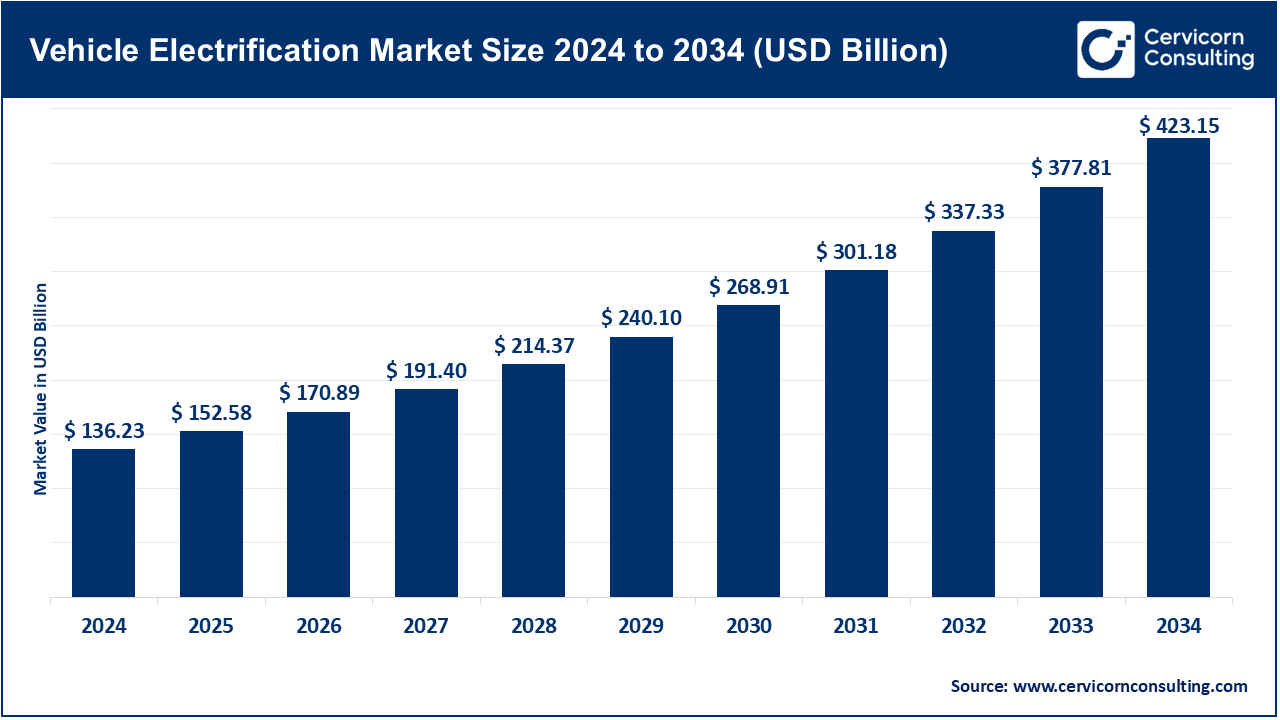
The global vehicle electrification market size was estimated at USD 136.23 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 423.15 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.32% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
The vehicle electrification market is expected to grow significantly owing to increasing regulatory pressure to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, rising fuel prices, and the global shift toward sustainable mobility solutions. Governments worldwide are incentivizing electric vehicle adoption through tax credits, subsidies, and stringent emission norms. Technological advancements in battery efficiency, lightweight materials, and power electronics are making electrified vehicles more affordable and practical. Additionally, automakers are investing heavily in electrification platforms to meet consumer demand for cleaner, connected, and more energy-efficient vehicles. Growth in charging infrastructure, along with evolving consumer preferences for lower operating costs, is further accelerating the electrification trend globally.
The global shift towards sustainable transportation, stringent emission standards, as well as the development of new batteries and powertrains drive growth in the vehicle electrification market. Increased electrification buttress fuel economy improvement, carbon emission reduction in addition to supporting lightweight automobile design across vehicle categories. Key innovations are electric drivetrains with regenerative braking and integrated thermal systems which enhance adoption. Growth is also fueled by government stimulus, investment into EV infrastructure and infrastructure as well as consumer willingness to spend more on green transport. Most OEMs and suppliers have started expanding production capability while some of them have strategic partnerships. As a result, vehicle electrification technology is a central component to the transformation of smart transportation all around the globe, making it cleaner and energy efficient.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 152.58 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 423.15 Billion |
| Projected CAGR from 2025 to 2034 | 13.32% |
| Dominant Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Product Type, Propulsion Type, Vehicle Type, Voltage Type, Application, Region |
| Key Companies | Robert Bosch GmbH, Continental AG, DENSO CORPORATION, Aptiv, Johnson Electric Holdings Limited, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, BorgWarner Inc., Magna International Inc., AISIN CORPORATION, Johnson Controls, ZF Friedrichshafen AG, Valeo SA, JTEKT Corporation, Hitachi Astemo, Ltd., Wabco Holdings Inc. |
Start-Stop Systems: Start-stop systems now automagically cut off and restart engines to reduce emission and fuel usage during periods of traffic idling. These systems are common in urban vehicles and mild hybrids. In September 2023 Bosch increased the responsiveness and integration of regenerative braking into start-stop technology for European hybrids, improving responsiveness and integration with regenerative braking. There was an increase in demand for start-stop modules in countries with stricter regulations fuel economy standards, as these systems have become a baseline requirement in many passenger hybrid cars. Light commercial vehicles also incorporate these systems. The entry level tier for electrification of most vehicles still heavily relies on these features.
Electric Power Steering (EPS): The replacing of traditional hydraulic steering by electric motors brings about new driver-assistance feature EPS improves energy efficiency. It reduces engine load while aiding advanced safety functions like lane keeping. Co-development of compact EPS units tailored for urban electric vehicles with a Chinese EV startup was struck by Nexteer Automotive in October 2024. Both developed and emerging markets are quick to adopt this technology. The enhancement EPS provides to autonomous driving makes it even more desirable, bolstered by the growing number of electric and software-controlled vehicles.
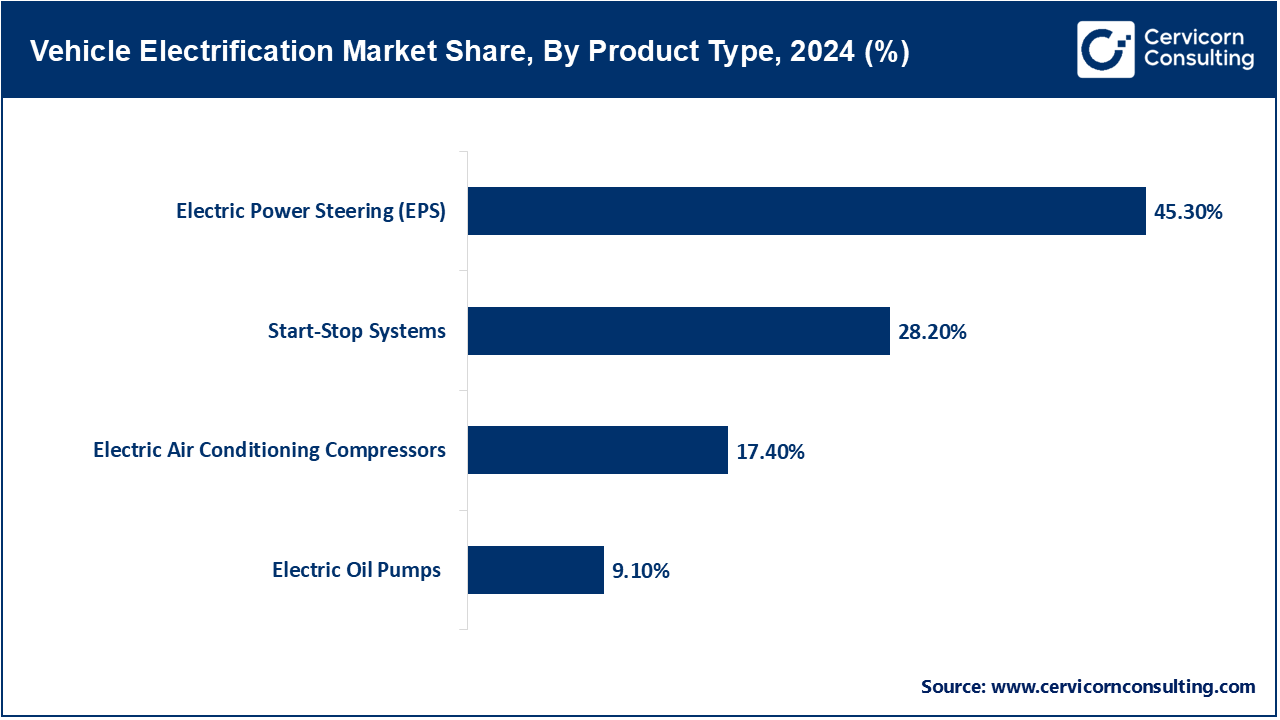
Electric Air Conditioning Compressors: These compressors function independently from the engine, making them suitable for EVs and hybrids. They enhance the efficiency of cabin cooling and decrease parasitic load on the vehicle. Denso announced a new electric compressor for battery electric SUVs that enables 20% more energy efficiency in June 2025. This type of compressor can aid in both cooling and thermal management of the battery systems. As comfort perception is prioritized among makers of EVs, adoption rate is rising. Tier-1 suppliers are extending their lines to incorporate high-voltage compact EV platforms with integrated sub stem compressors, making it essential parts for electric vehicles climate systems.
Electric Oil Pumps: In electrified drivetrains, lubrication maintains via Electric oil pumps do not require any engine power assistance. They help in cooling along with transmission efficiency in hybrid systems too. Hitachi Astemo released an advanced dual-speed electric oil pump for PHEVs with up to10% fuel economy boost in April 2024. Optimal lubrication is attainable during engine-off phases with this system. Electric oil pumps are now being designed into multi-speed transmissions and e-axles by automakers. Increased efficiencies tend to have smoother gear change as well as better thermal stability resulting into rise of their persistent use especially towards premium midrange and hybrids vehicles.
Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV): The entire class of battery electric vehicles or BEVs utilizes huge batteries for electrical energy with zero tailpipe emissions. This category of EVs is widely considered as the most sustainable Due to the need for charging stations, they stand out as the most sustainable EV Type. Tata Motors introduced Curvv ev on Januaury 2025 which was a mid-range battery electric coupe SUV electric vehicle. Tesla and BYD lead global volumes and innovation, citing their continued reign over the industry. The surging adoption of BEVs in Europe and China has soared due to stricter emission regulations, demonstrating how growth relates directly to technological advancements in batteries and decreasing production costs.
Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV): This newly released type of vehicle includes traditional fuel combustion engines alongside an electric motor, enabling HEVs to transform urban transport and aid fuel saving per charge cycles. These vehicles are great for city dwellers or people who regularly travel between rural areas. Following tax exemptions on registration fees in certain Indian states, Maruti Suzuki revealed an increase in booked hybrids by 140% year on year in their reporting issued July 2024. Many other SUV sedan hybrids were also announced from the same manufacturer as it seemed to be aimed strickly towards garnering market share while infrastructure needed for full EVs came to be built. While fully battery powered vehicles are still being developed and perfected at this time, HEV traders see tremendous progress still left until full system support becomes commonplace due integrating more robust supportive hybrid systems stronger battery pack integration than current levels deployed now.
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV): As a compromise between full electric vehicles and traditional internal combustion vehicles, PHEVs allow for external charging as well as operation in both electric-only and hybrid modes, providing flexibility and reduction in fuel use. They appeal more to consumers who are reluctant to fully transition into electric cars. Recently, Volvo Cars announced a refresh to their PHEV lineup slated for launch on May 2025. The updates included high electric-only range as well as faster charging support. These were aimed at fleet users and premium buyers. PHEVs help ease the transition from HEVs to BEVs in suburban areas and they're also essential in meeting short-term COâ‚‚ fleet targets in Europe. Their dual fuel benefit enables long drives while operating regionally as an urban EV.
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV): Hydrogen powered FCEVs generate electricity through fuel cells which only emit water vapor as waste. They offer long range travel with hydrogen’s speedy refueling options but lag without the necessary infrastructure. In March 2023, Toyota joined Hyundai's pilots FCEV trials with logistics partners based out of California and South Korea. Municipality adoptions of Toyota’s Mirai led limited municipal fleets depowered by FCEVs distributed throughout certain U.S cities. Although currently constrained within a niche market alongside much of the rest of the hydrogen infrastructure, attention is growing toward heavy-duty and commercial segments which helps garner investment towards green hydrogen improving overall ecosystem feasibility. In the meantime, these types of vehicles are seen to support long-term strategies within electrification plans Mix.
Passenger Cars: This group includes sedans, hatchbacks, and SUVs which are largely used for personal travel. Electrification within this category prioritizes comfort level, range, and cost-effectiveness. BYD surpassed Tesla in quarterly global EV sales in February 2025, with electric passenger car sales in Asia leading the surge. Fast charging, connected features have advanced along with range expansion. Government initiatives are aiding affordability of EVs in this segment. Compact and mid-size electric vehicles have dominated adoption trends globally. Globally, passenger electric vehicles still account for the major part of market growth.
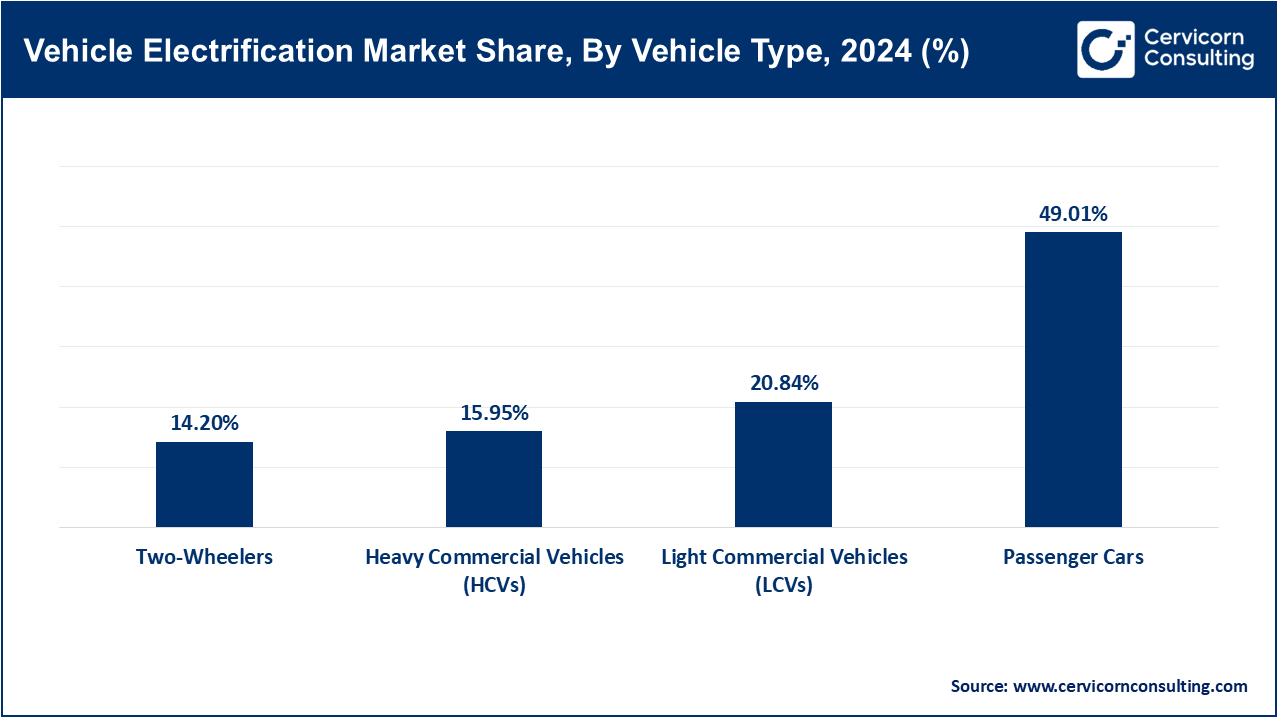
Light Commercial Vehicles (LCVs): This category includes vans and pickups employed for last-mile delivery as well as other commercial logistics uses. Fleet emission requirements and efficiency drive electrification. In October 2024 Ford announced Electric Transit van’s mass production For Europe targeted at fleet electrification for urban delivery center servicing. LCVs command lower operational costs and regulatory compliance working within city zones which offset urban operational challenges/ LC Volts are increasingly accepted by logistics companies. These are being implemented to combat congestion in populated areas cities facing heavy traffic streams congested areas. There is great potential for innovation regarding EV technology in this field.
Heavy Commercial Vehicles (HCVs): Trucks and buses are classified under these vehicles. Their electrification progress lags behind other segments, but it is critical for emissions reductions. Tata Motors launched a new line of electric intercity buses with high-capacity batteries in India this June 2025. On the other side, Daimler was testing long-haul electric trucks in Europe. Governments are subsidizing smart cities and public transport bus EV adoption. Charging infrastructure remains a challenge. Thorough HCV electrification is crucial in decarbonizing transport and logistical networks.
Two Wheelers: Includes scooters and bikes. Two electric scooters and bikes have been embraced by younger generations across towns in Asia due to their affordability. They serve as a good initial option for electrification in developing economies. India’s top EV two-wheeler Ola Electric announced an expansion at its FutureFactory in January 2025, boosting production capabilities further increasing access to these vehicles which serve personal mobility or gig economy commuting needs Boughton-lee Institute describes a battery swapping system being set up too aid fuel supply for two wheeled vehicles. Two-wheeler electrification also leads to oil consumption reduction, making them highly important economically as well as environmentally securing Asia-Pacific’s champion spot forecasted leading unit sales among EVs
12V: A 12V system is still commonplace in conventional vehicles and supports auxiliary functions such as lights and infotainment systems. In electrified vehicles, a 12V system is maintained for non-traction uses. Bosch provided reinforced control units for the hybrid vehicles that separates high and low voltage systems earlier this year. Although not utilized for propulsion, the 12V system mitigates safety risks and enhances comfort features which remain essential in equipment operations. OEMs strategize optimization with coordination routing from 12V to 48V for milled hybrids. This range will endure among legacy systems even as EV architectures advance while offering a reliable foundation for basic vehicle electronic components.
24V: The application of 24V systems is especially prominent in commercial vehicles along with heavy-duty machinery since it provides higher power than its predecessor. Its applications include lighting, HVAC, or sensor equipment feature more demanding energy circulation. Upgrade on the construction vehicles’ electric systems by Volvo Trucks in September of last year improved further compatibility with high-draw equipment charging. These systems aid in relieving battery strain during accessory operation periods. Other hybrids as well as delivery trucks utilize these platforms too, being advantageous when transitioning between mid-range voltage demand and full high-voltage operation. Among other advantages, reliability alongside proper balance of power make 24 volts indispensable among HCVs equipped with electrical drives.
48V: 48V systems are commonly used in mild hybrid vehicles where they support efficient start-stop mechanisms, regenerative braking, and electric turbocharging. In August 2024, Mahindra introduced a new 48V mild hybrid SUV within its XUV series in India. These systems enable reduction of fuel consumption and partial electrification without necessitating a full battery pack. To reduce cost and time of integration, Tier-1 suppliers have standardized 48V architectures. It allows entry-level mass-market vehicles to be positioned at an accessible level for electrification. The use of 48V platforms will increase in both developing and developed markets.
Above 48V (High Voltage Systems): Fully electric and plug-in hybrid vehicles utilize high-voltage systems (above 48V) as they facilitate fast-charging capabilities and enhance overall performance. Hyundai has announced the incorporation of an 800V architecture into the next-gen Ioniq models for ultra-fast charging by March 2025. Supporting larger motors, these systems significantly improve charging times; additionally, high-voltage system design is crucial for adequate thermal management and power density. Investment from automakers on high-voltage battery platforms is being made to improve BEVs appeal in the market; this defines the premium performance EV segment.
Powertrain Components: Comprising electric motors, controllers, inverters, and battery systems, the powertrain is energizing electrified propulsion ontwikkelingen. Bosch launched a high-efficiency motor-inverter for mid-sized EVs in Europe in June 2025. Henceforth, automotive makers shifted to integrated e-axles for higher space and cost efficiency. Innovation on powertrains continue to affect the vehicle performance, range and cost which remains critical for OEMs who are working with modular systems that can be used across various vehicle platforms. This still is the fastest evolving section of technology concerning EVs.
Vehicle Electrification Market Revenue Share, By Application, 2024 (%)
| Application | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Powertrain Components | 46.25% |
| Body Electronics | 28.37% |
| Infotainment and Telematics | 25.38% |
Body Electronics: Systems as lighting, mirrors and doors modules as well as HVAC are also included. More automated body systems as well as energy saving features are added with the electrification of body electronics system. Continental introduced new evolution adaptive brightness intelligent light control units for EV’s dated October 2024 continental smart body electronics initiative enables use with minimal energy expenditure while optimizing user experience in automation and propulsive energy efficiency. Peripheral AI expands these technologies interconnecting increasing their importance in designing top-line Evs.
Infotainment and Telematics: Infotainment systems have a two-part focus that includes entertainment as well as navigation systems, while telematics encompasses vehicle tracking and diagnostics. Both components are essential for connected EVs (Electric Vehicles). In April 2025, Tata Motors expanded its infotainment suite for EVs to include accurate real-time battery analytics and navigation to charging stations. Automakers are also offering OTA updates to improve functionality. Voice-activated controls, EV routing, and driver alerts have all been added to infotainment systems. Fleet monitoring and preventive maintenance are supported by telematics. This segment enhances the intelligence and appeal of EV ownership.
The vehicle electrification market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region.
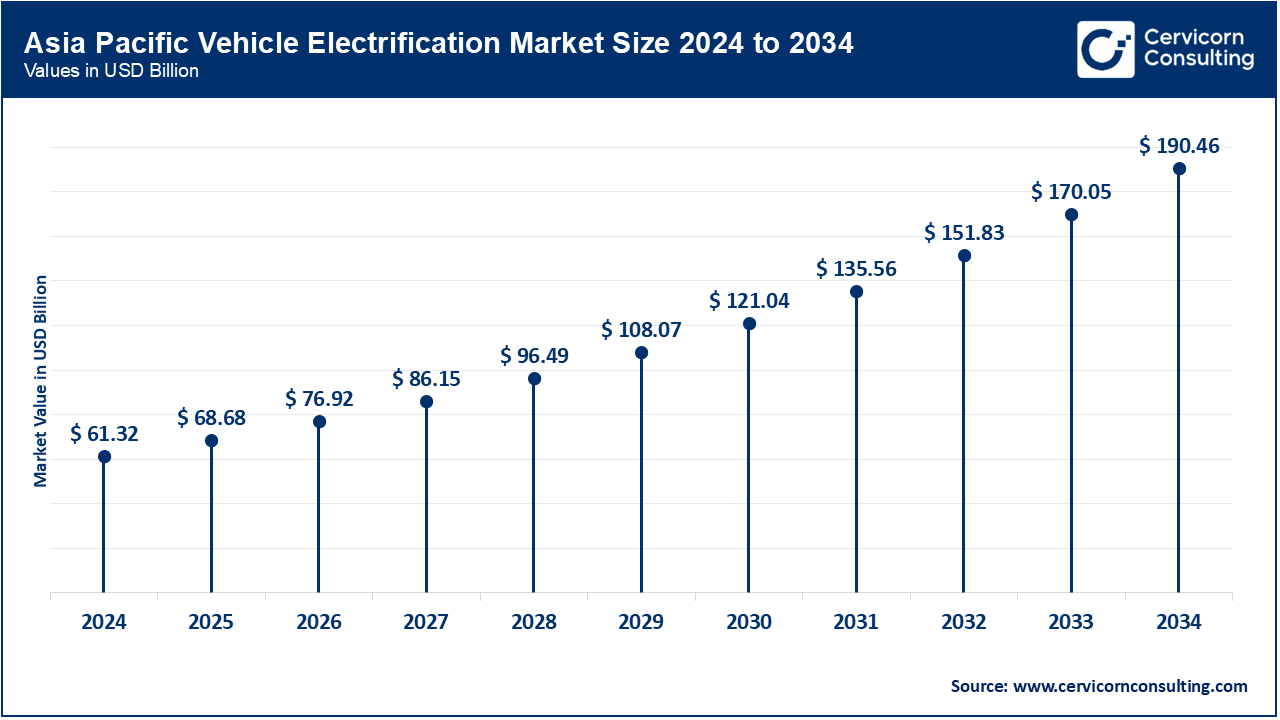
Favorable government policies combined with low-cost models has made Asia-Pacific the fastest growing market for electric vehicles. China continues to hold prominence on global sales of EVs along with India, Japan and South Korea expanding their incentive infrastructure further boosting manufacture and adoption across the region. In July of this year India extended its FAME-II scheme while Toyota strengthened their position by branching out battery production for Hyundai by Feb 2025after exceeding selling six million units in China in the prior year. Even Australia and New-Zealand started subsidizing them at a federal level towards the end on 2024 marking strengthening forward momentum serving Asia-Pacific as a focal point to this market along with enabling Johns supply-chain potential expansion.
North America is accelerating the electrification of vehicles with robust policy support, OEM investment, and increasing consumer acceptance, especially in the United States and Canada. North America is also leveraging local battery manufacturing and EV infrastructure with a cleaner transition of vehicle fleets. In March 2024, GM opened its Ultium battery plant in Tennessee. In 2022, Canada’s Ontario province invested investing $2B in EV supply chains. The United States has committed to deploying $15B under the 2023 Bipartisan Infrastructure Law to construct a national EV charging network. In January 2025 Mexico signed several key agreements with Tesla and BYD to strengthen localized EV assembly. North America is establishing itself as a global hub for EV production and innovation.
Europe remains a focal point for the regulation and deployment of EVs because of climate mandates, coupled with emissions policies on a supranational level. Accepted Poland, Germany, France, and the UK’s high EV acceptance projections facilitates plans to ban ICE sales by 2035. France crossing 25% share mark of EV’s in March of 2025 is marked by BMW's $1.7B investment into expanding EV production at its plants in Leipzig in July 2022. Stellantis pledged full electrification of European model line up by 2030 (Feb 2023). UK released ZEV mandates along with subsidy for home chargers issued in April 2024. EU however still leads the pack for sustainable vehicle transition due to mature regulation and groundwork already presentisch as UK doe not have higher collaboration level in geopolitics than continental ones.
Vehicle Electrification Market Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America | 25.80% |
| Europe | 22.50% |
| Asia-Pacific | 45.01% |
| LAMEA | 6.69% |
The region is making strides towards urban electrification in the LAMEA due to its gradual economic growth and infrastructural development. Brazil is leading EV adoption in Latin America with government partnerships, and alongside Saudi Arabia and the UAE's diversifying investments from oil, both nations are heavily aiding EV adoption. Brazil has also set a roadmap for 30% EV share in the fleet by 2030 as of June 2023. Under its Green Charger initiative issued in October 2024, the UAE added 100 charging stations and Lucid Motors began production of electric vehicles (EVs) in Saudi Arabia during early 2025. In March 2025, South Africa announced plans to establish an EV supply chain hub on the continent. Although these efforts lack cohesion, there is potential for regional breakthroughs within LAMEA’s developing markets.
The vehicle electrification industry is advancing through key partnerships focused on sustainable materials and circular production. In 2023, Borealis teamed up with TOMRA to expand recycled PP use in EV components. SABIC partnered with Plastic Energy in 2024 to supply circular polymers for lightweight EV interiors. ExxonMobil’s 2022 alliance with Cyclyx enhanced recycling feedstock for EV battery housings. LyondellBasell joined EEW Energy in 2025 to produce recycled PP for EV structures. TotalEnergies and Honeywell launched pyrolysis-based PP recycling in 2024. These collaborations support low-carbon, high-performance materials for electric vehicles.
Market Segmentation
By Product Type
By Propulsion Type
By Vehicle Type
By Voltage Type
By Application
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Vehicle Electrification
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Product Type Overview
2.2.2 By Propulsion Type Overview
2.2.3 By Vehicle Type Overview
2.2.4 By Voltage Type Overview
2.2.5 By Application Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.2 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Environmental concern and climate change awareness
4.1.1.2 Market demand volatility and alternates to oil
4.1.1.3 The Digital Shift in Automotive Technologies
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 Recuperation of range on EVs when compared to internal combustion engine vehicles
4.1.2.2 Heavily populated area made remote due to lack of chargers for EV
4.1.2.3 Dependency on rare earth elements and raw materials
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 Cybersecurity Issues of Electric Connected Vehicles
4.1.3.2 Ultimately balancing profitability and a surge in demand from OEM customers
4.1.3.3 Range anxiety along with misconceptions barriers
4.1.4 Market Opportunities
4.1.4.1 Technological integration (AI, 5G, edge computing) in EVs
4.1.4.2 Collaboration between OEMs and clean energy companies
4.1.4.3 Development of wireless and ultra-fast charging systems
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Vehicle Electrification Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Vehicle Electrification Market, By Product Type
6.1 Global Vehicle Electrification Market Snapshot, By Product Type
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Start-Stop Systems
6.1.1.2 Electric Power Steering (EPS)
6.1.1.3 Electric Air Conditioning Compressors
6.1.1.4 Electric Oil Pumps
Chapter 7. Vehicle Electrification Market, By Propulsion Type
7.1 Global Vehicle Electrification Market Snapshot, By Propulsion Type
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
7.1.1.2 Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
7.1.1.3 Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
7.1.1.4 Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV)
Chapter 8. Vehicle Electrification Market, By Vehicle Type
8.1 Global Vehicle Electrification Market Snapshot, By Vehicle Type
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Passenger Cars
8.1.1.2 Light Commercial Vehicles (LCVs)
8.1.1.3 Heavy Commercial Vehicles (HCVs)
8.1.1.4 Two-Wheelers
Chapter 9. Vehicle Electrification Market, By Voltage Type
9.1 Global Vehicle Electrification Market Snapshot, By Voltage Type
9.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
9.1.1.1 12V
9.1.1.2 24V
9.1.1.3 48V
9.1.1.4 Above 48V (High Voltage Systems)
Chapter 10. Vehicle Electrification Market, By Application
10.1 Global Vehicle Electrification Market Snapshot, By Application
10.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
10.1.1.1 Powertrain Components
10.1.1.2 Body Electronics
10.1.1.3 Infotainment and Telematics
Chapter 11. Vehicle Electrification Market, By Region
11.1 Overview
11.2 Vehicle Electrification Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
11.3 Global Vehicle Electrification Market, By Region
11.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
11.4 North America
11.4.1 North America Vehicle Electrification Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.3 North America Vehicle Electrification Market, By Country
11.4.4 U.S.
11.4.4.1 U.S. Vehicle Electrification Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
11.4.5 Canada
11.4.5.1 Canada Vehicle Electrification Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
11.4.6 Mexico
11.4.6.1 Mexico Vehicle Electrification Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
11.5 Europe
11.5.1 Europe Vehicle Electrification Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.3 Europe Vehicle Electrification Market, By Country
11.5.4 UK
11.5.4.1 UK Vehicle Electrification Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
11.5.5 France
11.5.5.1 France Vehicle Electrification Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
11.5.6 Germany
11.5.6.1 Germany Vehicle Electrification Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
11.5.7 Rest of Europe
11.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Vehicle Electrification Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6 Asia Pacific
11.6.1 Asia Pacific Vehicle Electrification Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.3 Asia Pacific Vehicle Electrification Market, By Country
11.6.4 China
11.6.4.1 China Vehicle Electrification Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.5 Japan
11.6.5.1 Japan Vehicle Electrification Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.6 India
11.6.6.1 India Vehicle Electrification Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.7 Australia
11.6.7.1 Australia Vehicle Electrification Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
11.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Vehicle Electrification Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7 LAMEA
11.7.1 LAMEA Vehicle Electrification Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.3 LAMEA Vehicle Electrification Market, By Country
11.7.4 GCC
11.7.4.1 GCC Vehicle Electrification Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7.5 Africa
11.7.5.1 Africa Vehicle Electrification Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7.6 Brazil
11.7.6.1 Brazil Vehicle Electrification Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
11.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Vehicle Electrification Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 12. Competitive Landscape
12.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
12.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
12.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
12.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
12.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 13. Company Profiles
13.1 Robert Bosch GmbH
13.1.1 Company Snapshot
13.1.2 Company and Business Overview
13.1.3 Financial KPIs
13.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
13.1.5 Strategic Growth
13.1.6 Global Footprints
13.1.7 Recent Development
13.1.8 SWOT Analysis
13.2 Continental AG
13.3 DENSO CORPORATION
13.4 Aptiv
13.5 Johnson Electric Holdings Limited
13.6 Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
13.7 BorgWarner Inc.
13.8 Magna International Inc.
13.9 AISIN CORPORATION
13.10 Johnson Controls
13.11 ZF Friedrichshafen AG
13.12 Valeo SA
13.13 JTEKT Corporation
13.14 Hitachi Astemo, Ltd.
13.15 Wabco Holdings Inc.