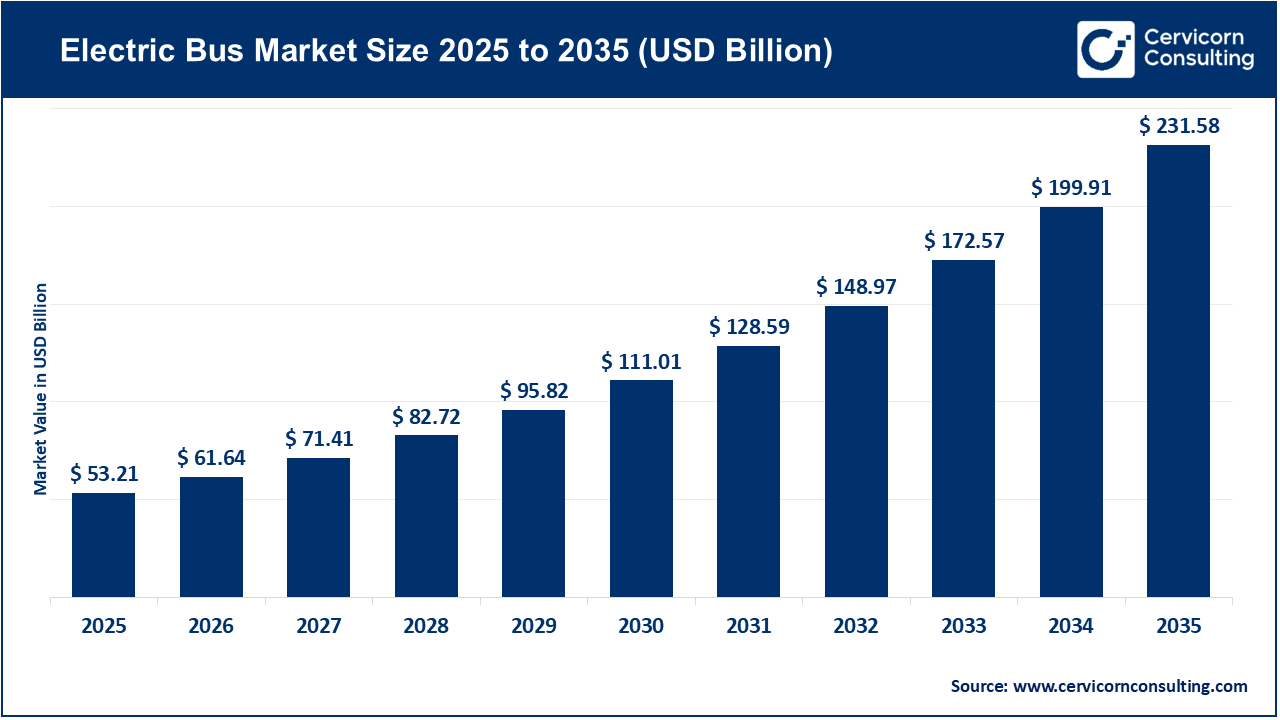
The global electric bus market size was valued at USD 53.21 billion in 2025 and is expected to surpass around USD 231.58 billion by 2035, exhibiting at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.8% over the forecast period from 2026 to 2035. The electric bus market is experiencing significant growth, mainly driven by environmental, economic, and regulatory factors. As of 2024, around 780,000 electric buses operate worldwide, with battery-electric models making up nearly 94% of the fleet. China accounts for over 90% of these deployments globally. Stricter emission regulations, zero-emission bus mandates, and clean-air policies implemented by governments in various regions are prompting transit authorities to switch from diesel to electric buses. Concerns about urban air quality, rising public demand to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and national climate goals have further accelerated this transition. Additionally, advances such as decreasing battery costs, higher energy density, and improved charging technologies have lowered operating expenses, reducing the total cost of ownership compared to traditional diesel buses and encouraging wider fleet electrification.
The shift to electric buses is also bolstered by public funding programs, pilot projects, and large-scale fleet electrification efforts, especially in public transportation. In Europe, battery-electric bus registrations rose by more than 40% in the first half of 2025, highlighting a swift replacement of internal combustion engine buses in city fleets. Emerging markets are also contributing to this trend. For example, India deployed over 1,500 electric buses between March 2023 and February 2024, an increase of approximately 80% year-over-year, driven largely by national incentives and regional tenders. Similar developments are seen in North America, where school districts and municipal agencies are increasingly adopting electric buses due to federal and state funding, lower maintenance costs, and greater vehicle reliability. Overall, these developments show that policy support, operational cost savings, and infrastructure growth are key drivers behind the global adoption of electric buses.
How the Rise in Government Mandates for Zero-Emission Public Transportation Is Driving the Electric Bus Market
Government mandates for zero-emission public transportation are a major driver of electric bus adoption. Many countries and cities now require transit agencies to purchase only zero-emission buses within set timelines, such as London’s commitment to a 100% zero-emission bus fleet by 2034 and California’s regulation that only zero-emission buses may be purchased after 2029 under its Innovative Clean Transit rule. This regulatory clarity removes uncertainty for fleet operators and pushes earlier electrification planning. It also encourages manufacturers to scale production and invest in technology. As policies tighten, government support often includes subsidies and grants - for example, under India’s EV scheme 14,028 electric buses received support with over INR 4,391 crore in funding and investments in charging infrastructure, which helps lower upfront costs for operators. Overall, these mandates help transform electric buses from pilot projects into a standard procurement choice for authorities seeking to achieve air-quality and climate goals.
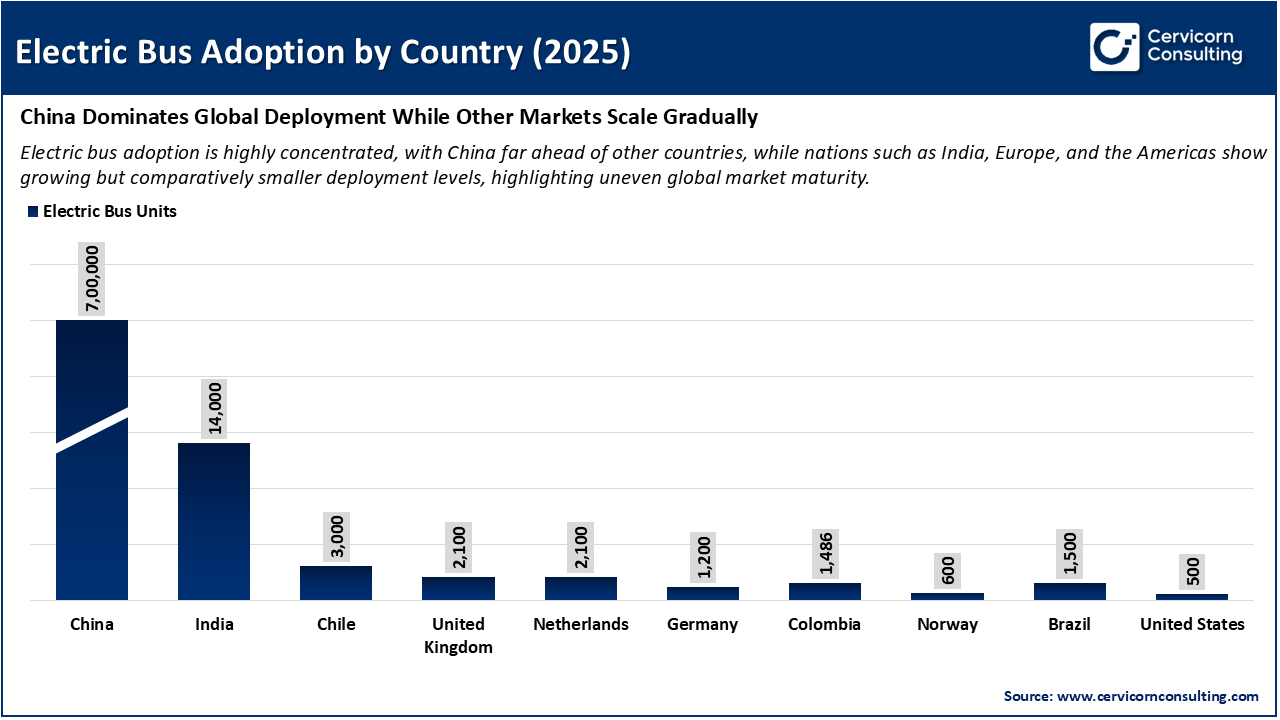
The image presents electric bus adoption by country in 2025, revealing a significant disparity in global distribution. China is projected to maintain a dominant position, supported by early policy initiatives, extensive public procurement, and a robust domestic manufacturing sector. India is expected to follow, largely due to government-led urban electrification efforts. In contrast, regions such as Europe, Latin America, and North America are anticipated to exhibit relatively lower adoption rates. This suggests that, although the deployment of electric buses is increasing worldwide, substantial market penetration is still primarily limited to a select group of leading countries.
1. Strong Growth in European Electric Bus Registrations
During the first half of 2025, Europe registered 5,315 battery-electric buses over 8 tons, representing an increase of approximately 41% compared to the same period in 2024. When all weight categories are included, total registrations reached 6,444 units, reflecting a year-on-year growth of about 49%. This upward trend in registrations indicates that transit agencies are rapidly deploying electric buses, which in turn demonstrates growing confidence among operators in electric bus technology and procurement processes. The higher adoption rates are also driving further investments in infrastructure, strengthening supply chain reliability, and encouraging manufacturers to expand production capacity for the European market.
2. Launch of Next-Gen Electric Bus Platforms by Major OEMs
Major manufacturers are now launching new electric bus platforms that offer enhanced range and capacity. For instance, Volvo has introduced the Volvo BZR electric bus and coach chassis, with certain models capable of achieving up to 700 kilometers on a single charge. These new electric configurations are being deployed in both Latin America and Europe. Such technological advancements are enabling electric buses to be used not only on urban routes but also for longer intercity services. As a result, electric buses are becoming a viable option for a wider range of transit networks and passenger segments, which is expected to accelerate the electrification of bus fleets.
3. Expansion of Double-Decker and High-Capacity Electric Bus Models
Global original equipment manufacturers are increasingly producing and delivering advanced high-capacity electric buses. In 2025, Alexander Dennis introduced updated versions of the Enviro500EV, a battery-electric tri-axle double-decker bus, featuring larger battery capacity and extended range for the North American market. At the same time, operators in Hong Kong and other regions are increasing their orders for these vehicles. The introduction of high-capacity electric buses enables transit agencies to serve major corridors more efficiently, supports the reduction of overall emissions, and meets the growing demand for passenger transport. This trend is expected to further accelerate the electrification of large urban bus fleets.
4. Growth in Global Electric Bus Adoption Rates Across Multiple Countries
Several countries, such as China, the Netherlands, Finland, Switzerland, and Denmark, have increased the share of electric buses in total bus sales from less than 6% to over 60% within a period of six years. This rapid expansion demonstrates the technical feasibility of large-scale electrification when supported by effective policy measures and investment. The significant change in sales composition indicates a structural transformation in the global bus market toward electrification. This development is likely to encourage other countries to implement similar policies, thereby accelerating the overall global demand for electric buses.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 61.64 Billion |
| Market Size in 2035 | USD 231.58 Billion |
| CAGR 2026 to 2035 | 15.8% |
| Dominant Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Propulsion, Battery Chemistry, Battery Capacity, Seating Capacity, Service, Fleet Ownership |
| Key Companies | BYD, Yutong Bus, Proterra, Volvo Buses, Daimler Buses, Tata Motors, Ashok Leyland, Alexander Dennis, Solaris Bus & Coach, VDL Bus & Coach, Ebusco, NFI Group, Scania, Higer Bus, CRRC Electric Vehicles |
The electric bus market is segmented into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. Here is a brief overview of each region:
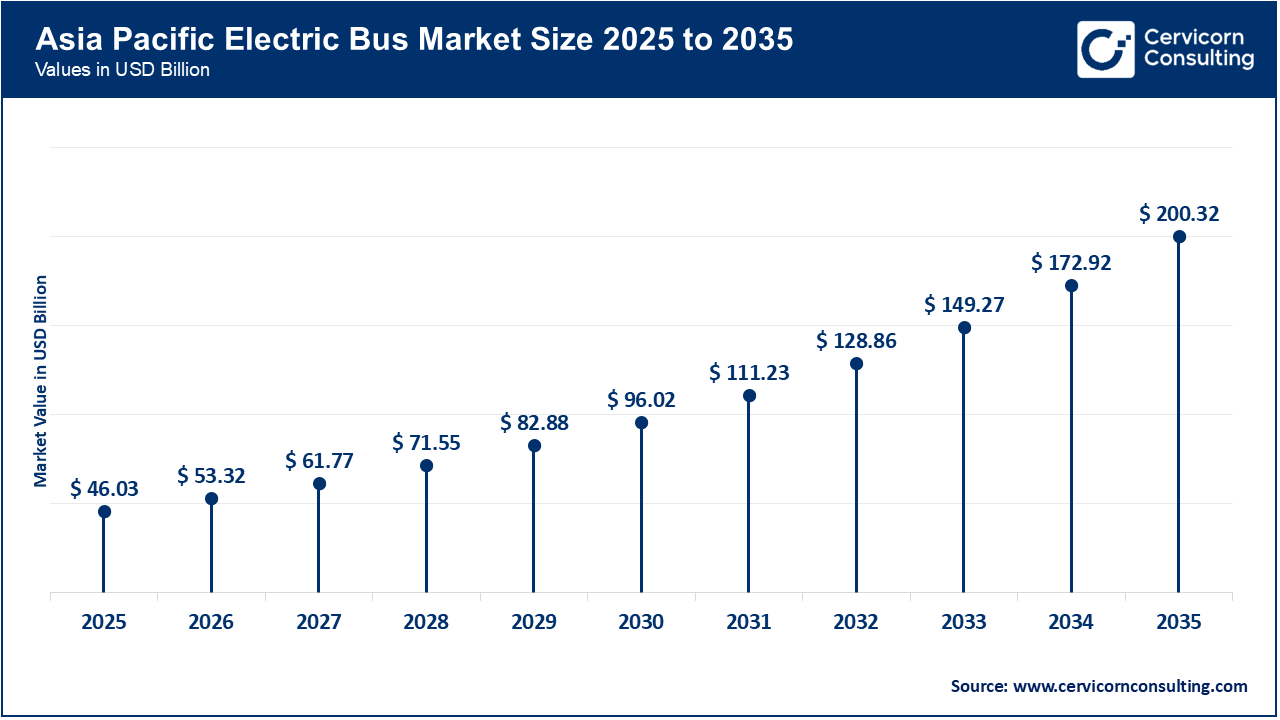
The Asia-Pacific electric bus market size was estimated at USD 46.03 billion in 2025 and is projected to exceed around USD 200.32 billion by 2035. In China, India, and Southeast Asia, national procurement programs and rapid manufacturing expansion have led to the region holding a dominant share of global electric-bus deployments. Centralized tenders and subsidy schemes have generated high-volume demand, enabling local OEMs to scale up production, develop vertical supply chains, and increase battery manufacturing. The entry of new foreign investments has further expanded regional capacity. As a result, unit costs have decreased and delivery lead times have shortened, making large-scale electrification programs more feasible for a growing number of cities.
Recent Developments:
The North America electric bus market size was valued at USD 1.70 billion in 2025 and is expected to surge around USD 7.41 billion by 2035. The electrification of fleets in the United States and Canada is being significantly driven by large federal stimulus and targeted school-bus programs. As a result, transit agencies and school districts are increasingly replacing diesel fleets with electric alternatives. Grants and incentives have reduced the initial costs for municipalities and school districts, which has improved the financial viability of these projects. This has encouraged the procurement of multiple vehicles and attracted OEM investment in local production and service networks. Additionally, the rise of state-level zero-emission bus mandates and utility partnership pilots has facilitated depot electrification planning and energy management. These developments are making large-scale rollouts more achievable for operators.
Recent Developments:
The Europe electric bus market size was reached at USD 4.74 billion in 2025 and is forecasted to hit around USD 20.61 billion by 2035. Across Europe, ambitious city and national zero-emission bus mandates have created predictable demand and led to large public tenders. This has motivated manufacturers to expand their capacity and adapt products to meet local market requirements. As procurement volumes increase, investments in charging infrastructure and service ecosystems are also rising. This is reducing the total cost of ownership and lowering procurement risks for transit authorities. The strong adoption of electric buses in several EU markets is resulting in their integration into standard urban fleets, rather than remaining limited to pilot projects. This trend is accelerating supplier consolidation and driving further technology improvements.
Recent Developments:
Electric Bus Market Share, By Region, 2025 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2025 (%) |
| Asia-Pacific | 86.5% |
| Europe | 8.9% |
| North America | 3.2% |
| LAMEA | 1.4% |
The LAMEA electric bus market was valued at USD 0.74 billion in 2025 and is anticipated to reach around USD 3.24 billion by 2035. In Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa, municipal pilot projects, international climate finance, and city-led procurement programs are playing a key role in initiating fleet electrification and developing the local project pipeline. Donor-backed and multilateral financing has reduced investment risks for cities, enabling the implementation of demonstrator projects that validate operational models. Successful pilot projects in countries such as Chile and Colombia have provided regional examples for replication. As a result, the expansion of local charging and maintenance capacity is supporting the potential for scaling up electrification across these regions.
Recent Developments:
The electric bus market is segmented into propulsion, battery chemistry, battery capacity, seating capacity, service, fleet ownership, and region.
The dominance of all-electric buses in the market can be attributed to their zero tailpipe emissions, reduced operating costs, and significant government backing. These vehicles have become a preferred choice for urban public transport systems, particularly where routes are predictable and depot charging infrastructure is available. Ongoing advancements in battery efficiency, coupled with declining battery costs, have enhanced both the range and reliability of BEVs, making them increasingly suitable for daily city operations. The widespread adoption of all-electric buses in regions such as China, Europe, and North America has further established BEVs as the leading propulsion technology in the sector.
Electric Bus Market Share, By Propulsion, 2025 (%)
| Propulsion | Revenue Share, 2025 (%) |
| All-electric (BEV) | 93.2% |
| PHEV | 3.6% |
| FCEV | 3.2% |
Fuel cell electric buses represent the fastest-growing propulsion segment, primarily due to increasing demand for extended range and rapid refueling capabilities. These buses are especially well-suited for intercity routes and high-utilization services, where minimizing charging downtime is essential. The implementation of government hydrogen strategies, along with pilot programs and investments in refueling infrastructure, is accelerating the adoption of fuel cell technology. Although current costs remain elevated, ongoing reductions in fuel cell prices and the expansion of green hydrogen supply are projected to drive significant growth in this segment.
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries have established themselves as the dominant chemistry in the electric bus market, largely because of their high thermal stability, extended cycle life, and cost-effectiveness. These characteristics make LFP batteries particularly suitable for public transport fleets that require a focus on safety, durability, and consistent daily operations. Their reliable performance in high-temperature environments and ability to withstand frequent charging cycles further enhance their suitability for urban bus applications. The extensive adoption of LFP batteries in Asia, particularly in China, has solidified their status as the preferred choice for large-scale electric bus deployments.
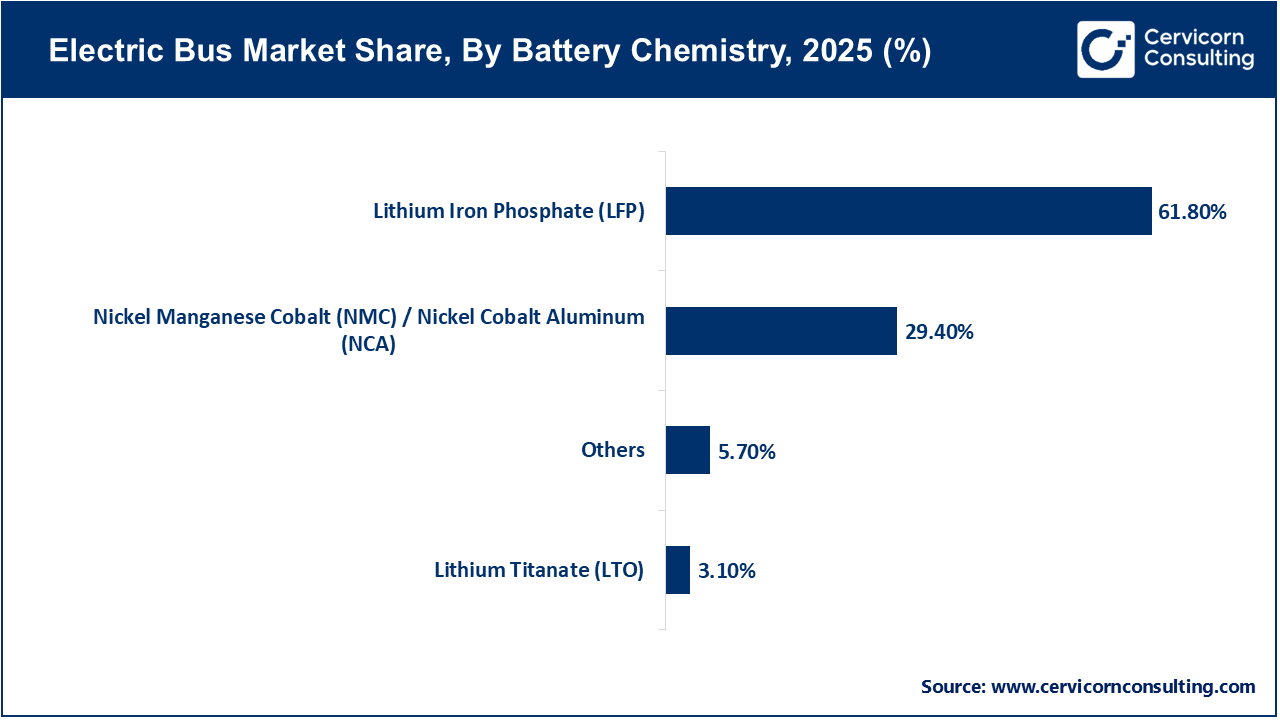
Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC) and Nickel Cobalt Aluminum (NCA) batteries are currently the fastest-growing battery chemistries in the electric bus sector, primarily because of their higher energy density. This advantage allows for longer driving ranges and reduced vehicle weight, which is particularly beneficial for intercity, coach, and high-capacity bus applications. Manufacturers aiming to deliver premium or long-range electric buses are increasingly adopting NMC and NCA chemistries. Ongoing advancements in safety features, battery management systems, and cost optimization are expected to further accelerate the adoption of these battery types in global markets.
The 100–300 kWh battery capacity segment leads the market because it provides an optimal balance among range, cost, and vehicle weight. This capacity range is particularly well-suited for intracity operations, as it enables daily driving requirements to be met without incurring excessive battery costs. The majority of standard 9-12 meter city buses are equipped with batteries in this range, making it the most prevalent configuration in the market. Additionally, the compatibility of these batteries with overnight depot charging has contributed to their widespread adoption by municipal transport operators.
Electric Bus Market Share, By Battery Capacity, 2025 (%)
| Battery Capacity | Revenue Share, 2025 (%) |
| Below 100 kWh | 11.6% |
| 100–300 kWh | 65.9% |
| Above 300 kWh | 22.5% |
Battery capacities exceeding 300 kWh constitute the fastest-growing segment in the market, primarily due to rising demand for longer range and high-capacity electric buses. Articulated buses, intercity coaches, and vehicles operating on extended duty cycles are increasingly reliant on larger battery packs to meet operational requirements. Recent advancements in fast-charging technology and improvements in energy density have enhanced the practicality of high-capacity batteries. As electric buses are deployed beyond city centers into regional and long-distance routes, this segment is projected to experience accelerated growth.
High-capacity electric buses hold a dominant position in the market, largely because of their widespread use in urban public transportation systems. These vehicles are typically deployed on high-demand routes, which allows operators to maximize passenger throughput and reduce emissions on a per-capita basis. Government initiatives often prioritize the electrification of larger buses to achieve greater environmental benefits per vehicle. Standard city buses, articulated models, and double-decker buses are included in this category, making it the most significant contributor to global electric bus volumes.
Electric Bus Market Share, By Seating Capacity, 2025 (%)
| Seating Capacity | Revenue Share, 2025 (%) |
| Low-capacity (≤20 seats) | 9.7% |
| Medium (20–40 seats) | 29.8% |
| High capacity (>40 seats) | 60.5% |
Medium-capacity electric buses represent the fastest-growing segment, fueled by increasing demand for feeder routes, suburban transportation, and flexible mobility solutions. These buses are being adopted for a variety of applications, including campus shuttles, airport transfers, and last-mile connectivity. Their lower cost and greater maneuverability compared to high-capacity buses make them particularly appealing to smaller cities and private operators. The expansion of smart city initiatives and the rise of demand-responsive transit services are further contributing to the rapid adoption of medium-capacity electric buses.
Intracity services are the leading segment in the electric bus market, primarily as a result of strong policy initiatives aimed at reducing urban air pollution and emissions. City routes typically involve predictable distances, frequent stops, and centralized depots, all of which make them well-suited for electrification. The majority of government incentives and zero-emission mandates are directed toward urban public transport fleets. Consequently, electric buses are most commonly deployed in city transit networks, serving as the foundation for global electric bus adoption.
Electric Bus Market Share, By Service, 2025 (%)
| Service | Revenue Share, 2025 (%) |
| Intercity | 19.6% |
| Intracity | 80.4% |
Intercity electric bus services are experiencing rapid growth, driven by advancements in battery technology and the expansion of charging infrastructure. Enhanced range capabilities and the availability of fast-charging solutions are enabling electric buses to operate effectively on regional and short-haul intercity routes. Both governments and transport operators are initiating pilot programs with electric coaches as part of broader efforts to decarbonize regional transportation. Additionally, rising fuel costs and increasing sustainability targets are prompting fleet operators to consider electric alternatives for intercity operations.
Government-owned fleets are the dominant force in the electric bus market, largely due to public transport electrification mandates and commitments to climate goals. Municipal and state transport authorities represent the largest segment of buyers, frequently benefiting from subsidies and centralized procurement initiatives. Government ownership facilitates large-scale deployment, ensures stable demand, and provides long-term contracts for manufacturers. The leadership of the public sector has been instrumental in positioning electric buses as a mainstream solution for public transportation.
Electric Bus Market Share, By Fleet Ownership, 2025 (%)
| Fleet Ownership | Revenue Share, 2025 (%) |
| Government | 54.7% |
| Private Fleet | 24.9% |
| Leasing & Rental | 12.3% |
| Ride-hailing Operator | 2.1% |
| Others | 6.0% |
Leasing and rental models represent the fastest-growing segment in fleet ownership, as operators increasingly look to minimize upfront capital expenditures. These approaches enable transit agencies and private fleets to adopt electric buses without assuming the risks associated with battery ownership and evolving technology. Leasing arrangements also facilitate more rapid fleet expansion and provide predictable operating costs. The emergence of battery-as-a-service and comprehensive mobility solutions is further accelerating the growth of this segment in both developed and emerging markets.
By Propulsion
By Battery Chemistry
By Battery Capacity
By Seating Capacity
By Service
By Fleet Ownership
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Electric Bus
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Propulsion Overview
2.2.2 By Battery Chemistry Overview
2.2.3 By Battery Capacity Overview
2.2.4 By Seating Capacity Overview
2.2.5 By Service Overview
2.2.6 By Fleet Ownership Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.2 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Government Zero-Emission Mandates and Policies
4.1.1.2 Lower Operating and Maintenance Costs
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 High Upfront Capital Cost
4.1.2.2 Charging Infrastructure Limitations
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 Grid Capacity and Energy Management
4.1.3.2 Battery Lifecycle and Recycling
4.1.4 Market Opportunities
4.1.4.1 Expansion into Intercity and High-Capacity Routes
4.1.4.2 Growth of Battery-as-a-Service and Leasing Models
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Electric Bus Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Electric Bus Market, By Propulsion
6.1 Global Electric Bus Market Snapshot, By Propulsion
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 All-electric
6.1.1.2 PHEV
6.1.1.3 FCEV
Chapter 7. Electric Bus Market, By Battery Chemistry
7.1 Global Electric Bus Market Snapshot, By Battery Chemistry
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP)
7.1.1.2 Lithium Titanate (LTO)
7.1.1.3 Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC) / Nickel Cobalt Aluminum (NCA)
7.1.1.4 Others
Chapter 8. Electric Bus Market, By Battery Capacity
8.1 Global Electric Bus Market Snapshot, By Battery Capacity
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Below 100 kWh
8.1.1.2 100-300 kWh
8.1.1.3 Above 300 kWh
Chapter 9. Electric Bus Market, By Seating Capacity
9.1 Global Electric Bus Market Snapshot, By Seating Capacity
9.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
9.1.1.1 Low-capacity (≤20 seats)
9.1.1.2 Medium (20–40 seats)
9.1.1.3 High capacity (>40 seats)
Chapter 10. Electric Bus Market, By Service
10.1 Global Electric Bus Market Snapshot, By Service
10.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
10.1.1.1 Intercity
10.1.1.2 Intracity
Chapter 11. Electric Bus Market, By Fleet Ownership
11.1 Global Electric Bus Market Snapshot, By Fleet Ownership
11.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
11.1.1.1 Government
11.1.1.2 Private Fleet
11.1.1.3 Leasing & Rental
11.1.1.4 Ride-hailing Operator
11.1.1.5 Others
Chapter 12 Electric Bus Market, By Region
12.1 Overview
12.2 Electric Bus Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
12.3 Global Electric Bus Market, By Region
12.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
12.4 North America
12.4.1 North America Electric Bus Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.4.3 North America Electric Bus Market, By Country
12.4.4 U.S.
12.4.4.1 U.S. Electric Bus Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
12.4.5 Canada
12.4.5.1 Canada Electric Bus Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
12.4.6 Mexico
12.4.6.1 Mexico Electric Bus Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
12.5 Europe
12.5.1 Europe Electric Bus Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.5.3 Europe Electric Bus Market, By Country
12.5.4 UK
12.5.4.1 UK Electric Bus Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
12.5.5 France
12.5.5.1 France Electric Bus Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
12.5.6 Germany
12.5.6.1 Germany Electric Bus Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
12.5.7 Rest of Europe
12.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Electric Bus Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
12.6 Asia Pacific
12.6.1 Asia Pacific Electric Bus Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.6.3 Asia Pacific Electric Bus Market, By Country
12.6.4 China
12.6.4.1 China Electric Bus Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
12.6.5 Japan
12.6.5.1 Japan Electric Bus Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
12.6.6 India
12.6.6.1 India Electric Bus Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
12.6.7 Australia
12.6.7.1 Australia Electric Bus Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
12.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
12.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Electric Bus Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
12.7 LAMEA
12.7.1 LAMEA Electric Bus Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.7.3 LAMEA Electric Bus Market, By Country
12.7.4 GCC
12.7.4.1 GCC Electric Bus Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
12.7.5 Africa
12.7.5.1 Africa Electric Bus Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
12.7.6 Brazil
12.7.6.1 Brazil Electric Bus Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
12.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
12.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Electric Bus Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 13. Competitive Landscape
13.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
13.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
13.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
13.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
13.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 14. Company Profiles
14.1 BYD
14.1.1 Company Snapshot
14.1.2 Company and Business Overview
14.1.3 Financial KPIs
14.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
14.1.5 Strategic Growth
14.1.6 Global Footprints
14.1.7 Recent Development
14.1.8 SWOT Analysis
14.2 Yutong Bus
14.3 Proterra
14.4 Volvo Buses
14.5 Daimler Buses
14.6 Tata Motors
14.7 Ashok Leyland
14.8 Alexander Dennis
14.9 Solaris Bus & Coach
14.10 VDL Bus & Coach
14.11 Ebusco
14.12 NFI Group
14.13 Scania
14.14 Higer Bus
14.15 CRRC Electric Vehicles