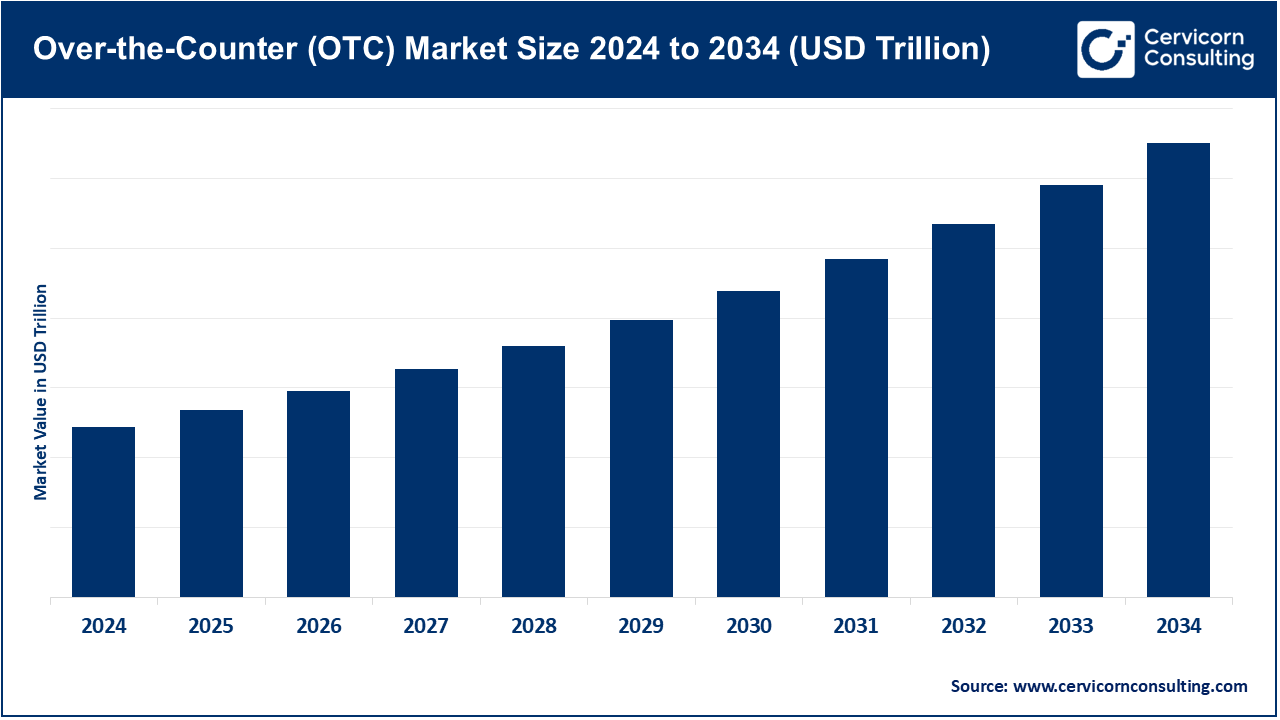
The global over-the-counter (OTC) market is expected to grow steadily at a CAGR of 7.3% from 2025 to 2034, with notional outstanding volumes projected to surpass USD 750–800 trillion by the end of 2025. This growth is driven by increasing demand for hedging instruments such as interest rate swaps, foreign exchange forwards, and credit default swaps, particularly as businesses and investors navigate volatile macroeconomic conditions, fluctuating interest rates, and currency risks. Regulatory reforms such as Dodd-Frank and EMIR have increased transparency and centralized clearing for many OTC derivatives, which has improved confidence and liquidity in the market, encouraging broader participation by institutional investors. The expansion of electronic trading platforms and swap execution facilities (SEFs) has also enhanced efficiency and reduced operational friction, further fueling market activity.
Key growth drivers include globalization of trade and finance, the rising complexity of risk management needs among corporates, and the increased use of derivatives for portfolio diversification. Emerging markets are becoming more significant contributors as financial institutions and corporations in Asia-Pacific and Latin America expand their use of OTC derivatives for hedging currency, interest rate, and commodity exposures. In addition, technological advancements such as algorithmic trading, real-time data analytics, and blockchain-based settlement solutions are expected to enhance market accessibility and reduce counterparty risk, supporting long-term growth of the OTC market.
What is the Over-the-Counter (OTC) Market?
The over-the-counter (OTC) market is a decentralized market where financial instruments such as stocks, bonds, currencies, and derivatives are traded directly between two parties rather than through a centralized exchange. Unlike exchange-traded markets, the OTC market operates through a network of dealers, brokers, and electronic platforms, allowing participants to negotiate terms such as price, quantity, and settlement directly. This market plays a crucial role in global finance by providing liquidity for instruments that are not listed on formal exchanges and by facilitating customized transactions that meet the specific needs of institutions, corporations, and investors.
The main benefits of the OTC market include flexibility, customization, and access to a wide range of instruments. OTC contracts can be tailored to match the exact requirements of the counterparties in terms of maturity, notional amount, and risk exposure—something that is often not possible with standardized exchange-traded products. It also allows companies to hedge specific risks, such as interest rate or currency fluctuations, more precisely. Additionally, OTC markets typically offer greater liquidity for certain securities (like bonds) and open investment opportunities for instruments that may not qualify for listing on major exchanges, thus supporting broader capital formation and risk management.
1. Continued Growth in Notional Outstanding
2. Shift Towards Centralized Clearing
3. Regulatory Enhancements and Oversight
4. Technological Advancements and Automation
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| OTC Market CAGR (2025 to 2034) | 7.3% |
| Leading Region | North America |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Instrument Type, Market Structure, Participant Type, Region |
| Key Companies | J.P. Morgan, Goldman Sachs, Citigroup, Bank of America, Morgan Stanley, Deutsche Bank AG, UBS Group AG, Barclays PLC, HSBC Holdings PLC, BNP Paribas S.A., Société Générale S.A., Wells Fargo & Company, Royal Bank of Canada, Mizuho Financial Group, Nomura Holdings, Inc. |
The OTC market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. Here is a brief overview of each region:
North America continues to lead in OTC derivatives trading, with the U.S. accounting for a significant portion of global activity. In 2024, the region saw notable advancements in market infrastructure and product offerings. For instance, the launch of the FMX Futures Exchange in September 2024 introduced a competitive alternative to established players like CME Group. FMX offers a combined platform for futures, repos, and foreign exchange trades, leveraging advanced trading technology to attract market participants. This move underscores the region's commitment to enhancing market efficiency and providing diverse trading options.
The APAC region is experiencing rapid growth in OTC derivatives trading, driven by regulatory reforms and increasing market participation. In 2024, Japan's derivatives market was set for expansion, with Tokyo and Singapore emerging as top locations for derivatives trading over the next three to five years. This trend reflects the region's evolving financial landscape and the growing sophistication of its markets. Additionally, mandatory reporting of OTC derivatives transactions, introduced as part of G20 reforms, has been a key focus in countries like Japan, Australia, Singapore, and Hong Kong, aiming to enhance transparency and reduce systemic risks.
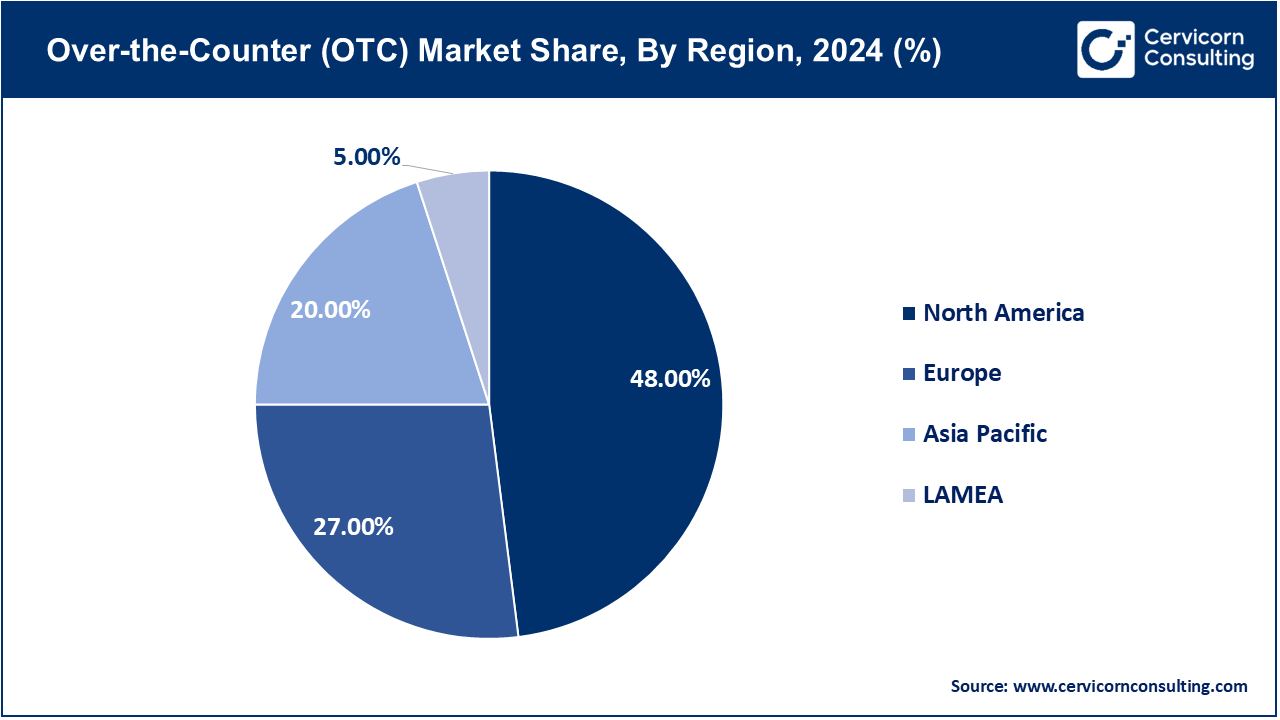
Europe's OTC market is undergoing significant changes, characterized by market consolidation and evolving regulatory challenges. In 2024, the European Energy Exchange (EEX) experienced a substantial increase in trading volumes, driven by new members and a shift from OTC trading to the exchange. This transition reflects the industry's response to heightened volatility in energy markets and the need for more transparent and efficient trading platforms. However, the European Banking Authority (EBA) highlighted the dominance of non-EU banks, particularly U.S. institutions, in key segments of the European derivatives market, raising concerns about financial autonomy and the need for strategic adjustments.
The LAMEA region is witnessing gradual growth in OTC derivatives trading, with emerging markets playing a pivotal role in this expansion. In 2024, the region's financial markets experienced increased activity, driven by rising demand for hedging instruments and greater integration into the global financial system. Strategic developments, such as the establishment of new trading platforms and the implementation of regulatory reforms, are contributing to the maturation of OTC markets in countries across Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa. These efforts aim to enhance market transparency, attract foreign investment, and foster economic stability in the region.
The OTC market is segmented into capacity, application, chemistry, end-user, and region.
Derivatives: OTC derivatives, including interest rate swaps, FX forwards, and credit default swaps, dominate the OTC market in terms of notional outstanding. Interest rate derivatives alone account for the largest share of global OTC exposure, reflecting their critical role in hedging against interest rate and currency risks.
Commodities: Commodity derivatives, particularly energy and metal contracts, are the fastest-growing segment. Increasing volatility in oil, gas, and precious metals, along with rising demand for hedging commodity price risk in emerging markets, has driven rapid expansion in OTC commodity trading.
Dealer Market: The dealer market remains the largest structure in OTC trading. Market makers provide continuous bid/ask quotes and liquidity for a wide variety of instruments, enabling efficient execution of large or customized trades between institutional participants.
Direct Negotiation: Bilateral, directly negotiated OTC contracts are growing quickly, especially in emerging markets and bespoke derivatives. This segment benefits from flexibility, allowing participants to tailor contract terms such as maturity, notional size, and settlement method according to specific risk-management needs.
Institutional Investors: Institutional investors, including hedge funds, pension funds, and insurance companies, dominate OTC markets due to their high trading volumes and large-scale risk-management requirements. They are key drivers of liquidity and market depth.
Corporates/Banks: Corporates and banks are the fastest-growing segment in OTC participation, increasingly using derivatives to hedge operational and financial risks. Rising globalization, cross-border trade, and currency exposure are pushing more corporates to adopt OTC instruments for risk mitigation.
The OTC market is predominantly controlled by a few large financial institutions, with U.S. banks holding a significant share in key segments. As of December 2023, U.S. banks accounted for nearly 28% of the European derivatives market, contributing to a total non-EU market share of 33.73% in that sector. This dominance is particularly evident in interest rate derivatives, commodity trading fees, and investment services. These institutions leverage their extensive global networks, advanced trading platforms, and comprehensive product offerings to maintain their competitive edge.
The competitive dynamics in the OTC market are also influenced by technological advancements and evolving regulatory frameworks. Market participants are increasingly adopting electronic trading platforms, algorithmic trading, and blockchain technology to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve transparency. For instance, the launch of the FMX Futures Exchange in September 2024 introduced a combined platform for futures, repos, and foreign exchange trades, leveraging advanced trading technology to attract market participants. Additionally, regulatory bodies are implementing reforms to address emerging risks and ensure the resilience of the financial system, influencing market strategies and operations.
Market Segmentation
By Instrument Type
By Market Structure
By Participant Type
By Region