Structural Steel Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
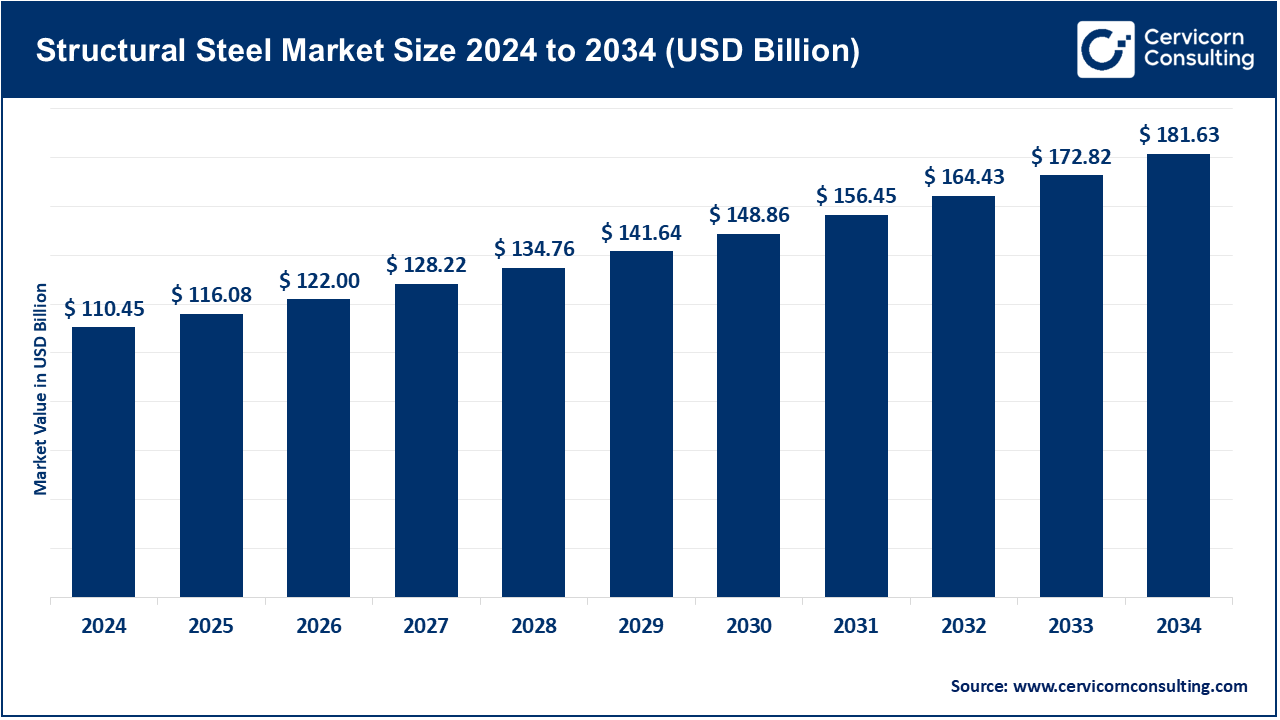
The global structural steel market size was valued at USD 110.45 billion in 2024 and is expected to surpass around USD 181.63 billion by 2034, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.1% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The global structural steel market, undergirded by several key factors, is growing. Rapid urban infrastructural developments, especially in emerging nations, stand out as one of the major factors. It is the immediate requirement for residential and commercial buildings brought about by urbanisation that boosts the demand of structural steel. On the infrastructure front, government-sponsored projects aiming at electricity generation plants, airports, and transportation networks are further accentuating the market growth.
Further, the use of structural steel is finding higher traction due to the increasing focus on green building practices. Steel is recyclable without any diminution of properties and thus compliments the green building certification systems and environmental norms. It is an eco-attribute that is gaining favour among developers keen on cutting down carbon footprints and spreading the message of circular economy. Moreover, these recent technological innovations on steel production and fabrication further enhance the efficiency of this material and reduce the costs of production. Mechanization and innovations in the field of high-strength, low-alloy steels, corrosion-resistant coatings, and fabrication processes help the evolution of structural steel to be of high efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Top Structural Steel Exporters in 2024
| Country |
Share, 2024 |
| China |
26.10% |
| Japan |
6.90% |
| South Korea |
6.20% |
| Germany |
5% |
| Turkey |
3.80% |
What is structural steel?
Structural steel is well known for its high strength-to-weight ratio, ease of fabrication, and adaptability for varied construction purposes. This ensures increased design flexibility and is deemed suitable for manufacturing via prefabrication, thus ensuring shorter construction timelines. It also holds a high compatibility level with other construction materials and can provide for exacting safety codes, making it a staple for contemporary engineering and architectural materials.
Globally, the structural steel market occupies a vital place under the construction and infrastructure industries. This sector forms the backbone of various applications-kills-a building, bridges, industrial facilities, and transportation systems. Structural steel means steel improperly allowed for making materials of construction in various shapes and sizes conceived of heavy loads and resistance to bending or deformation. Being versatile, strong, and recyclable, it finds application for structural frameworks and reinforcement.
Structural Steel Market Report Highlights
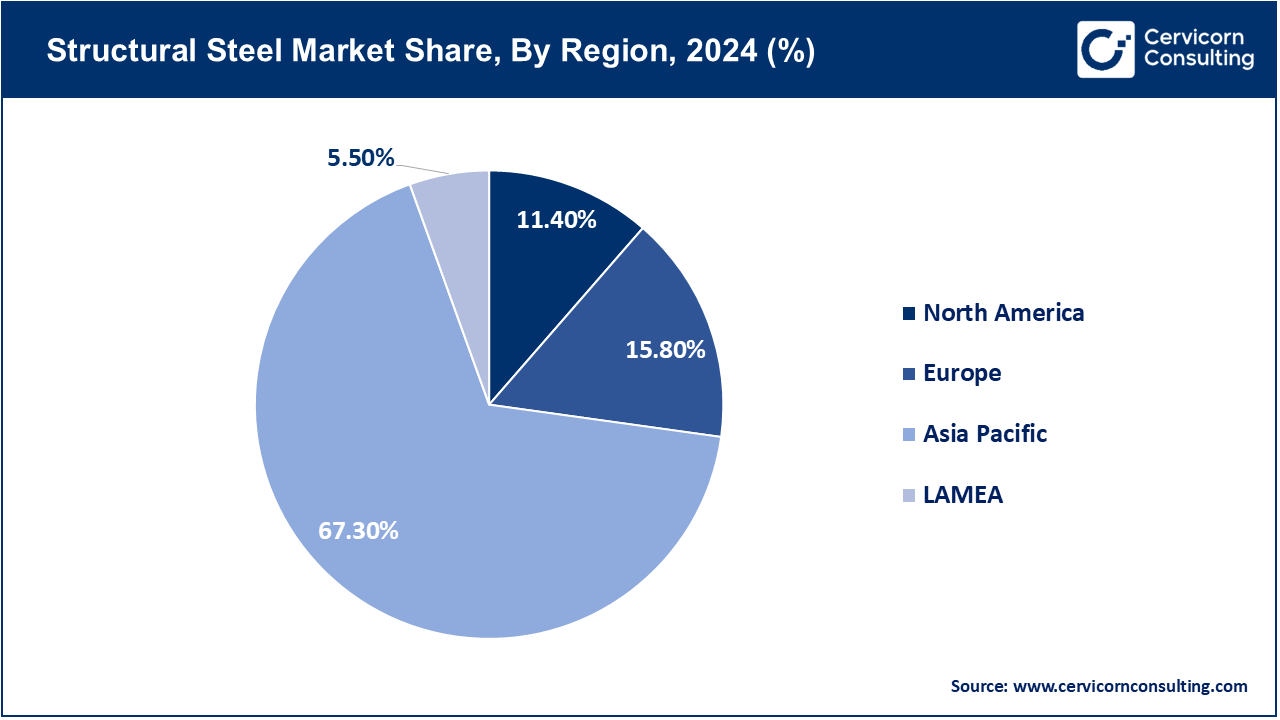
- By Region, Asia-Pacific has accounted highest revenue share of around 67.30% in 2024.
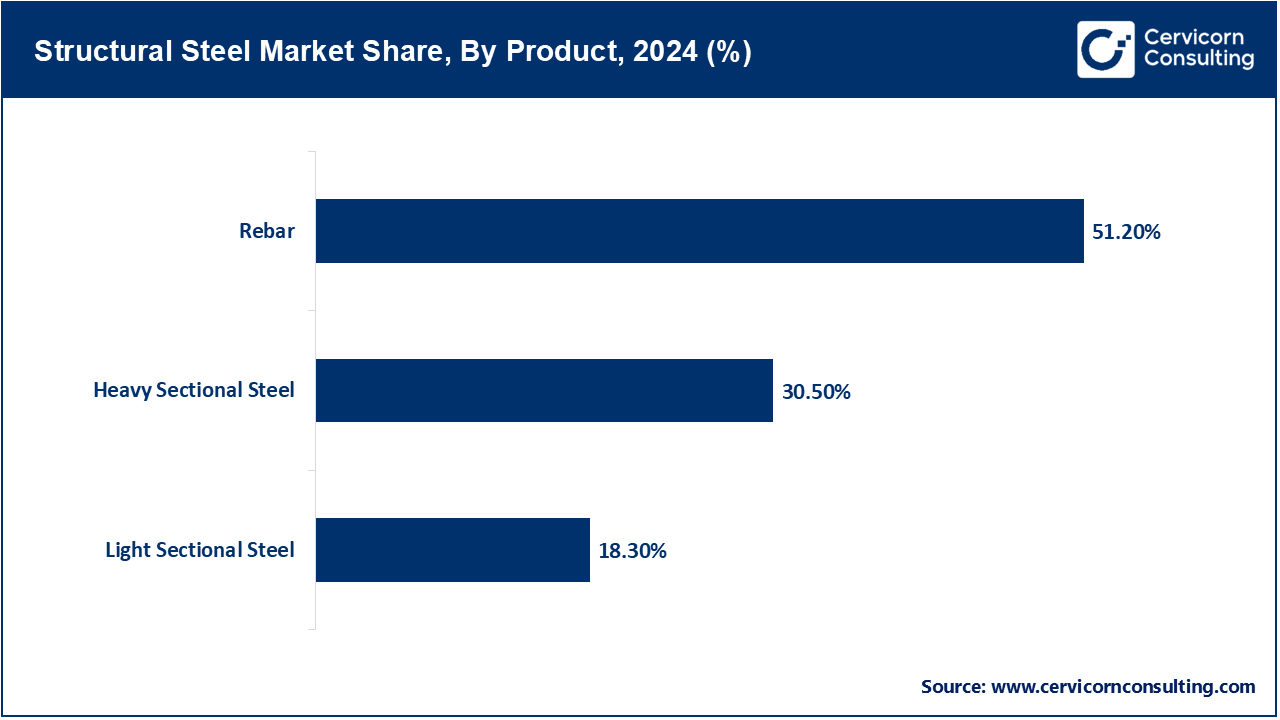
- By Product Type, the rebar segment in 2024 had about 51.20% of the revenue share. The Rebar segment leads in the global structural steel market due to its vast use in reinforced concrete structures. Rebars are needed in construction to improve tensile strength, especially in infrastructure works such as bridges, highways, and high-rise buildings. Thus, rebar is preferred by developing and developed economies due to their low economy, durability, and ease of handling. Urbanization process, increased investment into public infrastructure, and government-sponsored construction activations all process further demand for the rebar. By contrast, usage of rebars goes high in seismic zones for structural safety; hence they give a strong market led to heavy section steel and light section steel.
- By Steel Type, apart from the fact that it is first in industrial-scale production, it held a revenue share of approximately 37.60% in 2024 due to its scalability and very little carbon emissions, providing scope even for mixing with recycled scrap steel. Dominating the entire structural steel market of the world is the hot-rolled steel, owing to its wide-ranging industrial uses in construction, infrastructure, and heavy machinery. It is less costly due to its manufacturing process and is ideally suited for fabrication or large structural components such as I-beams, channels, and rails. Hot-rolled steel can be shaped and melded at high temperatures. This ensures anything from increased formability to quicker production matters, which makes it perfect for large-scale structural use. The demanding strength is thus supplied throughout high-rise urban development and infrastructure projects around developing economies, securing two leading spots among those serving the global structural steel market.
- By End-Use Industry, In 2024, the construction sector dominated, capturing a major market share of 46.20%. The construction segment reigns in the world structural steel market because of the numerous commercial, residential, and infrastructural developments incurred by it. Structural steel is favoured in view of its strength, durability, design flexibility, and cost efficiency for high-rise buildings, bridges, and stadium construction. Such demand is further caused by rapid urbanization and infrastructure development, together with green building programs in the emerging economies like China, India, and Southeast Asia. Added to this are public investments into smart cities and transportation networks. With this, the construction industry attains structural steel market dominance because of its adaptability to the demands of contemporary architecture and its seismic resistance.
Structural Steel Market Growth Factors
- Urbanization and Infrastructure Development Surge: Rapid urbanization in emerging economies is immensely raising the demand for structural steel. Governments of the developing economies are increasingly engaging in and funding major infrastructure-building activities such as construction of bridges, highways, rail networks, and urban mass transit systems to cater to the needs of the growing urban population. Considered as structural steel due to its strength and flexibility and durability, it acts as the primary material in such constructions, capable of bearing heavy loads and resisting severe weather conditions. Structural steel is further pushed into the modern urban infrastructure where high buildings, airports, and stadiums are concerned. Given the developing nations' drive to revamp infrastructure to accelerate economic growth and connectivity, the consumption of structural steel is set to grow. Steel is ideal for such development projects because it can be scaled and proved adaptable in crowded sites where vertical expansion is considered. Hence the infrastructure investments will grow consistently as urban populations grow globally, thus benefitting the market.
- Rising Demand for Prefabricated Buildings: Prefabricated and modular types of constructions are gaining popularity because of their cost efficiency, timely accomplishment, and low environmental impact. Structural steel becomes common to these building systems due to its uniform quality, ability to be fabricated, and easy assembling. The selections reduce the need for on-site labour and construction time, which ensure that price factors will be subjugated because of faster project execution. The upturn in demand for steel follows from pandemic recovery, with more prefabricated commercial space, residential units, and healthcare units being demanded. Steel serves modular construction in providing very diverse design flexibility requirements and some advanced architectural exigencies. Developers and contractors are now opting less for in situ methods to avoid project delays and meet sustainability criteria. Structural steel being recyclable and reusable is a green building practice. Going forward, the increased use of structural steel in prefabrication seems to be the obvious next step as the construction industry embraces faster, safer, and greener building methods.
- Expanding Industrial and Commercial Construction: Industrial growth especially in industries that involve manufacturing, logistics, and warehousing has put superlative demand on durable and economical building solutions. Structural steel fills this demand of the industry with its heavy-load capacity, resistance to extreme atmospheric conditions, and versatility of design. Commercial projects provided in the way of office complexes, shopping malls, and entertainment centres obtain the services of industrial structural steel due to its architectural flexibility and ease of customization. The global increase in e-commerce has provided a push to grow the demand for warehouses and distribution centres. Expansion of multinational companies and retail stores in emerging markets requires bigger industrial parks and commercial hubs. Structural steel is chosen for these buildings as they erect quickly and can be easily expanded later. Structural steel is meant to continue glorifying the fast pace and scale of development with the fast pace of industrial and commercial infrastructure, especially in Asia-Pacific and West Asia.
- Government Investments in Transportation and Energy Sectors: Governments worldwide are heavily investing in the modernization of transport infrastructure involving highways, railways, ports, and airports and energy infrastructure comprising power plants, oil refineries, and renewable energy facilities. Structural steel plays an important role in such construction owing to its strength and longevity as well as its ability to withstand dynamic and environmental stresses. In transportation infrastructure, steel is used in building bridges, terminals, and tunnels, whilst energy infrastructure requires steel for power transmission towers, wind turbine supports, and pipeline systems. Strategic developments such as the Belt and Road Initiative by China, India's National Infrastructure Pipeline, and the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act of the United States have been creating demand for structural steel. Moreover, with the global moves toward clean energy and grid modernization came new demand for steel for solar farms, wind energy structures, and smart grids. So, these major government-backed infrastructure investments could indeed guarantee the long-term growth of the structural steel market.
Structural Steel Market Trends
- Shift toward High-Strength and Lightweight Steel Grades: One important trend greatly determining the structural steel market is scenic preference for steel of high strength and light weight. Such varieties offer superior capacity to withstand imposed loads yet decrease the weight of the structure, thus improving energy efficiency and lessening the requirements for the foundation. Strengthening the observation stands with the trend in skyscraper constructions, long-span bridges, and mega infrastructure projects where strength to weight ratio plays an utmost important role. Manufacturers innovate with somewhat alloyed and thermomechanical treated grades bearing in mind weldability, durability, and corrosion resistance requirements. Likewise, lightweight steel construction offers easy construction and transport, which comes handy in difficult places at sites. This goes well with the sustainability notion-a lighter structure calls for fewer materials and less energy through the lifespan. While the industry aims to find a balance between the performance aspects and environmental considerations and convenience in terms of cost, the demand for next-generation steels has been on a rise.
- Integration of BIM and Smart Fabrication Technologies: BIM and smart fabrication tools are creating changes in the structural steel industry. 3D modelling is one of the key features of BIM and it works collaboratively in real time amongst architects, engineers, and contractors, hence avoiding lots of design errors, reworks, and other material wastes. These fabrication tools are used by structural steel fabricators to make the manufacturing process even more efficient, ensure precision, and save time and workforce. CNCs, welding machines, and robots indeed make very fast and uniform production. Gaining traction nowadays is the digital twin along with IoT-enabled monitoring systems, which facilitate predictive maintenance and lifecycle optimization of steel structures. With such developments, projects can be completed faster with fewer human resources and have a more secure working environment at the site. The shift toward digital and smart construction processes thus increases the appeal of structural steel for very complex and large infrastructure projects. As the digital transformation continues to become stronger in construction, the synergy created between BIM and steel fabrication should emerge as a mainstream approach.
- Sustainability and Green Building Certifications Driving Adoption: The concerns about environmental issues with some regulatory pressures have been changing the construction industry on sustainable grounds, hence benefiting the structural steel market. Steel is among maximum recyclable construction materials that can be recycled several times without degradation of quality; thereby, it is considered a fundamental unit in any green construction framework. In this regard, certifications such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method) are to take environmentally sustainable and recyclable materials into consideration in a scarce way, hence giving steel a preferred stature in construction projects. Additionally, the steel production methods have improved to lower carbon emissions and energy usage. The drive toward net-zero buildings and climate-resilient infrastructure further prompts developers to use steel instead of conventional materials like concrete or wood. On the other hand, governments continue to encourage sustainable construction by way of tax incentives and green finance, thereby giving a nudge to structural steel demand. Growing environmental concerns that have come to form part of design and execution processes continue to provide structural steel its place in the green economy.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 116.08 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 |
USD 181.63 Billion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 |
5.1% |
| Dominant Region |
Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments |
Product Type, Steel Type, End-Use Industry, Region |
| Key Companies |
Tata Steel, ArcelorMittal, Evraz PLC, Baogang Group, Gerdau S.A., Nippon Steel Corporation, JSW Steel, POSCO, SAIL, Anshan Iron & Steel Group Corporation |
Structural Steel Market Dynamics
Market Drivers
- Superior Strength-to-Weight Ratio of Structural Steel: Structural steel, with its high strength-to-weight ratio, permits the realization of stronger yet lighter structures, ranging from taller buildings to industrial centres and infrastructures. This way, architects and engineers utilize this property of steel to design buildings with longer spans and fewer columns, thus producing greater usable areas and selling points in terms of aesthetics. Reduced weight also means the savings of foundation costs, and better seismic performance of the building in an earthquake-prone area. Being very strong, it can resist any stress or load from wind or vibrations, making it suitable for large-sized structures like stadiums and bridges. Compared to an individual material concrete or wood, structural steel gives much more performance out of so little material; hence it is the reason to claim engineering efficiency and environmental sustainability. This end is what keeps on driving the use of structural steel in almost every sector of construction and infrastructure development.
- Faster Construction Timelines with Modular Steel Systems: Timelines have always remained an important factor in any modern construction scenario; hence, the structural steel shortens the project timelines significantly. Prefabricated steel components are manufactured off-site and assembled quickly with little or no delay on-site, which increases the speed and efficiency of construction. Such speed benefits are most appreciated in commercial and industrial buildings, where quicker occupancy generated a faster return on investment. Steel structures offer parallel workflow support in that preparations at the site can proceed alongside component fabrication. Steel, unlike concrete, does not require curing periods to get a head start on assembly. This modular approach also helps accuracy and reduces one-off errors on-site to ensure consistent quality. Hence, the fast drafting does cut labour costs and weather-related delays and safety risks. As the world slowly moves towards hurried urban development and speedy infrastructure deployment, structural steel's compatibility with modular and fast-track construction becomes a key force driving the growth of its respective market.
- Recyclability and Environmental Benefits of Steel: Steel is the most sustainable construction material because it is recyclable, durable, and environmentally friendly during its lifecycle. Steel recycling, being unlimited, permits re-use without compromising the technical properties of the material; thus, less pressure gets put on virgin resource extraction. This high demand for steel, therefore, causes it to be favoured in any green building whose intention is being environmentally conscious with respect to carbon footprint and consumption of resources. On the other hand, structural steel systems earn LEED and other environmental certificates, which render the materials highly desirable for environmentally minded developers. The industry for steel has also evolved quicker towards cleaner production methods, such as using electric arc furnaces running on renewable energy. Such measures reduce GHG emissions and enhance the overall environmental performance. With evolving regulatory regimes gazing construction emissions and sustainability being taken to the mainstream, more are giving the environmental side of structural steel as a competitive advantage over other materials, thereby ensuring its demand worldwide.
Market Restraints
- Unpredictable Iron Ore and Scrap Supply Dynamics: The structural steel industry basically needs iron ore and scrap metal flowing constantly into their supply chain; hence these raw materials are highly vulnerable to geopolitical disruptions, in one way or another, regulatory restrictions, or transportation constraints. Mining output at the global level undergoes fluctuations, wherein huge producers like Australia, Brazil, and China place real pressure on the costs of raw materials generated by demand-supply imbalances at any given time. Moreover, the sector of recycling is not insulated from such inefficiencies and imbalances in the collection systems that enable the import of steel scrap into one region of steel production on one side and another. These disruptions create price volatilities, which hinder manufacturers and contractors from long-term procurement planning. Hence, the sectors end up with a company barely able to maintain a steady margin and having to revise its pricing structure many times, ultimately restricting its competitiveness.
- Stringent Sustainability Compliance Mandates: As decarbonization increasingly comes into focus worldwide, increased pressure has been placed on steelmakers to comply with stringent environmental regulations aimed at reducing carbon emissions and energy consumption. Regulatory frameworks, the EU ETS, and carbon taxes at the national level are pressuring structural steel producers into low-carbon technologies that carry high capital investments. This forces the need to modernize old and obsolete plants, start using renewable energy, and apply the clean steel concept along clean steel plants via hydrogen production.
- Cost Barriers Due to Energy-Intensive Production: Structural steel production involves a considerable consumption of energy, especially in processes like the operation of EAF melting and blast furnace manufacture. Because of high electricity and fuel requirement, the sector is susceptible to rising energy prices. If producers have restriction or limited supply of renewable energy or cheap electricity, then producing cost will be too high, while end users will bear the burden. Installation of energy efficiency improvements such as secondary heat recovery or secondary fuel systems requires hefty investments; such costs barriers limit small-scale producers to grow and upgrade, eventually leading to industry consolidation and low innovation within the supply chain.
Market Opportunities
- Rising Demand for Earthquake-Resistant Structures: Structural steel is a first choice where earthquakes occur, considering aspects such as flexibility, strength-to-weight ratio, and energy absorption and dissipation during earthquake forces. Governments and urban planners in countries like Japan, the U.S., and Chile are in the process of amending their building codes to make construction with adequate materials more of a viable option than a constraint, thereby providing impetus for justifying the use of structural steel. These requirements increase the demand for specialized steel framework and bracing systems in both new construction and retrofitting of existing buildings. Manufacturers capable of offering certified seismic-grade steel solutions will reap the advantage of an increasing number of contracts from both public and private sectors, primarily concerning urban infrastructure, hospitals, schools, and high-rise buildings.
- Integration of Smart Technologies in Steel Fabrication: The integration of smart technologies - that is IoT sensors, BIM, and AI-based fabrication methods - is offering a new life in the steel industry. Smart steel fabrication leads to a higher level of precision in design, less waste of materials, and shortened project durations. Digitized construction sites that use real-time data tracking coupled with predictive maintenance ensure the highest efficiency and safety standards, thereby driving investments in upgraded production sites. This trend thus gives manufacturers a platform for differentiating themselves through innovation and opens new avenues for additional revenues pertaining to digital services and tailored solutions. Structural steel companies venturing into digital transformation have a huge competitive advantage as construction companies focus heavier on productivity and transparency.
- Government-Backed Urban Renewal Projects: To reconcile aging buildings, transportation systems, and energy grids, governments on an international scale are focusing on urban renewal and modernizing infrastructure across the board. Large projects under the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act in the U.S., the Smart Cities Mission in India, and urban redevelopment in China are stimulating volume demand in structural steel for bridges, airports, railway stations, and modular housing. Structural steel became a preferred material for rapid infrastructure growth because of its flexibility, ease of installation, and cost-effectiveness. Public-private partnerships (PPPs) and special economic zones enable long-term supplier contracts and foreign investments in steel production, particularly in emerging regions.
Market Challenges
- Navigating Fluctuating International Trade Policies: For the construction steel market, trade tariffs, anti-dumping duties, and import-export restrictions imposed by the major economies are significant factors. Trade tensions between steel-producing countries can develop unpredictable cost structures and incomplete market access-one would think about, for example, the U.S. and China or the EU and Turkey. Steel producers and exporters must create distance from the changing regulatory environment and oftentimes must restructure their supply chain strategy to be competitive-changing operations. This adds complexity to working globally and increases compliance costs-apart from companies that lean heavily on cross-border trade and foreign markets.
- Managing Construction Delays Due to Steel Shortages: Global supply chains interruptions caused by pandemics or port congestions or union strikes lead to periodic shortages of structural steel. These shortages cause time delays in projects and increase the costs for contractors; that almost always strain the relationships with developers and government agencies. Further, the uncertainty associated with delivery schedules also creates risks for participating in project bidding and planning, especially for big infrastructure projects subjected to tight timelines. Whereas companies not securing timely delivery often lose in bids or face penalties, this affects going concern profitability. A definite balance of inventory capacity with procurement flexibility cannot be mutually attained due to this dynamic challenge for steel fabricators and suppliers.
- Adapting to Rapid Shifts in Design Standards and Codes: As worldwide construction standards, safety codes, and design trends alter every instant in the structural steel domain, there is a dire need for continual adaptation. When updated building codes are issued with climate resilience, sustainability, or safety in mind, then manufacturers must go for redesign of their products, then reiterate their material specifications, train their staff, and so on. Such fast evolving factors, on the other hand, tend to prolong production cycles and increase time-to-market for new products. Smaller companies have fewer technical resources and finance at their disposal and are thus least capable of adapting to evolving regulations while competitively pricing their products. It thereby remains critical to keep oneself in a position of awareness to all code changes locally or internationally, ensuring temporary market access for high priority projects and structural integrity for tough architectural projects.
Structural Steel Market Segmental Analysis
Product Type Analysis
Heavy Sectional Steel: The heavy sectional steel segment has captured highest revenue share. Heavy section steel has very large structural sections such as I-beams, H-beams, wide flange beams over which building framework is constructed; hence it should be considered for large-scale industrial plants, bridges, shipyards, and multi-story complexes. Not only are these designed to carry very heavy loads, but they also confer structural stability and resistance to deformation on the structure. The heavy sections can support heavy vertical and lateral loads and are preferred for mega infrastructure and commercial development projects. The market for heavy-section steel is aided by rapid industrialization, mounting investments in transportation and energy infrastructures along with technological improvements in steel fabrication. However, very high costs and cumbersome logistics may prevent their application in smaller and medium-sized projects. Regardless, developing countries with massive-scale infrastructure development plans remain the main consumers of this product.
Light Sectional Steel: HSS is basically a tubular steel section used in structural steel framing. It is generally differentiated depending on the size/type of the section; thus, the term is called for short, whereas a structural steel section basically includes angles, channels, beams, and plates. These materials are greatly preferred because they are easy to handle, lightweight, and meet modern design standards. By virtue of lighter steel sections, assembly can be faster, and construction costs and construction time reduced. Being highly recyclable and energy-efficient, light steel sections are viewed as a solution for green building. Operations in the modular-building and DIY spheres are also seeing increased applications for light steel sections. With growing urban housing demands and changing construction norms focusing on sustainability, the demand for light steel sections is, therefore, anticipated to increase, especially in space-constrained urban areas.
Rebar: In construction via reinforced concrete, iron bars or reinforcing bars are used as products to augment the tensile strength of a concrete structure. They apply in foundations, columns, roads, bridges, dams, or tunnels. Rebarnorton steel, carbon type, comes in diameters, surface deformations, categories, and grades, depending on the needs of the structure. Rapid urbanization, government infrastructure development programs, and increase in residential and commercial constructions are the major factors that drive the demand for rebars worldwide. Being relatively cheaper as compared to other construction metals, rebars are abundantly available, hence their essential role in structural steel. Furthermore, growing interest in corrosion-resistant and earthquake-resistant rebars in both developed and developing countries further enhances its growth.
Steel Type Analysis
Hot-Rolled Steel: The hot-rolled steel segment has dominated the market. Hot rolling of steel is a very high-temperature treatment given to steel so that it becomes more malleable to shape and form. Strength and cheapness have made this steel type quite popular with construction, railroads, and manufacturing industries. It is perfect for structural components like beams, angles, and channels. Rougher surface finishes and relaxed tolerances are fine for heavy works like bridges, highways, and building frameworks where precision isn't required. Steel in this category is cheap, available in huge sizes, and with fast turnaround times-somewhat unusual in the structural steel market, especially for infrastructure, industrial, and commercial sectors.
Cold-Rolled Steel: Cold-rolled steel is produced through further processing of hot-rolled steel in room temperature, thereby producing a finer surface finish, tighter tolerances, and higher strength. It finds application wherever dimensional accuracy is important, and often ornamental finish is also given much consideration, as in precision structural parts, automotive frames, and appliances. It sits more expensive than hot-rolled steel but enhanced mechanical properties and smooth finish benefit high-performance engineering applications. Cold-rolled steel is carving out a niche in industries that require both strength and formability; however, these markets are smaller compared to the structural sector, principally on account of the high prices and smaller sizes available for cold-rolled steel.
Carbon-Manganese Steel: Carbon-Manganese steel has carbon and manganese to impart strength and hardenability and retain weldability. It is broadly used in construction and structural application due to the good balance of price, strength, and ductility. Suitable for buildings, pipelines, storage tanks, and bridges, the manganese content also improves the toughness and impact resistance, thereby making the material more dependable for dynamic loads. Its versatility and economy have made it one of the most common steels in structural applications worldwide, but it does not have enhanced corrosion resistance and performance in extreme conditions as advanced types of steel like HSLA.
High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) Steel: HSLA steels are developed to have better strength-to-weight ratio, along with adequate formability and weldability characteristics. Small amounts of alloying elements like copper, vanadium, or niobium will be present in it to ameliorate the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. These grades of steels are useful primarily in applications that call for performance and weight considerations such as high-rise buildings, bridges, and offshore structures. Because they are very strong, very light structural members are possible, which otherwise would not have been possible to carry loads. Being progressively more expensive than regular carbon steels, the HSLA steels are increasingly being exploited in modern infrastructure projects in the interest of longevity and sustainable design through less material usage.
Heat-Treated Carbon/Alloy Steel: The heat treatment of carbon and alloy steels alongside tempering and quenching gives the heat-treated steels their properties of strength, hardness, and resistance to fatigue. These steels are suitable for heavy-load structural applications and specialized industrial uses such as cranes, heavy machinery, and structural members in earthquake-resistant or high-stress applications. Suitable alloying elements, such as chromium, molybdenum, or nickel, may be added to improve toughness and corrosion resistance. Heat treatment increases the value of steels due to the elaborate processing involved. Therefore, due to its superior mechanical properties, heat-treated steel is reserved for use in critical infrastructure and high-performance engineering where structural steels are marginal in choice.
End-Use Industry Analysis
Construction: The construction segment accounted for a highest revenue share in the market. Difference resultant of construction sector consumes the maximum supply of structural steel, with strength being high, weight very low, flexibility good, and durability present in good measure. Structural steel is used in high-rise buildings, bridges, warehouses, and residential complexes. Rapid urbanization, increasing interventions by population, and infrastructure malleability in commercial terms further pushed market growth. Emerging economies are heavily investing in smart cities and transportation infrastructures, thereby enhancing further the demand. The market for steel increased further because of sustainable and green building materials. Prefabricated steel structures are gaining momentum for lessening construction time and cost. Earthquake-resistant and fire-proof designs are also enhancing the demand for steel.
Oil & Gas: In the oil & gas industry, structural steel is indispensable in building offshore platforms, pipeline systems, refineries, and drilling rigs. It resists corrosion in harsh atmospheres and weathers, pressure, and temperature extremes that are intolerable to his construction. With rising global demand, especially for offshore and deep-sea exploration, the need for stronger infrastructures supports steel consumption. The major contributions in demand are due to investments coming from the Middle East and North America into upstream and midstream operations. Lastly, the ability of steel to be fabricated into modular and custom designs brings along with itself a key impetus for the development of the sector.
Energy & Power: Structural steel plays an important role in facilities that generate power-like wind turbines, transmission towers, nuclear plants, and hydropower stations. The shift in demand toward renewable energy has created greater demand for durable high-performance materials. Steel being strong, malleable, and having a long lifecycle makes it ideal to stand up to heavy equipment or large installations. In the wind energy sector, structural steel finds its use in constructing towers and internal frameworks. Heavy investments in energy infrastructure, especially in the Asian and European regions, would thus provide a lot of opportunities for steel producers. Government efforts to modernize the grid and push energy security are the other growth factor in this segment.
Automotive & Transportation: Structural steel applications are used in chassis, body frames, railway tracks, and heavy vehicles in automotive and transportation industries. Considering the energy efficiency and emission regulations, structural steel provides tensile strength and safety, yet lighter in weight. Railway and highway applications demand structural steel for superior longevity and endurance under heavy workloads. The global development of electric vehicles (EVs) and increased rail connectivity projects are further upraising demand for steel. Further, high-strength and low-weight steel grades are facilitating greater penetration of steel in the new-age automotive industry, where performance, safety, and fuel efficiency are paramount considerations.
Shipbuilding: Depending upon the grade, structural steel is applied by shipyards in the construction of hulls, decks, and offshore erections due to corrosion resistance and load-bearing capacity. This kind of steel should be able to stand the rigors of a marine environment for naval vessels, cargo ships, and oil tankers. As maritime trade expands globally and new shipbuilding centres grow in the Asia-Pacific, primarily South Korea and China, steel consumption in this segment is on the rise. The introduction of new steel grades to further enhance life span and reduce maintenance only add to its appeal. Structural steel for shipbuilding looks strong growth because of addition in LNG carrier demand and green shipping initiatives.
Mining & Heavy Machinery: Structural steel is a very significant component in the mining and heavy engineering sector for the purpose of fabricating excavators, bulldozers, and parallel infrastructure within the mine. High stress and abrasion load-bearing factor make it appropriate for harsh, high-impact work. Increased demand for metals and minerals has kept mining activities in regions like Latin America, Africa, and Australia on the rise, thus driving steel demand. Heavy machinery also utilizes high-strength steel to achieve operational efficiency and safety. Automation and an increase in innovation of mining equipment are derived to higher demand of steel, as structural steel provides the reliability required for more sophisticated mechanical operations.
Structural Steel Market Regional Analysis
The structural steel market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region.
Why does the Asia-Pacific region dominate the global structural steel market?
- The Asia-Pacific structural steel market size was estimated at USD 74.33 billion in 2024 and is expected to exceed around USD 122.24 billion by 2034.
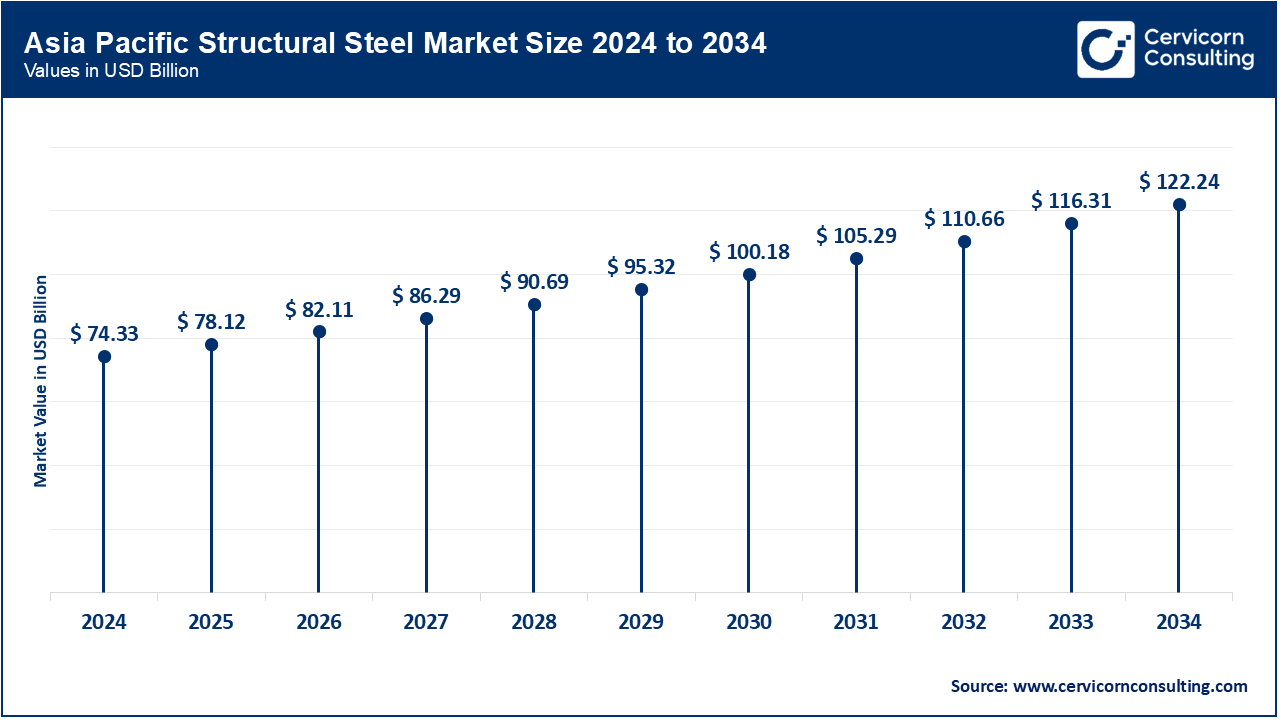
Asia-Pacific is a major global market owing to fast industrialization, urbanization, and heavy investments in infrastructure. China, having the greatest steel-production capacity with government-based projects such as the Belt and Road Initiative, leads the market. India comes in second due to heavy infrastructure development, smart city projects, and housing schemes. Southeast Asian countries experience good demand with commercial and residential constructions on the rise for them. Production and consumption are further increased by the region's competitive labour costs, availability of raw material, and good government policies. Investments in transportation, renewable energy, and manufacturing ensure further services to the growth of the market. Advances in steel manufacturing technologies, coupled with stronger adoption of prefabricated construction, especially in Japan and Korea, also keep on supporting the regional dominance. Therefore, Asia-Pacific is still the fastest-growing and most influential market for structural steel around the world.
Why has North America held a sustainable share in the structural steel market?
- The North America structural steel market size was reached at USD 12.59 billion in 2024 and is forecasted to hit around USD 20.71 billion by 2034.
Commercial building, energy infrastructure, and industrial development are some of the fields with healthy demand, thus taking the significant share of the North American market. The United States plays an important role in rehabilitating existent infrastructure, generating clean energy, and urban redevelopment projects on a large scale. Recently, demand for steel has increased because of the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act in the U.S. for steel used in roadways, bridges, and public buildings. Steady demand for energy and mining industries, especially in provinces like Alberta, supports the market in Canada. The region is also well-known for advanced steel fabrication technologies, and from the green building code perspective, working toward sustainable construction. The regional competitiveness could be affected by high labour costs and a high dependence on steel importations. That said, with healthy consumption in the domestic market and constant waves of investment in construction and infrastructure, the region continues to be a great player in the structural steel scene worldwide.
What are the key drivers of the Europe structural steel market?
- The Europe structural steel market size was accounted for USD 17.45 billion in 2024 and is predicted to record USD 28.70 billion by 2034.
Europe market is fuelled by industrial modernization, environmental policies, economical refurbishing of historic and public infrastructure. Germany, France, UK, and Italy being the major economies, promote the use of sustainable construction practices and circular economy concepts alongside energy-efficient building materials such as structural steel. Furthermore, the European green policies provide an impetus for steel recycling and the use of low-carbon technologies in steel production. The investments in smart cities and renewable energy infrastructures generate demand for steel as well. Some environmental norms and the higher cost of production take precedence against competitiveness vis-à-vis Asia. The automotive and transportation industries, especially in Germany, are also supportive of steel consumption. The Ukrainian conflict and price volatility of energy have also affected the European steel supply chain, thereby encouraging onshoring and supply chain resilience. Overall, Europe remains a mature yet evolutionary market for structural steel, with innovation and sustainability receiving top priority.
Why is the LAMEA region emerging in the structural steel market?
- The LAMEA structural steel market size was valued at USD 6.07 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to grow around USD 9.99 billion by 2034.
Structural steel enjoys slow but steady growth as an emerging market in the LAMEA zones. In Latin America, countries such as Brazil and Mexico focus on public housing and transportation networks, raising the demand for structural steels. Further eastward, the Middle East, headed by the UAE and Saudi Arabia, witness massive infrastructure expansion as part of their economic diversification plans, with NEOM and Vision 2030 being the prime contributors to steel demand. Africa is experiencing a kind of a slow growth because of government initiatives in infrastructure and urban development, led by Nigeria and South Africa. The political instability, fluctuating economic conditions, and limited steel-manufacturing opportunities within it are drawbacks faced by the region. This causes steel and raw materials to be imported, the price and availability of which keep fluctuating. However, the greater growth potential of LAMEA comes from untapped markets together with growing foreign direct investments into construction and industrial sectors.
Structural Steel Market Top Companies
Recent Developments
- In Aug 2024, the new product Essar Structural is from Stecol International Private Limited (SIPL). Being established under the aegis of Prime Minister Narendra Modi's 'AatmaNirbhar Bharat' paradigm, the launch of Essar Structural was another feather in India's infrastructure-capability offer. And growing infrastructure development in the country helped add demand to structural steel through this new product.
- In Sept 2024, Grippon Infrastructures unveiled JSW's Magsure coating for steel structures. Magsure opens a new chapter in the steel structures sector with cold-rolled steel, which has the best aluminium, magnesium, and zinc coating.
Market Segmentation
By Product Type
- Heavy Sectional Steel
- I-beams
- Universal Columns
- Angles (large-sized, thick)
- Steel Girders and Trusses
- Others
- Light Sectional Steel
- Lightweight Angles and Channels
- Flat bars
- Small I-beams and T-sections
- Others
- Rebar
By Steel Type
- Hot-Rolled Steel
- Cold-Rolled Steel
- Carbon-Manganese Steel
- High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) Steel
- Heat-Treated Carbon/Alloy Steel
By End-Use Industry
- Construction
- Oil & Gas
- Energy & Power
- Automotive & Transportation
- Shipbuilding
- Mining & Heavy Machinery
- Others
By Region
- North America
- APAC
- Europe
- LAMEA



