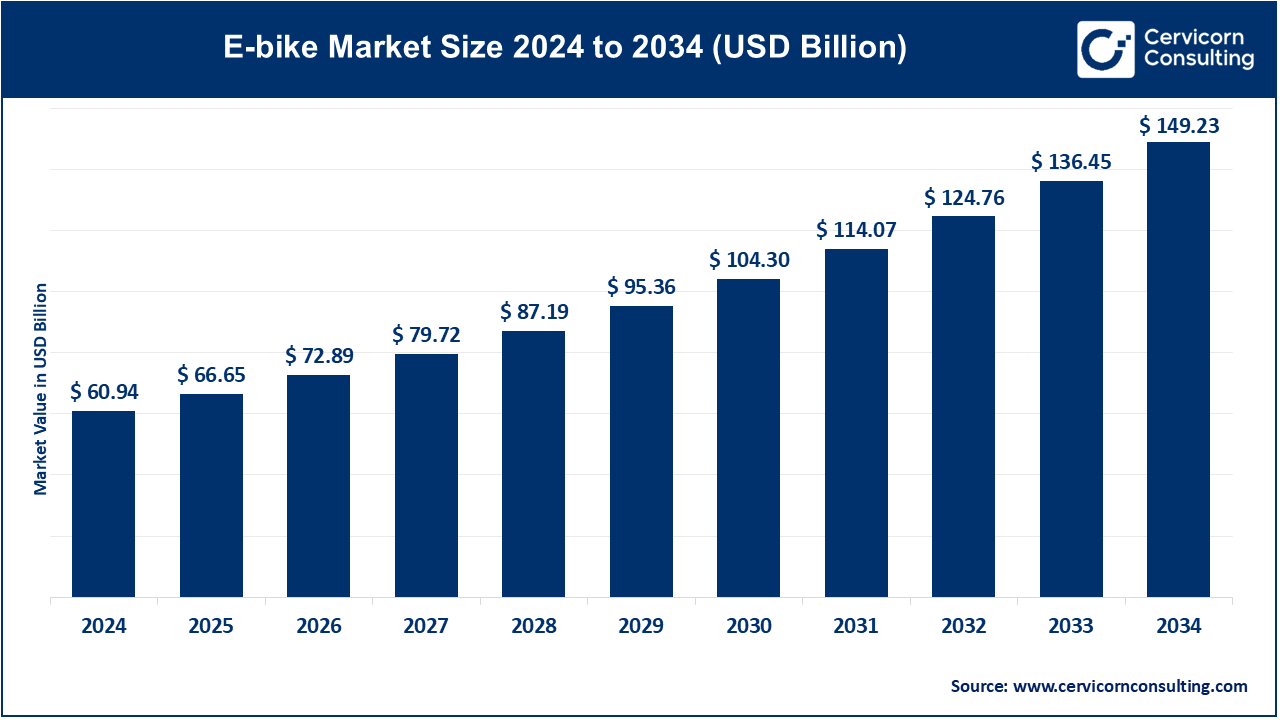
The global E-bike market size was reached at USD 60.94 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 149.23 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.36% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The e-bike market is expected to grow significantly due to rising fuel costs, increased environmental awareness, urban congestion, and government incentives promoting sustainable and affordable personal mobility solutions.
Electric bikes, or e-bikes, are a modern redesign of traditional bicycles. They have an electric motor and battery which assists with pedaling, making it easier to travel further and faster. Riders can utilize less effort due to having pedals that amplify the motion. Pedal-assist e-bikes and throttle-operated e-bikes are two classifications of e-bikes, with varying functions. E-bikes are great alternatives for commuting, transportation of goods, relaxing or exercising, and do not emit harmful substances unto the environment. Unlike cars, e-bikes help diminish traffic congestion and reduce carbon footprints. There are regulations for e-bikes where they are only allowed to go 25–28 km/h (15–20 mph). The increasing adoption rates of e-bikes are due to new advances in technology and the search for more environmentally friendly transportation methods.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 66.65 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2033 | USD 136.45 Billion |
| Projected Market CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 9.36% |
| High-impact Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Product, Drive Mechanism, Class, Battery, Speed, Mode of Operation, Component, Battery Capacity, Motor Weight, Motor Power, Region |
| Key Companies | Giant Manufacturing Co. Ltd., Yadea Group Holdings Ltd., Pedego Electric Bikes, Merida Industry Co. Ltd, Trek Bicycle Corporation, Accell Group N.V., Brompton Bicycle Ltd., Yamaha Motor Company, Pon.Bike, Aima Technology Group Co. Ltd. |
Pedelecs: Specifically, participants are supported in pedaling with a Pedelec or pedal electric cycle which provides motor assistance up to a speed of 25 km/h. These Pedelecs became famous in Europe and Asia because of their accessibility and simple operation and compliance with the law. Casual cyclists, as well as urban commuters, are the primary drivers of adoption as they attempt to blend exercise and leisure.
Speed Pedelecs: Designed for long-distance and performance commuting, speed pedelecs offer motor assistance up to 45 km/h. Because of their capability, such e-bikes are often subject to insurance, registration, and even helmet requirements. These are favored in markets where infrastructure supports high speed cycling, and appeal to professionals seeking an alternative to motor vehicles for daily travel.
Throttle on Demand: Scooters and mopeds are to cars as throttle-controlled e-bikes are to bicycles, no paddling is required for operation, only a twist or push to the throttle. This type of pedelec is common in Asia and North America, catering to consumers motivated by ease of use and low physical demand. For some countries, this classification prohibits broader circulation due to regulations on motorized vehicles making it problematic in Europe.
Scooter or Motorcycle: E-scooters and e-motorcycles resemble traditional two-wheelers in design but are powered electrically. These are used for longer urban trips and in shared mobility fleets. With rising interest in personal electric vehicles, these models serve as car replacements in crowded cities, but often fall outside standard e-bike regulations and require licensing and insurance.
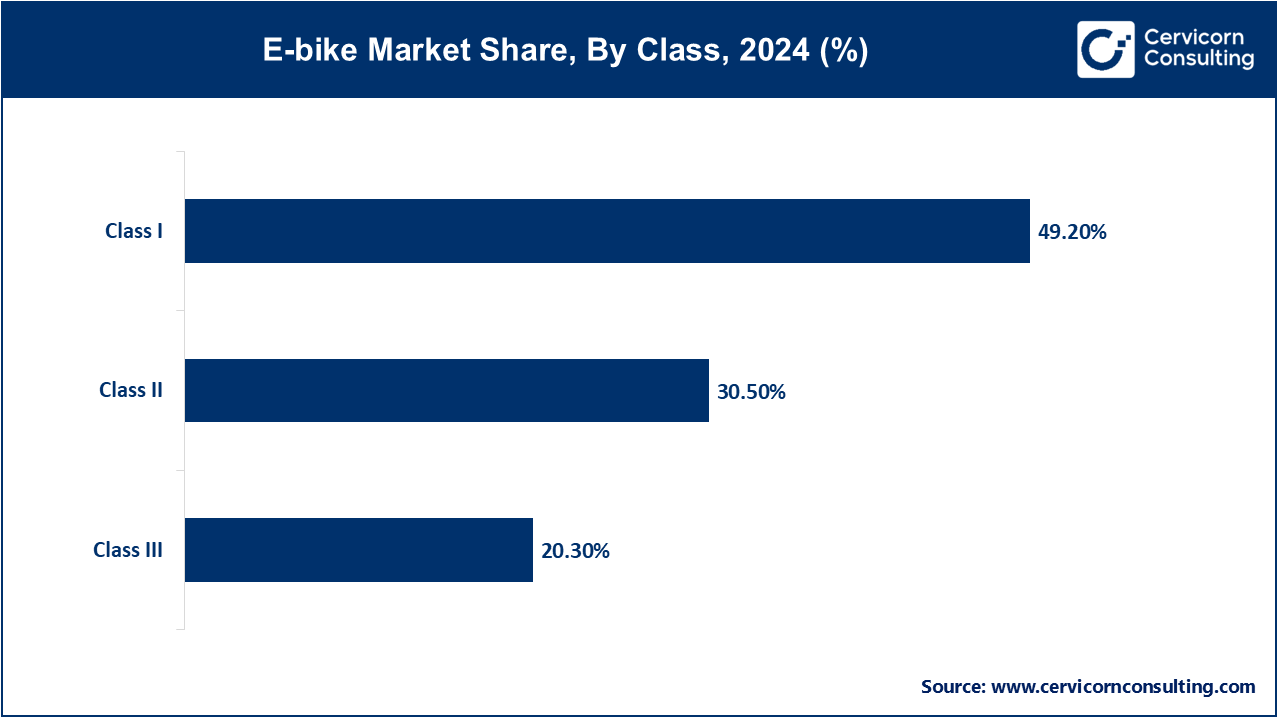
Based on class, the market is classified into class I, class II, and class III. The class I segment dominated the e-bike market in 2024.
Hub Motor: In hub motor e-bikes, the motor is integrated into the hub of the front or rear wheel. They can be found in entry level models, are inexpensive, and have low maintenance. They assist in propulsion, but their lack of torque management makes them ineffective in more challenging off-road environments. Most suitably for regions with lower altitudes, infrequent short walks tends to erratic jogs, and frequent simple drives in suburban areas. Best inhabited sparsely populated flat regions provides the best scope.
Mid-Drive: A mid-drive e-bike motor mounted at the crankset provides optimal balance, efficiency, functional torque control, and augments primary performance. These systems perform effectively on steep terrain making them suitable for mountain biking and heavy-duty use. Although pricier, they provide improved natural ride feel and battery efficiency during rigorous biking. Dominating the premium segment in Europe, mid-drive motors are popular because dual e-bikes/mountain bikes are expensive.
Others: Shaft-drive and friction drives are categorized as outliers, they deviate from the customary hub or mid-drive configurations. Because of these systems’ low efficiency and complex maintenance requirements, they tend to be less common. However, their application in specialty or custom-designed e-bikes can be beneficial. Their market adoption is limited and mostly for research purposes.
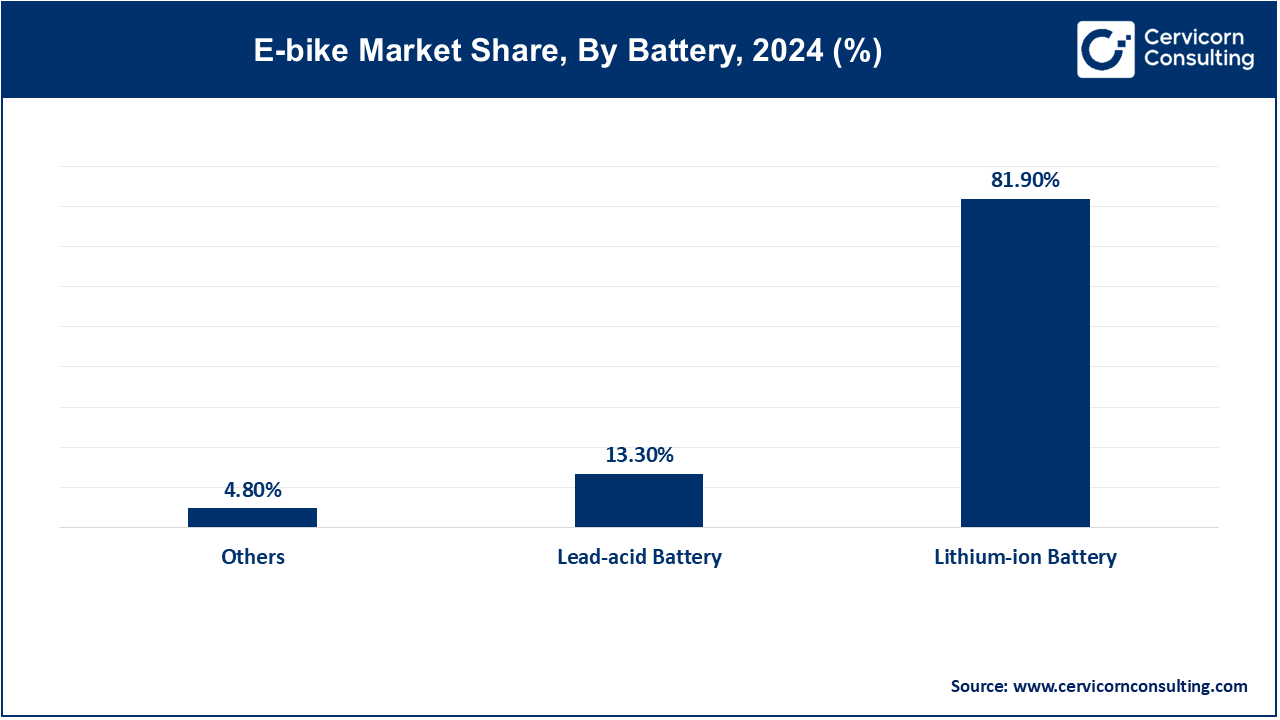
Based on battery, the market is classified into lead-acid battery, lithium-ion battery, and others. The lithium-ion battery segment dominated the market in 2024.
The E-bikes market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region
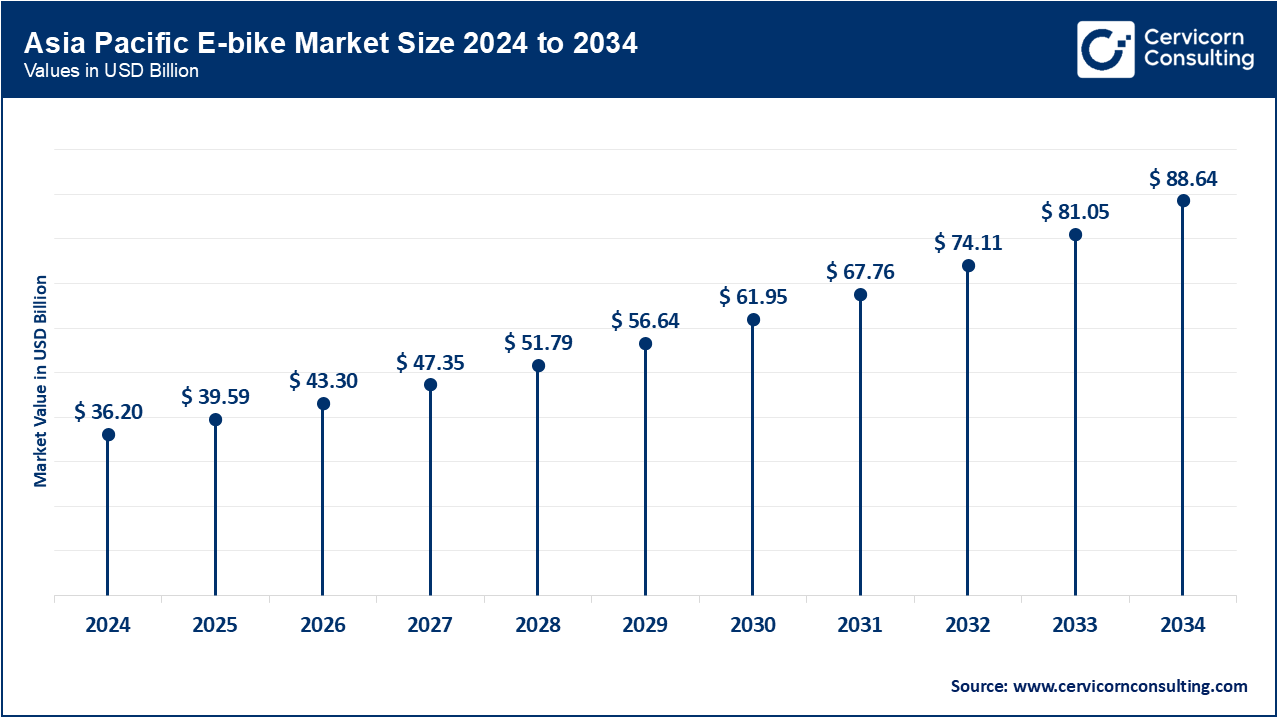
The Asia-Pacific E-bike market size was exceeded at USD 36.20 billion in 2024 and is forecasted to grow around USD 88.64 billion by 2034. The leading players by volume in the Asia-Pacific region are China, India, and Japan. China's steep infrastructure investment enables it to dominate the global supply chain. Economically, urban policies restricting gas two-wheelers and subsidizing electric-enabled vehicles assures continued demand. India is increasingly emerging faster owing to fuel price pressures and environmental concerns. However, challenge remains with infrastructure and price sensitivity in rural areas. Southeast Asia's exports are diversifying the region’s markets.
The North America E-bike market size was valued at USD 6.64 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 16.27 billion by 2034. The North America is steadily growing with upcoming opportunities due to increasing fuel costs, environmental consciousness, and traffic congestion in metropolitan areas. In Canada and the US, e-bikes are increasingly being used for urban commuting as well as recreation. Demand is also increasing due to government incentives such as California’s e-bike rebate program as well as new bike lane construction. However, the limited cycling culture in some states and high e-bike costs remains a challenge. Shared micromobility programs and corporate wellness programs are expected to further aid market growth in this region.
The Europe E-bike market size was estimated at USD 18.10 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 44.32 billion by 2034. Europe is still the global leader, with e-bike adoption being led by Germany, Netherlands, and France. The market is more mature in Western Europe, and this can be attributed to a well-established cycling culture and spending by the government in the regions. The region greatly benefits from environmental policies that encourage using low-emission transportation. EU policies toward climate neutrality as well as domestic subsidies still create demand. Increasing use of speed pedelecs and cargo e-bikes for commercial purposes is also noted. However, saturation of the market in Western Europe drives manufacturers to explore opportunities in Eastern Europe.
E-bike Market Revenue Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America | 10.90% |
| Asia-Pacific | 59.40% |
| Europe | 29.70% |
E-bike adoption is slower than average growth in the LAMEA region which provides with challenges and opportunities. Increasing fuel prices and traffic congestions in Latin America, especially in Brazil, Mexico and Colombia is supporting the growth of e-bikes as economical solutions to urban mobility woes. But poor cycling infrastructure alongside high costs of imports will slow these benefits down. UAE and Saudi Arabias’s forward-looking vision policies are integrating e-bikes into smart city frameworks, spearheading e-bike usage in the region, although extreme heat and low awareness are two hindering factors. Africa suffers from stunted development but interest due to low-cost transportation keeps rising. The region still has long-term potential, as government and private stakeholders look more into cleaner mobility solutions.
Recent collaborations in the e-bike industry reflect a strategic push toward technological advancement, sustainability, and mobility-as-a-service integration. Leading players such as Giant Manufacturing Co. Ltd., Yadea Group Holdings Ltd., Pedego Electric Bikes, and Merida Industry Co. Ltd are forming alliances with software firms and mobility platforms to integrate IoT, AI-based diagnostics, and connected features. These partnerships aim to enhance user experience, streamline fleet management, and improve energy efficiency. Additionally, joint ventures are enabling localized manufacturing and distribution, reducing supply chain dependency and promoting faster adoption in emerging urban markets. Some notable examples of key developments in the E-bikes Market include:
Market Segmentation
By Product
By Drive Mechanism
By Class
By Battery
By Speed
By Mode of Operation
By Component
By Battery Capacity
By Motor Weight
By Motor Power
By End Use
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of E-bike
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Product Overview
2.2.2 By Drive Mechanism Overview
2.2.3 By Class Overview
2.2.4 By Battery Overview
2.2.5 By Speed Overview
2.2.6 By Mode of Operation Overview
2.2.7 By Component Overview
2.2.8 By Battery Capacity Overview
2.2.9 By Motor Weight Overview
2.2.10 By Motor Power Overview
2.2.11 By End Use Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.2 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Urbanization and Traffic Congestion
4.1.1.2 Rising Fuel Prices
4.1.1.3 Integration with Smart City Initiatives
4.1.1.4 Environmental Issues
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 High Initial Costs
4.1.2.2 Limited Charging Infrastructure
4.1.2.3 Market Saturation in Developed Regions
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 Issues Relating to Battery Life and Efficiency
4.1.3.2 Lack of Charging Facilities
4.1.3.3 Supply Chain Disruptions
4.1.4 Market Opportunities
4.1.4.1 Expansion in Emerging Markets
4.1.4.2 Corporate Adoption for Employee Commutes
4.1.4.3 Integration with Renewable Energy
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global E-bike Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. E-bike Market, By Product
6.1 Global E-bike Market Snapshot, By Product
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Pedelecs
6.1.1.2 Speed Pedelecs
6.1.1.3 Throttle on Demand
6.1.1.4 Scooter or motorcycle
Chapter 7. E-bike Market, By Drive Mechanism
7.1 Global E-bike Market Snapshot, By Drive Mechanism
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Hub motor
7.1.1.2 Mid-drive
7.1.1.3 Others
Chapter 8. E-bike Market, By Class
8.1 Global E-bike Market Snapshot, By Class
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Class I
8.1.1.2 Class II
8.1.1.3 Class III
Chapter 9. E-bike Market, By Battery
9.1 Global E-bike Market Snapshot, By Battery
9.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
9.1.1.1 Lead-acid Battery
9.1.1.2 Lithium-ion Battery
9.1.1.3 Others
Chapter 10. E-bike Market, By Speed
10.1 Global E-bike Market Snapshot, By Speed
10.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
10.1.1.1 Up to 25 KM/H
10.1.1.2 25-45 KM/H
Chapter 11. E-bike Market, By Mode of Operation
11.1 Global E-bike Market Snapshot, By Mode of Operation
11.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
11.1.1.1 City/Urban E-bikes
11.1.1.2 Mountain E-bikes
11.1.1.3 Trekking/Touring E-bikes
11.1.1.4 Cargo E-bikes
11.1.1.5 Others (Cruiser)
Chapter 12. E-bike Market, By Component
12.1 Global E-bike Market Snapshot, By Component
12.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
12.1.1.1 Battery
12.1.1.2 Electric Motors
12.1.1.3 Motor Controller
12.1.1.4 Frame with Forks
12.1.1.5 Others (Brake Systems, Wheels & Gears)
Chapter 13. E-bike Market, By Battery Capacity
13.1 Global E-bike Market Snapshot, By Battery Capacity
13.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
13.1.1.1 Below 250W
13.1.1.2 251W to 450W
13.1.1.3 451W to 650 W
13.1.1.4 Above 650W
Chapter 14. E-bike Market, By Motor Weight
14.1 Global E-bike Market Snapshot, By Motor Weight
14.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
14.1.1.1 <2 kg
14.1.1.2 >2 kg -<2.4 kg
14.1.1.3 >2.4 kg
Chapter 15. E-bike Market, By Motor Power
15.1 Global E-bike Market Snapshot, By Motor Power
15.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
15.1.1.1 <40nm
15.1.1.2 >40nm-<70nm
15.1.1.3 >70nm
Chapter 16. E-bike Market, By End Use
16.1 Global E-bike Market Snapshot, By End Use
16.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
16.1.1.1 Personal
16.1.1.2 Commercial
Chapter 17. E-bike Market, By Region
17.1 Overview
17.2 E-bike Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
17.3 Global E-bike Market, By Region
17.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
17.4 North America
17.4.1 North America E-bike Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
17.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
17.4.3 North America E-bike Market, By Country
17.4.4 U.S.
17.4.4.1 U.S. E-bike Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
17.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
17.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
17.4.5 Canada
17.4.5.1 Canada E-bike Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
17.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
17.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
17.4.6 Mexico
17.4.6.1 Mexico E-bike Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
17.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
17.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
17.5 Europe
17.5.1 Europe E-bike Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
17.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
17.5.3 Europe E-bike Market, By Country
17.5.4 UK
17.5.4.1 UK E-bike Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
17.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
17.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
17.5.5 France
17.5.5.1 France E-bike Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
17.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
17.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
17.5.6 Germany
17.5.6.1 Germany E-bike Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
17.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
17.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
17.5.7 Rest of Europe
17.5.7.1 Rest of Europe E-bike Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
17.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
17.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
17.6 Asia Pacific
17.6.1 Asia Pacific E-bike Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
17.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
17.6.3 Asia Pacific E-bike Market, By Country
17.6.4 China
17.6.4.1 China E-bike Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
17.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
17.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
17.6.5 Japan
17.6.5.1 Japan E-bike Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
17.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
17.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
17.6.6 India
17.6.6.1 India E-bike Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
17.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
17.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
17.6.7 Australia
17.6.7.1 Australia E-bike Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
17.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
17.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
17.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
17.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific E-bike Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
17.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
17.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
17.7 LAMEA
17.7.1 LAMEA E-bike Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
17.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
17.7.3 LAMEA E-bike Market, By Country
17.7.4 GCC
17.7.4.1 GCC E-bike Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
17.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
17.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
17.7.5 Africa
17.7.5.1 Africa E-bike Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
17.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
17.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
17.7.6 Brazil
17.7.6.1 Brazil E-bike Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
17.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
17.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
17.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
17.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA E-bike Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
17.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
17.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 18. Competitive Landscape
18.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
18.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
18.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
18.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
18.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 19. Company Profiles
19.1 Giant Manufacturing Co. Ltd.
19.1.1 Company Snapshot
19.1.2 Company and Business Overview
19.1.3 Financial KPIs
19.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
19.1.5 Strategic Growth
19.1.6 Global Footprints
19.1.7 Recent Development
19.1.8 SWOT Analysis
19.2 Yadea Group Holdings Ltd.
19.3 Pedego Electric Bikes
19.4 Merida Industry Co. Ltd
19.5 Trek Bicycle Corporation
19.6 Accell Group N.V.
19.7 Brompton Bicycle Ltd.
19.8 Yamaha Motor Company
19.9 Pon.Bike
19.10 Aima Technology Group Co. Ltd.