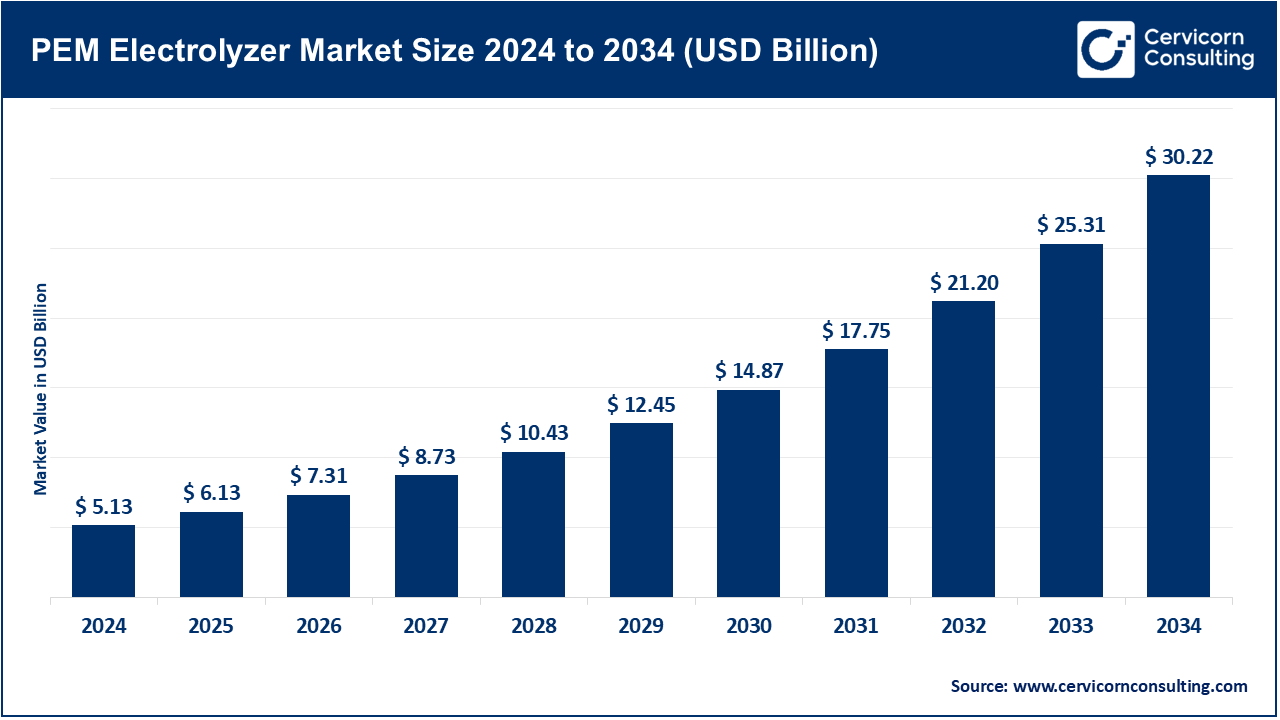
The global PEM electrolyzer market size was reached at USD 5.13 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 30.22 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.40% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
The PEM (Proton Exchange Membrane) electrolyzer market is driven by the accelerating global energy transition. Countries are now formulating comprehensive hydrogen roadmaps supported by financial incentives, such as the US’s Inflation Reduction Act and the auctions under the EU Green Deal, which aim to decarbonise, enhance industrial competitiveness, increase resilience, and achieve energy self-sufficiency. At the same time, advancements in electrolyzer technologies designed to reduce reliance on precious catalysts, such as iridium, increase system lifespan, improve efficiency, and declining renewable energy prices are lowering the levelized cost of green hydrogen. All of these factors create an optimal economic environment for expanding the use of PEM electrolyzers in fuel cell electric vehicles, industrial feedstock, and power-to-gas energy storage.
Moreover, the growing need for clean hydrogen is accelerating the PEM electrolyzer market growth. High-purity hydrogen is crucial for fuel-cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) and the expanding hydrogen refueling network, making PEM electrolyzers vital. Additionally, heavy industries such as steel, chemicals, ammonia, and refining are increasingly seeking to use hydrogen to replace fossil fuels and are utilizing PEM systems to produce green hydrogen and green ammonia. Furthermore, the flexible operation of PEM electrolyzers can aid in grid services by either absorbing excess renewable power or providing frequency balancing, thus generating ancillary revenue and enhancing grid stability.
The global green Hydrogen production market is on the rise as a result of shifting strategies for emission reduction and the adoption of new renewable technologies. The Proton Exchange Membrane electrolyzer which has the ability to rapidly respond to power changing availability from wind and solar, is preferred due to its ease of use and compact design Moreover, these systems supply high-purity hydrogen critical for transport, industrial applications, and energy storage.
Corporative and governmental bodies are massively investing financially towards scaling production of green electolyzers due to the carbon neutrality target policies and funds incentives. Recently, research has focused on catalysts, membranes, and system integration which increase efficiencies while decreasing costs. As the hydrogen economy advances, strategic collaborations between energy corporations, researchers, and other electrolyzer manufacturers are becoming more normal while these systems emerge as a core technology aimed for a low carbon sustainable energy system.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 6.13 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 30.22 Billion |
| Projected Market CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 19.40% |
| Top-ranking Region | North America |
| High-growth Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Capacity, Material Type, Application, Region |
| Key Companies | Air Liquide, Air Products and Chemicals, Inc., Cummins Inc., Erre Due s.p.a., Elogen, Giner, ITM Power, LARSEN & TOUBRO LIMITED, Nel ASA, ostermeier H2ydrogen Solutions GmbH, Plug Power, Siemens Energy |
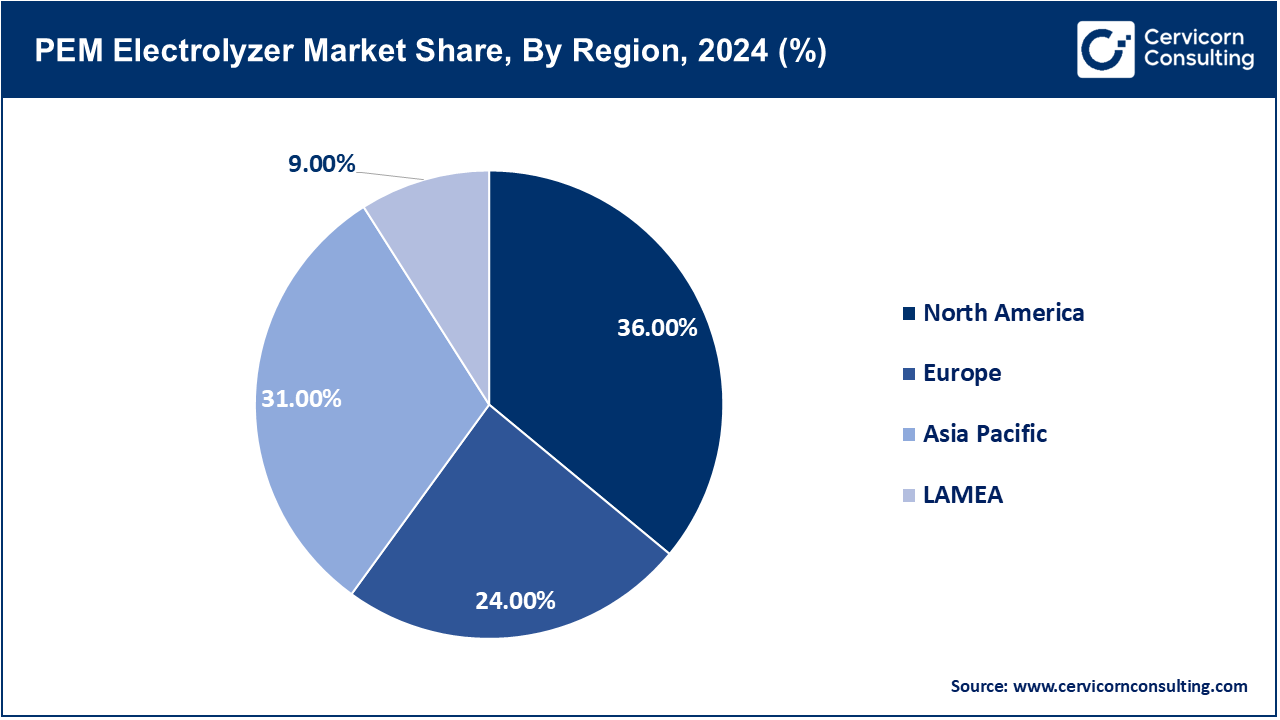
The PEM electrolyzer market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region
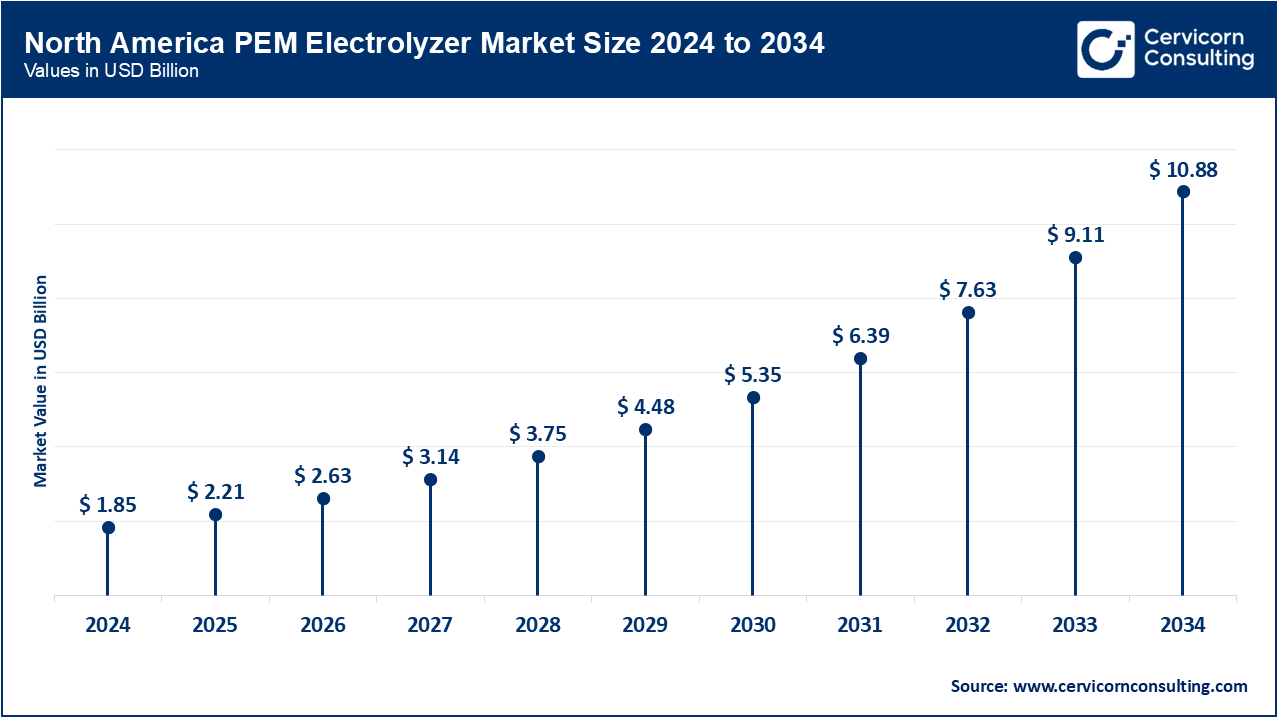
In September 2024 the DOE awarded roll-to-roll manufacturing innovation USD 0.008 billion to scale PEM electrolyzers and fuel cells in America. Canada’s Clean Fuels Fund Of 2021 (CAD 1.5 billion) is now funding green electrolyzers for electrical and industrial use with pilot projects being executed in Alberta. Mexico is assessing hydrogen-to-power demonstrations as part of the national clean energy strategy integrated with CFE’s studies done post-2023. North America-wide, policies like the US IRA tax credits and Canada’s federal promotion are aggressively incentivizing implementation and PEM manufacturing. All these actions signal heightened momentum toward hydrogen resilience and industrial decarbonization.
Europe’s REPowerEU strategy of 2023 allocated 10 Mt of renewable hydrogen by 2030 along with supporting electrolyzer deployment through the European Hydrogen Bank. Germany’s funding in 2023 of BASF’s 54 MW PEM electrolyzer with USD 0.14 billion government aid marks one of Europe’s largest PEM projects. UK proposed spending USD 2.7 billion on a green hydrogen fund which includes trials of membrane-based electrolyzers powered by wind offshore in December 2023. France aims for 6.5 GW of electrolyser capacity by 2030 as part of their hydrogen roadmap and already has HYVIA’s Flins plant which produced PEM fuel cells and electrolyzers in 2022 so, is able to self-supply. The acceleration of integrated industrial hydrogen systems throughout Europe is remarkable.
China’s electrolyzer capacity stood at 1.2 GW by the end of 2023, accounting for nearly fifty percent of the global total. This was supported by the 2021-2035 hydrogen plan and provincial subsidies. India implemented its National Green Hydrogen Mission in January 2023 allocating funds of INR 17,490 crore (~USD 2.4 billion) for 5 Mt production and 1.5 GW electrolyzer tenders through SIGHT. Japan’s revised Basic Hydrogen Strategy for June 2023 plans to disburse JPY 15 trillion (approximately USD 100 billion) by 2038 with an aim to supply 3 Mt hydrogen by 2030 while commencing 10 MW PEM Fukushima renewable electrolysis plants. Through ARENA, Australia funded USD 0.04 billion up until 2020 and approved a 200 MW plant in Whyalla in November 2024. In 2024 South Korea completed construction of H2 pipelines in Ulsan as well as 188 kilometers of H2 Green Hydrogen Town backbone infrastructure.
Brazil initiated the National Green Hydrogen Program in 2023, which expects to pilot PEM electrolyzers alongside wind-solar farms in the northeast region. In the UAE, COP28 Dubai Declaration (Dec 2023) approved reciprocal certification systems aimed at low-carbon hydrogen exchange. Saudi Arabia in early 2024 awarded projects under its Vision 2030 framework which incorporated PEM-backed green ammonia plants at NEOM, backed by sovereign wealth funding. South Africa’s Department of Mineral Resources and Energy progressed with the draft plans 2024 concerning hydrogen economy strategies centered around PEM Electrolyzers for the establishing of platinum group catalysts. These projects highlight growing concern with regard to hydrogen as an energy export and as a resource for industrial transformation for the region.
≤ 500 Kw: Small PEM electrolyzers (≤500 kW) are well suited for remote power and industrial pilot sites. In 2023, Europe’s small electrolyzer market was approximately valued at US$ 0.124 billion, where PEM units over 60% of the installations in the ≤500 kW range. It is also notable that in May 2024, SECI of India was awarded tenders for electrolyzers, including sub-500 kW units, under the SIGHT program for 295 MW. North America commissioned a 1 MW PEM electrolyzer at Amazon’s Colorado fulfillment center in Jan 2024 for forklift fueling. These compact units are also supported by policy incentives, like the U.S. IRA, which are vital for rural electrication and spearhead hydrogen pilot hubs. Advancements in durability of stacks and modular design make these more feasible. government-backed tenders and projects are increasingly relevant in these local hydrogen ecosystems.
> 500 kW – 2 MW: Mid-scale PEM electrolyzers (0.5–2 MW) serve industrial parks, ports, and refueling stations. India’s 2024 electrolyzer tender under SIGHT included units up to 2 MW, with 23 companies bidding over 2.8 GW cumulative capacity. In the U.S., Plug Power commissioned a 1 MW PEM electrolyzer in Colorado for supplying hydrogen to over 225 fuel-cell forklifts. Europe’s Hydrogen Valleys pilot projects integrate these mid-sized units with wind and solar, supported by EU Innovation Fund and REPowerEU grants. These systems balance scalability and flexibility, meeting both on-site generation and grid support roles. Permitting reforms in EU countries (2023-2025) further enable deployment. Their prevalence in transportation and industry signals growing adoption in hydrogen demand zones.
Above 2 MW: Large-scale (> 2 MW) PEM electrolyzers are well-suited for utility-scale integration and industrial decarbonization. Siemens/EWE issued plans for a 280 MW PEM plant in Emden, Germany, with projected commissioning in 2027, receiving USD 5.2 billion EU funding under IPCEI. Europe’s global electrolyzer pipeline is expanding, however, Reuters highlights only 12% have reached FID, and projection suggests undershooting EU targets. North American project pace continues to lag, aside from notable efforts such as Canada's Coyote Hâ‚‚. The US IRA tax credit appears poised to incentivize commercial-scale installs. Green steel and other chemicals and large power-to-X systems depend critically on these systems. Their deployment emphasizes the shift towards scale of clean hydrogen.
Power Generation: The electrolyzers are undergoing wider utilization in seasonal and grid balancing storage. In Europe, the Hydrogen Valley pilots funded by REPower EU are showcasing integrated storage-support hybrid systems. These systems are projected to reduce LCOH by 10% in comparison to electrolysis done independently, according to the DOE estimates. Focusing on the North American side, there is an interest in using hydrogen as a backup for grids with higher renewables share. Other examples are the Emden PEM projects aimed at COâ‚‚ reduction in the power sector. Construction and regulatory frameworks from US and EU strategies on energy transition further strengthen hydrogen’s role as a flexible generation asset.
Transportation: Hydrogen mobility fuels buses, trucks, and trains thus increasing the demand for PEM electrolyzers. The German Hydrogen Strategy of 2023 allocated USD 10.2 billion to train decarbonization and fueling infrastructure expansion. South Korea has a goal of 30,000 Hâ‚‚ trucks by 2030. In Colorado, Plug Power has a 1 MW electrolyzer that services fuel-cell forklifts and India has a 2024 tender that features transport specific devices. Spain’s Hympulso initiative and California’s SoHyCal facility are expected to advance hydrogen fueling pilots in 2024. These regionally directed projects strengthen policymakers’ goals for transport.
Industry Energy: Companies like data centers and glass and cement production are looking into onsite hydrogen power generation. In Europe, hydrogen is proposed for industrial energy use under REPowerEU targets, and pilot plants are already in construction. In North America, mid-scale PEM units are already in use in Clean Power Generation Integrated Industrial Parks. U.S. government grants and pilot programs, like_ Hydrogen Shot_ by the DOE, aim to minimize fossil gas dependence in industrial applications. Industrial users become interested in captive hydrogen generation as electrolyzer costs drop due to gas-less energy resilience and improving reliability.
Industry Feedstock: PEM hydrogen is increasingly used as feedstock by the refining and steel industries, ammonia and methanol production. The Siemens/EWE Emden plant will provide 26,000 t/year green hydrogen for industrial consumption. Low-carbon feedstock procurement becomes mandatory for EU member states with new CBAM obligations since October 2023. Finland's aim of a 1 GW PEM electrolyzer by 2030 includes support for ammonia production. There are global efforts to retrofit grey hydrogen plants with PEM stacks as stationary units which the US DOE and the EU support. These changes get additional justification from climate ambitions and financial incentives based on feedstock decarbonization.
Building Heating & Power: Hydrogen is emerging as a clean energy candidate for building-level heating and power in Europe. Demonstrators under REPowerEU include PEM electrolyzers paired with fuel cells for commercial buildings in Germany. DOE grants in 2024 are funding microgrid installations using PEM for emergency backup power. These systems are cleaner than diesel generators for sustaining emergency power in critical hospitals and services. Even though these systems are still in pilot testing, they are gaining supportive policy attention, especially for curtailing methane emissions from cities.
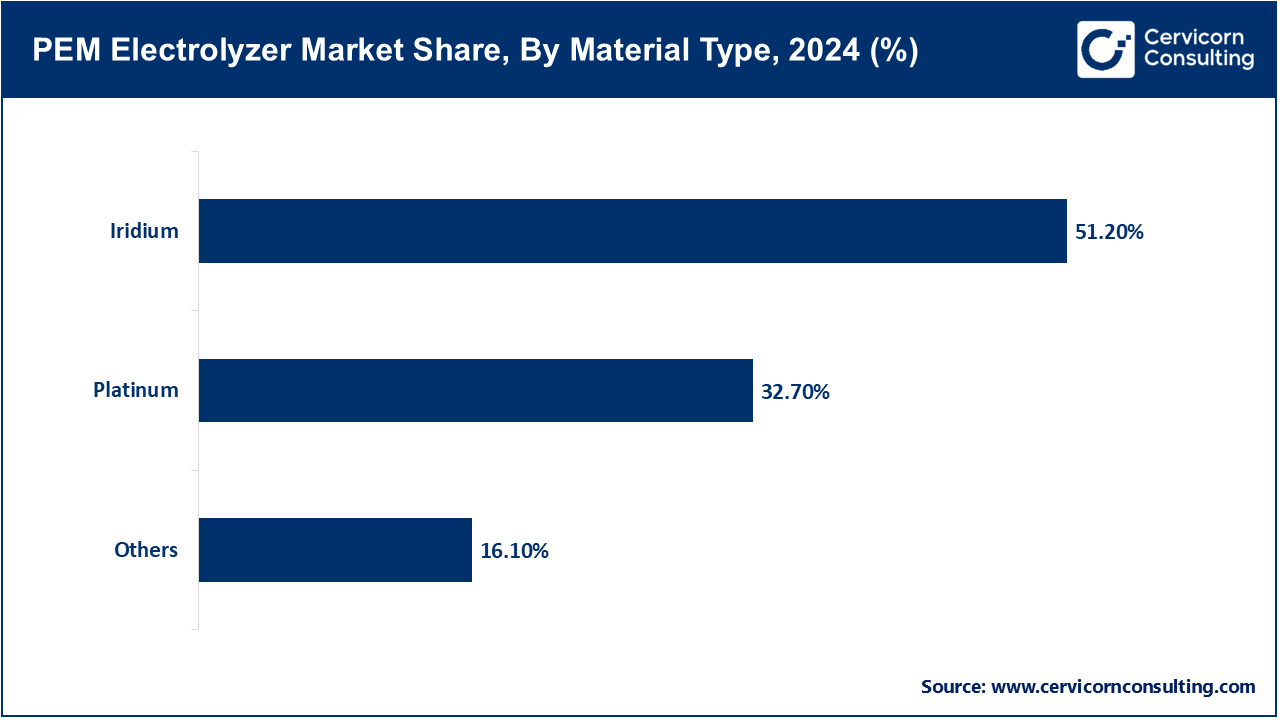
Based on material type, the market is classified into iridium, platinum and others. The iridium segment dominated the market in 2024.
Recent partnerships in the PEM electrolyzer industry emphasize innovation and clean energy collaboration. Siemens Energy and Air Liquide formed a joint venture in 2023 to industrialize PEM electrolyzer manufacturing in Germany, targeting 3 GW annual capacity by 2025. Cummins partnered with Tata Motors and Indian Oil Corporation under India’s National Green Hydrogen Mission to accelerate PEM deployment. Plug Power joined forces with Fortescue and Olin Corporation to establish large-scale PEM-based hydrogen production hubs in the U.S. ITM Power and Linde collaborated to deploy next-generation PEM systems for industrial decarbonization across Europe. Nel ASA partnered with Statkraft to deliver green hydrogen from PEM units for mobility and ammonia synthesis. These alliances are accelerating electrolyzer scaling, reducing cost, and integrating hydrogen into global energy systems.
Market Segmentation
By Capacity
By Material Type
By Application
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of PEM Electrolyzer
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Capacity Overview
2.2.2 By Material Type Overview
2.2.3 By Application Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.2 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Electric Vehicle & FCEV Expansion
4.1.1.2 Energy Security & Localization
4.1.1.3 Catalyst Efficiency & Cost Reductions
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 Raw Material Scarcity
4.1.2.2 Infrastructure Gaps
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 High Capital Expenditure
4.1.3.2 Raw-Material Scarcity
4.1.4 Market Opportunities
4.1.4.1 Decarbonization Drive
4.1.4.2 Fuel Cell Vehicle Adoption
4.1.4.3 Second-Life Battery Integration
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global PEM Electrolyzer Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. PEM Electrolyzer Market, By Capacity
6.1 Global PEM Electrolyzer Market Snapshot, By Capacity
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 ≤ 500 kW
6.1.1.2 > 500 kW – 2 MW
6.1.1.3 Above 2 MW
Chapter 7. PEM Electrolyzer Market, By Material Type
7.1 Global PEM Electrolyzer Market Snapshot, By Material Type
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Iridium
7.1.1.2 Platinum
7.1.1.3 Others
Chapter 8. PEM Electrolyzer Market, By Application
8.1 Global PEM Electrolyzer Market Snapshot, By Application
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Power Generation
8.1.1.2 Transportation
8.1.1.3 Industry Energy
8.1.1.4 Industry feedstock
8.1.1.5 Building Heating & Power
Chapter 9. PEM Electrolyzer Market, By Region
9.1 Overview
9.2 PEM Electrolyzer Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
9.3 Global PEM Electrolyzer Market, By Region
9.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
9.4 North America
9.4.1 North America PEM Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.3 North America PEM Electrolyzer Market, By Country
9.4.4 U.S.
9.4.4.1 U.S. PEM Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
9.4.5 Canada
9.4.5.1 Canada PEM Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
9.4.6 Mexico
9.4.6.1 Mexico PEM Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
9.5 Europe
9.5.1 Europe PEM Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.3 Europe PEM Electrolyzer Market, By Country
9.5.4 UK
9.5.4.1 UK PEM Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
9.5.5 France
9.5.5.1 France PEM Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
9.5.6 Germany
9.5.6.1 Germany PEM Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
9.5.7 Rest of Europe
9.5.7.1 Rest of Europe PEM Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6 Asia Pacific
9.6.1 Asia Pacific PEM Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.3 Asia Pacific PEM Electrolyzer Market, By Country
9.6.4 China
9.6.4.1 China PEM Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6.5 Japan
9.6.5.1 Japan PEM Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6.6 India
9.6.6.1 India PEM Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6.7 Australia
9.6.7.1 Australia PEM Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
9.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific PEM Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
9.7 LAMEA
9.7.1 LAMEA PEM Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.3 LAMEA PEM Electrolyzer Market, By Country
9.7.4 GCC
9.7.4.1 GCC PEM Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
9.7.5 Africa
9.7.5.1 Africa PEM Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
9.7.6 Brazil
9.7.6.1 Brazil PEM Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
9.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
9.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA PEM Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 10. Competitive Landscape
10.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
10.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
10.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
10.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
10.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 11. Company Profiles
11.1 Air Liquide
11.1.1 Company Snapshot
11.1.2 Company and Business Overview
11.1.3 Financial KPIs
11.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
11.1.5 Strategic Growth
11.1.6 Global Footprints
11.1.7 Recent Development
11.1.8 SWOT Analysis
11.2 Air Products and Chemicals, Inc.
11.3 Cummins Inc.
11.4 Erre Due s.p.a.
11.5 Elogen
11.6 Giner
11.7 ITM Power
11.8 LARSEN & TOUBRO LIMITED
11.9 Nel ASA
11.10 ostermeier H2ydrogen Solutions GmbH
11.11 Plug Power
11.12 Siemens Energy