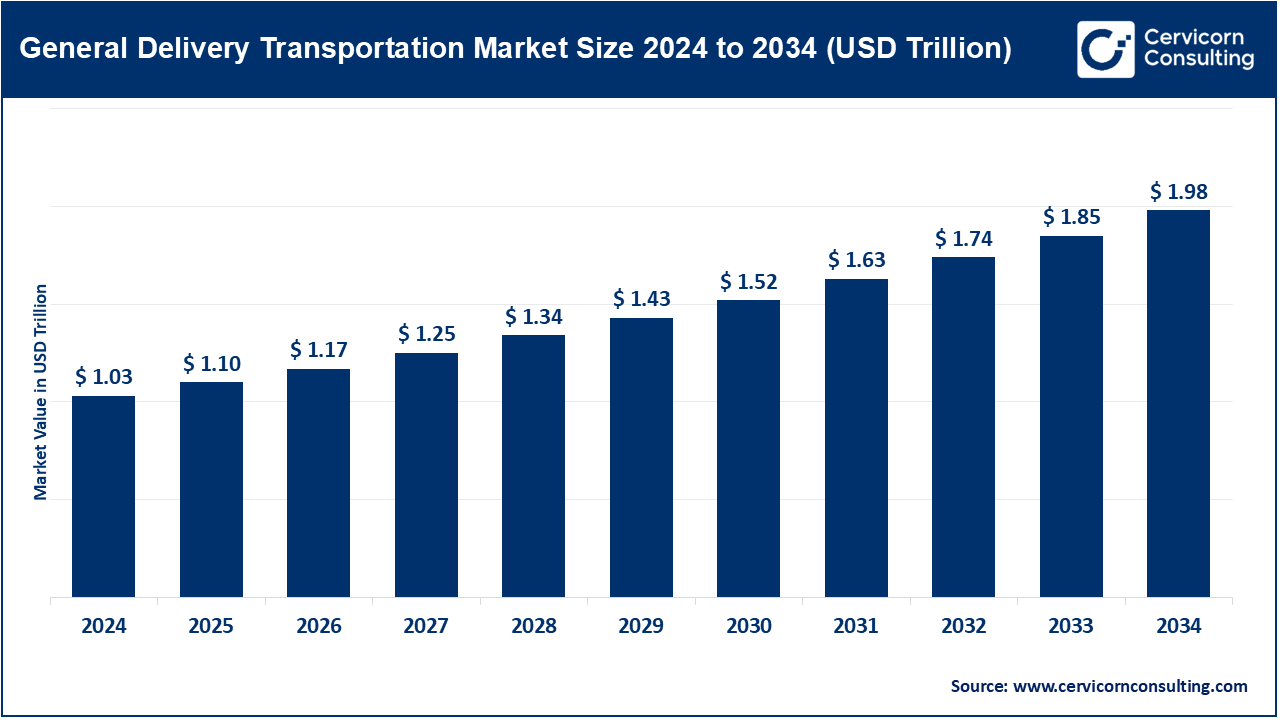
The global general delivery transportation market size was valued at USD 1.03 trillion in 2024 and is expected to surpass more than USD 1.98 trillion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.5% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The general delivery transportation market is expected to grow at a significant rate owing to the surge in e-commerce demand, urbanization, and last-mile delivery services. Increasing consumer expectations for faster delivery, coupled with advancements in route optimization, vehicle telematics, and logistics automation, are further driving market expansion. Additionally, government investments in smart infrastructure and green mobility solutions are enhancing the scalability and efficiency of general delivery networks worldwide.
The general delivery transportation market centers on moving packages and freight swiftly within linked logistics networks. Its expansion follows booming e-commerce, an appetite for speedy shipments, and increasingly global supply chains. Firms now deploy real-time tracking, artificial intelligence, and even self-driving vehicles to gain edge. Spending on digital tools and greener practices is quickening the pace of innovation. Collaborations with technology suppliers, plus rules favoring eco-friendly transport, are reshaping the arena. In short, the industry is evolving into a smart, data-led system that fuels world trade.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 1.1 Trillion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 1.98 Trillion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 8.5% |
| Dominant Region | North America |
| Rapid Growth Area | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Express Parcel Delivery, Freight & Supply Chain Logistics, Last-Mile Delivery, Reverse Logistics, Warehousing & Fulfillment Services, Region |
| Key Companies | Amazon, FedEx Corporation, United Parcel Service (UPS), Deutsche Post DHL Group, Maersk, CMA CGM, Kuehne + Nagel, SF Express, Royal Mail Group, ZTO Express, Poste Italiane, TFI International, Australia Post, PostNL, Austrian Post |
Domestic Express: The domestic express segment dominates the market. India Posts 2022-23 annual report shows it handled more than 2.1 billion domestic express parcels, an 18 percent rise over the previous year. Building on the National Logistics Policy 2022, the department expanded its delivery networks throughout 2023 to support scalable infrastructure. Automated barcode scanners, required by the PM Gati Shakti initiative, track each shipment and sharply cut misdeliveries. Compliance with the Consumer Protection (E-commerce) Rules likewise secures prompt refunds and accurate billing. Taken together, these measures modernize and streamline the country’s domestic express delivery sector.
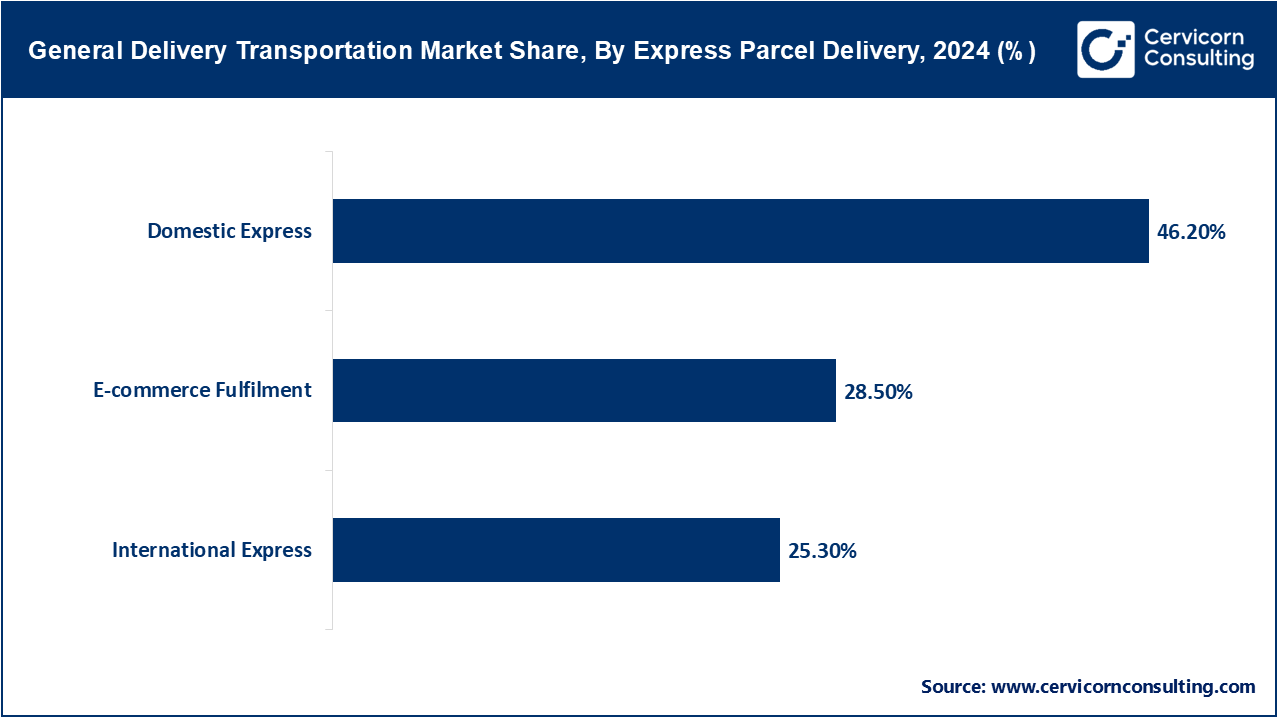
International Express: Customs figures from India's Directorate General of Foreign Trade show that express international parcel traffic climbed 28 percent between April and October 2024, year on year. The late-2023 launch of ICEGATE e-clearing trimmed clearance times by an estimated 35 percent, according to the Central Board of Indirect Taxes. Under the National Logistics Policy, multiple agencies now exchange postal, airline, and courier information, allowing smooth, real-time oversight. Consequently, the World Banks Logistics Performance Index 2023 places India twenty-second for international express delivery efficiency- a marked improvement. New 2025 air-freight agreements with European Union partners also cut out stacks of unnecessary paperwork. Simultaneously, regulators mandate electronic pre-declarations, strengthening security and further reducing hiccups. Taken together, these reforms create a sturdier, more compliant system for urgent global shipments.
E-commerce fulfilment: Government figures show logistics centres handled over 1.5 billion orders in FY 2023-24, a twenty-percent jump on the year before. To safeguard food and other perishables, the National Logistics Policy now demands temperature-controlled storage for online shipments. The 2024 Union Budget also cut GST on digital tracking tools used in e-commerce warehouses, easing technology costs. Late in 2023, major logistics firms received SCALE awards from the CII Institute of Logistics in recognition of their readiness to deploy AI in fulfilment. Agency audits confirm that processing times fell from forty-eight to thirty hours after RFID systems were activated under PM Gati Shakti. Meanwhile, amendments to the Consumer Protection Act now obligate online sellers to specify clear delivery windows. Taken together, these developments point to stronger efficiency, regulatory compliance and customer service across the e-commerce supply chain.
Air Freight: The air freight segment leading the market. The Airports Authority of India reports that air cargo crossed 4.2 million tonnes in 2023, a 12% rise over 2022. PM Gati Shakti and recent national logistics reforms have cut average airport dwell time to 2.2 days. Starting January 2024, the CBIC has made electronic invoicing compulsory for all air shipments, improving tax visibility. An MoU signed in March 2024 between the DGCA and Emirates also widened export routes. Revised security rules under the Air Cargo Security Programme now require full end-to-end tracking for high-value loads. The new, high-tech cargo terminal opened in Hyderabad in 2024 boosts handling capacity by 25%. Together, these regulatory and infrastructural upgrades fortify Indias air freight industry.
Ocean Freight: According to the Ministry of Shipping, container traffic climbed 8% in 2024, reaching 90 million TEUs. Implementation of RFID tagging through the NLDB cut average port dwell time from three days to 2.6 days. Under the Gati Shakti drive, new coastal highways cut last-mile trips by around 15% and the updated Coastal Shipping Policy added tax breaks, pushing volumes up another 5%. In 2023, larger berths at Mundra and Visakhapatnam sped loading and unloading, while a new rule requiring e-bills of lading made documents clearer for everyone. Those moves together show how blending policy support with fresh infrastructure is giving ocean freight a healthy lift.
Land freight: Land freight still relies heavily on trucks; the Logistics Performance Index says about 65% of all cargo moves this way, and 2023 volumes expanded another 10%. Meanwhile, the Railway Ministry is pushing ahead with its Dedicated Freight Corridor work on schedule, planning phased openings for early 2025. By mid-2024 every state had adopted e-way bills, cutting the delays that used to plague border crossings. New regulations now ask heavy trucks for digital fitness certificates, and upgrades at toll plazas plus the wider use of FASTag have sliced wait times at barriers by around 25 percent. Tough enforcement of axle-load rules, backed by regular weigh-bridge checks, protects both roads and vehicles. Together these measures boost efficiency and keep the countrys land-freight network in line with its own regulations.
Cold Chain: Cold Chain After moving $5.9 billion in temperature-sensitive medicines abroad in 2024, India is proving itself a rising hub for chilled exports, official EximIndia numbers show. Under the Prime Ministers Krishi Sinchai Yojana, by late 2024 planners approved 372 cold-storage schemes, boosting national capacity by an extra 38 million metric tonnes. Now the FSSAI and CDSCO insist that Internet-of-Things sensors track every degree from truck to syringe during vaccine delivery. Smart automation inside cold warehouses, backed by central grants, expanded by 30 per cent during 2023-24. Reports for 2024 also say post-harvest waste in fruits and vegetables dropped from 15 per cent to 8 per cent as the colder supply network spread. Meanwhile leaders Snowman Logistics and DHL widened their service areas under the public-private rules issued early in 2024. Taken together, these shifts signal a fast, coordinated upgrade across Indias cold-chain logistics.
B2C (Business-to-Consumer): Records from the Department of Consumer Affairs indicate that in 2024, 68 percent of city shoppers were offered same-day delivery, a clear rise from the 52 percent logged in 2022. As part of the National Logistics Policy issued in 2022, all B2C courier firms must now register with authorities and set up complaint windows, a move meant to boost accountability. Consumer appetite for rapid delivery drove a 15 per cent rise in e-fulfilment centres handling groceries and everyday goods in 2023. Amendments to the Consumer Protection Act, effective 2024, now require retailers to spell out delivery times and refund terms. In the same year, regulators began issuing night-delivery permits on selected corridors, giving couriers extra leeway while honouring local safety laws. Compulsory GPS-based live tracking has also trimmed misdelivery rates by 12 per cent. Together, these new rules and tech upgrades have made the final leg of business-to-consumer logistics more dependable than ever.
General Delivery Transportation Market Revenue Share, By Last-Mile Delivery, 2024 (%)
| Last-Mile Delivery | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| B2C | 75.60% |
| B2B | 16.50% |
| On-Demand Delivery | 7.90% |
(Business‑to‑Business): According to DGFT trade statistics, B2B parcels hit 800 million units in FY 2023-24, a 22 percent year-on-year gain. Under the National Logistics Policy, B2B couriers must now keep all records electronically as part of GST e-invoicing. Also, the number of small fulfilment hubs located near factories climbed 18 percent in 2024, trimming average delivery distance by roughly 10 kilometres. Fresh government notices now push logistics companies to enshrine service-level agreements that promise timely delivery in line with micro, small and medium enterprise support schemes. At the same time, trial drone flights for last-mile business-to-business links to hard-to-reach locations are advancing under the 2025 Drone Rules. A late-2023 court judgement further clarified liability boundaries between suppliers and transport contractors. Together, these trends are building a faster, legally sound ecosystem for business deliveries.
On-demand delivery: licensing records show that approvals for such platforms under the IT Act jumped 40 per cent in 2023-24. Dynamic routing, required by the Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Rules 2022, now checks every journey against load and safety rules. In late 2024, state-led trials of drone delivery took place in Andhra Pradesh and Telangana under official pilot schemes. Real-time identity verification, called for by the IT (Intermediary Guidelines) Rules 2021, protects each online transaction. To ease congestion in city centres, urban councils drafted new rules for delivery aggregators in 2024. Together, these legal and digital reforms offer a faster, safer, and nationally compliant framework for on-demand deliveries.
Handling Returns, Recycling, and Product Recalls: This segment ensures efficient routing of returned, recalled, or recyclable products. Retailers and logistics firms like UPS and FedEx expanded reverse logistics programs in 2023 to manage post-consumer waste and recalls more efficiently. With regulatory pressure mounting, especially in electronics and healthcare, firms now deploy AI-driven traceability and secure disposal mechanisms. In 2023 UPS Healthcare introduced a recall-ready shipping service for medical devices that meets FDA standards. The offering reduces the ecological footprint yet keeps manufacturers in step with laws on hazardous materials and patient safety.
Product Returns & Exchanges: The product returns & exchanges segment accounted for highest revenue share in 2024. Returns and exchanges have become a major headache for online retailers, especially during the holiday rush. To ease peak volumes and shorten queues, USPS and DHL in 2023 rolled out neighborhood drop-off points in suburban areas. Merchants increasingly rely on automated bar-code scanners that issue refunds almost instantly and preserve inventory records. Many retailers also install self-service kiosks so shoppers can return items with minimal staff involvement. All these processes sit under strict data-protection and consumer-rights rules, so returned goods are either resold, fixed, or disposed of in an environmentally sound manner.
Recycling & Waste Management: Move-and-tally waste programs help companies hit green targets and stay inside the law. The job covers the pick-up, sorting, and reprocessing of old electronics, cartons, and spoiled stock. In 2024 Best Buy broadened its e-recycling drive, safely handling millions of pounds under state guidelines. Logistics partners now tag every load with smart trackers and work only with certified recovery firms. Europe's Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment directive, along with a fragmented array of U.S. e-waste statutes, obliges companies to log each hand-off or transfer under threat of costly fines; as a result, manufacturers now track every device with near-obsessive care whenever they aim to bolster their sustainability scores.
Asset Recovery Logistics: Reverse logistics takes dead, lost, or returning inventory and squeezes value from it either by cleaning, repairing, and reselling, or by careful strip-down so still-working components can flow back into production. Companies like Amazon and Apple operate extensive systems that inspect, sort, and redirect these returned devices into their secondary-market streams. In 2023 Dell Technologies upgraded its service so that results fit the reporting rules demanded by enterprise sustainability boards. Such moves also satisfy growing legal and ESG pressures because regulators and consumers alike expect companies to cut landfill waste. The strategy therefore delivers revenue, protects the brand, and stays within the letter of electronics reuse and recycling law around the world.
Supporting Storage, Sorting, and Dispatch Functions: These basic warehouse tasks support both forward shipments and product returns. In early 2024 Amazon and Flipkart upgraded their hubs, adding AI and cameras to sort orders and spot mistakes. Facilities still follow strict safety, zoning, and labor rules, especially when goods must stay cool or are classified as hazardous. Modern robotics, paired with lengthy conveyor networks, now drive same-day delivery by shifting goods faster than any worker. Automatic sorters exchange real-time data with last-mile locators, enhancing visibility and ensuring transport and stock records comply with regulations.
Third-party fulfillment (3PL): Independent providers handle storage, selection, packing, shipping, and returns for companies wishing to hand over logistics. Late in 2023 DHL Supply Chain expanded services in Ontario to cover medical-device returns, a sector loaded with compliance rules. Such partners let clients meet mandates on temperature, labeling, and complete audit paperwork without building their own facilities. 3PL networks are vital for small and medium enterprises that cannot pay for a national transport and storage grid. With IoT sensors, live dashboards, and open APIs, companies can monitor accuracy and remain on the right side of tax laws, import-export rules, and consumer rights.
Micro-fulfillment centers: small, city-located stockrooms-help stores ship goods quickly and accept local returns almost on the spot. Chains such as Walmart and Kroger now place AI-driven hubs near downtown blocks, cutting travel times and return lines. In 2024 Ocado responded to sharp last-mile demand by adding new layers of automation to its own chain of MFCs. These compact facilities shine whenever an order contains delicate food, temperature-sensitive items, or products tied to health regulations. By fitting within urban zoning and trimming vehicle miles, MFCs support sustainability goals while meeting the rapid, compliant service sought by shoppers in crowded cities.
The general delivery transportation market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region.
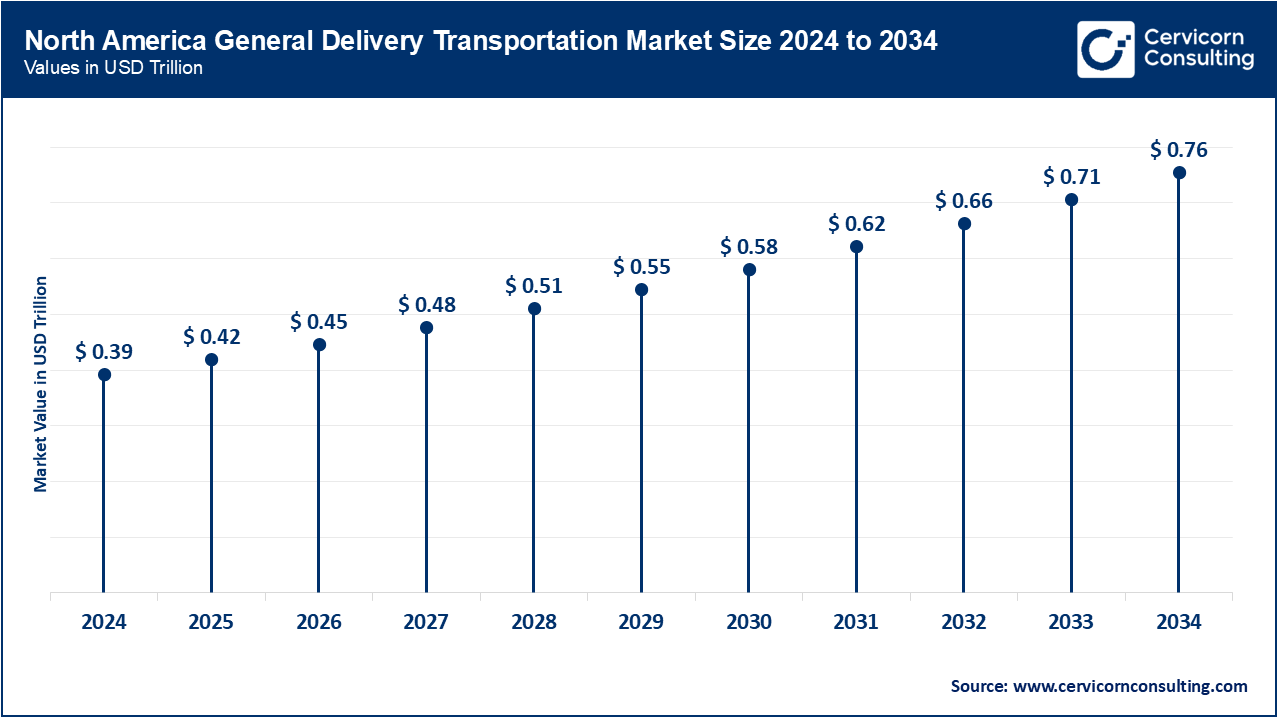
In 2023, U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) approved the Green Corridors low-emission freight guideway near Laredo to reduce border congestion and cut emissions by 75%, symbolizing binational infrastructure efforts. Canada’s Canadian Pacific Kansas City railway network now spans 20,000 mi across the continent, connecting Mexico, U.S., and Canada after its 2023 merger, despite tariff threats — maintaining trade flows worth $475 bn from Mexico and $419 bn from Canada in 2023, per U.S. ITC. Mexico saw infrastructure strain despite its first ULSD export from Dos Bocas in 2025, revealing gaps in domestic transport pipelines and rail. Investment in border warehouses in Laredo, El Paso, and Guadalajara continues, driven by nearshoring trends and supported by legal permits and cross-border coordination.
Australias 2023 Infrastructure Yearbook notes growing freight traffic alongside alarming road deaths-1,266 in 2023 and projected 1,300 in 2024-leading to a AUD 6.51 billion safety push. Indias National Logistics Policy and Sagarmala/Bharatmala schemes for 2023-24 launched 279 port-rail projects and 44 economic corridors to speed intermodal movement. Chinas MIIT broadened digital freight tracking, now required for every express shipment under revised logistics rules taking effect in 2024. Japans Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport tightened refrigerated transport standards through 2023 FSSAI-style food safety harmonization. South Korea, responding to government tech mandates, poured resources into smart ports and AI-driven distribution centers in late 2024.
The UK Department for Transport shows that domestic freight moved 1.55 billion tonnes in 2023-about 167 billion tonne-kilometres by road, 24 billion by water and 16 billion by rail. Road haulage volume slipped 4 to 5 per cent compared with 2022, yet the HGV driver shortage has held vacancy near 19 per cent because retirements and pay rivalry continue. Across the border, Germanys Federal Transport Ministry will in 2024 enforce a digital truck law that obliges e-invoices and telematics on all heavy goods vehicles. Meanwhile, France transport officials have issued a 2023 mandate for electronic waybills and route optimisation for inter-regional loads. Taken together, these policies and broader digitisation efforts are designed to lift efficiency while ensuring legal compliance amid rising competitive pressure on Europes logistics sector.
General Delivery Transportation Market Revenue Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America | 38.20% |
| Europe | 22.50% |
| Asia-Pacific | 31.30% |
| LAMEA | 8% |
Brazil s Transport Ministry says freight moved 7% more in 2023, thanks to grain and mine traffic, yet old highways still slow progress. The UAE s 2024 Logistics White Paper notes 68% of goods travel by truck while new Jebel Ali warehouses live under digitized customs rules. Saudi Arabia, meanwhile, pledged SR 1 trillion (~US$267 billion) from 2023 onward, adding 27 shipping routes and eight Jeddah port zones plus a 2024 e-doc platform aimed at 4.5 Mt of yearly air cargo and 80% private-sector growth. South Africas 2024 transport review points to upgraded freight links between main ports and the rail network, supported by PPP road projects that pursue better efficiency.
Recent partnerships in the general delivery transportation industry highlight a decisive shift toward AI-driven logistics, automation, and cross-industry innovation. Amazon is expanding its collaboration with Zoox to accelerate autonomous delivery vehicle deployment, focusing on seamless last-mile connectivity. FedEx and Salesforce are integrating AI-powered CRM solutions to enhance customer experience and predictive delivery insights. UPS is partnering with Arrival to develop electric, modular delivery vans tailored for urban environments, while DHL collaborates with Google Cloud to embed AI and machine learning for dynamic route planning and supply chain resilience. Meanwhile, Maersk is teaming up with Microsoft Azure to leverage cloud-based logistics orchestration and digital twin technologies. These partnerships reflect a broader movement toward sustainable, smart, and scalable transportation frameworks reshaping global delivery infrastructure.
Market Segmentation
By Express Parcel Delivery
By Freight & Supply Chain Logistics
By Last-Mile Delivery
By Reverse Logistics
By Warehousing & Fulfillment Services
By Region