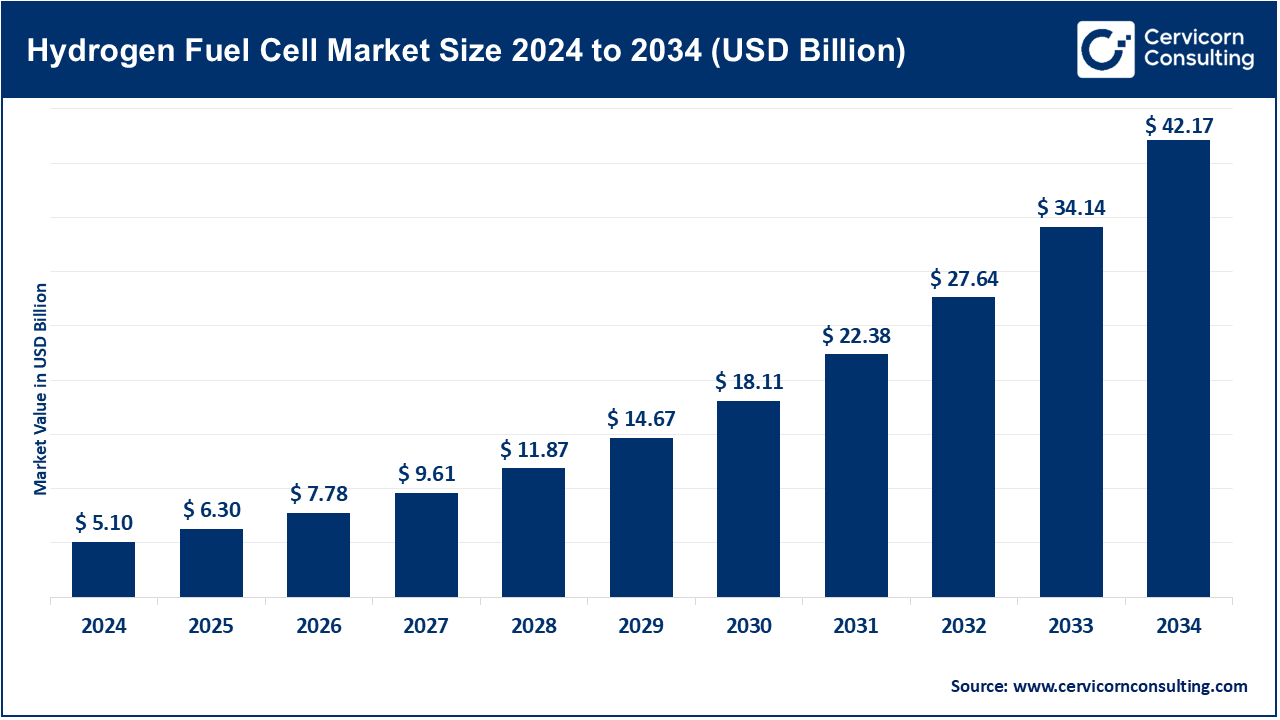
The global hydrogen fuel cell market size was estimated at USD 5.10 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 42.17 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23.52% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
The hydrogen fuel cells market growth is driven by an infrastructure development, growing concern over energy security, and the need for clean energy. Increasing and growing concern about the energy security also NestGen are impacting fuel cells use in the transportation ion, industrial operations, and stationary power generation processes because boast high efficiency while maintaining zero emissions. Specialized advancements in the production of the green hydrogen such as proton exchange membranes and compact stacks are enhancing cost effectiveness and scalability. Adoption is bolstered by international collaborations, governmental policies, funding for pilot projects, and other type of policy initiatives. Increased spending on R&D, expanded manufacturing capacities, and stronger collaboration across different sectors are all being pursued simultaneously by leading corporations which is anticipated to enhance the availability of hydrogen fuel cells, transforming energy systems to more sustainable, resilient, and low-carbon alternatives.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 6.30 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2025 | USD 42.17 Billion |
| Projected Market CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 23.52% |
| Dominant Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Type, Technology, Company Size, Application, End User, Region |
| Key Companies | AFC Energy, Audi, Ballard Power Systems, Bloom Energy, BMW, Ceres Power, Cummins, Daimler, Doosan Fuel Cell, FuelCell Energy, Fuji Electric, Hyster-Yale, Honda Motor, Horizon Fuel Cell, Intelligent Energy, Kyocera, MAN SE, Nedstack Fuel Cell, Nikola |
Air-Cooled: The air-cooled systems contributed the highest revenue share in the market. The air-cooled systems utilize air for both the heat control and cooling processes, thus, they are suitable for compact and lightweight systems with low to moderate power needs. They are vertically integrated in portable devices and small mobility platforms. Recently in July 2023, Ballard Power launched an advanced air-cooled PEM fuel cell stack designed for UAVs and small logistics vehicles, enhancing both lifespan and thermal efficiency. This launch was driven by the increasing last mile delivery and drone market. These systems have a lower level of complexity and a lower cost of construction and maintenance, which also enables greater accessibility in developing regions. Manufacturers are focusing on outdoor ruggedized designs for these systems.
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue Share, By Type, 2024 (%)
| Type | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Air-Cooled | 67.40% |
| Water-Cooled | 32.60% |
Water Cooled: Water cooled systems are well suited for high load application vehicles such as trucks, buses, and industrial equipment. These systems are effective for sustained high power consumption. Hyundai has recently implemented upgrades to their overheating wear and range capable hydrated trucks which utilizes water cooled fuel stack mounted systems. These advancements make prolonged transport routes more commercially viable. Public transit and transport logistics fleets heavily utilize these systems. Adoption rates are rising in the US, South Korea, and Europe. The long-term deployment of systems hinges on the efficiency of the cooling mechanisms employed.
Polymer Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFC): The PEMFC segment has registered highest revenue share. Due to low operating temperature and quick start-up, PEMFCs can be used in portable and automotive applications. These are the most commercialized fuel cells. Toyota has already released the third-generation PEM fuel cell as of June 2024, featuring greater power density and lesser platinum use. It is intended for use in SUVs and light trucks. PEMFCs continue to lead in global FCEV deployments. Efforts are being made to increase retention levels. Partnerships are with OEM are increasing to include marines and railroads.
Direct Methanol Fuel Cells (DMFC): DMFCs are most appropriate for military and portable devices as they utilize liquid methanol fuel. In February of 2025, a Japanese electronics firm developed a compact fuel DMFC charger which provides over 15 hours of backup power greatly improving usability. DMFCs are still used in areas with unreliable access to grid power. They are increasingly being used for military purposes and for disaster management. Work continues in areas of energy density, methanol crossover, and other refinements. According to Frost & Sullivan, there is significant potential in DMFC developing markets.
Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells (MCFC): MCFCs are primarily utilized in stationary industrial and utility scale power systems since they operate at the highest temperature of all fuel cells. In addition, MCFCs can use natural gas or biogas as fuel. Recently, FuelCell Energy expanded the operation of their MCFC power plants in California to provide low-emission energy to wastewater facilities, thus aiding in the integration of carbon capture technologies. Adoption of MCFCs in decentralized power networks is on the rise. The extreme operating temperature allows for co-generation applications. Focus areas for the near future include longevity of the stacks and boosting system efficiency.
Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cells (PAFC): PAFCs employ phosphoric acid as an electrolyte which maintains stable output and is more useful for stationary power with integrated heat recovery. They work at intermediate temperatures which is best for hospitals and universities. In August 2022, Doosan Fuel Cell PAFC South Korea dispatched a PAFC system to a medical center to reduce dependence on diesel and allow for a 24/7 functioning system. The unit also supplied heat used for sterilization and HVAC systems. PAFCs are known for reliability and long operating hours, and competition is sparse in the mid-temperature region. There is a focus on improving thermal output and reducing size.
Others: This category incorporates the rarer SOFCs and AFCs fuel cells which are beneficial for their high efficiency and fuel flexibility. Their primary applications are in the stationary and aerospace industries. Bloom Energy's new modular SOFC system designed for hydrogen and biogas hybrids to be used at industrial parks was announced in January 2025. These systems allow multi-fuel flexibility and are designed for continuous operation. AFCs are regaining popularity due to their use in aerospace and defense applications. This category is driven by innovative technology.
Portable: Powering portable fuel cells and other field and tactical applications with quiet clean sources of power. These systems are invaluable where traditional utility grid capacity is unserviced and the cost for power from diesel generators is too prohibitive. In Germany, in April 2023, SFC Energy announced next generation hydrogen powered flexible generator for responsive multifunctional emergency footprint capability. The unit helped backup areas severely flooded. These systems are gaining adoption in telecom towers as well. Portability and durability remain key R&D areas. The segment continues to be driven by miniaturization.
Stationary: The stationary segment accounted for the largest share of market revenue. Stationary fuel cells offer continuous or backup power to buildings, data centers, and utilities, giving a zero-emission alternative to diesel generators. Microsoft began a hydrogen fuel cell trial in November 2024 to replace gensets at a data center in Washington to ensure reliable uptime during grid outages which aids long-term climate goals. These systems are now being adopted in commercial real estate and hospitality. New emerging models are hybrids with solar and batteries. Stack life and efficiency remain critical.
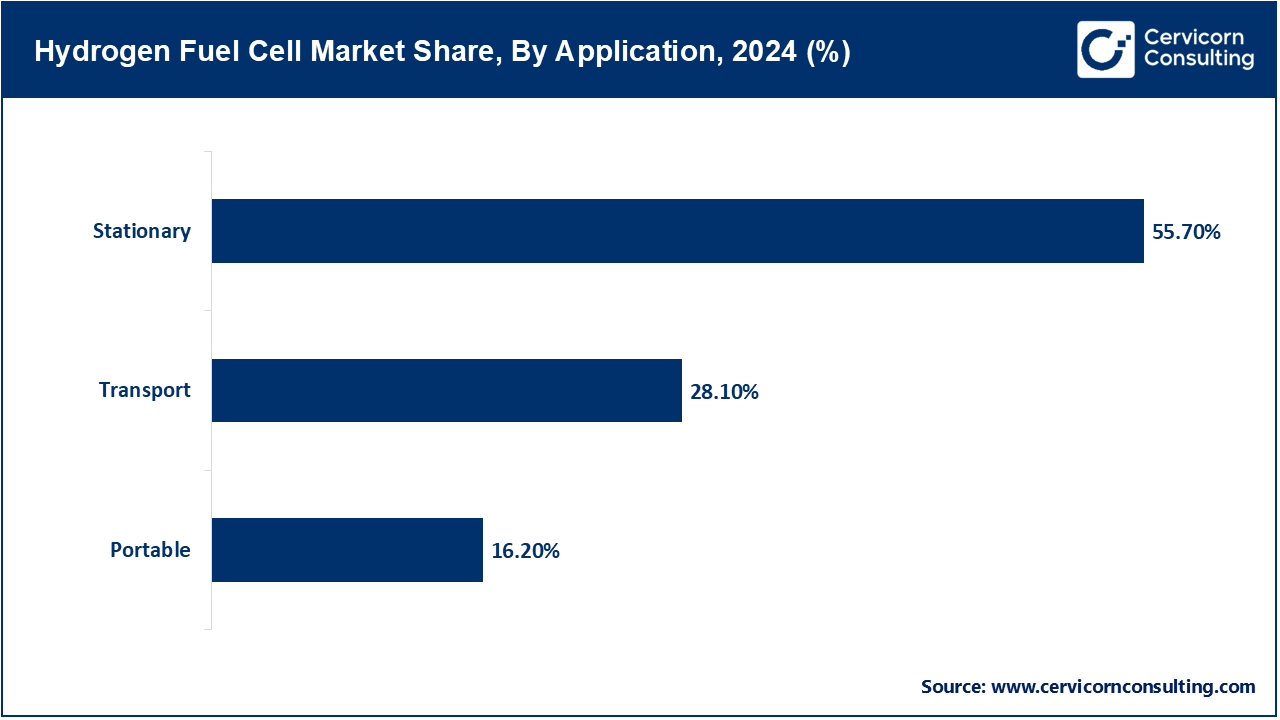
Transport: Fuel cells offer long ranges and quick refueling, making them ideal for buses, trucks, and trains, where batteries still fall short. These vehicles emit only water vapor. Hyundai fuel cell stacks supported the operation of over 500 fuel cell buses added in Seoul in December 2024 as part of the city's green mobility initiative. The city aims to exceed 1,300 fuel cell electric buses (FCEBs) by 2026. Transport still accounts for the bulk of PEMFC applications. Adoption is accelerating due to infrastructure expansion. There is still keen interest from global OEMs.
Defense: For military operations, supplied power packs, ground vehicles, and fuel cells equipped drones are needed for silent operation, extended range, and lean power in remote areas. In March 2023, the U.S. Army started field testing unmanned ground vehicles powered by fuel cells which boosts field mission stealth and endurance efficiency. Hydrogen is less logistically burdensome than diesel. Military agencies are making investments in off-grid energy technologies. Key competitive advantages include silent operation with low heat signature and modular integration.
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue Share, By End User, 2024 (%)
| End User | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Defense | 21.13% |
| Fuel Cell Vehicles | 32.62% |
| Utilities | 46.25% |
Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCEVs): FCEVs are powered by onboard generated hydrogen combustion electricity, offering long range and fast refueling when compared to battery vehicles. They are ideal for fleet vehicles and areas with existing refueling infrastructure. Joint development of a hydrogen-fueled SUV was announced in October 2023 by BMW and Toyota, targeting 2028 global production. This expands their engineering and market reach. FCEVs are being adopted for delivery vans and pickup trucks as well. There is rising consumer demand in Europe and the Asia-Pacific region. Focus is on fuel economy and cost equivalence.
Utilities: Hydrogen fuel cells are used by utilities to balance grids, manage peak load, and store renewable energy. These systems offer backup and baseload power with zero emissions. In August 2024, RWE of Germany commenced a pilot project which uses hydrogen fuel cells to provide supplementary power during low wind periods at offshore wind farms. This integration lessens curtailment and enhances grid resilience. Electric utilities regard fuel cells as potential replacements for gas peaker plants. Closed-loop electrolyzer to fuel cell systems remain in testing stages. Policy support seems to be fostering progress.
Large Enterprises: The large enterprises have maintained a leading position in the market. Large corporations utilize hydrogen fuel cells on a logistical scale within the fleet management, logistics, and energy systems sectors. They often team up with tech companies to meet impact goals. In June 2023, Amazon enhanced hydrogen integration with Plug Power by outfitting fuel-cell forklifts and testing hydrogen delivery vans at its distribution centers. This is in line with its 2040 net-zero emissions commitment. Corporate buyers drive down technology costs. Their scale suffices for pilot-to-deployment transitions. There is strong funding appetite within e-commerce and retail.
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue Share, By Company Size, 2024 (%)
| Company Size | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Large Enterprises | 69.60% |
| Small and Medium Enterprises | 30.40% |
Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs): Niche components, testing services, and ever more specialized applications enable small to medium enterprises (SMEs) to work on fuel cell innovation. They tend to be agile due to government grants. In February 2025, one UK-based SME revealed a lightweight, extended flight time hydrogen drone for agricultural aerial monitoring. These firms excel at miniaturization and specialize in other narrow domains. Their collaboration with universities is common. Their size facilitates rapid prototyping. Regulatory frameworks and IP protections are critical for SME expansion.
The hydrogen fuel cell market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region.
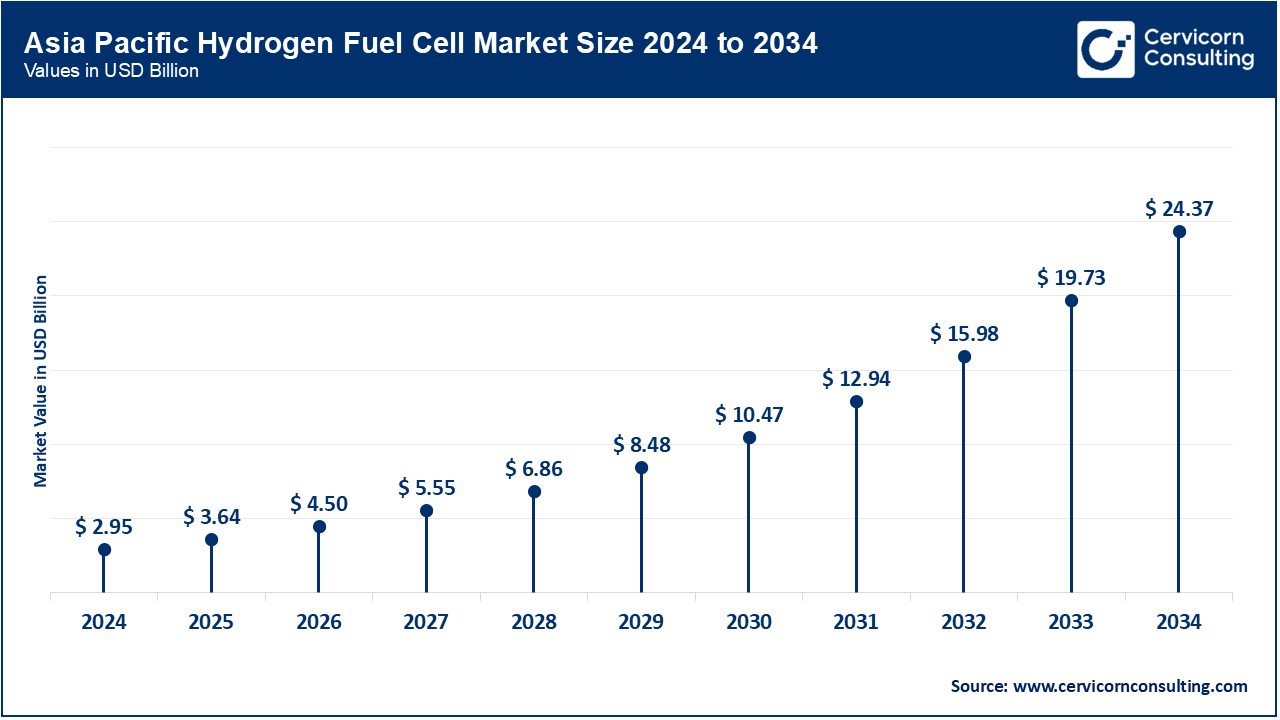
The Asia-Pacific region holds the largest market share. The increasing dominant factors of highway construction, automotive industry, and decarbonization goals are increasing growth in the region. Japan, China, and South Korea are the leaders in the market. South Korea reaffirmed its green mobility strategy by planning to deploy 1,200 hydrogen buses and 50 refueling stations by 2026. Japan continues promoting hydrogen through its Basic Hydrogen Strategy and vehicle trials conducted in Tokyo. China is facilitating the use of hydrogen in urban transport and around heavy industry hubs. India and Australia are focusing on green hydrogen for national energy security. For manufacturing scale and offering potential, APAC is even more important.
The North America is on a remarkable growth trajectory thanks to certain policies developed for the clean energy transition, strengthening of federal subsidies, and interest and development from the automotive, logistics and stationary power industries. The U.S. seems to be in the lead with ongoing investment into hydrogen infrastructure, while Canada and Mexico are developing planning approaches to close the gap. In October 2023, the U.S. Department of Energy announced the launching of seven clean hydrogen hubs with $7 Billion of funding to support early adopter of clean hydrogen in transportation, and other sectors. The Canadian Government has a $0.3 billion commitment to hydrogen projects, with a strategically narrower focus towards green hydrogen exports. Mexico is considering hydrogen as a decarbonization option for cement and steel. Hydrogen powered rail is being piloted in the region as well. Increased partnership with the public and the private sector is needed to scale up.
Europe is recognized around the world as the most advanced region in the world for the adoption of hydrogen fuel cells. The EU Hydrogen Strategy continues to provide favorable elements, and the climate targets are a critical component. Germany, France, and the Netherlands are leading in hydrogen infrastructure as well as de-carbonization of transport and industry. In April 2024 Germany introduced a funding program worth USD 1.06 billion for the installation of hydrogen truck and refueling stations along transcontinental freight corridors. France is increasing the number of Hydrogen buses under its national plan for green mobility. The UK and Spain are incorporating hydrogen into their energy storage systems. Italy and the Netherlands are concentrating on fuel cells in ports and shipping. Europe’s regulatory framework accelerates both demand and innovation.
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America | 16.50% |
| Europe | 21.10% |
| Asia-Pacific | 57.80% |
| LAMEA | 4.60% |
LAMEA is working towards decarbonization goals set for the region and is an emerging market. Brazil is looking into hydrogen mobility for transportation and industrial applications and is working alongside the Middle East on hydrogen exports. NEOM Green Hydrogen Project in Saudi Arabia started infrastructure construction in June 2023 and hopes to hit their 2026 goal of 650 tons/day of green hydrogen. Brazil started feasibility studies for hydrogen-based trains and long-haul vehicles. Egypt is expanding hydrogen mobility and electrolyzer manufacturing, while the UAE is launching it into other parts of Africa where it hopes to capitalize from future solar-linked projects. Investment and policy is rapidly gaining traction.
The hydrogen fuel cell industry is driven by major players like AFC Energy, Audi, Ballard Power Systems, Bloom Energy, and BMW, who are leading innovation in clean mobility and power solutions. These companies are developing efficient fuel cell stacks, zero-emission vehicles, and scalable hydrogen infrastructure. In January 2024, Ballard Power Systems partnered with Quantron AG to roll out hydrogen trucks in Europe. BMW advanced its iX5 Hydrogen fleet, while Audi continued R&D under the Volkswagen Group. Bloom Energy expanded its SOFC tech for industrial use, and AFC Energy launched hydrogen-powered EV chargers. Together, they are reshaping the future of sustainable transport.
Market Segmentation
By Type
By Technology
By Company Size
By Application
By End User
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Hydrogen Fuel Cell
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Technology Overview
2.2.2 By Type Overview
2.2.3 By Company Size Overview
2.2.4 By Application Overview
2.2.5 By End User Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.2 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Faster refuelling vs. battery EVs in logistics applications
4.1.1.2 Public-private partnerships in infrastructure development
4.1.1.3 Electrification of Public Transit Systems
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 Transport and storage concerns of hydrogen
4.1.2.2 Complex logistics of hydrogen supply chain
4.1.2.3 Postponements in policy execution or subsidy rollouts
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 Understaffed skilled workforce for hydrogen technologies
4.1.3.2 Longer waiting periods for hydrogen refueling stations compared to EV chargers
4.1.3.3 Long commercialization timelines for innovations
4.1.4 Market Opportunities
4.1.4.1 Remote and off-grid fuel cell applications
4.1.4.2 Unmanned vehicles powered by hydrogen
4.1.4.3 Integration of fuel cells in data centers and telecommunication towers
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market, By Technology
6.1 Global Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Snapshot, By Technology
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Direct Methanol Fuel Cells
6.1.1.2 Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells
6.1.1.3 Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cells
6.1.1.4 Polymer Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells
6.1.1.5 Others
Chapter 7. Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market, By Type
7.1 Global Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Snapshot, By Type
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Air-Cooled
7.1.1.2 Water-Cooled
Chapter 8. Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market, By Company Size
8.1 Global Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Snapshot, By Company Size
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Large Enterprises
8.1.1.2 Small and Medium Enterprises
Chapter 9. Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market, By Application
9.1 Global Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Snapshot, By Application
9.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
9.1.1.1 Portable
9.1.1.2 Stationary
9.1.1.3 Transport
Chapter 10. Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market, By End-User
10.1 Global Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Snapshot, By End-User
10.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
10.1.1.1 Defense
10.1.1.2 Fuel Cell Vehicles
10.1.1.3 Utilities
Chapter 11. Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market, By Region
11.1 Overview
11.2 Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
11.3 Global Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market, By Region
11.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
11.4 North America
11.4.1 North America Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.3 North America Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market, By Country
11.4.4 U.S.
11.4.4.1 U.S. Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
11.4.5 Canada
11.4.5.1 Canada Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
11.4.6 Mexico
11.4.6.1 Mexico Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
11.5 Europe
11.5.1 Europe Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.3 Europe Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market, By Country
11.5.4 UK
11.5.4.1 UK Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
11.5.5 France
11.5.5.1 France Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
11.5.6 Germany
11.5.6.1 Germany Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
11.5.7 Rest of Europe
11.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6 Asia Pacific
11.6.1 Asia Pacific Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.3 Asia Pacific Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market, By Country
11.6.4 China
11.6.4.1 China Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.5 Japan
11.6.5.1 Japan Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.6 India
11.6.6.1 India Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.7 Australia
11.6.7.1 Australia Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
11.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7 LAMEA
11.7.1 LAMEA Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.3 LAMEA Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market, By Country
11.7.4 GCC
11.7.4.1 GCC Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7.5 Africa
11.7.5.1 Africa Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7.6 Brazil
11.7.6.1 Brazil Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
11.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 12. Competitive Landscape
12.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
12.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
12.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
12.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
12.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 13. Company Profiles
13.1 AFC Energy
13.1.1 Company Snapshot
13.1.2 Company and Business Overview
13.1.3 Financial KPIs
13.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
13.1.5 Strategic Growth
13.1.6 Global Footprints
13.1.7 Recent Development
13.1.8 SWOT Analysis
13.2 Audi
13.3 Ballard Power Systems
13.4 Bloom Energy
13.5 BMW
13.6 Ceres Power
13.7 Cummins
13.8 Daimler
13.9 Doosan Fuel Cell
13.10 FuelCell Energy
13.11 Fuji Electric
13.12 Hyster-Yale
13.13 Honda Motor
13.14 Horizon Fuel Cell
13.15 Intelligent Energy
13.16 Kyocera
13.17 MAN SE
13.18 Nedstack Fuel Cell
13.19 NIkola