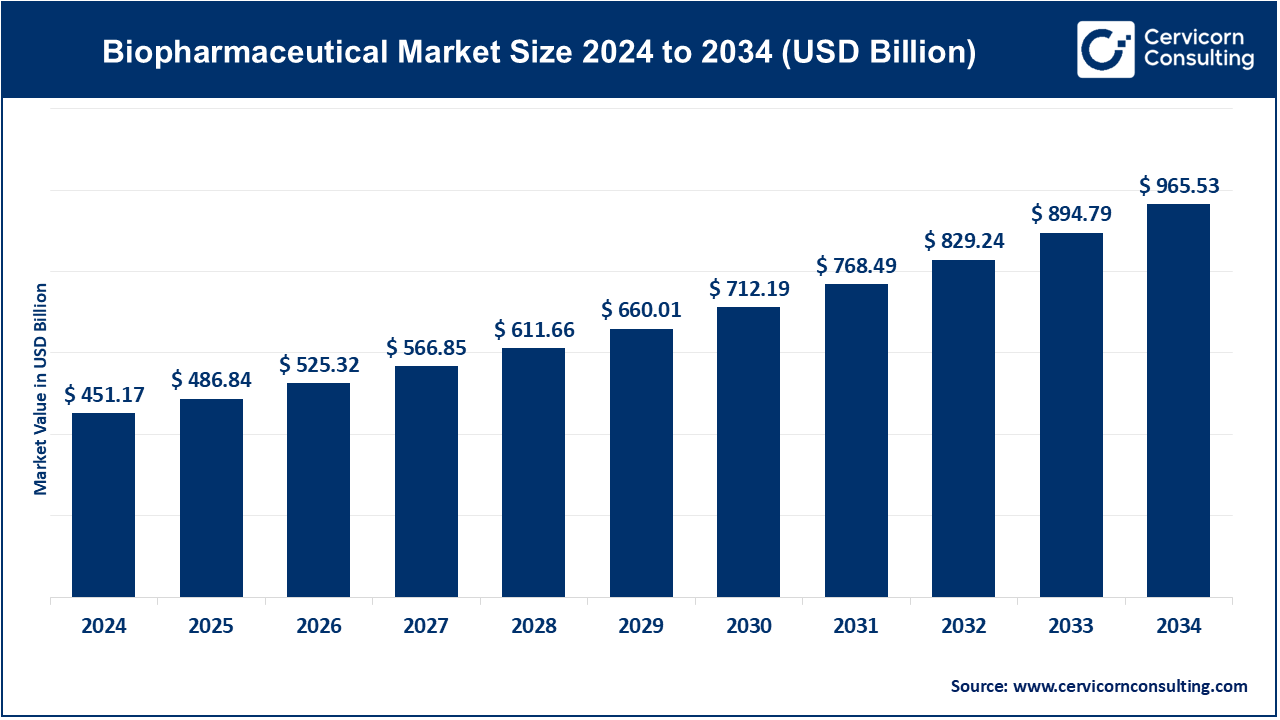
The global biopharmaceutical market size was reached at USD 451.17 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 965.53 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.9% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
The development of complex biologic therapies like monoclonal antibodies, vaccines, and gene therapies falls under the biopharmaceutical market. Its focus is directed towards more sophisticated and accurate precision medicine biotechnology disease management. The rising prevalence of chronic diseases coupled with an increasing focus on research and development (R&D) activities is driving the market growth. The application of artificial intelligence (AI) alongside other digital tools automates almost all processes in drug development and clinical trial processes. AIs augment the automation of other manual tasks and processes. Interdisciplinary collaboration between pharma companies and research centers fosters innovative solutions. The support of safety and efficacy monitoring through regulatory entities bolsters funding control. It appears that the global healthcare system is about to shift to more efficient individualized treatment.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 486.84 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2033 | USD 894.79 Billion |
| Projected Market CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 7.9% |
| Principal Region | North America |
| Booming Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Type, Drug Type , Drug Development Type, Formulation, Route of Administration, Prescription Type, Distribution Channel, Application, End User, Region |
| Key Companies | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Novartis AG, AbbVie Inc., Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc., Merck & Co., Inc., Pfizer Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Sanofi, GSK plc., AstraZeneca, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Biogen, Eli Lilly and Company, Amgen Inc. |
Growth of emerging markets with increasing healthcare access
Increased market growth for biosimilars due to patent expirations
Supportive reimbursement policies for innovative therapies
Stringent and lengthy regulatory approval pathways
Limited patient access due to affordability issues
Challenges in biosimilar interchangeability and acceptance
Collaboration between pharma and biotech and technology firms
Improvements of vaccine technologies and pandemic threats
Therapeutics for uncommon diseases are becoming more in demand
Navigating the global regulatory challenges
Significant capital investment needed to manufactuter biologics
Nanobiotechnology in medicine
Insulin: In Merilog received FDA approval in February 2025, making it the first rapid‑acting insulin biosimilar and thereby broadening the range of available biosimilars beyond long-acting ones. This enhances the access and affordability for the approximately 8 million Americans using insulin. With more than 38 million people having diabetes in the U.S., the introduction of biosimilars is instrumental for lowering costs. This development also comes with the hopeful prospects of insulin independent therapies with the 2023 approval of the Donislecel allogeneic islet cell therapy. These advances represent a shift towards combining analog and cellular therapies. As a result, broader insurance coverage is likely. They are striving to make full use of innovation in the insulin ecosystem. Insulin innovations are incessantly on the rise.
Vaccine: Vaccination developments from 2023-2025 drew strategic funding and regulatory attention which greatly increased the pace of innovation. In 2024, the FDA's advisory panels revised the COVID-19 booster and boster-mucosal nasal vaccines entered the early trial phases. That same year BARDA funded mRNA-based influenza vaccines as part of pandemic prepper initiative. These actions mark the transition to more flexible and programmable approaches to rapid vaccine development. There is increased responsiveness, including the adaption to more innovative regulations which allow for swifter maneuvering with these new techniques. The next level for vaccine science is being more agile and adaptable. This strengthens strategies to stave off future pandemic responsiveness endeavors.
Hormone: During the 2023�2025 period there was considerable advancement in the therapies and alternatives to hormone treatment. Donislecel received approval in 2023 and now administers pancreatic hormones through islet cell transplantation, enabling a large patient population to sustain insulin free for long periods of time during periods of active disease. Concurrently, the standard of medical care with peptide hormone analogues and biomanufactured enzymes has also progressed. Legislative policies have been refined regarding the passage in budget or regulatory edicts aimed at orphan hormone therapies. The increasing number of patients with chronic diseases always sways the government to support these therapies. Enhanced manufacturing flows are expanding improvement of scale and lower costs. There is a substantial increase in patient access with depth of the pipeline.
Interferon: There was less activity in approvals of therapies on the use of interferon from 2023 to 2025, but the research for newer formulations does not stop. Interferon and interleukin analogues are being reformulated to incorporate increased safety in previously novel methods of application. Regulators are considering emerging fast-track pathways to designation for some implied towards hepatitis, irrespective of the additional multiple sclerosis focus. NIH-funded research is evaluating the role of adjuvants in vaccine using interferon for a therapeutic purpose. Current standards and policies for production ensure the new works are consistent and less adverse effects. The scientific base, although lacking approvals, remains strong with no new coming out. Product quality and the associated therapeutic claim are ensured by persistent governmental control. There are still possibilities of considerable advances regarding interferon for currently unused potential in those physiological factors.
Erythropoietin: Erythropoietin (EPO) has not seen FDA approval for any new formulations in 2023-2025. It continues to serve as a fundamental treatment option for peripheral anemia resulting from chronic kidney disease and for patients undergoing chemotherapy, which impacts more than 2 million Americans each year. The previously authorized biosimilars continue to improve access and affordability for patients. Safety protocols still impose stringent requirements regarding batch uniformity and antibody scrutiny within biopharmaceutical production systems. NIH-sponsored clinical trials seek to fine-tune the dosing schedule and lower the chance of cardiovascular complications. Other government surveillance systems have begun tracking adverse events to support product safety. EPO remains entrenched in contemporary clinical practice amid supportive legislation and regulations. It is subject to continual quality improvement, which justifies its intensified use.
Biopharmaceutical Companies: The biopharmaceutical sector continues to lead both on innovation and on new regulatory policies. Recent FDA clearances such as Merilog, Donislecel, and new vaccine strategies depict strong interagency cooperation. Shift to platform-based designations and priority review adoption indicates more cooperation and synergy from this side of the government. NIH funding for early-stage research also sponsors directed drilling industry pipelines. As these companies build portfolios in gene therapy, vaccines, and biosimilars, they increasingly interact with regulators. Investment in the quality and compliance of manufacturing has also increased greatly as a result. The US innovation ecosystem and its sustained future competitiveness are both strengthened by this synergy.�
Clinical Research Institutes: Clinical research institutes are widely recognized for their contribution towards the translation of therapies from the bench to the bedside for novel treatments. The nasal COVID vaccine clinical trial spearheaded by the NIH in August 2024, as well as the ongoing islet cell therapy studies, are prime examples of this. Advanced collaborations with FDA as well as NIH clinical networks have gained efficiency in the translation of scientific breakthroughs. A considerable amount of work has also been done towards the development of the mRNA influenza vaccine by institutes. Dozens, if not hundreds, of advisory panels report from various institutes and federally employed scientists, incorporating these academic-evaluative insight directly into regulatory policies. Such legal and financing frameworks have formed these partnerships. Because of this, CRIs remain a pillar to the national R&D infrastructure and as the intermediaries of innovation diffusion.
Health and Care (Hospitals/Clinics): Hospitals and clinics function as primary distinct access points for advanced biologic therapies within the health system. They were some of the first adopters for Merilog, Donislecel and updated COVID-19 boosters under the FDA�s guidance. Clinics are testing outcome-based reimbursement models for gene therapies with newer insurance plans. There is comprehensive post-marketing surveillance for full adherence to safety regulations. Addressing legal frameworks for redistribution also ensures Equitable access programs are implemented. End-user facilities also generate essential real-world effectiveness and tolerance data for maintenance of approval. Such advancements strengthen their role in the continuum between innovation and patient care. �
Diagnostic Labs: Through advanced molecular testing, diagnostic laboratories enable precision medicine and are indispensable. They support therapies like islet cell transplants and TCR-based cancer treatments by delivering high-integrity genomic data. Between 2023 and 2025, better stratification of patients into trial groups for treatment saw the supporting approval of companion diagnostics. Labs also adapted SARS-CoV-2 variant testing to support the updated booster rollouts. Compliance with CLIA and other accreditation standards assures reliability of the test results. Submission of laboratory data strengthens regulatory submissions for biologics. Education diagnostic labs provide treatment matching and alignment with regulations is crucial.
Blood Disorders: Therapeutics of blood disorders, specifically cellular interventions, are changing the standard of care. The approval of Donislecel�s is a landmark advancement in type-1 diabetes treatment, significantly reducing dependence on insulin. NIH-led follow-up trials are working to optimize the long-term efficacy and immunosuppression protocols of the transplant. Also, biosimilar EPOs continue to enhance cost-effective treatment of anemia. Regulatory policies support the evolution of clinical practice paradigms through combination treatment strategies. Government supervision increases through the imposition of quality criteria and patient safety surveillance. The legal framework remains conducive to innovation in the field of hematology owing to sustained R&D investment.
Oncology: Oncology remains one of the most attractive therapeutic areas for innovative biologic therapies and vaccines. Regulations in 2024 provided policy-driven recommendations for platform-based vaccine and mRNA use in cancer. Novel approaches for vaccines used by US advisory armed were based on COVID-19 models. Designation of fast-track and RMAT has greatly advanced the development of cell-based oncology therapies. Early stage immuno-oncology clinical trials performed at clinical research institutes are governed by Evolving legal pathways encompassing accelerated approvals and long-term safety monitoring. There is strong collaboration between developers of new medicines and public health institutions which make oncology a primary area of focus for biopharma expansion and public health initiatives.
Infectious Diseases: The development of new vaccines for infectious diseases illustrates a sound investment in public health policy. COVID-19 nasal vaccines are being clinically tested at NIH, demonstrating a broadening immune response strategy. Development of the flu vaccine received considerable federal funding in anticipation of future pandemic threats. The ADAPT Updates were incorporated into clinical practice preceding the midyear Booster Strain Recommendations. Expedited vaccine authorizations to address public health emergencies continue under the streamlined EUA process. Legal preparedness frameworks strengthen stockpiling and response initiatives. Collaborations between the government and the biopharma industry are now central to the infectious disease product development value chain. This establishes a useful benchmark for readiness to respond to future outbreaks.
Neurological Diseases: The increasing focus on gene and cell therapies targeting neurological disorders can be attributed to modern regulatory frameworks. The 2024 FDA approval of Lenmeldy for pediatric leukodystrophy was a remarkable milestone. Orphan and RMAT designations facilitated the establishment of expedited review processes alongside patient registries. NIH funding is directed toward the development of platforms aimed at addressing the CNS and ensuring long-term safety of the interventions. New supporting policies came in the form of outcome-based reimbursement payments. Advisory panels are developing strategies for active monitoring of post-approval CNS gene therapies. It is becoming evident that sustained regulation coupled with continuous innovation is propelling the neurology field forward.
Cardiovascular Diseases: The use of biologic therapies for treating cardiovascular conditions is in the early development stages with some regulatory support for their use under expedited pathways. NIH-funded trials are investigating mRNA-mediated angiogenesis strategies in heart-failure cohorts. FDA guidance is shifting to support the inclusion of these therapies under accelerated pathways. There continues to be support for early-stage RCTs on gene targets related to hypertension and heart disease. Laboratories are developing companion diagnostics for advanced biologics patient stratification. Public funding supports the initiation of the trial data and the criteria that are set for inclusions. Legal bodies are streamlining the modalities for approval and post-market regulation to align with these new methods which places cardiovascular biologics to scale further down the line.
Immunology: Immunology continues to be one of the fastest evolving areas with developing biologic and vaccine offerings. In 2024, more than the previously established reasons for prescribing omalizumab was approved towards helping patients with food allergies mark it as an extension of indications. There has been even more support for new monoclonal antibodies targeting allergies and autoimmune diseases. NIH provides funding for assays and biomarker development which is useful in the creation and monitoring of therapies. Designs that allow fast-track processes are widespread in regard to immuno-oncology and biologics for allergies. Monitoring capabilities after granting marketing permissions still follows strict safety protocols. There is strong legal supervision post-authorization to maintain the standard of quality along with monitored care. Solutions based on immunology to treat illnesses interface with frontline therapy development and implementation.
The biopharmaceutical market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here�s an in-depth look at each region
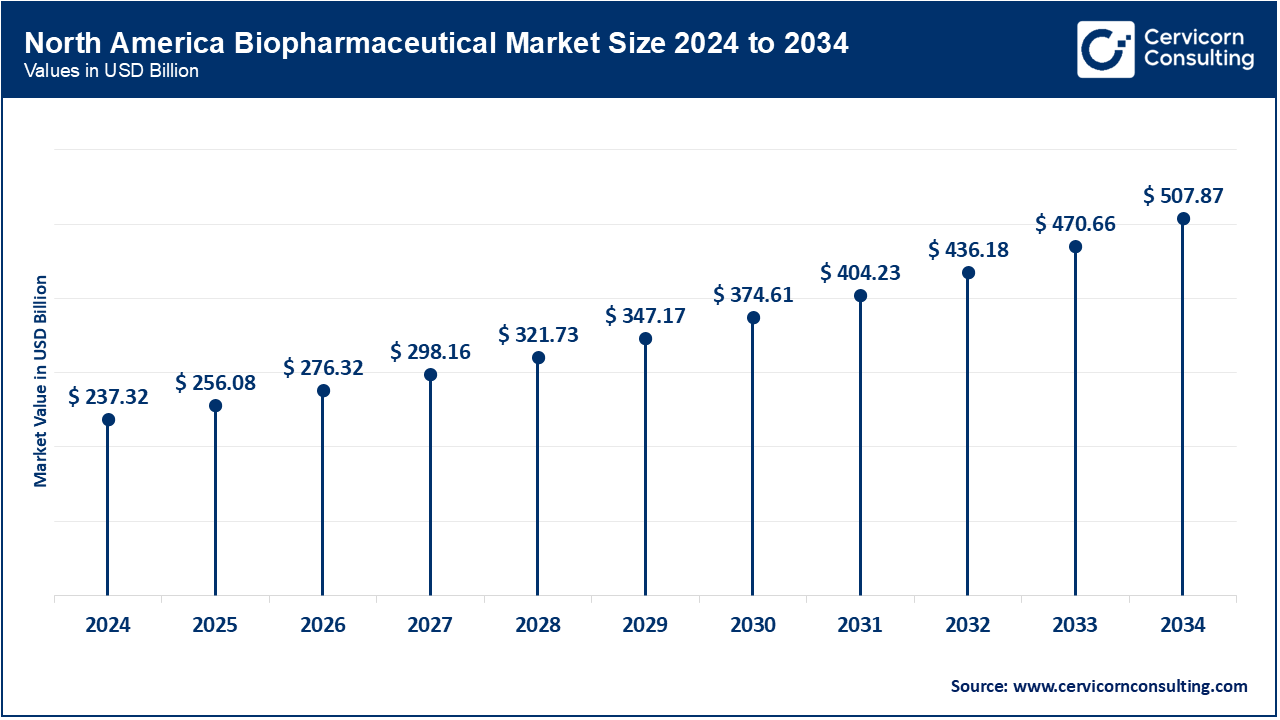
The North America biopharmaceutical market size was valued at USD 237.32 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 507.87 billion by 2034. In 2024, the FDA accepted 126 new drugs (including 16 biologics), showing continued advancement, especially for rare diseases and cell therapy. Canada underscored this trend by approving Beqvez, Pfizer's one-time gene therapy for hemophilia B, in December 2023, with US and EU greenlights in early 2024, while Mexico�s COFEPRIS is actively assessing other gene-therapy dossiers. The FDA also approved a record 19 new biosimilars across all therapeutic areas in late 2024, further increasing competition. These approvals also came with new fast-track and RMAT designations for oncology and metabolic therapies. Heuristic alterations shift North America�s forefront position in biologics and gene therapy. Efforts to standardize regulations across borders continue improving the time needed from approval to marketing.
The Europe biopharmaceutical market size was valued at USD 102.42 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 219.18 billion by 2034. The biopharma chronicle of Europe in the years 2023-2025 tells the story of significant progress as EMA in 2023 approved Roctavian, the gene therapy for hemophilia A. In February of 2024, Casgevy, the first CRISPR-based therapy for sickle cell and beta-thalassemothia, received conditional marketing authorization and NHS plans began enabling treatment for hundreds. Germany and France are now adopting accelerated review and real-world evidence integration frameworks in biosimilars like ustekinumab�s mid-2024 approval. The UK also reinforced its lead in gene-editing regulation by approving casgevy in nov 2023. Health systems are piloting outcome-based reimbursement models for novel therapies.
The Asia-Pacific biopharmaceutical market size was estimated at USD 85.27 billion in 2024 and is predicted to surpass around USD 182.49 billion by 2034. The Asia-Pacific region is moving up the ladder in biopharma innovation because of policy support, increasing R&D investments, and favorable initiatives. In April 2023, China�s NMPA BD111 gene-editing therapy received clearance for Phase III HSV trials at several hospitals, and the US FDA had earlier provided orphan drug designation in 2022. India has enabled CAR-T var-cel non-Hodgkin�s lymphoma therapy delivery through Hospital Clinic Barcelona and Bengaluru centers by mid-2024. Japan is also actively pursuing regenerative and cell therapy approvals for acceleration through Sakigake. The post-COVID-19 infrastructure build for Australia includes mRNA vaccine development. Public�private partnerships are emphasizing the South Korean biotech hubs for advanced therapy translation and regulatory capacity building.
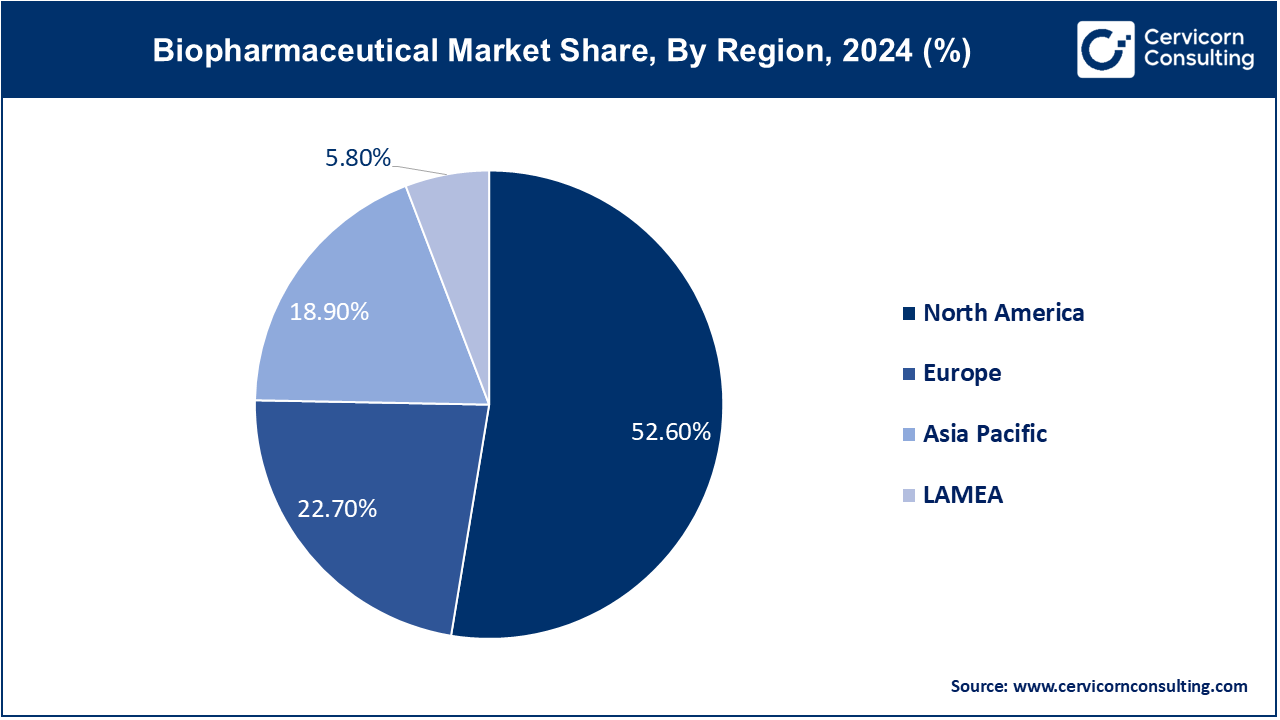
The LAMEA biopharmaceutical market size was valued at USD 26.17 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 56 billion by 2034.�During 2023-2024, Brazil�s ANVISA is streamlining biosimilar registrations and gene-therapy evaluation processes. These expansions, alongside the TAC-funded mRNA COVID-19 vaccine mRNA enabled infrastructure expansion, will occur after TBAV�s 2023 voluntary control program. In 2024, dedicated biotech zones and fast access frameworks for cell and gene therapies will be established in Saudi Arabia and the UAE. By the end of 2023, South Africa�s SAHPRA has enhanced the local capacity for clinically pertinent biosimilars, hosting trial governing the first-in-region biosimilars and vaccine studies. There are new public-private initiatives introduced to expand services for advanced therapies, shaping a new LAMEA strategy that brings in line with shifting global practices. The consolidation of these initiatives alongside the GCC and Mercosur regulatory agreements accelerates access across borders for regions to strengthen alignment with global practices.
The biopharmaceutical market is led by major companies such as F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Novartis AG, AbbVie Inc., Johnson & Johnson, Merck & Co., and Pfizer Inc., which are pioneering innovations in biologics, gene therapies, and cell-based treatments. These industry leaders are investing heavily in advanced R&D platforms and leveraging cutting-edge biotechnologies like CRISPR, mRNA, and monoclonal antibodies to accelerate drug development. Collaborations with academic institutions and regulatory agencies have streamlined approvals, enabling faster patient access. Recent breakthroughs include gene therapies for rare diseases and novel biosimilars enhancing treatment affordability. Strategic mergers and acquisitions have expanded pipeline depth and manufacturing capabilities globally. Their focus on personalized medicine and scalable biomanufacturing is redefining patient care and expanding the global biopharmaceutical footprint. These efforts continue to drive growth and innovation across the healthcare ecosystem.
Recent partnerships in the Biopharmaceuticals Market highlight a strong emphasis on innovation and integrated healthcare solutions. Roche has partnered with Moderna to advance mRNA therapeutics beyond vaccines into oncology and rare diseases. Novartis collaborates with CRISPR Therapeutics to accelerate gene-editing therapies for blood disorders. Pfizer teamed up with BioNTech to expand their mRNA pipeline into personalized cancer vaccines. Johnson & Johnson joined forces with Apple to develop digital health tools supporting medication adherence and patient monitoring for injectable biologics. These alliances enhance R&D efficiency, speed regulatory approvals, and improve patient outcomes through next-generation therapies. Collectively, they are reshaping drug development and delivery in the biopharmaceutical ecosystem.
Market Segmentation
By Type
By Drug Type
By Drug Development Type
By Formulation
By Route of Administration
By Prescription Type
By End-user
By Application
By Distribution Channel
By Region