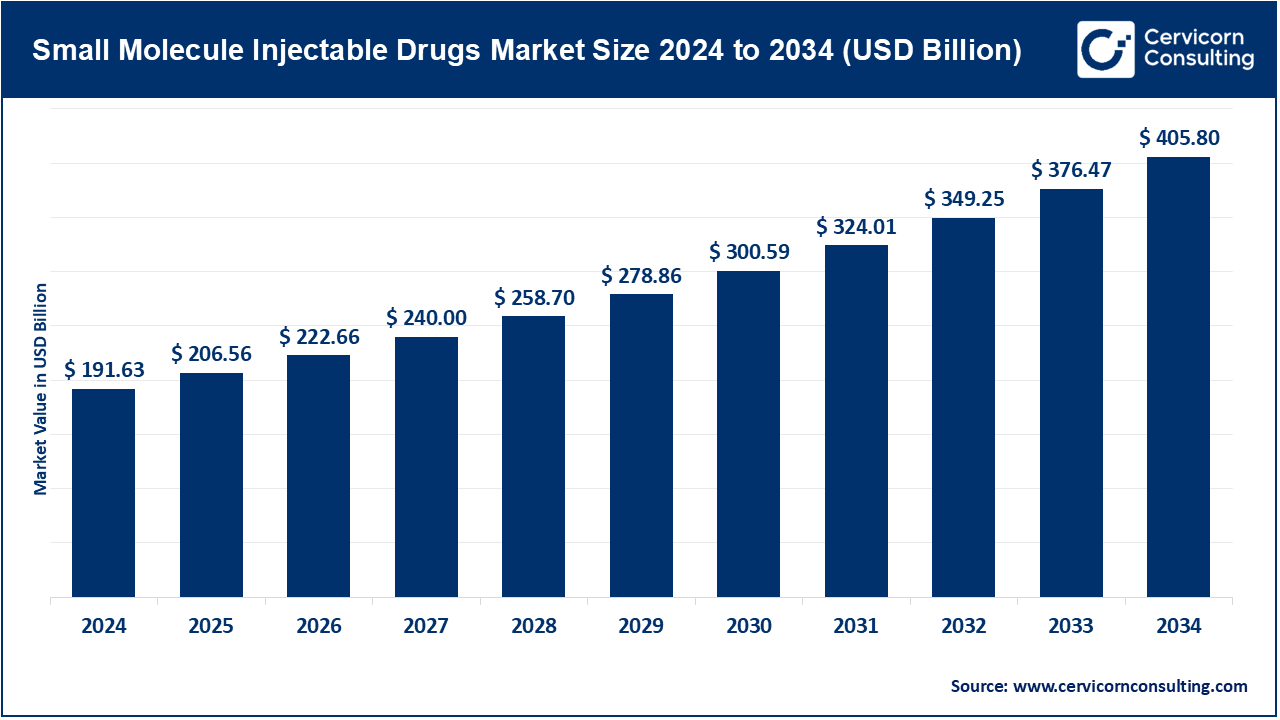
The global small molecule injectable drugs market size was valued at USD 191.63 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 405.80 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.79% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
The steady increase in chronic and non-communicable diseases-cancer, diabetes, heart disorders, autoimmune conditions, and respiratory ailments-has sharply raised the demand for injectable therapies. According to the World Health Organization (WHO, 2024), non-communicable diseases (NCDs) account for 74% of global deaths, with cardiovascular diseases, cancer, chronic respiratory diseases, and diabetes as the top contributors. WHO projects cancer cases to rise by 60% globally by 2040, driving strong demand for oncology injectables such as paclitaxel and docetaxel. These diseases often need quick and effective treatments, and small molecule injectables are perfect for that. The trend is particularly pronounced in North America and the Asia-Pacific, where stronger healthcare systems are expanding market capacity. In oncology, drugs such as paclitaxel and docetaxel have long been staples; with rising cancer diagnoses worldwide, the need for these injectable therapies only grows louder.
The small molecules injectable drugs market is an important part of the pharmaceutical industry. These drugs help treat serious, long-term, and life-threatening conditions. They are light in weight, stable, and absorbed quickly. This makes them ideal for injection, especially in hospitals and critical care environments. The United States spends the most on health care, providing more than $12,000 per person each year. Germany, Switzerland, and Norway spend between $6,000 and $7,000 per person, after the United States. Spending ranges from $4,000 to $6,000 year per person in France, Sweden, Canada, Japan, Australia, and the United Kingdom. These countries devote between 9 % and 17 % of their overall economic output to health care each year.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 206.56 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 405.80 Billion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 7.79% |
| Dominant Region | North America |
| Fastest Expanding Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Drug Class, Indication, Route of Administration, Distribution Channel, Region |
| Key Companies | Pfizer Inc., Merck & Co., Inc., Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Novartis AG (including Sandoz), AstraZeneca plc, Fresenius Kabi AG, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd., Cipla Ltd., Hikma Pharmaceuticals PLC, Aurobindo Pharma Ltd. |
Chemotherapy Agents: The chemotherapy agents segment has generated highest revenue share. Driven by rising global cancer incidence, the market is expanding faster than many observers expected. Classic agents-paclitaxel, docetaxel and cisplatin-remain mainstays for treating solid tumors and hematological malignancies alike. Injectable forms offer almost complete bioavailability, allowing cytotoxic drugs to enter the circulation swiftly and with predictable activity. As research produces novel oncology compounds and treatment centers proliferate worldwide, this product category is set for continued robust growth.
Anti-Infectives: Injectable anti-infectives, such as ceftriaxone and meropenem, are critical for treating serious bacterial infections, especially in hospitals. In settings where oral antibiotics might not act promptly or efficiently, such as intensive care units, post-operative care, and sepsis management, these drugs are particularly crucial. Additionally, the need for novel injectable solutions that can target a larger range of bacteria has increased because to the growing problem of antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
Cardiovascular Drugs: Injectable small molecule drugs like heparin, nitroglycerin, and adenosine play a critical role in acute care settings, particularly for managing heart attacks, arrhythmias, and hypertension crises. These medications provide immediate relief and are often utilized in emergency rooms and during surgical procedures. Given that cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death worldwide, this segment consistently drives market volume.
Analgesics and Anesthetics: Pain-relief medicines like fentanyl, morphine, and even lidocaine tidy up sore, hurting spots and make patients comfortable. Doctors grab them in the operating room, after big injuries, and with people who have serious, long-lasting illness. Because shots work fast and can be dosed finely, needles beat pills every time big, sudden ache shows up.
Hormonal Agents: This group includes injectables like insulin (technically a peptide), testosterone, and corticosteroids, which are vital for managing endocrine and inflammatory disorders. Injecting hormones allows for controlled release and improved absorption, making them especially effective for chronic therapy.
Others: This catch-all category includes antipsychotics, antiepileptics, and gastrointestinal agents. Long-acting injectables in mental health treatment are gaining popularity because they can enhance compliance and reduce the chances of relapse. Each drug class contributes uniquely to the injectable small molecule market, with chemotherapy, anti-infectives, and cardiovascular drugs leading the way due to their urgent need in life-saving therapies.
Oncology: Oncology stands out as the largest and most prominent indication segment, responsible for nearly half of the total market share. Small molecule injectables play a crucial role in cancer therapy thanks to their capacity for delivering rapid, potent, and targeted treatment. Most standard chemo drugs-paclitaxel, cisplatin, doxorubicin-show up in veins rather than mouths because they treat solid tumors and blood cancers better that way. More people getting diagnosed with cancer, easier access to clinics, and cutting-edge injectable targeted drugs all keep demand in this space growing fast. On top of that, hospitals like needles over pills since they deliver the exact dose exactly when needed, making the body absorb the drug more reliably.
Infectious Diseases: This group of drugs is really important whenever doctors are handling serious bacterial bugs, sepsis, pneumonia, or other sudden infections. Small injectable medicines such as ceftriaxone, meropenem, and vancomycin give teams quick, powerful help. Because of spreading drug resistance and germs that strike inside hospitals, the need for these shots has shot up. In places where pills just won t work, these injectables often become the only option that buys time or even saves a life.
Cardiovascular Diseases (CVD): One of the biggest causes of death in the world today is cardiovascular disease. Small molecule injectables used to treat thrombotic diseases, arrhythmia, and myocardial infarction are in high demand as a result. In emergency and surgical care, medications like nitroglycerin, adenosine, and heparin are commonly used. They are crucial for acute and critical care interventions due to their quick beginning of action.
Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases: This growing area includes disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis. Used to manage flares and overall disease control, injectable corticosteroids and immunosuppressants are commonly administered. These therapies often use targeted delivery systems to combat inflammation throughout the body.
Others: This category includes various indications such as pain management, diabetes (like injectable metformin analogs), mental health (including long-acting antipsychotics), and gastrointestinal disorders. Each of these areas benefits from the rapid action and sustained release capabilities of injectables. Collectively, these indication-based segments highlight the versatility and essential role of small molecule injectables in modern medicine, with oncology, infectious diseases, and cardiovascular conditions leading in both volume and value.
Hospital Pharmacies: Within the pharmacy channel, hospital pharmacies possess distinct strategic importance, controlling a significant share of the market, often cited to be more than 65–70%. This leading share stems from the clinical use of most injectable drugs which remain intra-patient and emergency in nature and require direct supervision from trained personnel. The preference for IV (intravenous) drugs in these settings amplifies the role of hospital pharmacies.
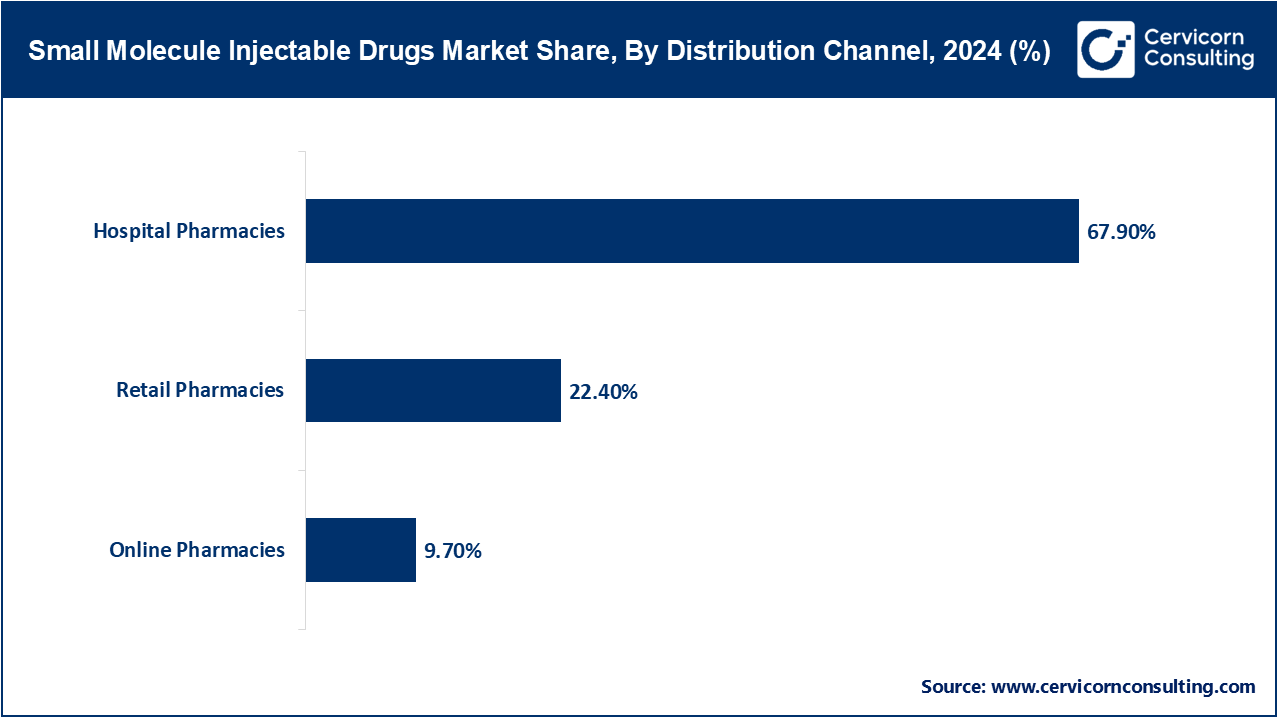
Retail Pharmacies: On the other hand, retail pharmacies, including chain drugstores and independent outlets, are becoming increasingly significant, particularly with the growing availability of self-administered injectable drugs. Subcutaneous and intramuscular injectables, like insulin, hormone therapies, and long-acting antipsychotics, are now more accessible to patients via retail channels. This trend is supported by the ongoing movement toward decentralized care and managing chronic diseases in community settings.
Online Pharmacies: To conclude, internet pharmacies are growing rapidly but their share of retail and hospital pharmacies is still low. The pandemic fueled the e-commerce boom, leading to more digital adoption in the healthcare space as well as a preference for home delivery. Online platforms are particularly beneficial for chronic therapy injectables that require consistent refills, such as those for diabetes and fertility treatments. However, challenges such as cold chain logistics, regulatory obstacles, and the need for proper administration still restrict the use of online pharmacies for more complex or acute injectable medications.
There is a noticeable rise in healthcare awareness and per capita income, along with broader insurance coverage, making advanced treatments more accessible to the population. Additionally, India and China are emerging as global hubs for contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs) because of their lower labor and production costs, paired with high-quality outputs. These countries are important producers of generics for injection and they export these products around the world and are instrumental in international supply chains. China holds over 30% of the global CDMO market share, with competitive production costs and a strong record in producing high-quality generic injectables for global export. In case of Japan, the injectable medications are in great demand in elderly people and oncologists because of the aged population.
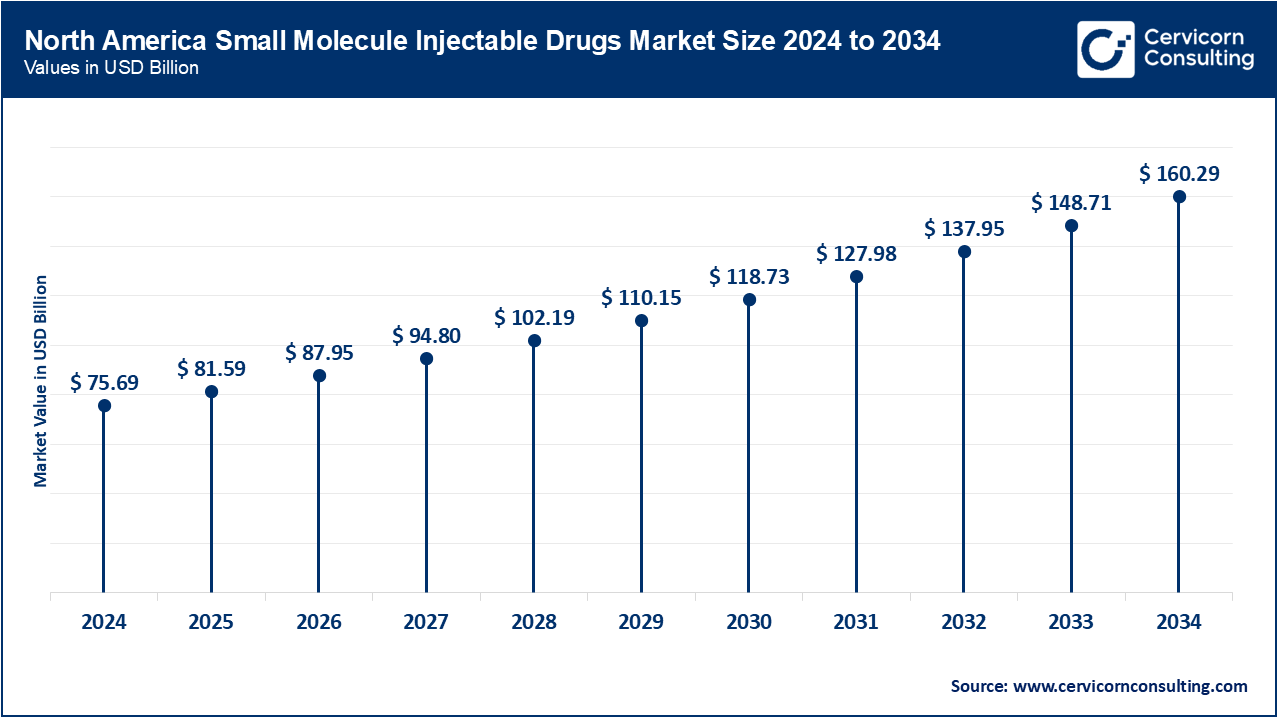
North America is currently at the forefront of the market, holding about 39.50% of the global share as of 2024. This dominant position can be attributed to substantial healthcare expenditure, a well-established biopharmaceutical industry, and the widespread use of advanced injectable therapies, notably for cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and autoimmune conditions. Here, the United States is important due to the strong research and development pipeline, high market for branded and generic injectables, and favorable regulations like FDA fast track approvals. These therapies have strong demand in the country because of the aging population along with the high prevalence of chronic illnesses. U.S. pharmaceutical companies increasingly outsource sterile injectable manufacturing to India, China, and Europe, with India alone holding 600+ USFDA-approved plants capable of serving the North American market.
Europe comes next with almost 27.10% of the market share. Germany, France, UK, and Italy are primary contributors as they have well developed health care systems and are increasing spending on biosimilars and other generic injectable medicines due to a shift towards cost-effective healthcare management. Although European regulatory frameworks can be quite stringent, they are also harmonized across the region, simplifying pharmaceutical distribution between countries. There is an upward trend in hospital-based treatments, cancer care, and vaccination efforts, all driving the increasing use of small molecule injectables. In light of previous supply chain disruptions, governments in Europe are now promoting domestic production of sterile injectables to decrease reliance on imports. Major players like Pfizer, Novartis/Sandoz, Teva, Merck, and AstraZeneca lead the market with extensive portfolios that include drugs for oncology, anti-infectives, pain management, and cardiovascular diseases.
Small Molecule Injectable Drugs Market Revenue Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America | 39.50% |
| Europe | 27.10% |
| Asia-Pacific | 23.40% |
| LAMEA | 10% |
Countries in Latin America and the Middle East & Africa (MEA) may not have the largest markets, but they are gaining traction due to healthcare infrastructure and hospital investments. Brazil and Mexico are leading the region, thanks to the government and private sector healthcare initiatives. Brazil’s pharmaceutical market is the largest in Latin America, valued at over USD 30 billion in 2023, with injectables accounting for 18% of total drug sales. Government programs like Farmácia Popular and expansion of the Unified Health System (SUS) hospitals have improved patient access. Also, in MEA countries such as South Africa, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE are heavily investing in local drug manufacturing, improving access to injectable therapies for both infectious and chronic diseases. The small-molecule injectable drugs market is currently a dynamic space, influenced by both large pharmaceutical companies and nimble specialty firms. There's a lot of innovation happening, along with strategic partnerships and expanded manufacturing capabilities.
Market Segmentation
By Drug Class
By Indication
By Route of Administration
By Distribution Channel
By Region