The global epoxy resin market size was accounted for USD 12.56 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 22.71 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.1% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. An epoxy resin is any of reactive prepolymers and polymers with epoxide groups. These thermosetting resins are widely used with hardeners or curing agents to produce human durable materials with chemical resistance. Because they show very good adhesion, corrosion resistance, and so forth-they have many applications in the industrial and commercial fields.
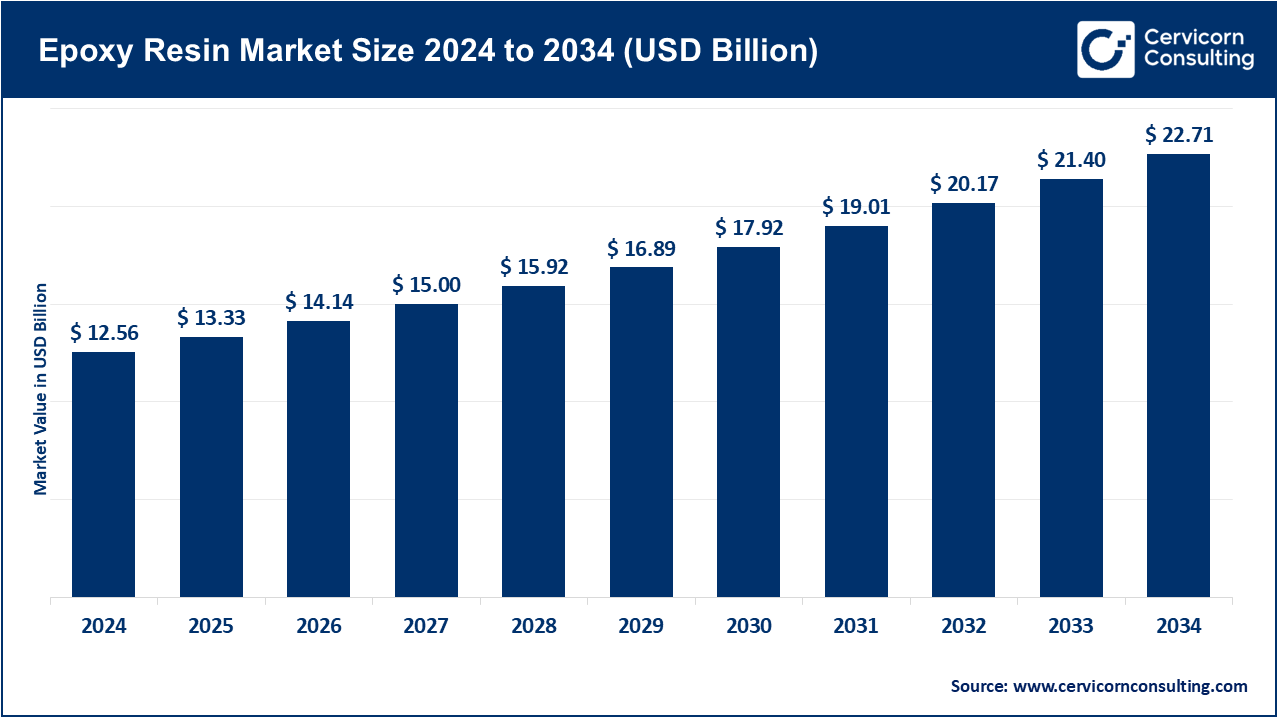
The global epoxy resin market is growing at a slight rate, propelled into high momentum by exhibiting extensive uses in many end-use industries such as construction, automotive, aerospace, electrical and electronics, marine, and wind energy. Epoxy resins in construction are used in coatings, adhesives, and composites to impart strength to a structure and enhance its durability. In electronics, they act as encapsulants and insulations, protecting delicate electronic components. A recent growth in adoption is being recognized in the renewable energy sector, mainly in wind turbine blades and solar panels, due to the light weight and strong mechanical profile that the resin provides. Furthermore, in the greater emphasis on eco-friendly, bio-based epoxy resin-product manufacturers push hard into innovation, thus allowing the product to blossom.
Among the few with the greatest influence on the automotive and aerospace industry's demand for this material is the need for materials that are light and high in performance. Due to concerns to reduce vehicle weight for better fuel efficiency and environmental significance, epoxy-based composites and adhesives have been deployed by manufacturers. The other big driver is the fast growth of the construction industry in emerging countries wherein epoxy flooring systems and coatings are categorized as the best for durability, resistance to abrasion, moisture, and chemical resistance. The market has been further fuelled by the explosive growth of the electronics sector, especially in the areas of consumer electronics, telecommunications, and electric vehicles. In electrical circuits and components, epoxy resins are used for insulation and thermal stabilization. Also, heightened R&D activities and improvements in manufacturing processes have led to the development of specialized epoxy formulations for niche applications.
Top Epoxy Resin Exporting Countries in 2024
| Countries | Share (%) |
| South Korea | 23% |
| China | 20% |
| United States | 13% |
| Japan | 8% |
| India | 7% |
| Taiwan | 6% |
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 13.33 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 22.71 Billion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 6.1% |
| Dominated Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Form, Type, Curing Method, Application, End Use Industry, Region |
| Key Companies | Olin Corporation, DIC Corporation, China Petrochemical & Chemical Corporation, Nan Ya Plastics Corporation, Hexion Inc. (Westlake Chemicals), Chang Chun Group, Kukdo Chemical Co., Ltd., Huntsman Corporation, Aditya Birla Chemicals, Sika Group, Others |
The epoxy resin market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region.
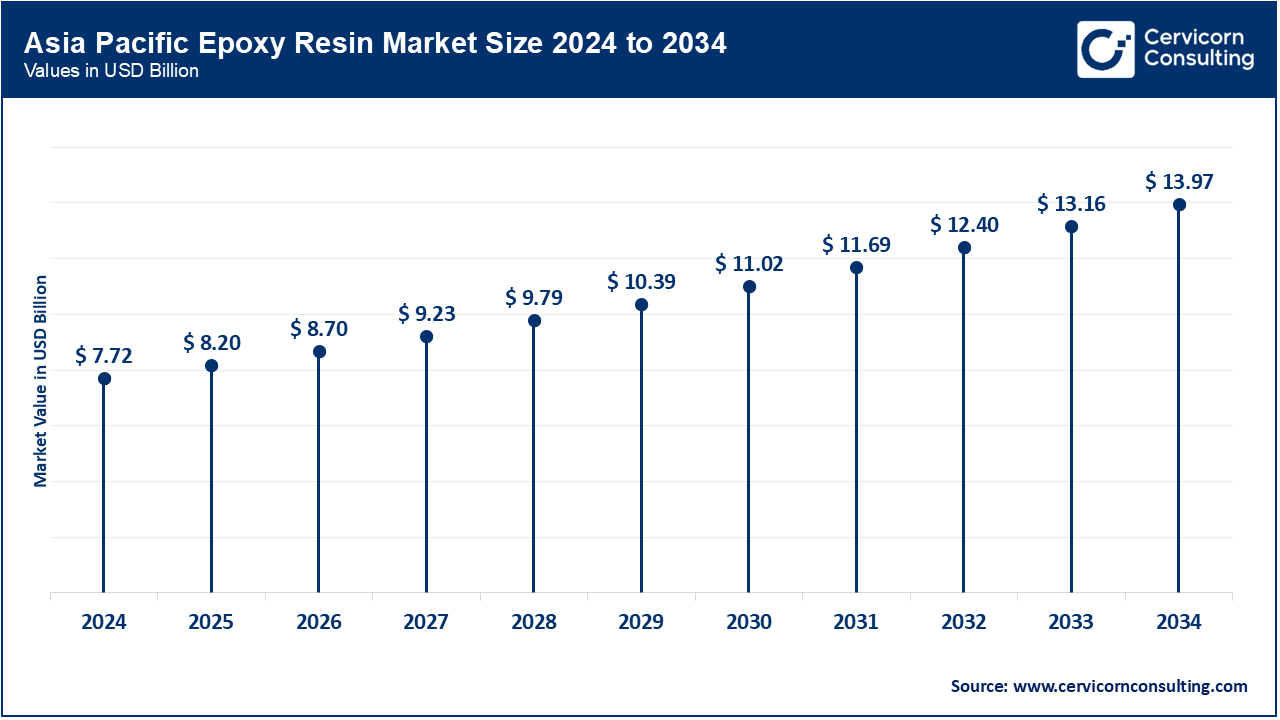
Due to relatively faster industrialization and urbanization processes in countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea, Asia-Pacific has been witnessing EPC resin sales and demand. Construction, automotive, electronics, and wind energy sectors sit on the other side of this demand in terms of whopping Great Growth. Epoxy resin is used in China, the largest producer and consumer, in huge infrastructure works and number of electronics works manufacturing, plus, the installation of wind turbines. Infrastructure development and growing middle-class demand have increased epoxy usage in India and Southeast Asia, especially for coatings and adhesives. The region offers opportunities to epoxy manufacturers as it has cheap manufacturing costs besides a large labour force and government support for industrial growth. Hence, APAC is the fastest growing and largest market for epoxy resin in the world.
The North American region is determined by several key sectors, such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and construction. The U.S. governs the region with high R&D investments and increased awareness of the benefits of lightweight and durable materials. Epoxy resins find the widest use in wind turbines and infrastructure repair. However, due to the mature economy of the region and strict environmental regulations governing resin formulations, the market growth is sluggish. Sustainability-focused initiatives and bio-based resins are gaining prominence, driving future demand. Hence, North America carries a steady market weight, courtesy of its focus on innovation and composite and high-performance applications on industrial and consumer levels.
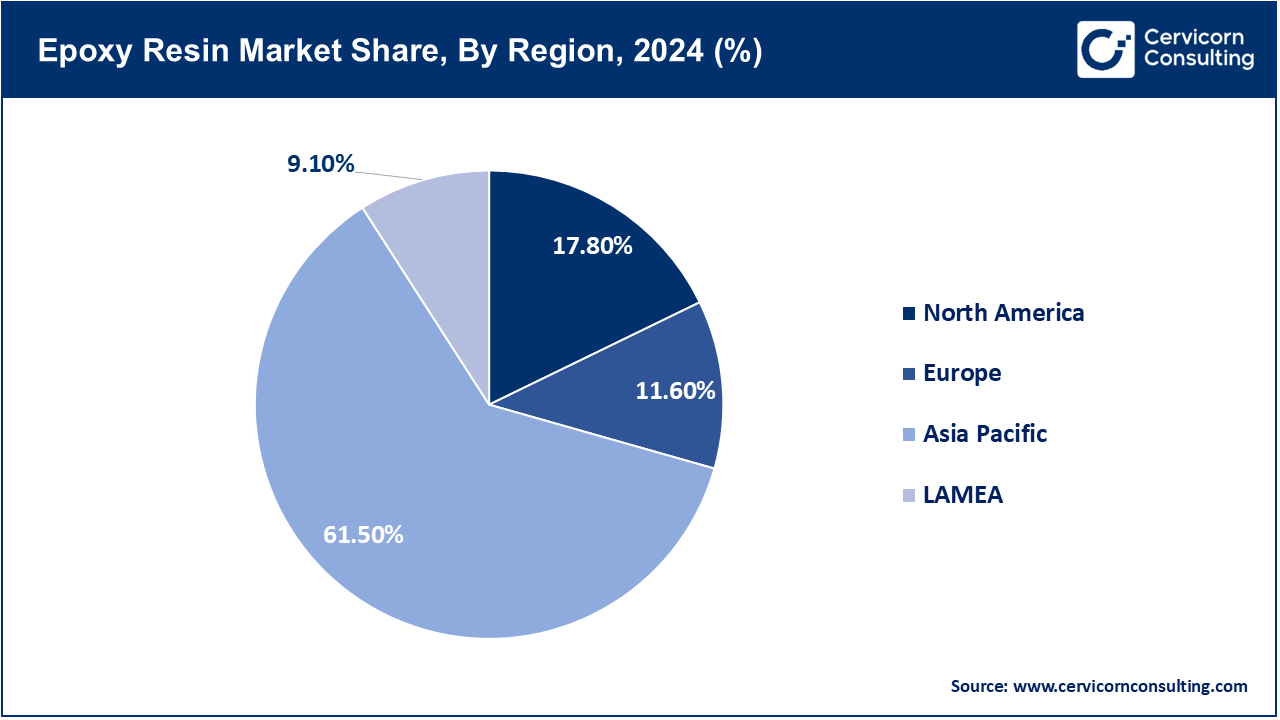
Environmental regulations inhibit European markets; sustainability and innovation drive the same. Due to the highly advanced automotive, aerospace, marine, and construction sectors, Germany, France, and UK stand tall in production and consumption. The preference for epoxies is growing in composites and adhesives because of the need for lightweight materials and energy-efficient solutions. Wind energy infrastructure development in Northern Europe also contributes to demand. From stricter regulations arose more R&D in bio-based and low-VOC epoxy systems. The market grows steadily, although it is much more innovation-driven as opposed to volume-driven. Europe's adherence to green manufacturing continues to play an enormous role in shaping the resin landscape.
The LAMEA, being in a developing stage, has its demand driven by infrastructure development, oil & gas, construction, and other automotive sectors. Brazil and Mexico govern Latin America, supported by economic reforms and growth in manufacturing. Increasing petrochemical investments and construction projects mainly in the UAE and Saudi Arabia intensify epoxy demand in the Middle East. Africa is slowly embracing epoxy-based materials for infrastructure and utilities. However, limited industrial bases and some regulatory challenges prevent a too-rapid growth spur. By overcoming these constraints, the surge of foreign investments and urbanization throughout the region assures great growth prospects for epoxy resin applications in the long term.
Liquid: The liquid segment held highest revenue share in the market. The liquid one is said probably to be the most used resin because basically of its adhesion properties, good mechanical strength, and chemical resistance. It finds application in areas where easy processing is required, such as coatings, adhesives, composites, and building materials. Liquids can provide a wide range of viscosities, allowing it to be customized for specific end-use concentrations. It finds enormous use in construction and automotive industries because of its application on substrates like concrete, metals, or wood. Liquid epoxy systems are usually applied in formulating high-performance paints and protective coatings that provide protection to the structures placed in corrosive or harsh environments. The key benefit is the possibility of curing at ambient temperature, which surely saves on processing time. Notwithstanding, it is important to check for pot life as well as the curing environment in use. Also, another advantage of the liquid epoxy resin is the ability to vary curing agents, thereby increasing its application value in many industrial and commercial fields. Demand is further enhanced with increasing infrastructure development and electronics encapsulation.
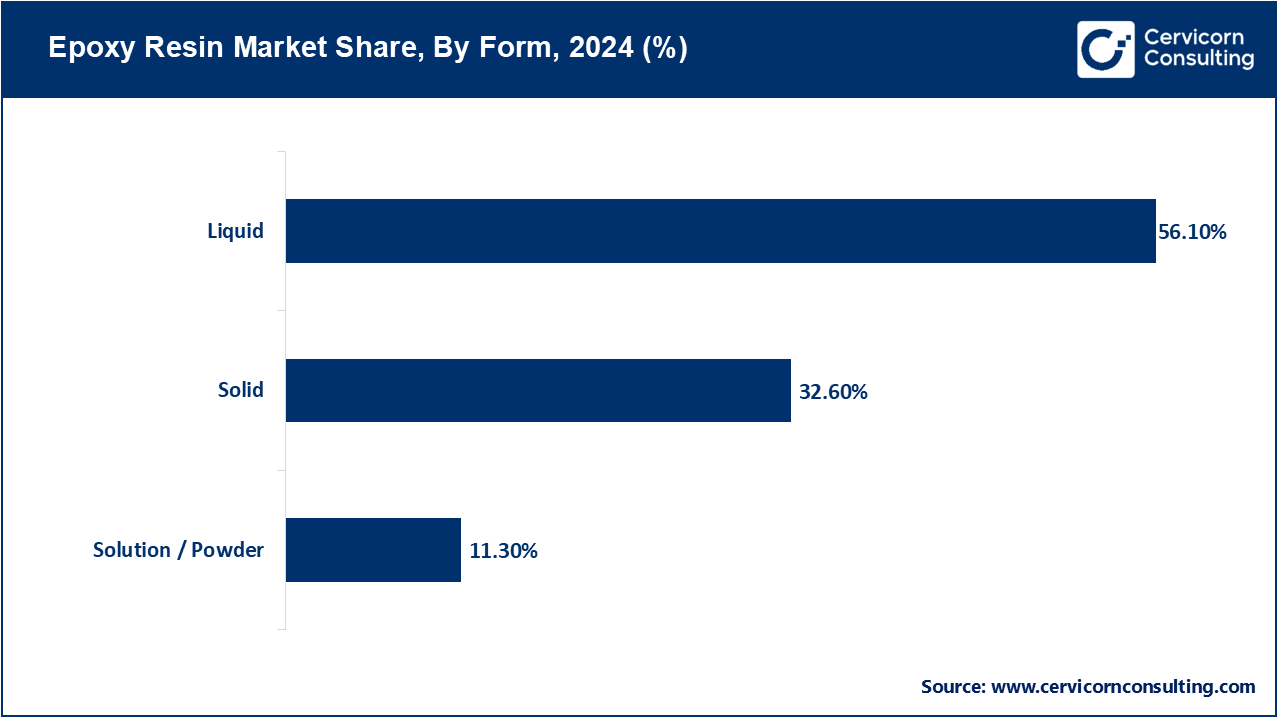
Solid: Solid epoxy resins are used in applications where a high molecular weight, very low volatility, and high performance are essential. There are solid at room temperature and associated with powder coatings, hot melt adhesives, electrical laminates, and insulation systems. It is of utmost advantage to provide thermal and electrical insulation in applications like printed circuit boards and electrical components. These solid epoxies have almost perfect dimensional stability coupled with moisture resistance and durability. Other than liquid grades, usually, solid epoxy resins are heat-processed; hence are suitable for thermosetting applications where quick curing is a must. Added to that, they are environmentally friendly particularly in powder coatings where no solvents are used, subsequently making them the desired choice for many industries attempting to cut down solvent emissions. Electronics production, industrial coatings, and automotive applications create greater demand for solid epoxy. With sustainability and regulatory pressure mounting, the demand for low-emission coating systems will work to further the desirability of solid epoxy forms.
Solution / Powder: Solution or powder epoxy resins are also known as solid resins dissolved in solvents or free-flowing powder resins; as such, they are used especially for solvent-based paints, coatings, and thermosetting powder coatings. In coating applications for metal substrates and automotive refinishing, the higher degree of control of solution viscosity and application properties is required. Being dry powders, paint powder epoxy resins need to be dry-applied and cured with heat. There is an increasing demand for powder coating products, as they are perceived as resistant and okay for the environment by people purchasing items such as household appliances, pipelines, or architectural components. They also boast advantages such as zero or low emissions of VOCs, higher transfer efficiency, and minimum-wastage powder coatings, which meet the increasingly demanding environmental regulations. Powder coatings derived from epoxy resins are widely used industrially because of their outstanding corrosion, chemical, and abrasion resistance. The segment experiences growth because of an increase in demand for energy-efficient and sustainable coating technologies. Their usage is sometimes limited because of substrate heat sensitivity and application cost, and such factors are having attention focused on innovative formulation improvement.
DGBEA: The DGBEA emerged as the top revenue-generating segment in the market. It is synthesized by the reaction of epichlorohydrin with bisphenol A. It possesses excellent adhesion property, chemical resistance, electrical insulation, and mechanical property. Resin compositions of DGBEA form the basis for industrially oriented coatings, adhesives, composites, and electric laminates. The viscosity is low, and they are easily processed to form liquid formulations for paints and varnishes. They find great utility in flooring, grouting, and protective coatings in construction. They are also widely used in consumer electronics for insulating purposes. DGBEA resins are the cheapest available in several grades by molecular weight and thus remain predominant in the market sector at the global level.
DGBEF: DGBEF epoxy resins are obtained from bisphenol F and offer comparatively lower viscosity and higher chemical resistance than DGBEA. Thin coatings are an ideal application for DGBEF resin, such as electronic encapsulation, composites, and marine coatings. DGBEF resins provide better thermal and mechanical properties; hence, they are used for specialized applications in aerospace and automotive industries. Being highly reactive with curing agents and superior performances in corrosive environments, they are much desired by niche industries despite being priced higher than the DGBEA resins. A lower molecular weight and increased flexibility appear to be the reasons for increasing use in highly specialized, high-performance end-use applications.
Novolac Epoxy Resins: Novolac epoxy resins are multi-functional resins with a high number of epoxy groups per molecule, derived from phenol-formaldehyde novolac. They exhibit exceptional chemical resistance, heat resistance, and mechanical strength. These properties make them ideal for high-performance coatings, corrosion-resistant linings, and electrical laminates. Their ability to withstand aggressive environments—such as in oil & gas pipelines, chemical processing plants, and marine structures—makes them suitable for highly demanding industrial applications. However, they require elevated curing temperatures and are typically used in conjunction with specific hardeners. Despite their higher cost, the unmatched performance in thermal and chemical stability makes Novolac resins increasingly attractive in harsh operating conditions.
Aliphatic Epoxy Resins: Aliphatic epoxy resins come with a non-aromatic backbone that offers several remedies against UV rays and weathering. Hence, their application is highly favoured for outdoor applications, ranging from protective coatings to automotive topcoats, to construction materials. Because of the imperviousness against yellow migration and chalking along with degradation by environmental agents, aliphatic epoxies are also thought far superior to aromatic epoxies and better suited for exterior-grade finishes. The higher flexibility and lesser toxicity make them suitable for applications such as medical adhesives or consumer items. However, with a lesser mechanical strength and chemical resistance than the aromatic types, this convinces their stay away from structural uses. Yet, their niche demand has been witnessed to increase lately due to changing environmental parameters.
Glycidylamine Epoxy Resins: Known for their extremely high mechanical and thermal properties, glycidyl amine resins are high-performance nitrogen-containing epoxies. Aerospace, electronics, and high-performance composites are some of the common applications in which these resins are used. They resist extreme environments, show better chemical resistance, and maintain a high Tg. Structurally, they are promoted as adhesives and laminates that resist heat well in conjunction with advanced curing agents. They justify the cost in crucial applications, however, since they are much more expensive and difficult to process than others. The higher demand for these resins is therefore witnessed in sectors that require long-term durability and dimensional stability under thermal stresses, especially in defences and aviation.
Others: Epoxy resins in this group consist of a specialized range of competitors, such as cycloaliphatic epoxy resins, halogenated resins, and bio-based epoxies. Being able to resist arcs and offer dielectric properties makes the cycloaliphatic types favourable for electric insulation. As bio-based resins become accepted increasingly in view of being eco-friendly alternatives to the traditional ones derived from petrochemicals, halogenated epoxies are still used for flame-retardant applications. Research and development in this field is unlikely to slow down as green chemical innovations emerge and as regulatory pressures keep mounting. At present, they have a somewhat reduced presence in the market; however, these categories are projected to grow faster because of the rising interest in sustainability and the changing end-user demands in consumer goods, electronics, and renewable energy.
Cold Cure: Cold cure resins cure at room temperature without the application of heat. Thus, they are used especially in places where heat cannot be brought in, namely construction, repairs, or outdoor purposes. These resins are more appreciated for their ease of use and application in situ than in other infrastructure projects, such as in bridge repairs, flooring, or pipeline coatings. They usually cure slower and may have slightly less mechanical strength than thermally cured systems; however, with the developments in cold cure formulations, their strengths in weather resistance and durability were improved. Their other selling points include being more energy-saving and less demanding in terms of equipment, hence the popularity of these systems in developing countries or low-temperature environments.
Thermal Cure: For thermal cure epoxies, high temperature causes the resin to cure initiate and complete its cure. It makes it very popular for materials with superior mechanical properties, excellent chemical resistance, and stability upon exposure to high temperature; hence, it is mainly used for high-quality aerospace, automotive, electronics, and industrial machineries. The oven or heated melding methods ensure this uniformity in cross-linking of the resin system which simultaneously reduces the probability of certain defects. Even being an equipment-based system, the thermal cure system is preferred for an advanced manufacturing process for strength and longevity. The segment is increasingly driven by the rising demand for heat resistance and structural integrity, particularly in load-bearing or high-temperature environments. The ongoing technologies in rapid thermal cure are decreasing the cure cycle, thereby enhancing yield.
UV Cure: UV-Curing epoxy utilizes ultraviolet light to initiate rapid polymerization, usually finishing curing in a matter of seconds to minutes. Such systems find their ideal application in precision settings such as electronics, optical components, and medical devices wherein speed is of essence along with clarity of cure and low temperature for curing. The UV curing method thereby consumes low energy, uses no solvent, and provides an environmental touch, supporting clean manufacturing processes. On the contrary, UV curing requires substrates that promote UV penetration and is not suitable for thick or opaque layers. Due to a growing trend for miniaturization and cleanroom compatibility, UV cure epoxy resins are fast gaining popularity in markets such as electronic packaging, fibre optics, and specialty coatings.
Moisture Cure: Moisture cure epoxy resins act by curing after absorbing moisture from the atmosphere and hence are excellent in applications prone to moisture or water. These resins possess good adhesion, water-resistant properties, and durability and are mostly used in design, marine coatings, and concrete sealants. Being very advantageous in outdoor and repair applications where maintaining temperature is a challenge, moisture cure systems allow application flexibility and are typically single component, making storage and handling easier. However, their rates of curing depend greatly on ambient humidity and temperature, thus creating some variability in their performances. Nevertheless, continuous innovations of formulation are on their way to improving the consistency of these products as well as expanding their applications in infrastructure and waterproofing.
Paints & Coatings: The paints & coatings segment held the highest revenue share in the market. Due to adhesion, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength properties, epoxy resins find application in paints and coatings. These coatings are used extensively in infrastructure, automotive, marine, and industrial equipment for protective and decorative purposes. These are high-performance coatings, and their durability corresponds to corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and moisture resistance. Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures work to Favor the sale of waterborne and solvent-free epoxy coatings. Thus, with the rapid expansion of construction and renovation projects worldwide, especially in the Asia-Pacific region, demand for epoxy-based coatings has kept this segment at the lead in the market.
Adhesives & Sealants: Epoxy resins find utility in adhesives and sealants due to strong bonding ability, durability, and resistance to environmental degradation. Epoxy adhesives are used in construction, automotive, aerospace, and electronics in joining different types of materials comprising metal, plastic, and wood. Structural adhesives based on epoxy provide long-term stability under adverse conditions. In terms of sealants, they provide excellent gap-filling properties and weather resistance. Growing construction activities, automotive production, and electronics assembly force the growth of demand for epoxy adhesives. Moreover, innovations in two-component and fast-curing epoxy systems are rendering them applicable for an even wider range of industries.
Epoxy Resin Market Revenue Share, By Application, 2024 (%)
| Application | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Paints & Coatings | 41.30% |
| Adhesives & Sealants | 21.90% |
| Composites | 28.20% |
| Others | 8.60% |
Composites: Being matrix resins of composites, they provide high strength-to-weight properties, along with thermal stability and chemical resistance. These find applications in aerospace, wind energy, automotive, and sports industries. Weight reduction in aerospace and automotive sectors increases fuel efficiency using epoxy resin composites. They find use in the wind energy industry for manufacturing durable and lightweight turbine blades. As trends towards sustainability and lightweighting are growing, epoxy-based composites have come into limelight as a high-performance alternative to traditional materials. Hence, the segment experiences high demand for advanced materials for high-tech and energy applications.
Electronic Encapsulation: From the electronics perspective, encasing and potting epoxy resins are applied for use as insulating materials against weather changes, heat, moisture, and dust. These resins provide protection to vulnerable electronic components like semiconductors, sensors, and circuit boards vulnerably affected by weather conditions and mechanical stresses. The need for applying epoxy resins grows exponentially with the increase in the miniaturization of electronic devices and their complexity, thereby, ensuring high reliability and longevity of components. The application base of epoxies is increasing, which includes consumer electronics, automotive electronics, and industrial controls. With the increase of electronic devices and smart technologies worldwide, the demand for superior encapsulating materials such as epoxy resins continues to rise further.
Others: The others segment comprising all possible epoxy resins applications such as flooring, tooling, melding, and marine coating. In epoxy flooring systems, epoxy finishes are employed in commercial and industrial buildings due to their chemical resistance and easy maintenance. Epoxies for Mold making and tooling maintain dimensional stability and offer precision. Marine applications Favor epoxy for its ability to resist water and hostile environmental conditions. They also do epoxy applications in arts and crafts, jewellery, and DIY craft. Compared to major segments, this is smaller in volume, yet the versatility of epoxy resins continues to support growth in these niche and specialized applications.
Building & Construction: The building & construction segment accounted for the largest share of market revenue. Epoxy resins are by far one of the greatest things ever in the construction industry with their high mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and bonding strength. Special floor systems, adhesives, concrete coatings, and sealants are the application sectors for the epoxy resins. The rise in urbanization in metropolises causes a surge in commercial infrastructures and residential buildings, all of which demand epoxies. Their common uses include sealing against water ingress, corrosion protection, and structural reinforcement. Moreover, these were used even more intensely in green buildings to meet the needs of sustainable infrastructure and durable materials around developing territories throughout APAC and Latin America.
Automotive & Transportation: Within automotive and transportation employments, epoxy resins help in lightweight composite parts production, bonding, and coating. Light-weighting of epoxy parts to maintain fuel efficiency and emissions acts as the main criterion. The application of epoxies improves resistance to corrosion, wear, and tear in several automotive components. They are equally used for the body panels, parts under the hood, structural adhesives, and paints. With EVs coming up and stringent emission norms, there has been an even steady mounting demand for materials, which exhibit performance and low weight, which is driving innovation in both passenger and commercial vehicle segments worldwide.
Epoxy Resin Market Revenue Share, By End-Use, 2024 (%)
| End-Use | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Building & Construction | 37.40% |
| Automotive & Transportation | 20.10% |
| Electrical & Electronics | 32.30% |
| Others | 10.20% |
Electrical & Electronics: Epoxy resins are essential in the electrical and electronics industries for their superb insulating properties, resistance to heat, and resistance to moisture. These resins are used widely in packaging and encapsulation of semiconductors, transformers, printed circuit boards, insulators, and motors. Environmentally, the resins shield from degradation, electrical leakage, and mechanical shock. The demand for miniaturized, high-performance electronic devices in the consumer electronics sector, telecommunication equipment, and renewable energy systems sees the use of epoxy resins in the industry keeping pace with demand. Another factor contributing to their growing importance is the jump to smart and 5G-enabled devices.
Others: These are technologies that cut through aerospace, marine, industrial machinery, and consumer goods. In aerospace and marine industries, these epoxies are prized to synthesize lightweight high-strength composites and to resist abrasion or wear-out in tough environmental conditions. Epoxies in industrial machinery are used in coatings, adhesives, and melded parts. In terms of consumer goods, epoxies are being used for items like sports goods or furniture-that require strong glossy finishes and durability. Although this segment is smaller than the others, its diverse applications and growing focus on high-performance materials offer a significant push to the market growth.
Market Segmentation
By Form
By Type
By Curing Method
By Application
By End-Use Industry
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Epoxy Resin
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Form Overview
2.2.2 By Type Overview
2.2.3 By Curing Method Overview
2.2.4 By Application Overview
2.2.5 By End User Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.2 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Infrastructure & Construction Boom in Emerging Economies
4.1.1.2 Electronics & Semiconductor Industry Expansion
4.1.1.3 Accelerated Urbanization Fuelling Construction-Grade Epoxy Demand
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 Dependency on Petrochemical Feedstocks
4.1.2.2 Limited Compatibility with Flexible Substrates
4.1.2.3 High Production and Processing Costs
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 Technological Barriers in Product Innovation
4.1.3.2 Low Awareness in Underdeveloped Regions
4.1.3.3 Regulatory Delays Impacting Product Launches
4.1.4 Market Opportunities
4.1.4.1 Rising Adoption in Electric Vehicle Components
4.1.4.2 Smart Infrastructure Projects Boosting Resin Use
4.1.4.3 Emerging Markets Driving Industrial Coatings Demand
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Epoxy Resin Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Epoxy Resin Market, By Form
6.1 Global Epoxy Resin Market Snapshot, By Form
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Liquid
6.1.1.2 Solid
6.1.1.3 Solution / Powder
6.1.1.4 Communication and Control Systems
Chapter 7. Epoxy Resin Market, By Type
7.1 Global Epoxy Resin Market Snapshot, By Type
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 DGBEA
7.1.1.2 DGBEF
7.1.1.3 Novolac
7.1.1.4 Aliphatic
7.1.1.5 Glycidylamine
7.1.1.6 Others
Chapter 8. Epoxy Resin Market, By Curing Method
8.1 Global Epoxy Resin Market Snapshot, By Curing Method
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Cold Cure
8.1.1.2 Thermal Cure
8.1.1.3 UV Cure
8.1.1.4 Moisture Cure
Chapter 9. Epoxy Resin Market, By Application
9.1 Global Epoxy Resin Market Snapshot, By Application
9.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
9.1.1.1 Paints & Coatings
9.1.1.2 Adhesives & Sealants
9.1.1.3 Composites
9.1.1.4 Electronic Encapsulation
9.1.1.5 Others
Chapter 10. Epoxy Resin Market, By End-User
10.1 Global Epoxy Resin Market Snapshot, By End-User
10.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
10.1.1.1 Building & Construction
10.1.1.2 Automotive & Transportation
10.1.1.3 Electrical & Electronics
10.1.1.4 Others
Chapter 11. Epoxy Resin Market, By Region
11.1 Overview
11.2 Epoxy Resin Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
11.3 Global Epoxy Resin Market, By Region
11.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
11.4 North America
11.4.1 North America Epoxy Resin Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.3 North America Epoxy Resin Market, By Country
11.4.4 U.S.
11.4.4.1 U.S. Epoxy Resin Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
11.4.5 Canada
11.4.5.1 Canada Epoxy Resin Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
11.4.6 Mexico
11.4.6.1 Mexico Epoxy Resin Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
11.5 Europe
11.5.1 Europe Epoxy Resin Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.3 Europe Epoxy Resin Market, By Country
11.5.4 UK
11.5.4.1 UK Epoxy Resin Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
11.5.5 France
11.5.5.1 France Epoxy Resin Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
11.5.6 Germany
11.5.6.1 Germany Epoxy Resin Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
11.5.7 Rest of Europe
11.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Epoxy Resin Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6 Asia Pacific
11.6.1 Asia Pacific Epoxy Resin Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.3 Asia Pacific Epoxy Resin Market, By Country
11.6.4 China
11.6.4.1 China Epoxy Resin Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.5 Japan
11.6.5.1 Japan Epoxy Resin Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.6 India
11.6.6.1 India Epoxy Resin Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.7 Australia
11.6.7.1 Australia Epoxy Resin Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
11.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Epoxy Resin Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7 LAMEA
11.7.1 LAMEA Epoxy Resin Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.3 LAMEA Epoxy Resin Market, By Country
11.7.4 GCC
11.7.4.1 GCC Epoxy Resin Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7.5 Africa
11.7.5.1 Africa Epoxy Resin Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7.6 Brazil
11.7.6.1 Brazil Epoxy Resin Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
11.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Epoxy Resin Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 12. Competitive Landscape
12.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
12.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
12.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
12.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
12.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 13. Company Profiles
13.1 Olin Corporation
13.1.1 Company Snapshot
13.1.2 Company and Business Overview
13.1.3 Financial KPIs
13.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
13.1.5 Strategic Growth
13.1.6 Global Footprints
13.1.7 Recent Development
13.1.8 SWOT Analysis
13.2 DIC Corporation
13.3 China Petrochemical & Chemical Corporation
13.4 Nan Ya Plastics Corporation
13.5 Hexion Inc. (Westlake Chemicals)
13.6 Chang Chun Group
13.7 Kukdo Chemical Co., Ltd.
13.8 Huntsman Corporation
13.9 Aditya Birla Chemicals
13.10 Sika Group