Boat-to-Grid (B2G) Technology Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
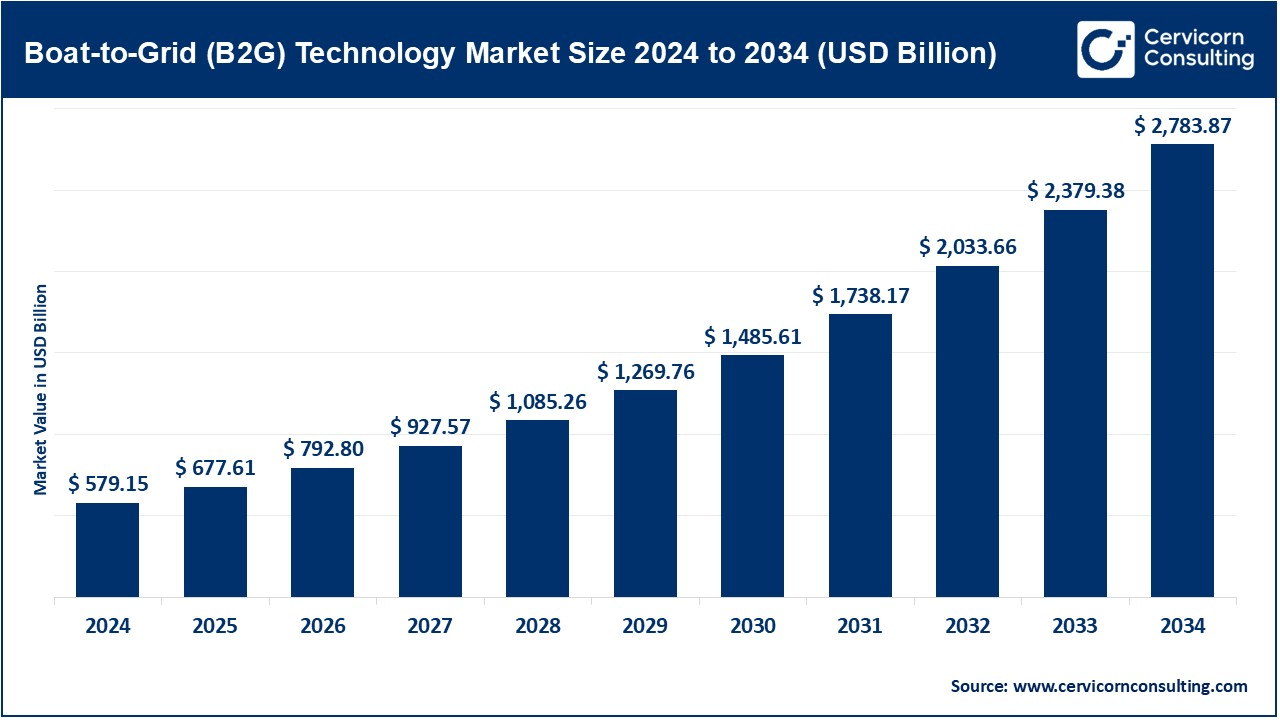
The global boat-to-grid (B2G) technology market size was valued at USD 579.15 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 2,783.87 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034. The boat-to-grid technology market will witness substantial growth as it remains one of the key factors, that complements the wider shift towards the use of green energy and fuels the electrification of transportation, and the development of the storage systems of the future. Thus, a B2G market would ensure an energy storage distributed system by using boats as mobile energy batteries. Thus, this B2G technology serves as a parallel energy storage solution for the enhancement of grid stability. The main stimulants for B2G development are increasing demand for electric/hybrid marine vessels, the improvement in the grid and energy storage technologies, and new governmental laws related to better flexibility in a situation that involves a high need for decentralized energy storage solutions.
"Boat-to-grid" (B2G) may be a modern strategy of interfacing ships, particularly those utilized for oceanic exercises, to the electrical network arrange. It is basically vehicle-to-grid (V2G) innovation that has been adjusted for ships, which may be both vitality customers and providers. When batteries are utilized on board electric or cross breed ships, supply and ask may be balanced, particularly when startling renewable essentialness is conveyed. The boat-to-grid thought is still in its early stages, but it might contribute to the broader incline of green essentialness integration and versatile system organization, which would lead to more attempted and genuine and long-lasting control. �
The boat-to-grid (B2G) technology market is primarily driven by the global push for decarbonization, the need for flexible grid management solutions to integrate renewable energy, advances in electric vessel technology, and the growing infrastructure supporting electric vessels. As these factors continue to evolve, B2G systems are expected to play an increasingly important role in both the maritime and energy sectors, offering new opportunities for energy storage, grid stability and sustainability.
Growth Factors
- Shipping Industry Decarbonisation at a Rapid Pace: There is increasing pressure from governments and international organizations such as the International Maritime Organization (IMO) to reduce emissions from the shipping industry. Regulations to reduce shipping's greenhouse gas emissions, as well as global commitments to reduce carbon footprints, are pushing for the adoption of clean energy technologies such as electric and hybrid boats that can be integrated into the power grid. The shipping sector is a significant contributor to global carbon emissions. As electric and hybrid boats become more common, boat-to-grid (B2G) technology offers a way to decarbonize vessel operations and contribute to the broader goal of reducing emissions from the energy grid.
- Growth in Port and Infrastructure Development: Ports are really stepping up their game by pouring money into electrification and charging setups to improve electric boat docking and grid connections. This new infrastructure is key for helping boats connect smoothly with the electrical grid, which is super important for the success of B2G. Additionally, electrified port facilities can serve as central points for energy exchange between boats and the grid, further supporting B2G initiatives.
- Growing Cost Advantages and Financial Incentives: By leveraging their boats for energy storage and selling it to the grid during peak times, boat owners can effectively cut their expenses. Considering hybrid or electric systems could be smart for them, especially since there are financing options tailored for B2G needs. This is really important in high-demand areas, where energy prices can jump during peak times, making B2G engagement a lot more beneficial.
Market Trends
- Growing Demand for Energy Storage and Supply: Boats, particularly those with big battery systems, like commercial vessels or electric ferries, may store grid electricity when there is surplus power available, as during off-peak hours or when renewable energy sources like solar and wind generate more than is required. Their ability to feed the stored energy back into the grid helps to stabilize the energy supply during times of increased demand or when the production of renewable energy declines.
- Growing Renewable Energy and Grid Adaptability: The rise of inconsistent renewable energy sources, including wind and solar, in the global energy framework demands innovative solutions for energy storage and distribution. B2G technology allows boat batteries to store renewable energy during abundant periods and reintegrate it when output is low or demand is high, enhancing grid stability and enabling greater integration of renewable energy.
- Increasing Electrification in the Maritime Sector: The rise of hybrid and electric vessels in commercial shipping and marine industries is driving B2G. Ports are investing in energy management systems and charging stations to accommodate these vessels, making it easier to manage energy flows and connect boats to the grid, thus enhancing the concept of B2G.
- Collaboration Between Shipping and Energy Sectors: Utility companies, energy suppliers, and marine operators are collaborating to create integrated systems that allow ships to act as dynamic energy storage devices. Pilot studies are being conducted to assess the viability of boat-to-grid (B2G) systems, which explore how boat batteries can increase grid stability through partnerships between ports, grid management, and electric ferry operators.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 677.61 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 |
USD 2783.87 Billion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 |
17% |
| Key Segments |
Technology, Vessel Type, Application, End User, Region |
| Key Companies |
Siemens AG, ABB Ltd., Schneider Electric, General Electric (GE), W�rtsil� Corporation, Rolls-Royce Power Systems, Yanmar Co., Ltd., Tesla Inc., Nidec Corporation, Vestas Wind Systems, Man Energy Solutions, Norwegian Electric Systems (NES), PowerCell Sweden AB, Caterpillar Inc., DNV GL, Eelpower Ltd., Eidesvik Offshore, Vigo Marine, Soventix, Bollinger Shipyards |
Market Dynamics
Market Drivers
Increasing Use of Electric and Hybrid Boats
- The global maritime sector is experiencing a shift towards electric and hybrid vessels, particularly in ferries, cargo ships and smaller boats. This trend is driven by the need to reduce emissions, improve fuel efficiency and reduce operating costs. Electric boats are ideal for B2G systems due to their superior battery capacity. The number of ships that mix conventional and electric engines is increasing. With their larger battery banks capable of storing significant energy, these boats are perfect for advancements in B2G technology.
Growing Regulatory Support and Government Incentives
- Governments are introducing policies and regulations that encourage the use of electric and hybrid boats. Subsidies, grants and tax incentives for boat operators are encouraging investment in electric propulsion and energy storage systems that support B2G technology. Regulatory pressures related to carbon emissions are driving the maritime sector to transition to electric-powered vessels and creating opportunities for B2G to play a role in achieving national or regional carbon reduction targets.
Market Restraints
Large Initial Investment and Costs
- The purchase costs of electric and hybrid boats, including their energy storage systems (batteries), remain high. Although costs have decreased over the years, they still represent a significant barrier for boat owners, especially smaller operators, to switch to electric boats and participate in B2G systems. Developing and upgrading infrastructure such as charging stations, energy management systems and port facilities to support B2G systems requires significant investment. Ports may need to undertake costly upgrades to integrate electric boats into the grid, which can be a deterrent for smaller or less well-funded ports.
Regulatory and Legal Hurdles
- The regulatory framework for integrating boats into the power grid is not yet standardized, which may complicate the widespread adoption of B2G systems. Different countries and regions have different policies regarding energy storage, grid management and maritime operations, making it difficult to implement a unified approach to B2G integration. Regulations on the environment, energy markets, and international shipping create difficulties for B2G systems in the energy and maritime fields. Liability problems can occur when boats connect to the grid, particularly if there is damage or instability. Clearer rules are needed to tackle these challenges and facilitate B2G operations.
Market Opportunities
Developments in Electric Boat and Battery Technology
- The rapid development of boat battery and electric propulsion systems is critical to enable B2G. With their enhanced energy storage and release capabilities, electric and hybrid boats are perfectly positioned for B2G systems. Advances in battery technology, including higher energy densities and longer lifespans, are making it more viable for boats to store energy for longer periods and release it back into the grid without significant performance degradation.
Evolving Smart Grid Technologies
- Distributed energy resources like B2G systems will be simpler to incorporate as power networks are "smarter" and more digitally linked. Smart grids help ensure that power is used efficiently while allowing for the smooth integration of boat-to-grid systems into overall grid management plans. They enable the management of energy flow between boats and the grid. By utilizing boat-to-grid systems, we can encourage boats to tap into grid power through demand response strategies, which will lead to increased adoption.
Market Challenges
Problems with Battery Life and Durability
- B2G contact may result in numerous cycles of charging and draining, reducing boat battery life. The use of boat batteries for grid interactions raises questions regarding their long-term feasibility and the potential financial burden of needing to replace them sooner than expected. B2G energy systems and batteries may be costly and difficult to maintain, particularly for boats used in challenging marine environments. Moreover, ongoing maintenance and monitoring are required to ensure that these batteries continue to be reliable and effective over time.
Operational Issues and the Use of Vessels
- Boats are not always docked or idle long enough to participate in B2G systems. Many commercial ships, especially those carrying heavy loads, are seldom in port for extended periods of time. This restricts the amount of time a boat may send energy to the grid or engage in B2G energy storage. Managing a fleet of boats participating in B2G could be a logistical challenge, especially in terms of optimising the timing of loading, unloading or returning to port. Management systems are needed to coordinate this, but developing these systems can be complex and costly.
Segmental Analysis
Technology Analysis
Energy Storage Systems: Energy storage systems are key in boat-to-grid applications, where electric vessels act as mobile storage units that store energy during off-peak hours and feed it back into the grid when demand is high. These include lithium-ion batteries, solid-state batteries and second-life batteries.
Electric Propulsion Devices: Innovations in electricity-converting technology have paved the way for mechanical movement in ships. A standout aspect of this technology is the B2G-compatible hybrid electric system, which improves efficiency by combining electric motors with standard engine systems.
Grid Connectivity and Power Electronics: VRF technology enables ships to supply electricity back into the grid using inverters, energy management systems, and bidirectional charging systems. The smart grid integration helps manage energy flow and ensures consistent communication between the vessels and the grid.
Systems for Control and Communication: To optimize the connection between electric vessels and the grid while monitoring energy consumption, they can communicate through cloud computing, IoT technology, and AI-based management solutions.
Vessel Type Analysis
Passenger Vessels: These vessels, including electric ferries, water taxis and cruise ships, can be integrated into B2G systems by storing energy at berth and supplying energy to the grid during peak periods.
Cargo Vessels: These larger vessels can offer greater energy storage capacity and are potential participants in B2G systems, especially in areas with high energy demand. Various boats, such as cargo ships, electric container ships, and bulk carriers, are used by the maritime industry to transport commodities.
Recreational and Leisure Vessels: Motorboats, sailboats, and electric yachts provide unique opportunities for connecting with local energy networks in remote or off-grid areas, particularly along the coast or in recreational regions.
Fishing Vessels: Electric fishing boats are a type of fishing vessel. In areas where the maritime industry is implementing energy-efficient projects, smaller fishing boats might be involved in B2G activities.
Hybrid Vessels: Machines that mix classic fossil fuel engines with electric systems are great for B2G. They can run independently from the grid and join the electricity network when necessary.
Application Analysis
Lattice Stability and Energy Storage: Excess energy produced by renewable sources (wind, solar) is stored in electrical containers and released when grid demand is high. Grid stabilisation is aided by this, particularly in regions where renewable energy is widely used.
Implementing Green Energy Sources: Boats can play a key role in integrating solar or wind energy into networks by intervening as energy storage devices.
Sea Traffic: Electrical ferries and leisure vessels can reduce emissions and integrate into grid systems and contribute to decarbonization efforts in maritime transport.
Port Operations: Electric boats are used in port operation and offer energy storage and network support. You can store excess energy that are generated from the port operation and deliver them to the network again.
End-User Analysis
Supply Company: Utilities can leverage B2G systems to manage grid balance and optimize energy distribution. They can use electric vessels as mobile energy storage units to stabilize local grids and help balance supply and demand.
Commercial Maritime Operators: The operators include shipping companies, cargo operators, and ferry services that integrate electric vessels into their fleets, either for environmental benefits or as part of green energy strategies.
Governments and Communities: Governments and municipalities can use B2G technologies to support sustainable transport solutions, reduce carbon emissions and to ensure more reliable energy in ports or coastal regions.
Energy Suppliers: Companies that offer renewable energies and develop microgrids or smart grid solutions can integrate electrical boats as part of their energy storage and distribution networks.
Private Users: Private users include owners of electric yachts, leisure boots and small fishing providers who can take part in local B2G systems, especially in remote or off-grid regions.
Regional Analysis
The boat-to-grid (B2G) technology market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. Here is a brief overview of each region:
North America: The North American boat-to-grid technology industry is expected to grow significantly due to government support, maritime electrification advancements, and renewable energy integration, as both the US and Canada prioritize reducing carbon dioxide emissions in the maritime sector. The rise of electric and hybrid vessels is contributing to a more resilient electrical grid, especially within commercial shipping and ferry operations. Innovative zero-emission initiatives that facilitate boat-to-grid systems are currently being piloted in ports like Los Angeles and Vancouver. With additional investments, North America could emerge as a leader in the global boat-to-grid market.
Europe: Europe is making significant financial investments in environmentally friendly marine technologies as part of its commitment to reduce carbon emissions. The European Commission's "Fit for 55" mission aims to cut greenhouse gas emissions by 55% by 2030, focusing on energy production, renewable technologies, and marine electrification. The EU is spending money on smart grid infrastructure to make using electric boats more efficient. Scandinavian countries and the UK are leading in hybrid and electric ferries that can support local renewable energy grids, particularly in island nations like Denmark and Greece.
Asia-Pacific: As one of the world�s most dynamic maritime regions, with major maritime hubs like China, Japan, South Korea, and Australia, APAC is well-positioned to leverage Boat-to-Grid (B2G) systems to address its energy challenges, particularly the integration of renewable energy and improving grid stability. B2G technology helps stabilize the grid by storing extra renewable energy when production is high and returning it to the grid when production is low. The use of electric and hybrid vessels is increasing in the Asia Pacific, particularly in China, Japan, and South Korea, due to the need to lower emissions and meet strict environmental rules like the IMO standards. Governments in this region are providing incentives to support the development of electric vessels, assisting in covering the higher costs of electric boats and necessary infrastructure for B2G systems.
LAMEA: LAMEA countries like Brazil, South Africa, and the UAE are investing in renewable energy projects, especially solar and wind. Boat-to-grid (B2G) systems may help stabilize the grid by storing excess renewable energy in electric boats and releasing it when needed, balancing supply and demand for better energy security. Brazil and the UAE are using hybrid and electric vessels to cut emissions in maritime transport, which can work with B2G systems. Smart grid technologies are also being developed in these regions. With ongoing government support and collaboration, LAMEA can use boat-to-grid technology for energy resilience and economic growth.
Boat-to-Grid (B2G) Technology Market Top Companies
- Siemens AG
- ABB Ltd.
- Schneider Electric
- General Electric (GE)
- W�rtsil� Corporation
- Rolls-Royce Power Systems
- Yanmar Co., Ltd.
- Tesla Inc.
- Nidec Corporation
- Vestas Wind Systems
- Man Energy Solutions
- Norwegian Electric Systems (NES)
- PowerCell Sweden AB
- Caterpillar Inc.
- DNV GL
- Eelpower Ltd.
- Eidesvik Offshore
- Vigo Marine
- Soventix
- Bollinger Shipyards
- Kongsberg Gruppen
- Golden Gate Zero Emission Marine
- Naval Group
- Triton Submarines
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- Lloyd's Register
- Van der Velden
- ZES (Zero Emission Services)
- Corvus Energy
- Navico
- BMT Group
- Ocean Infinity
- Teledyne Marine
Recent Developments
- In November 2024, Volvo Penta, in collaboration with Varberg Energi and Ferroamp, will test Boat-to-Grid (B2G) technology to explore the possibility of enabling batteries for electric and hybrid boats to support the electrical grid. The goal of this step-by-step process is to explore, learn and test how this technology can ultimately accelerate the electrification of maritime recreation.
- In June 2024, BlueGrid and Aqua superPower are the driving forces behind the first transatlantic vessel-to-grid marine electrification initiative. This transatlantic partnership will deploy bi-directional chargers and electric vessels in Plymouth, UK, and Halifax, Canada. These real-world installations will feature V2G capabilities in both software and hardware, onshore and aboard the vessels.
- In May 2024, BlueGrid a global market leader in high-output electric motor systems Evoy, and aluminum boat manufacturer ABCO announced the successful demonstration of the first high-power vessel-to-grid (V2G) globally. With the help of this cutting-edge V2G technology, electric vessel batteries and electrical grids may exchange power in both directions, giving owners of electric vessels new revenue streams and providing much-needed energy storage to electricity networks to help balance intermittent renewable electricity output.
Market Segmentation
By Technology
- Energy Storage Systems
- Electric Propulsion Systems
- Grid Connection and Power Electronics
- Communication and Control Systems
By Vessel Type
- Passenger Vessels
- Cargo Vessels
- Leisure and Recreational Boats
- Fishing Vessels
- Hybrid Vessels
By Application�
- Energy Storage and Grid Stabilization
- Renewable Energy Integration
- Maritime Transport
- Port Operations
By End-User�
- Utility Companies
- Commercial Maritime Operators
- Governments and Municipalities
- Energy Providers
- Private Users
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- APAC
- LAMEA
