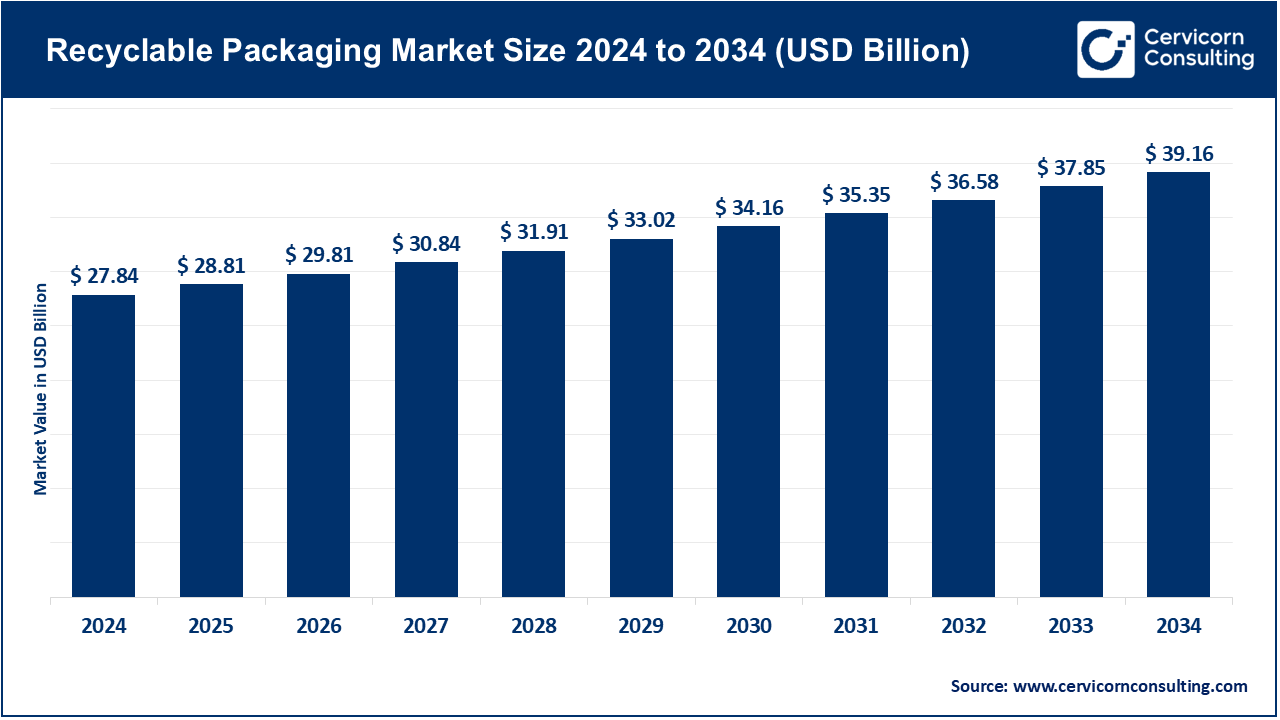
The global recyclable packaging market size is estimated at USD 28.81 billion in 2025 and is expected to be worth around USD 39.16 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.10% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034. The recyclable packaging market is expected to grow significantly owing to rising environmental awareness, stringent government regulations on single-use plastics, and shifting consumer preference toward sustainable and eco-friendly packaging solutions. Industries across food & beverage, personal care, and e-commerce are increasingly adopting recyclable materials to meet ESG goals and regulatory mandates. Additionally, advancements in biodegradable polymers, paper-based solutions, and closed-loop recycling systems are fostering innovation. Corporate sustainability initiatives and the circular economy model are further driving demand for recyclable packaging across developed and emerging markets.
What is recyclable packaging?
Any packaging material that can be gathered, processed, and remanufactured into new goods or materials is considered recyclable packaging. In this procedure, used packaging is gathered and transported to a recycling center where it is sorted by kind of material (e.g., plastic, glass, paper, aluminum). Following sorting, the materials are cleaned, shredded, melted, or disassembled into their constituent parts. The need for virgin resources is subsequently decreased by using these components as raw materials to make new packaging or other products. Recyclable packaging aims to reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills, preserve natural resources, use less energy, and emit fewer greenhouse gases than manufacturing from scratch.
The recyclable packaging market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region.
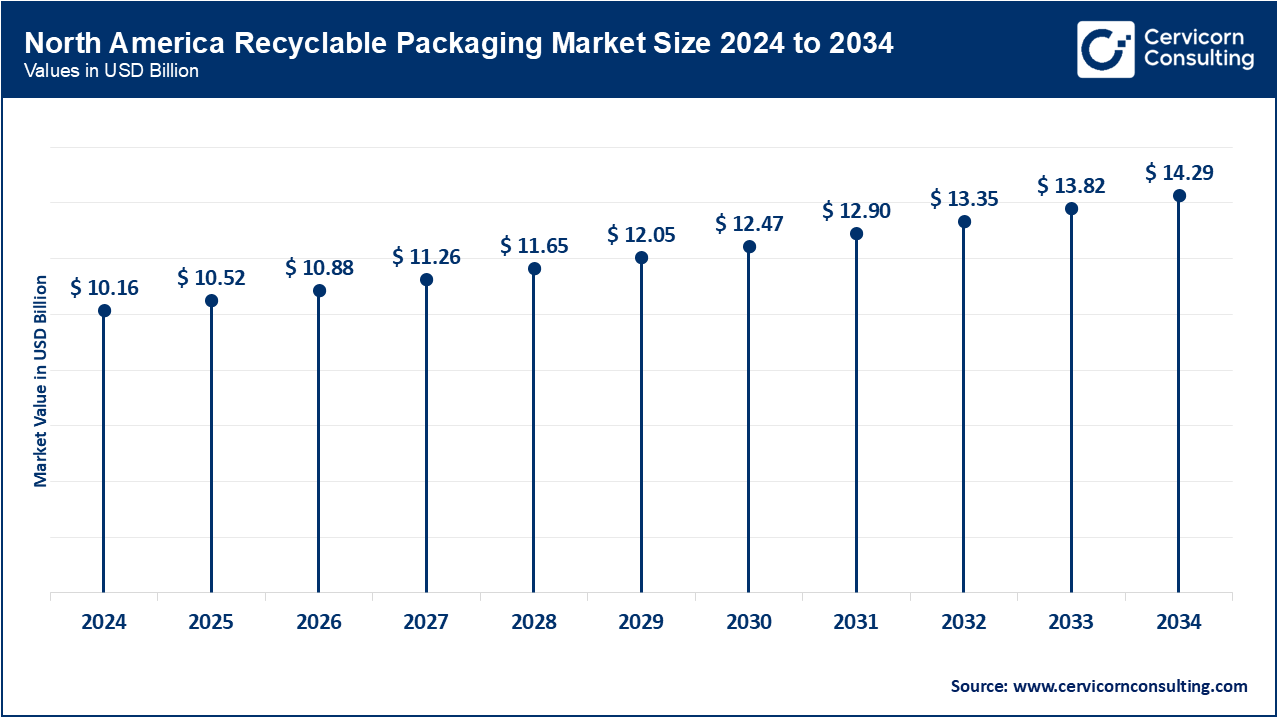
North America currently dominates the market, supported by robust regulatory environments, vigorous corporate sustainability pledges, and a well-established recycling network. The United States and Canada are progressively implementing circular packaging frameworks characterized by mandated recycled content, evolving extended producer responsibility statutes, and enhanced eco-labeling schemes. Simultaneously, an escalating consumer preference for plastic-free and biodegradable alternatives—particularly within the food, personal care, and e-commerce industries—stimulates ongoing innovation. In response, key retailers and manufacturers are channeling substantial investments into reusable and recyclable packaging ecosystems designed to fulfil ambitious climate targets.
Europe continues to lead the global market, propelled by strict EU directives, including the Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive and the Green Deal. Notable countries—Germany, France, and the Netherlands—exhibit exceptional recycling performance and a well-developed circular economy infrastructure. In this environment, there is a pronounced transition to fiber-based and mono-material packaging, especially within fast-moving consumer goods and healthcare. Reinforced by extended producer responsibility schemes and impending plastic banns, the sector is accelerating its adoption of sustainable, recyclable, and compostable alternatives.
Within the Asia-Pacific marketplace, surging urban migration, the deepening of manufacturing ecosystems, and a sharpening public focus on environmental stewardship are jointly propelling growth in the market. China, Japan, India, and South Korea have articulated cohesive national strategic documents aimed at improving recycling performance and curbing specific polymer categories; yet, the divergent maturation of municipal collection systems hampers the uniform realization of these regulatory objectives. The e-commerce boom and the expansion of the ready-to-eat sector continue to support demand for packaging types that facilitate reprocessing. Leading global corporations are tailoring their sustainability roadmaps to regional and local contexts, recognising the emergence of a fledgling yet increasingly vocal cohort of environmentally conscious consumers in developing markets.
Recyclable Packaging Market Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America | 36.50% |
| Europe | 33.20% |
| Asia-Pacific | 24.80% |
| LAMEA | 5.50% |
The LAMEA market is developing rapidly, driven by heightened consumer awareness, state-sponsored waste minimisation initiatives, and an influx of foreign investment targeting circular-economy enterprises. Brazil and Mexico are expanding their waste-collection and recovery networks, while the Gulf Cooperation Council states are embedding sustainabl packaging within comprehensive circular-economy strategies. The persistent inefficacy of materials recovery and sorting facilities—made more acute by inconsistent application of regulatory frameworks—remains a significant bottleneck impeding progress toward environmentally sustainable packaging alternatives. At the same time, increasing disposable incomes within expanding middle-class populations, together with vigorous retail sector expansion, is driving the more widespread adoption of recyclable and compostable substrates throughout a broadening array of industrial sectors.
Glass & Paper: Glass and paper remain the cornerstones of recyclable packaging because of mature recovery networks and limited impact on natural systems. Glass is the material of choice for food and beverage containment, owing to its chemical inertness and the ability to cycle infinitely without loss of quality. Paper, meanwhile, dominates secondary and tertiary packaging, ranging from transport boxes to cushioning sheeting. Heightened environmental awareness and regulatory mandates to phase out single-use plastics are prompting enterprises to substitute traditional plastic with paperboard cartons, corrugated cases, and glass bottles. Such transitions bolster the circular economy by curbing dependency on newly extracted raw materials and by closing recovery loops for both materials and energy inputs.
Plastic: The plastic segment dominated the market. Recyclable polymers particularly PET, HDPE, and LDPE continue to undergird lightweight, mechanically durable packaging solutions. While plastic waste remains under critical examination, enhancements in sorting and reprocessing technologies, together with stricter regulatory frameworks, are accelerating the uptake of mono-material structures capable of re-entering production cycles with greater ease. Mandated, clear on-package recycling messaging and design-for-recyclability protocols are narrowing the deficit in post-consumer recovery. Owing to favorable density, cost, and barrier performance, plastics are unlikely to retreat from the market; nevertheless, the rollout of formulations engineered for simpler recycling is imperative for satisfying extended producer responsibility schemes and for realizing ambitious net-zero packaging trajectories.
Tinplate, Wood & Aluminum: Tinplate, wood, and aluminum are quietly gaining ground in packaging, their recyclability the linchpin of their rising appeal. Tinplate and aluminum perform admirably at forming barriers and, in fully closed-loop systems, revert almost to virgin-grade purity; this capability is especially prized in food and personal-care lines. Wood, limited to premium containers and inner packaging, leverages its compostability and rich tactile quality. The confluence of a consumer preference for visible natural fibers, strict renewable-forestry standards, and expanding metal-loop logistics is widening the material’s footprint in brands committed to circularity.
Biodegradable Plastics and Recycled Papers: Biodegradable plastics and recycled fibers are being positioned as frontline defenses against landfill mass and plastic pollution. Approved for industrial composting and conventional paper streams alike, they either bio-degrade or reincarnate with a lowered environmental cost. Latest biopolymer blends are now standard in food films, mulch films, and cosmetic packaging; recycled paper remains the default for boxes and cushioning. Growth in both categories is being driven by a deepened feedstock supply, rising consumer preference for sustainable options, and retailer-imposed targets to drive landfill diversion ever higher.
Paper & Cardboard: The paper and cardboard continue to hold a preeminent position in the market due to their inherently simple recycling pathways, extensive collection networks, and minimal environmental impact per kilogram. These materials form the core of transport cartons, retail overwraps, and food service trays. As e-commerce volumes continue to expand, producers are increasingly selecting both rigid corrugated and lightweight kraft grades that provide the necessary drop and crush resistance without a disproportionate ecological burden. Recent innovations in biobased, water-repellent coatings and optimized, low-migration inks enhance their barrier performance, allowing these substrates to rival traditional plastic protective films while remaining clearly within a sustainable materials lifecycle.
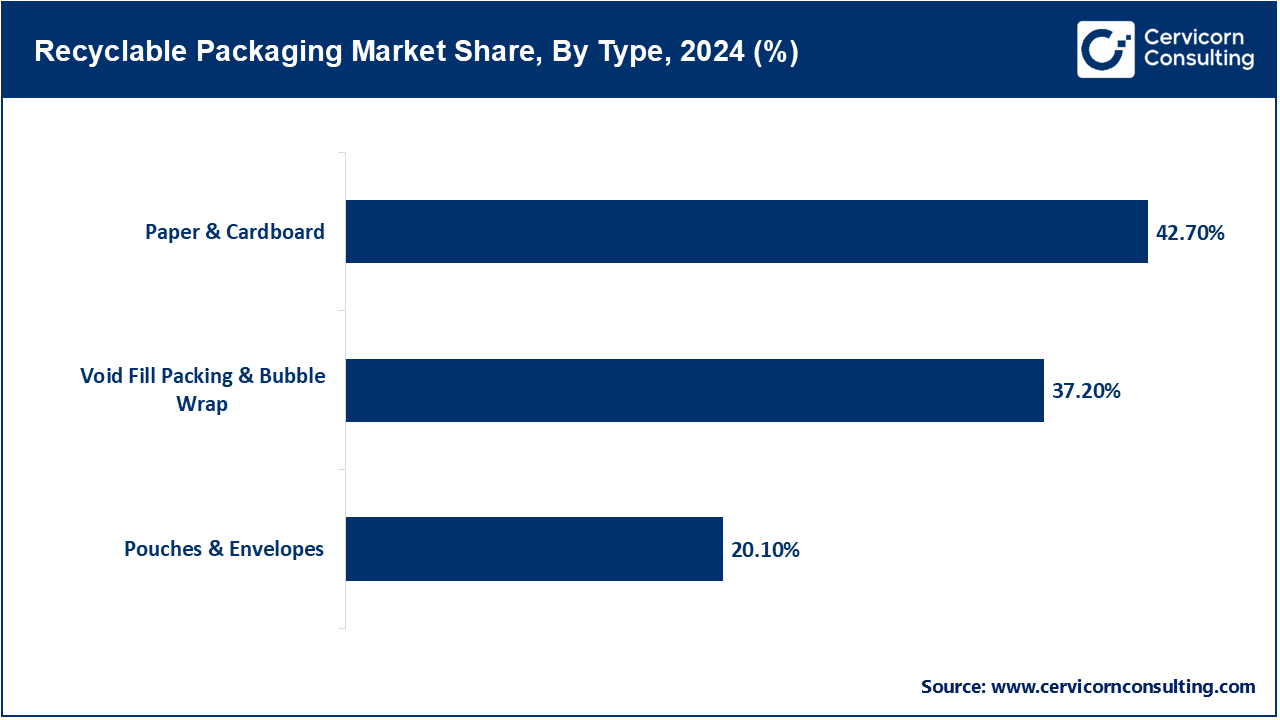
Void-fill and bubble wrap: Protective void-fill solutions and bubble wrap continue to be crucial safeguarding elements, particularly for e-commerce logistics and the transport of premium electronics. While the segment has traditionally relied on fossil-derived polymers, it is now moving quickly to recyclables and compostable options, notably molded-paper void fillers and inflatable pillows manufactured from monolayer films that are fully recyclable. Market acceptance of these greener alternatives is being accelerated by stricter legislation on non-recyclables and by an industry-wide commitment to mitigate the environmental footprint of last-mile logistics. Current formulations are carefully engineered to match the impact resistance of earlier products while advancing detailed corporate sustainability benchmarks.
Pouches and envelopes: Pouches and mailing envelopes produced from recyclable substrates are becoming the standard, especially for flexible applications in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. Recent breakthroughs in monolayer laminates and recyclable film constructions enable producers to phase out conventional multipolymer barriers that complicate recycling. The revised configurations are consequently lighter, more economical, and occupy less volume, thereby diminishing both transportation emissions and the consumption of raw materials. Partners throughout the supply chain are actively interfacing with recycling systems to confirm that the updated pouches integrate seamlessly with existing collection networks, thereby consolidating this packaging category as a crucial contributor to the sustainable progress of both primary and secondary supply chains.
Food and Beverage Sector: The food and beverage sector is now an industry-leading initiative, motivated by an ethos of environmental responsibility and the imperative of safeguarding product quality. Beverage cartons, recycled PET containers, glass jars, and trays engineered for industrial composting are gradually supplanting traditional plastic alternatives, embodying a dual allegiance to consumer protection and ecological balance. Multinational producers are channelling resources into closed-loop recovery schemes, recyclable adhesive labels, and mono-material flexible laminates designed to curtail landfill-bound waste. Heightened consumer expectations, emerging regulatory codes, and rigorous retailer mandates are collectively propelling the integration of recyclable packaging throughout the entire value chain.
Recyclable Packaging Market Share, By End-Use, 2024 (%)
| End-Use | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Healthcare Industry | 20.90% |
| Personal Care & Cosmetics Industry | 33.50% |
| Food & Beverages Industry | 45.60% |
Health Sector: Progress toward recyclable packaging in healthcare continues, yet remains tempered by rigorous sterilization demands and intricate regulatory landscapes. Recyclable polymers and paperboard are progressively appearing in blister packs, outer cartons, and flexible films. In parallel, pharmaceutical R&D teams are advancing the design of recyclable laminates and mono-material constructs, propelled by robust corporate sustainability pledges. Hospitals and pharmaceutical supply chains are now facing intensified expectations to minimize packaging waste while remaining strictly compliant with regulatory waste-management frameworks. This simultaneous objective is steadily, if cautiously, increasing the penetration of recyclable materials throughout the entire supply network.
Personal care and cosmetics sector: The personal care and cosmetics sector is embedding recyclable packaging even more deeply into product design and supply chains, driven by a growing base of consumers who treat sustainability as a non-negotiable product attribute. Brands are reformulating packaging portfolios to include post-consumer-recycled plastics, glass, and novel fibre-based materials, signalling a broad-based, albeit measured, commitment to circularity. Brands are replacing conventional containers with glass jars, aluminum tubes, and recyclable plastics, often oriented toward minimalist, refillable designs. This segment harmonizes premium presentation with environmental stewardship, bolstered by a multitude of firms committing to measurable circular packaging targets. Escalating consumer demand for transparent ingredient sourcing, ethical supply practices, and waste reduction is especially salient in Europe and North America, sustaining robust support for recyclable packaging initiatives across an expanding variety of product categories.
Market Segmentation
By Material Type
By Type
By End-Use
By Region