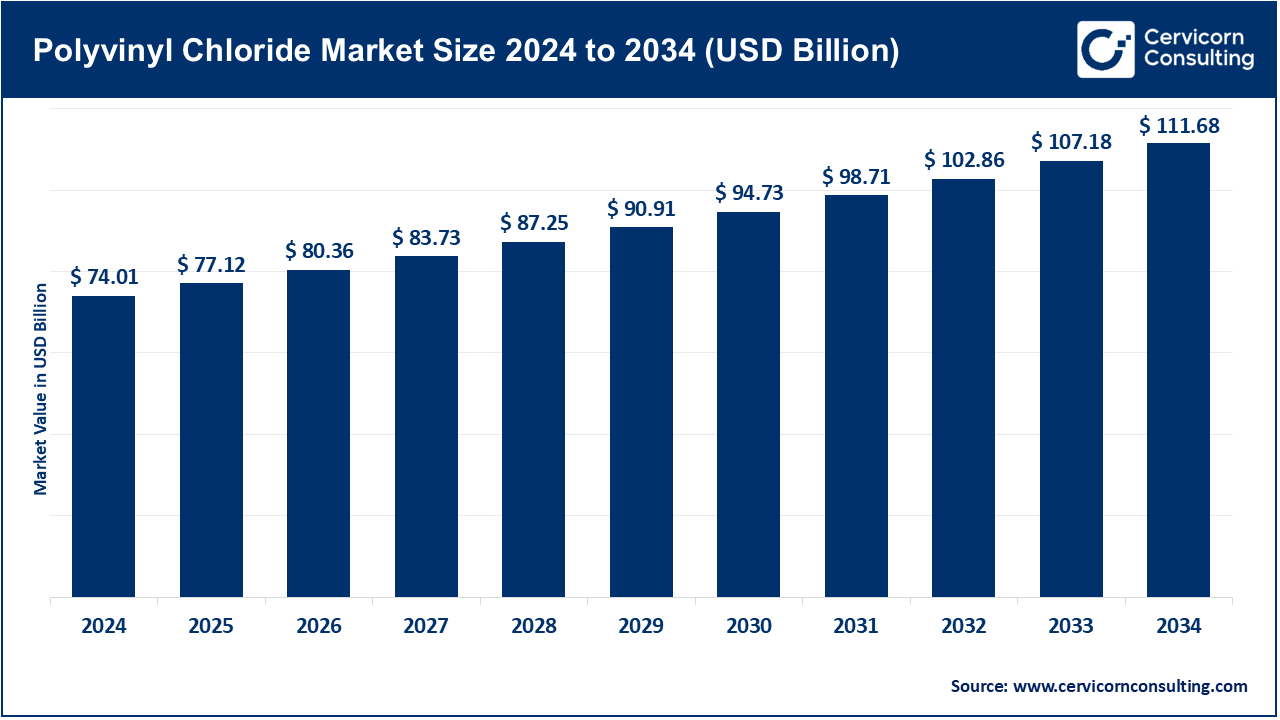
The global polyvinyl chloride market size was estimated at USD 74.01 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 111.68 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.2% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
The global polyvinyl chloride market talks about the production, distribution, and applications concerning this plastic polymer widely applied across various industries. PVC enjoys preference for its durability, chemical resistance, low cost, and versatility, which cost-benefit applications in construction materials, medical devices, automotive components, and consumer goods. Two basic forms exist: rigid and flexible; each type has different applications such as rigid PVC for piping, profiles, and flexible PVC for flooring, cables, and packaging.
Several primary factors are fuelling the growth of the PVC market globally. One prominent factor is the rapid urbanization and infrastructure development taking place across the world, notably within emergent countries. PVC is extremely common across pipes, window frames, doors, and sidings and thus, making it an indispensable material for construction and real estate sectors. The automotive and electrical industries have increased demand for the materials to be light yet strong. Being resistant to corrosion and good insulation properties, this PVC is in enhanced demand in the electrical cable industry. Furthermore, its biocompatibility and sterilization compatibility offered additional growth in the medical application for making IV bags, tubing, and blood containers. The growing trend of replacing traditional materials such as metals and wood with PVC for economic and ease-of-locking-of-maintenance purposes will further strengthen worldwide demand for it.
The focus for opportunities also lies in guiding the market towards tremendous growth via innovation in areas related to bio-based and recyclable PVC materials. Being the matter of utmost concern today, manufacturers are looking for eco-friendly alternatives and closed recycling systems to solve the present environmental issues. With Asia-Pacific and Africa witnessing tremendous opportunities due to the growth of the construction industry, PVC finds a huge demand for government infrastructure projects and population growth. Further penetration of PVC into smart cities, water management systems, and green building would carve out other application avenues. Furthermore, ongoing improvements in manufacturing technologies, including automation and precision compounding, could outweigh opportunities to enhance product quality and reduce production costs. All these factors signal that the global PVC market is on an upward trajectory, having the scope for innovation, regional expansion, and adaption to sustainable development trends.
Top Countries Dominating the Asia-Pacific PVC Market
| Countries | Share, 2024 (%) |
| China | 58% |
| India | 18% |
| Japan | 10% |
| South Korea | 7% |
| Indonesia | 4% |
| Vietnam | 3% |
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 77.12 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 111.68 Billion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 4.2% |
| Dominant Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Type, Form, End Use, Region |
| Key Companies | Hanwha Group, Ineos, Ercros, Occidental Petroleum Corporation, Orbia, Formosa Plastics Corporation, KEM ONE, Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd., Vynova, Westlake Corporation, Others |
Rigid PVC (uPVC): The rigid PVC segment has held leading position in the market. This rigid PVC, also called unplasticized PVC or uPVC, is very durable and stiff—with a wide application in construction and infrastructure-related works. It resists chemicals, weather, and UV rays. Hence, applications such as pipes, window frames, doors, and profiles would always lean heavily on uPVC. Unlike the flexible one, it does not incorporate plasticizers and possesses greater rigidity and environmental resistance. Long in-use duration and almost negligible maintenance needs place it well with the architectural community for use in homes and commercial buildings. Being flame resistant and moisture resistant, rigid PVC finds utilization for cladding and cable insulation and an industrial equipment. Recycling possibilities of the material are a further plus for its eventual use in green buildings. Rise in construction activity all over the world, especially in emerging economies, is a good sign for the buoyant demand for uPVC.
Polyvinyl Chloride Market Revenue Share, By Type, 2024 (%)
| Type | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Rigid PVC (uPVC) | 42.80% |
| Flexible PVC | 36.30% |
| Others | 20.90% |
Flexible PVC: Flexible PVC is prepared by the addition of plasticizers, such as phthalates, which soften the rigid polymer and allow for greater flexibility and elasticity. This flexible PVC finds its greatest use in applications where could be bending and movements, such as electrical cable insulation, medical tubing, inflatable products, and automotive interiors. This adaptability, ease of processing, and cost-effectiveness become a crucial competitor in materials especially in consumer goods and industrial applications. Nonetheless, safety concerns of environmental and health impacts of some plasticizers have aroused considerable regulatory quality and call for non-phthalate alternatives. Despite these challenges, technological developments in bio-based and safer plasticizers are sustaining the demand. It provides excellent resistance to water, chemicals, and abrasion and thus, also strengthens its importance in the sectors where both durability and flexibility are required, in the packaging, footwear, and textile industries alike.
Low-smoke PVC: Low-smoke PVC is a special type of PVC designed to keep smoke and toxic gas release to a minimum during combustion. Being low in halogens and containing flame-retardant additives, it is used in those areas where fire safety imposes utmost consideration about being confined or heavily populated. In emergencies, such PVC increases visibility and reduces health risks. The promulgation and enforcement of multiple regulatory frameworks, which gave fire safety utmost emphasis in construction and infrastructure, therefore ultimately led to widespread adoption of low-smoke PVC across geographies. Low-smoke PVC also retains most of the core properties of regular PVC, such as durability, corrosion resistance, and processability. With an increasing consciousness of fire hazards and environmental impact, a growth in demand for low-smoke halogen-free alternatives can be witnessed. This demand is thus pressuring manufacturers to engage in R&D and realize sustainable and safer flame-retardant solutions based on low-smoke PVC formulations.
Chlorinated PVC (C-PVC): Being produced by chlorinating standard PVC resin, chlorinated PVC increases its chlorine content and greatly improves its heat and chemical resistances. It is used largely for hot and cold-water pipes and fire sprinkler systems as well as for chemical handling applications where temperatures and corrosive substances are higher. It offers higher mechanical strength, better thermal stability, and superior flame resistance than regular PVC, thus being fit for both plumbing systems industrially and residentially. Increased demand for efficient, durable piping systems in the construction and chemical industries is, in fact, driving the adoption of C-PVC. Moreover, since it can also withstand a higher range of pressures and temperatures, it turns to be a cheaper alternative to metal pipes. Easy to install, long life, and low maintenance requirements are further contributing an advantage to C-PVC's enlarging market share worldwide, especially in regions which struggle to keep up with rapid urbanization and infrastructure development.
Pipe & Fittings: This segment stands as the dominant form segment in the PVC market, comprising construction, plumbing, water distribution, sewage, and irrigation systems. The rigid PVC properties that make it suitable to be used as pipes and fittings are great durability and corrosion resistance, coupled with affordability and ease of installation. This material finds applications in both pressure and non-pressure industrial uses for potable water supply and drainage systems. The increase in urbanization, infrastructure development, and agricultural modernization all fuels the demand for PVC piping systems across the globe. Innovations like molecular-oriented PVC (PVC-O) are further strengthening and lengthening the life of these systems. Additionally, the replacement of the old and rusting cast and ductile iron pipes with corrosion-resistant PVC pipes in developed countries further boosts this segment. Favourable regulations for lead-free pipes and increased smart city projects are other factors contributing to the growth of the market.
Films & Sheets: PVC films and sheets are considered flexible or semi-rigid and are used mainly for packaging, signage, medical, construction, and automotive applications. These qualities include excellent clarity, chemical resistance, and ease of thermoforming for blister packaging, food wraps, and shrink films. Rigid PVC sheets find application in wall cladding and roofing membranes. In the medical field, PVC films are used for manufacturing IV bags, blood bags, and pharmaceutical blister packs that require hygiene and sterilizability. Growth in the packaging and healthcare sector, particularly in emerging economies, accelerate demand. Also, the sustainability trend will foster manufacturers in producing recyclable and bio-based PVC films.
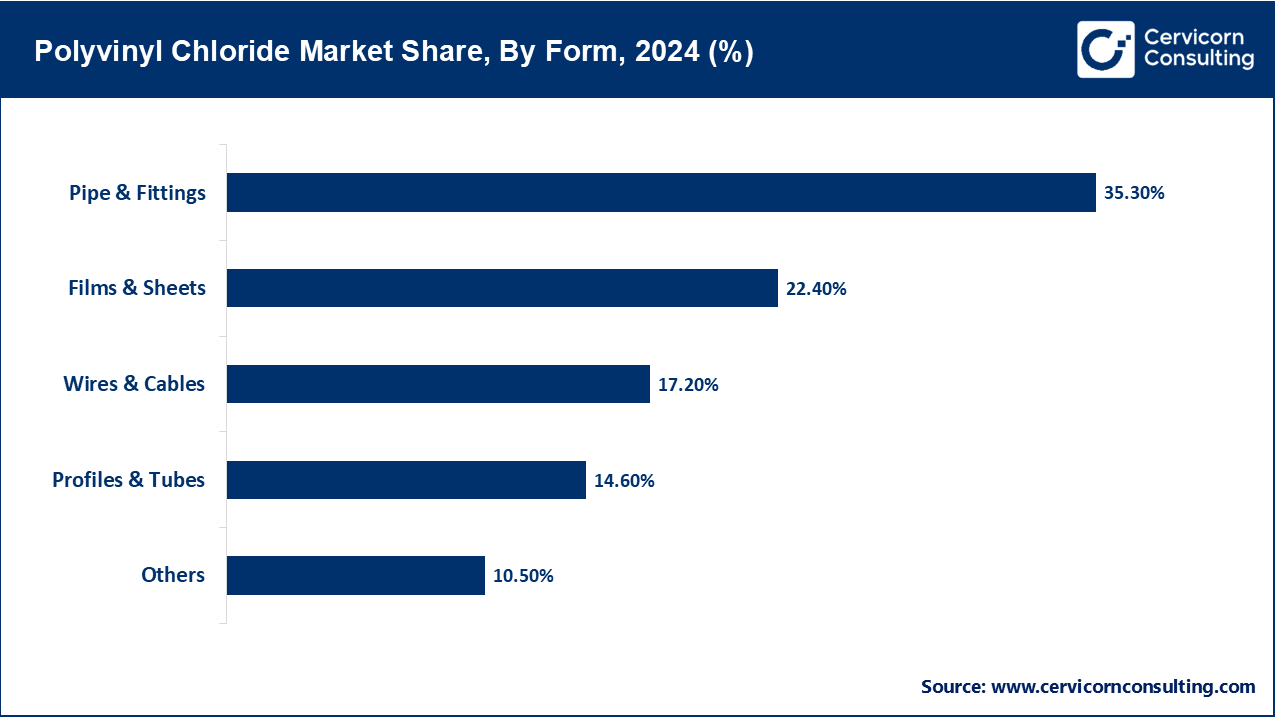
Wires & Cables: In the insulation and sheathing of cables, PVC proves to be major application. It is flame-retardant and flexible, resistant to chemicals, and cheap, so it is applied to insulation for electrical wiring in household, commercial, and industrial sectors. It includes applications of power, telecommunication, and automotive wiring. However, the growth in renewable energy installations, electric vehicles, and infrastructure modernization has been giving impetus to the demand for PVC-insulated cables. Besides installation growth, engineering developments in the formulations of fire-retardant PVC have been able to satisfy stricter safety codes in the construction and transportation sectors. Also, in respect of outdoor and underground cable applications, it must resist environmental stressors like moisture and sunlight.
Profiles & Tubes: PVC profiles and tubes are used extensively for window and door frames, curtain rails, cable trunking, and furniture edging. The segment is enriched by PVC's good structural strength, low thermal conductivity, and resistance against moisture and termite attacks. In buildings, uPVC profiles are preferred for energy-efficient and weather-resistant window systems. PVC pipes find application in air conditioning, chemical transportation, and medical devices. Demand in facilities for residential and commercial building applications is high. It is through green building trends and growing DIY home improvement projects that demand for lightweight and customizable PVC profiles and tubes is increasing across the globe.
Others: It basically captures a whole array of specialized PVC applications that include PVC-coated fabric, inflatable structures, toys, footwear soles, medical tubes, credit cards, and consumer items. These niche applications make use of the flexible nature, durability, and economy of PVC. One prominent building uses of PVC plus PU synthetic leather in fashion upholstery, flooring, and wall coverings. It is also used industrially in conveyors and tank linings. Since it responds well to different additives that allow manufacturers to produce materials with specific levels of flexibility, colour, texture, and resistance properties, the industry is very dynamic. As the manufacturing industries become diversified and are always evolving, there is continuous evolution in the others segment too as it sees applications in 3D printing, smart textiles, and biodegradable PVC blends.
Building & Construction: The building & construction segment stands as the dominant in the PVC market. Great builders use the sector to consume PVC in large quantities, further asserting PVC's qualities of durability, weathering capability, and cheapness. It can be found in pipes and fittings, window profiles, and doors. With rigid PVC (uPVC) offering the necessary strength and fire resistance needed in structural works-Less corrosion and deterioration are guaranteed in plumbing and drainage systems-from chemicals and moisture, respectively. Development in residential and commercial infrastructures in emerging economies hence gives rise to the flood of energy-efficient PVC materials and solutions for green building. Consequently, being lightweight and easy to install act as a great driver for PVC in prefabricated construction.
Automotive: PVC finds huge applications in the automotive business for interior and exterior considerations. It is valued for its flexibility and interesting aesthetics together with good cost performance: dashboards, door panels, underbody coatings, wiring insulation, floor mats are just some of the numerous applications of PVC. Flexible PVC is great at minimizing vibration to enhance the passengers' comfort. It also meets stricter regulatory requirements for fire resistance and mechanical durability. PVC is also employed for lightweight components, promoting fuel efficiency by enabling an overall reduction in vehicle weight. An increase in demand for flame-retardant, special performance materials like PVC is going together with the production of electric vehicles (EVs). Additionally, the packaging aligns itself with automotive sustainability goals, further encouraging its popularity.
Electrical & Electronics: PVC conversely has a balanced, multifaceted application profile with its major specifications that include the electrical and electronics field for insulation of wires, cables, or connectors. It has good dielectric strength, being flame retardant, and it can resist chemical attacks and moisture, thus making it suitable for electrical insulation. Besides, it gives flexibility and discretion to the installers, ensuring that it will provide good service even under harsh environmental conditions. PVC compounds and formulations can be adjusted for a specified voltage or temperature range, thus making them suitable for use in consumer electronics, industrial machinery, and power distribution systems. In this section, demand for PVC continues to increase with respect to investments being made in telecommunications and electrification, particularly in developing areas. On the other hand, the introduction of smart gadgets for energy saving and energy-efficient home appliances requires materials that can be relied upon and certified to be safe.
Healthcare: PVC is of medical importance in the making of IV bags, tubing, blood bags, catheters, etc., because of its biocompatibility, clarity, and sterility. Flexible PVC allows the safe transfer of fluids, while rigid PVC is used to make containers and several components for diagnostic equipment. It can be easily sterilized through a variety of processes including gamma radiation and ethylene oxide gas. PVC remains a mainstay in disposable and reusable medical items owing to its cost-effectiveness and ready availability. In tandem with phthalate-free PVC developments, which allay safety concerns, there is an increase in applications of this medical-grade material in sensitive applications such as neonatal and dialysis care. The growth of global healthcare infrastructure and increasing demand for single-use medical supplies will further drive the growth.
Packaging: In general, PVC finds its application in rigid and flexible packaging because of its characteristics of clarity, barrier properties, and sealing properties. In blister packs, clamshell containers, shrink wraps, and labels are some of the packaging applications it finds. In pharma packaging, it is used for the safe packaging of tablets and capsules. In food packaging, it helps in enhancing shelf-life by protecting its contents against oxygen and moisture. Rigid PVC helps in giving strength and tamper resistance, while the flexible one is used in wraps and films. It is considered one of the most versatile materials since it can be moulded into almost any shape commonly needed in consumer and industrial products. PVC becomes more essential with rising consumer demands for hygienic and tamper-proof packaging, especially after the COVID crisis. Relevant to sustainability concerns is the innovation of recyclable and bio-based PVC packaging.
Consumer Goods: It is used in various consumer products such as furniture, footwear, toys, stationery, sports gear, and even home décor products. Lightweight, durable, waterproof, and inexpensive are the attributes of PVC that accord it precedence among materials used for mass-produced articles. In footwear, for instance, flexible PVC is used in manufacturing soles and sandals. In furniture, it is used in faux leather upholstery and wall coverings. That moldability and the safety features of PVC make it attractive for toys and household tools. Customized colours, finishes, and appearances further increase consumer interest. Also, the prevailing trend for affordable and durable home-related products in emerging markets will continue to lift the growth of the segment. Recent developments of non-toxic PVC formulations will go a long way in easing safety and environmental concerns in consumer use.
Others: Industrial applications, agriculture, signage, and marine constitute the other segment. Some agricultural uses include irrigation pipes, greenhouse films, and water storage systems, where PVC is preferred for its resistance to chemicals and UV. The rigid PVC sheets are used in the signage and advertising industry for their longevity and ability to accept print. Because of its ability to resist salt water and corrosion, marine applications grade PVC is used in the manufacturing of boat fittings and flotation devices. Industrial uses include its application for factory flooring, wall cladding, and chemical handling systems. Inability to develop in terrible and varied environments is due to the adaptability and service life. As emerging applications such as back sheets for solar panels and composite materials develop, this segment will develop with new things.
The PVC market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region.
North America holds a significant share in the global PVC market on account of demand from matured construction and renovation industries in the USA and Canada. Due to its durability, water resistance, and cost-effectiveness, the region highly utilizes PVC in construction materials such as pipes, siding, and flooring. Moreover, the demand gets further enhanced with a growing focus on modernizing infrastructure and water management systems. Healthcare is another industrial sector that is of importance as PVC finds wide application in medical devices and packaging. Strict environmental regulations have brought with them innovations in sustainable PVC formulations and recycling initiatives. Hence, the regional market landscape also gets shaped by technological advancements in bio-attributed and non-phthalates plasticizers. Relative to emerging markets, growth is moderate, but region still holds importance because of applications towards high-value products and industrial standards.
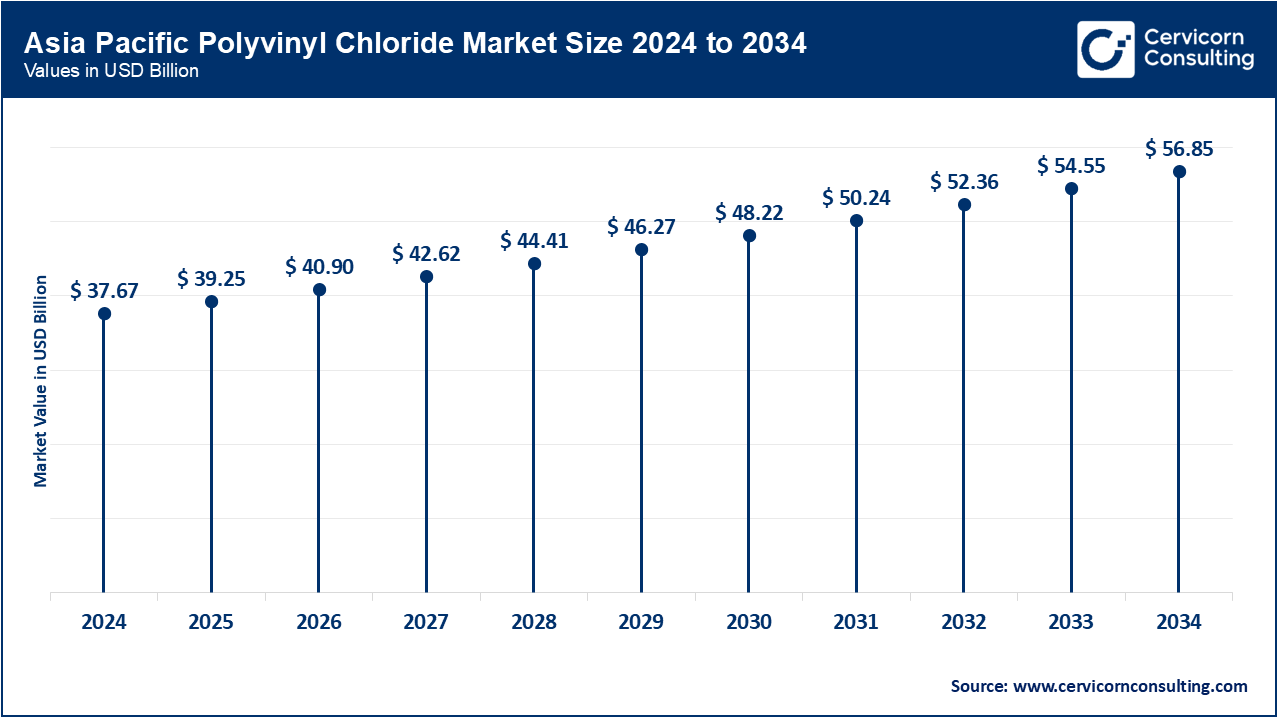
The Asia Pacific dominates the global PVC market, with solid demand from major end-use areas like building & construction, automotive, packaging, and electrical & electronics. China, India, Japan, and South Korea are the prominent supply regions. Considerable weightage is given to China for the construction and infrastructure projects being huge, and due to rapid urbanization and government investments in smart cities. India also witnesses healthy growth with rising demand for affordable housing and water supply systems through PVC pipes, along with the growth of the automobile sector. Besides, many PVC producers in the region and cheap production along with promotion through trade policies contribute to enhancing the regional production capacities. Because of sustainability concerns, along with recycling technologies, market dynamics are further enhanced. Backed by fast industrial growth, the region has an enormous population along with demand for urban infrastructure, thereby making the Asia Pacific region the largest influencer in the global PVC landscape.
The Europe is characterized by strict environmental regulations, advanced recycling initiatives, and a high focus on sustainable construction practices. Countries like Germany, France, Italy, and the UK contribute majorly and use PVC in making energy-efficient buildings, automobile constructions, and medical requirements. The region further promotes the circular economy wherein companies engage in mechanical and chemical recycling of PVC products. In addition, Europe's mature automotive sector applies PVC in interior trims, low underbody coatings, and cable insulation, valuing flexibility and low cost from the value proposition. Construction also benefits from PVC's thermal efficiency and corrosion resistance, in line with requirements for green building standards. Regulatory framework, such as the REACH, with activities like Vinyl Plus, lead the market into the emerging development of low-emission and recyclable PVC grades. Although growth here is less compared to Asia-Pacific, it leads in sustainable innovation and quality PVC applications.
Polyvinyl Chloride Market Revenue Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America | 24.80% |
| Europe | 19.20% |
| Asia-Pacific | 50.90% |
| LAMEA | 5.10% |
LAMEA provides an opportunity in the global PVC market as infrastructure development, urbanization, and investments in water and sanitation intensify. Latin America hosts huge markets in Brazil and Mexico, wherein construction, packaging, and agriculture demand PVC. On the other hand, the Middle East, with countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE, heavily invests in mega infrastructure and smart city projects that aid PVC consumption for pipes, profiles, and fittings. In Africa, developmental projects require inexpensive yet durable construction materials, and PVC meets this criterion. However, economic volatility, low local production, and heavy dependency on imports pose hindrances to the market. Still, government-supported housing schemes, water distribution improvements, and rising population are creating long-term demand potential in this region.
Market Segmentation
By Type
By Form
By End-Use Industry
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Type Overview
2.2.2 By Form Overview
2.2.3 By End User Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.2 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Expansion of Water Supply and Irrigation Projects
4.1.1.2 Rising Urbanization and Industrialization in Emerging Economies
4.1.1.3 Growing Use of PVC in Medical Devices and Packaging
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 Environmental and Health Concerns Related to PVC Production
4.1.2.2 Volatility in Raw Material Prices (Especially Crude Oil and Ethylene)
4.1.2.3 Stringent Regulatory Restrictions on Plastic Usage and Waste Disposal
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 Competition from Alternative Eco-Friendly Materials
4.1.3.2 Volatility in Global Supply Chains and Trade Restrictions
4.1.3.3 Limited Recycling Infrastructure for PVC Waste
4.1.4 Market Opportunities
4.1.4.1 Increased Infrastructure Development in Asia and Africa
4.1.4.2 Technological Advancements in PVC Processing and Additives
4.1.4.3 Increasing Use of PVC in 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Polyvinyl Chloride Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Polyvinyl Chloride Market, By Type
6.1 Global Polyvinyl Chloride Market Snapshot, By Type
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Rigid PVC (uPVC)
6.1.1.2 Flexible PVC
6.1.1.3 Low-smoke PVC
6.1.1.4 Chlorinated PVC (C-PVC)
Chapter 7. Polyvinyl Chloride Market, By Form
7.1 Global Polyvinyl Chloride Market Snapshot, By Form
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Pipe & Fittings
7.1.1.2 Films & Sheets
7.1.1.3 Wires & Cables
7.1.1.4 Profiles & Tubes
7.1.1.5 Others
Chapter 8. Polyvinyl Chloride Market, By End-User
8.1 Global Polyvinyl Chloride Market Snapshot, By End-User
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Building & Construction
8.1.1.2 Automotive
8.1.1.3 Electrical & Electronics
8.1.1.4 Healthcare
8.1.1.5 Packaging
8.1.1.6 Consumer Goods
8.1.1.7 Others
Chapter 9. Polyvinyl Chloride Market, By Region
9.1 Overview
9.2 Polyvinyl Chloride Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
9.3 Global Polyvinyl Chloride Market, By Region
9.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
9.4 North America
9.4.1 North America Polyvinyl Chloride Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.3 North America Polyvinyl Chloride Market, By Country
9.4.4 U.S.
9.4.4.1 U.S. Polyvinyl Chloride Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
9.4.5 Canada
9.4.5.1 Canada Polyvinyl Chloride Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
9.4.6 Mexico
9.4.6.1 Mexico Polyvinyl Chloride Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
9.5 Europe
9.5.1 Europe Polyvinyl Chloride Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.3 Europe Polyvinyl Chloride Market, By Country
9.5.4 UK
9.5.4.1 UK Polyvinyl Chloride Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
9.5.5 France
9.5.5.1 France Polyvinyl Chloride Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
9.5.6 Germany
9.5.6.1 Germany Polyvinyl Chloride Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
9.5.7 Rest of Europe
9.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Polyvinyl Chloride Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6 Asia Pacific
9.6.1 Asia Pacific Polyvinyl Chloride Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.3 Asia Pacific Polyvinyl Chloride Market, By Country
9.6.4 China
9.6.4.1 China Polyvinyl Chloride Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6.5 Japan
9.6.5.1 Japan Polyvinyl Chloride Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6.6 India
9.6.6.1 India Polyvinyl Chloride Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6.7 Australia
9.6.7.1 Australia Polyvinyl Chloride Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
9.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Polyvinyl Chloride Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
9.7 LAMEA
9.7.1 LAMEA Polyvinyl Chloride Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.3 LAMEA Polyvinyl Chloride Market, By Country
9.7.4 GCC
9.7.4.1 GCC Polyvinyl Chloride Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
9.7.5 Africa
9.7.5.1 Africa Polyvinyl Chloride Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
9.7.6 Brazil
9.7.6.1 Brazil Polyvinyl Chloride Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
9.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
9.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Polyvinyl Chloride Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 10. Competitive Landscape
10.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
10.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
10.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
10.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
10.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 11. Company Profiles
11.1 Hanwha Group
11.1.1 Company Snapshot
11.1.2 Company and Business Overview
11.1.3 Financial KPIs
11.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
11.1.5 Strategic Growth
11.1.6 Global Footprints
11.1.7 Recent Development
11.1.8 SWOT Analysis
11.2 Ineos
11.3 Ercros
11.4 Occidental Petroleum Corporation
11.5 Orbia
11.6 Formosa Plastics Corporation
11.7 KEM ONE
11.8 Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.
11.9 Vynova
11.10 Westlake Corporation