Asthma Treatment Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
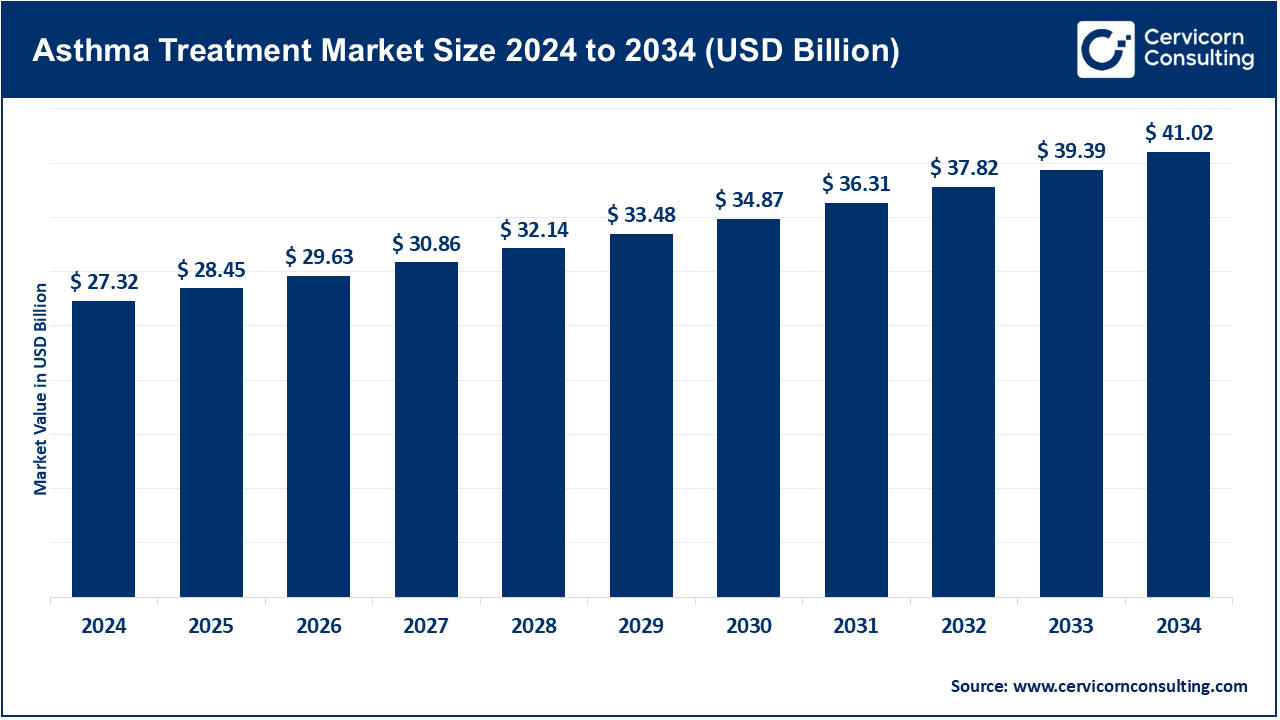
The global asthma treatment market size was reached at USD 27.32 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 41.02 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.9% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The asthma treatment market will grow at a significant rate owing to increasing prevalence of respiratory disorders, rising pollution levels, and advancements in biologics and inhalation therapies. Additionally, improved awareness, early diagnosis, and government initiatives to enhance healthcare infrastructure are driving demand for innovative and personalized asthma management solutions.
The prevalence of asthma, as well as pollution levels, is directly contributing to the rapid growth of the asthma treatment market. The market continues to expand due to advancements in personalized medicine as well as new innovations such as biologics, smart inhalers, and AI-powered monitoring tools. These advancements increase adherence to treatment protocols and precision in treatment execution. As pharmaceutical companies work on more precise therapeutics for complex asthma, symptom monitoring is being automated digitally in real time. Integration of technology with health care is developing advanced systems for the delivery of care. Focused innovation stemming from policies for expedited approval is being amplified. All in all, the shift is in the direction of more responsive, nimble, sophisticated systems for asthma care that prioritize the patient.
Asthma Treatment Market Report Highlights
- By region, North America has accounted highest revenue share of around 39.5% in 2024.
- By treatment, the long-term control medications segment has recorded a revenue share of around 64% in 2024, owing to rising chronic asthma cases and the need for daily symptom management, long-term control drugs dominate the treatment segment.
- By route of administration, the inhaled segment has recorded a revenue share of around 68% in 2024, owing to fast lung absorption, improved efficacy, and fewer systemic effects, inhaled delivery remains the most preferred administration method.
- By distribution channel, the retail pharmacies & drug stores segment has recorded a revenue share of around 45% in 2024 due to high prescription volumes and accessibility in retail and hospital pharmacies, inhaled products lead distribution in asthma treatment.
- By patient type, the adult patients (18–64 years) segment has recorded a revenue share of around 50.5% in 2024, due to greater diagnosis rates and occupational exposure, adults represent the majority of asthma patients using long-term therapy solutions.
- By technology integration, the smart inhalers segment has recorded a revenue share of around 40.1% in 2024 due to growing use of digital inhalers with tracking features, technology-integrated inhaled therapies dominate innovation in asthma care.
Asthma Treatment Market Growth Factors
- The increased burden of asthma on public health: asthma is a chronic inflammatory condition of the respiratory system; episodes of breathlessness and wheezing characterize the disease. Major public health issues were recorded in 2025, with approximately 345 million asthma sufferers globally, stemming alongside a shocking registration of 345,000 deaths a year attributed to the chronic ailment. The urban population of adolescents has a greater prevalence than their rural counterparts, sitting at almost 12% versus 9%. In 2024, data from India revealed that figure standing at 35 million. It was confirmed by WHO reports in early 2025 that Africa is facing a sharp rise in the under-diagnosing the disease. This was discussed further in a 2024 WHO workshop which attributed the surge primarily to persistent urbanization. The data indicates that the patient population continues to increase resulting in an ever-growing need for sophisticated treatment and monitoring systems.
- Increased Air Pollution and Allergens: Pollution comprises harmful substances like PMâ‚‚.â‚… and NOâ‚‚ which worsen asthma both in severity and incidence. Evidence in 2024 indicated approximately one-third of new childhood asthma cases in Europe were associated with PMâ‚‚.â‚… exposure. Pediatric asthma rates alongside poor air quality in Southeast Asia and Africa from 2023–2025 contributed to the region’s rapid urban growth. Indoor allergens, specifically mold and dust mites, persist as enduring triggers in the humid Southeast Asian regions. The Middle East’s emerging climate phenomena of dust storms in 2024 also exacerbated respiratory health. WHO’s 2025 summit on environmental health placed focus on these matters, calling for stricter controls on pollution. This situation continues to create a heightened need for public health measures as well as medication and monitoring systems.
- Developments in Biologics and Monoclonal Antibodies: Biological agents are designated treatments that use antibodies to alter immune responses in severe asthma. Between 2023 and 2025, Tezepelumab underwent extensive adoption after receiving approval for self-administration in early 2023. By mid-2024, the CHRONICLE registry reported that 67% of new biologic initiations in severe asthma were on Tezepelumab or dupilumab. Next generation agents’ Phase III trials continued through 2024, demonstrating a marked reduction in exacerbation as compared to standard care. Label expansions now include treatment for nasal polyposis and COPD, with regulatory confirmation anticipated in 2025. Real-world efficacy data that supports wider use of biologics in asthma therapy was presented at an FDA advisory meeting in 2024. These advances reinforce the rapid and profound impact that biologics are having on the treatment of asthma.
Asthma Treatment Market Trends
- Shift Towards Personalized and Precision Medicine: The treatment of asthma is increasingly advanced; it aims at delineating patient biomarkers and profiles to maximize the treatment impact. By 2023, the selection of biologics was based on eosinophils, IgE, and certain TSLP pathway markers. The approval of Tezepelumab for TSLP-driven asthma marked another milestone in mid-2023. Then, in late 2024, dupilumab gained an overlapping indication for asthma and COPD. Companion diagnostic tests started to be reimbursed by most North American and European health systems by 2025. During an EU Council meeting in 2024, the use of precision medicine for chronic respiratory diseases was highlighted as a cost-containment strategy. The healthcare system is transforming toward integrated diagnostics, decreasing dependence on non-targeted therapies, and increasing funding for targeted investigations based on specific phenotypes.
- Self-Administered and Home-Based Treatments: The home-based aspect of asthma management allows patients to adjust their medication dosages without needing to visit a clinic. Self-care options became available in 2023 with the subcutaneous, biannual dosing of long-acting injectable biologics like depemokimab. Projected regulatory approval of smart inhalers equipped with home-based digital adherence tracking systems for 2024-25 is likely to further enhance adherence metrics. Real-world pilot studies conducted in European clinics indicate a 30% reduction in hospital visits from these regions. 2024 saw regulators change guidelines to allow remote initiation of therapy alongside at-home training. There was also increased use of North American digital coaching for proper inhaler technique. There is a shift toward the decentralization of asthma care, which enhances patient empowerment while alleviating clinic burden.
- Expansion of Telehealth Services for Asthma: Telehealth embraces virtual platforms for asthma education, monitoring, and management. In low-income nations, WHO-guided tele-asthma initiatives slashed emergency visits by 70% by 2023. In 2024, the Indian Digital Health Mission initiated remote area-centric teleconsults for asthma. Mid-2024 saw the integration of remote spirometry with inhaler feedback into primary-care telehealth. European and North American insurers began reimbursing tele-asthma services in 2025. This expansion of telehealth not only enhanced healthcare access but also bridged the urban-rural divide. This surge in telehealth services is now fundamental to optimizing asthma care systems.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 28.45 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 |
USD 41.02 Billion |
| Projected Market CAGR 2025 to 2034 |
5.90% |
| Top-ranking Region |
North America |
| Top Expanding Region |
Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments |
Treatment, Route of Administration, Patient Type, Technology Integration, Distribution Channel, Region |
| Key Companies |
AstraZeneca, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., GlaxoSmithKline plc, Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH, Roche Holding AG / Novartis AG, Merck & Co., Inc., Koninklijke Philips N.V., Sanofi-Aventis SA, MundiPharma. |
Asthma Treatment Market Dynamics
Market Drivers
- Increased Incidence of Asthma Due to Urbanization and Lifestyle Changes: Sedentary living and urbanization, along with pollution, sharply elevate the incidence of asthma. Between 2023 and 2025, global asthma cases increased from 300 million to approximately 334 million. The prevalence among adolescents in urban areas reached 12%. By 2024, Indian metropolitan regions will have documented close to 35 million diagnosed cases. From 2023 to 2025, studies conducted in the Eastern Mediterranean region reported the prevalence among children in urban areas to be greater than 11%. Air pollution resulting from industries was juxtaposed with changing lifestyles as leading accelerants in the WHOs urban health reports for 2024. The increasing volume of asthma patients in urban centers is, in turn, increasing the need for diagnostic, therapeutic, and management innovation. This demographic trend indicates more aggressive strategies for capturing new market segments.
- Need for Biologics and Controllers for Severe and Uncontrolled Asthma: Advanced asthma therapies include new-generation biologics, as well as advanced controllers aimed at staving off severe or uncontrolled asthma. The persistent global asthma-related death toll of 345,000 per year during 2023-2025 mirrors a rising prevalence of the condition, indicating considerable gaps in treatment. OECD countries have been urged to shift treatment protocols to prioritize biologics for uncontrolled eosinophilic asthma. As of early 2025, half of patients with severe asthma were placed on biologics, instead of being treated with escalating doses of ICS. Approval of Nucala for COPD in 2025 demonstrates both cross-disease applicability and greater market potential. Medications aimed at reducing the frequency of exacerbations and dependence on steroids are in demand. Enhanced insurance reimbursement policies are leading to greater use of these drugs which, sequentially, stimulates further development in the therapeutic pipeline.
- Initiatives Focused on Screening as well as Early Clinical and Pharmaceutical Action: Early diagnostic measures along with timely action are required in order to prevent the emergence of chronic health conditions. Following 2023, global initiatives by WHO and Global Asthma Network Enhanced screening and early diagnosis for asthma globally. From 2023 to 2025, pilot projects testing digital diagnostic tools in rural areas of low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) showed a reduction of up to 70% in emergency visits. National asthma registries were introduced in India in late 2024 which allowed for earlier patient identification and tracking. Outcomes were greatly improved with early pharmacological intervention using ICS/LABA combination therapy. Symptom tracking and virtual consultations became available through apps in 2024. There has also been an increase in the need for services related to healthcare education, diagnostics, and digital care tools due to the rising focus on health. Clinical diagnosis through digital applications along with virtual consultations foster remote healthcare access, improving the overall standard of care.
Market Restraints
- Prohibitive Pricing of Inhalers and Biologic Therapies: Advanced inhalers and biologics offer powerful treatments but remains inaccessible for many. Biologics often surpassed the per capita health expenditure in low-income countries as of 2025. In these regions, only one-third of public clinics had basic inhaled corticosteroids in 2024. In middle- and higher-income countries, insurer prior-authorization backlogs stunted initiation of biologics in over 40% of cases during 2023-2024. High patient out-of-pocket costs further limited access despite proven efficacy. Trials of outcomes-based reimbursement models started in late 2024, yet there is still rarity in widespread implementation. Cost-related inaccessibility remains the primary barrier to equitable care and market penetration.
- Lack of Access to Asthma Care Diagnostics in Low Middle Income Countries: Quality asthma care entails appropriate diagnosis, medication, and follow-up. Approximately 79% of asthma-related deaths in 2024 were in low to middle-income countries. The absence of diagnostic tools persists in more than half of these regions. Their rural clinics remain incapable of offering digital or biological services. There was a very limited expansion of primary care provider training programs through the year 2025. Further cold chain distribution of biologics into remote areas. Asthma services are still hampered by infrastructure and resource gaps.
- Complications and Side Effects of Steroid Use: Low bone density and stunted growth are recognized side effects of inhaled corticosteroids (ICS), especially for children. There were reports of overprescription of short-acting reliever inhalers. Many practitioners are noting some negative effects with that trend. The WHO and some country-specific organizations issued health alerts as early as 2025, marking steroid misuse, highlighting the need for safer alternatives. Patients, in their own reports, expressed anxiety related to the side effects, which made them less adherent to treatment. Even though there are biologics that reduce the need for steroids, many regions still have limited access to them. The regions most impacted by these barriers are those where the long-term consequences of treatment non-adherence are likely to be most pronounced.
Market Opportunities
- Collaborations Between Biotech Firms and Tech Companies: Collaborations between biotech and tech firms combine drug development with digital enablement. In early 2024, GSK acquired Aiolos Bio to advance respiratory biologic platforms. Pilots pairing smart inhalers with app-based adherence tracking were rolled out in Europe through late 2023 and early 2024. Public-private programs under EU and WHO frameworks demonstrated better clinical outcomes and engagement in 2024. Regulatory agencies increasingly supported such integrated digital therapeutics from 2023 onward. These synergies use real-time data for adherence reinforcement and precision deployment. The result is a powerful market opportunity merging pharmaceuticals and digital health.
- Digital Services in Respiratory Health: Specific programs are already funding telemonitoring devices for asthma and other areas of respiratory health. Between 2023 and 2025, funding was allocated for telemonitoring in several countries under the WHO PEN and GARD programs. In 2024, the NHMD of India released asthma modules targeting rural regions. Also in 2024, the EU Horizon Programs were initiated to fund the development of connected inhalers. New grant programs designed to screen for AI-powered primary care were introduced in late 2023. These government policies tend to reduce the burden of innovation and entrepreneurship on the private sector. There is a greater opportunity for widespread adoption of digital solutions when complemented with subsidized public funding.
- Advances in biologics asthma therapy focusing on specific subtypes: Biologics aim to make asthma treatment more effective by personalizing therapy to the specific subtypes, as with eosinophilic asthma which is treated with tezepelumab and TSLP-driven asthma which is treated by depemokimab. Both medications received approval from 2023 to 2025. Ongoing clinical trials are investigating agents aimed at rare phenotypes, including those with high periostin levels until 2025. Dupilumab’s label expansion will incorporate nasal polyposis and later COPD in 2025 showcasing multifunctional utility. Regulatory frameworks are starting to embrace treatment segmentation utilizing biomarkers. These Phentermine-based drugs are overwhelming insurance companies because of their apparent cost-efficiency resulting in wider acceptance. Such markets are characterized by high profitability and reduced competition.
Market Challenges
- Incorporation of Smart Devices Data into Clinical Workflows: Smart respiratory devices capture vast amounts of data that could be useful for clinical workflows; however, integration into practice is lacking. As of 2025, most health facilities still do not have standardized APIs or EHR interoperability for inhaler data. As of 2024, more than 65% of clinicians reported a feeling of inadequacy regarding their interpretation of digital adherence metrics. Compliance frameworks such as HIPAA and GDPR emphasize the need for sound data governance practices, while the AI and ML on healthcare regulations of 2024 remain stagnant, demonstrating a lack of forward-thinking. Because of insufficient data integration, digital devices are underutilized. To enable truly holistic and fully digital asthma care, gaps in healthcare provider education, compliance, data sharing and interoperability frameworks need to be addressed.
- The Algorithms of Asthma Care as An Example of Ethical AI: Integrating Explainability, Fairness, and Informed Consent. A perspective on ethical AI in asthma care incorporates explainability, fairness, and informed consent. Expected regulations for EU and US digital therapeutics in 2025 center on explainability and bias as primary concerns. Trust issues with AI systems described as operating on “black box” principles were reported by 33% of survey participants in 2024. Companies have legal, ethical, and privacy obligations under informed consent and privacy shielding. EMA/FDA draft guidance in 2023-2024 emphasized compliance, trust, innovation, and the vital role of patient participation framing the use of AI as a sustainable integration of health services. As evolving prerequisites accrue, trust frameworks are still paramount.
- Remote Biologic Delivery: Quality Control Challenges. Preserving the cold-chain and batch consistency makes biologics critical to quality control. Regulatory scrutiny of Tezepelumab and Depemokimab manufacturers from 2023 to 2025 was more rigorous. There were episodic cold-chain therapeutic failures in 2024. Raw material production was halted due to geopolitical disruptions in late 2023. There were increasing compliance complexities from an expanding multi-site biotech market with diverse regulatory environments, as well as logistical cost constraints which delayed regional launches. To have a presence in the market, companies must maintain reliable supply chains and adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
Asthma Treatment Market Segmental Analysis
Treatment Analysis
Long-Term Control Medications: These are daily treatments, usually inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) and long-acting bronchodilators, aimed at reducing airway inflammation and preventing exacerbations of asthma. The WHO reports that as of 2023, only about 50% of low or middle-income countries, often referred to as lower-income countries, regularly stock essential ICS medications. These health systems have restricted the procurement and distribution of long-term agents to combat under-treatment through 2024. Tezepelumab and dupilumab injections—now positioned alongside ICS for severe cases—were approved in 2022 and 2023. The FDA endorsed tezepelumab for home-administered biologic control in early 2025. These policies illustrate the worldwide focus on integrating proactive and preventive strategies in the management of asthma.
Asthma Treatment Market Revenue Share, By Treatment, 2024 (%)
| Treatment |
Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Long-Term Control Medications |
64% |
| Quick-Relief Medications |
36% |
Quick-relief Medications: SABAs are classified as Short-Acting Bronchodilators which are a type of quick-relief medication. During an acute asthmatic episode, bronchospasm responds to SABAs quickly and effectively. As reported by the World Health Organization in 2024, approximately 70% of primary care clinics in underserved countries have SABAs available. Despite this, dependable access to these medications remains a challenge. Recent WHO asthma surveys indicate a disproportionate reliance on rescue inhalers, emphasizing short-term relief rather than long-term prevention. Patient education aimed at the overuse of rescue devices has been mandated as of mid-2024 in many national guidelines. An exacerbation of environmental triggers from 2023-2025 has heightened the need for quick-relief medication management. Subsidized inhalers are now being distributed to at-risk populations during high-pollution seasons. These policies strive to balance urgent responsiveness with sustainable control.
Route of Administration Analysis
Injectables: The Injectable route encompasses biologics given subcutaneously or IV for severe asthma. Tezepelumab's home administration approval in early 2023 marked a milestone for non-hospital biologic administration. According to mid-2024 data from the CHRONICLE registry, 67% of severe-asthma biologic starts were with injectables, including dupilumab and tezepelumab. The mid-2024 expansion of labeled use added nasal polyps and COPD overlap. In 2025, insurers reimbursed home-administered injectables based on outcomes-based contracts. This route offers unparalleled convenience and accessibility for severe asthma therapy.
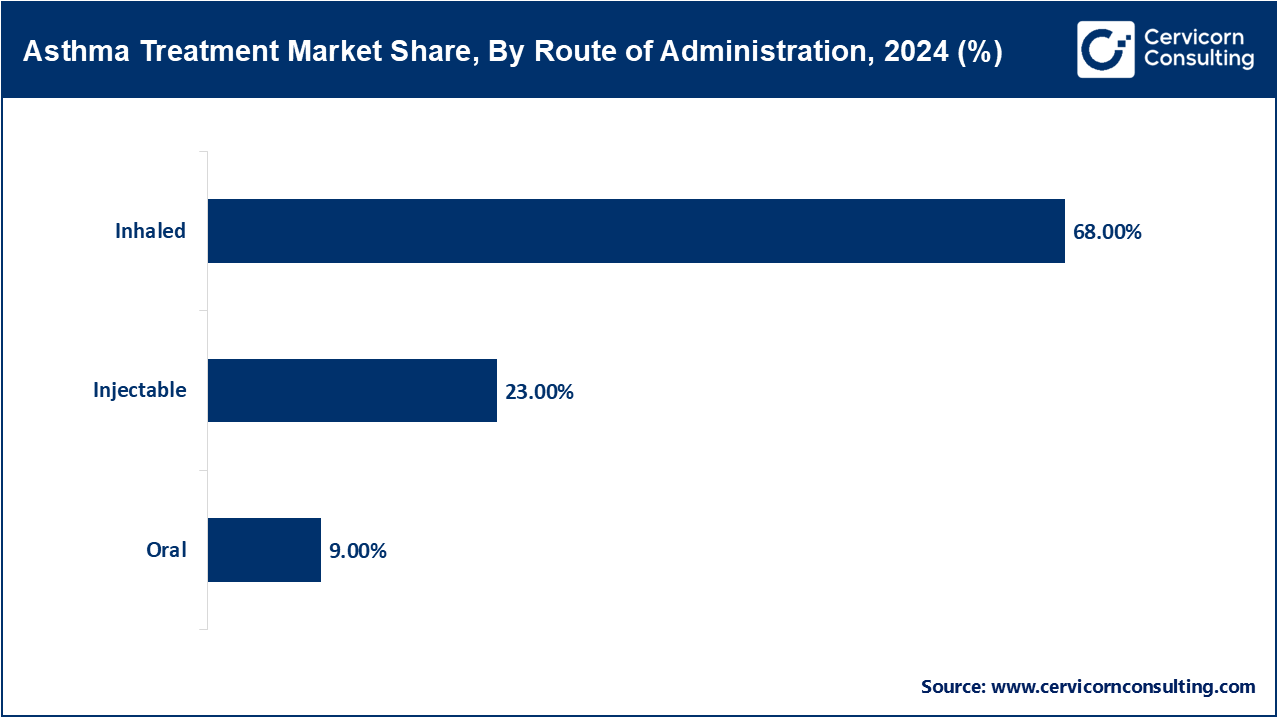
Oral: In the case of asthma which is moderate to severe, it can be managed with leukotriene modifiers and system corticosteroids. In the year 2023, WHO stated that oral controllers were included in approximately 20% of asthma management plans within LMICs. Justifications for prescribing oral montelukast for long-term control were confirmed with the updates to Essential Medicines List in late 2024, however, there are still concerns regarding the systemic steroid pills and the potential for side effects, over-prescription, and a lack of justified clinical uses. As of early 2025, there was a shift in WHO guidance towards reducing the use of oral steroids and favoring inhaled or biologic therapies. These policy changes seem to strive to provide an adequate therapeutic benefit while minimizing the risk of adverse events.
Inhaled: The Intermittent reliever and Combination Inhaler ICS, LABA are the most frequently utilized and therefore, the most served routes. As stated ICS is available in over 80% of pharmacies in high- and middle-income countries as per the 2023 WHO report. In 2024, WHO encouraged the adoption of inhaler devices without propellants to reduce carbon emissions. Additionally, in 2025 there was an announcement about a partnership between a major inhaler manufacturer and several international organizations for disease control to provide subsidized inhalers to rural regions in Africa. In February 2024, select clinics in Europe initiated the piloting of digital-dose counter inhalers, which enhance monitoring adherence. The basic and advanced levels of asthma care still primarily utilize inhalation as the method of delivery.
Distribution Channel Analysis
Hospital Pharmacies: Biologics and sophisticated therapies are increasingly important to modern hospital pharmacy practice. According to WHO, as of 2024 more than 90% of hospital pharmacies in high-income countries stock asthma biologics. Tezepelumab, which was approved for hospital use in 2023 and will be authorized for home use in 2025, demonstrates the importance of this channel. In late 2024, pharmacies in several regions began to incorporate smart inhaler monitoring systems into their standard operating procedures. Those hospitals are now training and supervising complex dose and education systems for advanced asthma therapies. Thus, hospital pharmacies function as both logistics and teaching centers for asthma care.
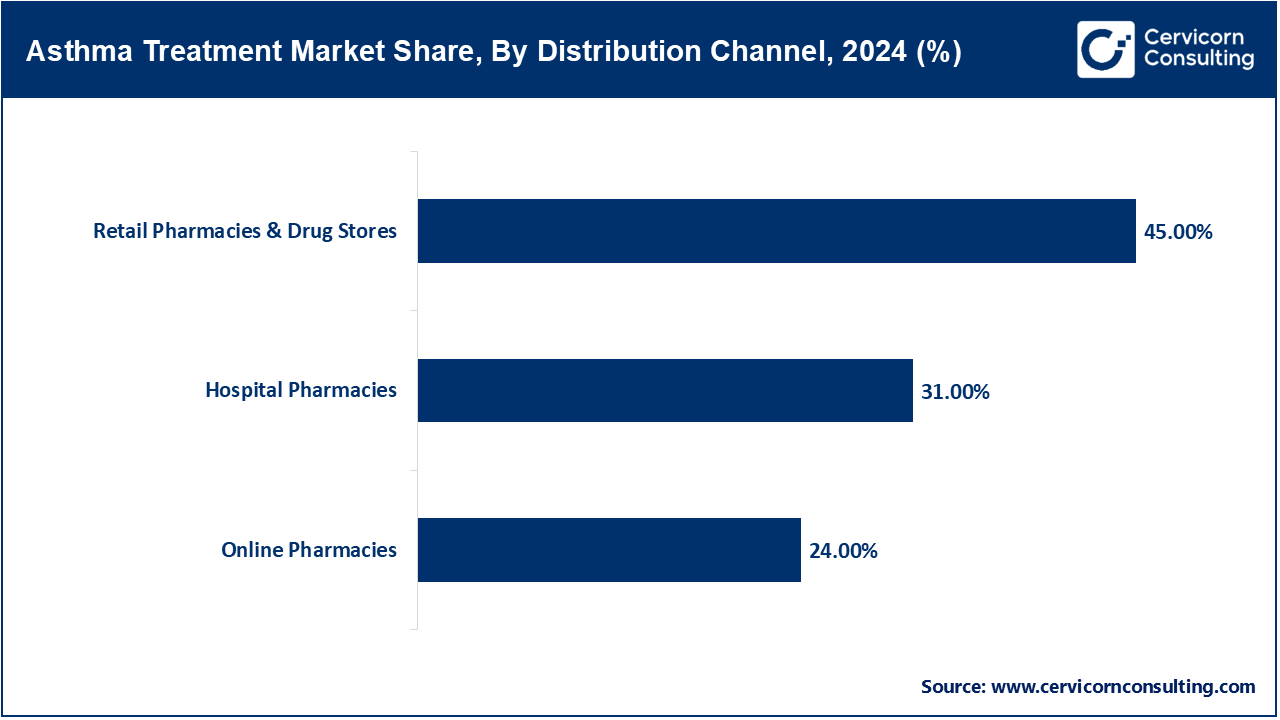
Retail Pharmacies & Drug Stores: Retail pharmacies are the first point of contact for both OTC and prescription inhalers and oral medications. WHO 2024 estimates suggest 75% of retail pharmacies located in urban areas have ICS/LABA combo inhalers. Early in 2025, a national drug code change enabled the tracking of smart inhalers at the retail level. Many retail chains in Europe and North America started offering inhaler technique teaching in 2023. Collaboration between retailers and digital health companies to embed inhaler-tracker apps into inhalers is on the rise. This area continues to be important for patient education, access, and proactive management.
E-Pharmacies: E-pharmacies sell asthma medication through e-commerce platforms, which increases convenience and potentially access. Since 2023, the WHO has been tracking the quality of online listings for OTC medications, finding that approximately 10% of listed digital products for asthma lacked proper verification. Laws passed during 2024-2025 regulated online sales to require confirmation of prescription, validation, and authenticity of the products being sold. During the coronavirus period, there was a 40% increase in the sales of refill and OTC medications and most of those gains have remained. As of 2024, telehealth services have partnered with licensed pharmacies enabling integrated prescribing and delivery. The online channels are widening the range, especially for the rural elderly and people with physical disabilities.
Patient Type Analysis
Pediatric patients aged 0 to 17 years: Pediatric asthma describes children with persistent inflammation of the airways accompanied by wheezing and dyspnoea. Asthma affects about 300 million people globally in 2023 with children accounting for a significant portion; the WHO approximates 0.7 per 100,000 pediatric deaths annually. In rural Karnataka, India, around 4% of children are reported to have current wheezing, with 63.9% of those cases being classified as severe, which indicates a major therapeutic gap illustrating slack. Schools in Africa report ≤33% formally diagnosed. From 2023-2025, pilot programs for digital monitoring apps and smart inhalers have been conducted in children. In the educational environment, innovations such as portable wheeze detectors are being tested. These attempts illustrate the persistent stagnation in the timely diagnosis within the context of prompt multi-dimensional frameworks, adherence scaffolds, medication distribution systems, and proactive medication frameworks addressing system gaps.
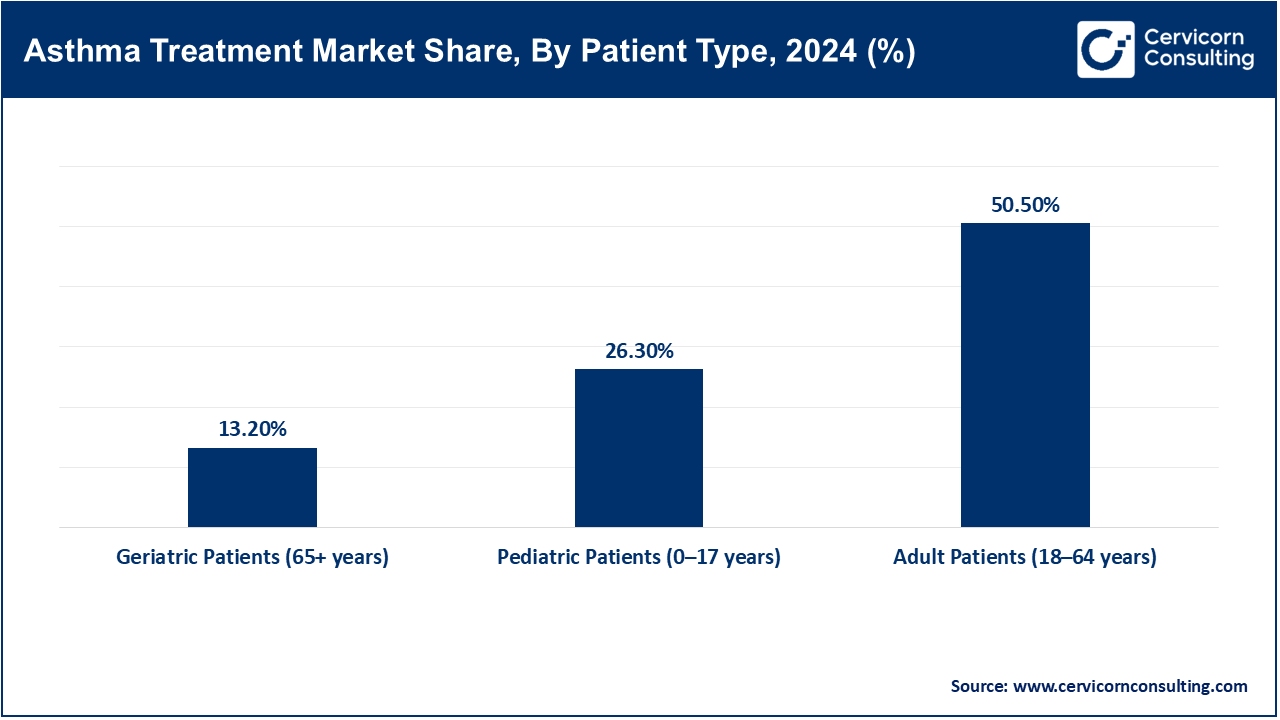
Adult Patients (18–64 Years): This cohort includes working adults in the chronic stage of the disease. In 2021, the US recorded over 20 million adults with asthma, resulting in $94,000 worth of hospital admissions and nearly 1 million ER visits each year. Relief medications and digital inhalers that sync with smartphones are more commonly used during this stage. In 2023, the AAAAI and CDC authorized remote monitoring codes for smart inhaler and mobile spirometer users. Per Baystate Noble Hospital pilot studies, AI-enabled RPM apps reduced ER visits by thousands between 2023 and 2025. These systems strengthen clinician supervision and enhance chronic adherence. The adult asthma strategy pivoted to focusing and refining chronic illness management with sophisticated analytics.
Geriatric Patients (65+ years): Asthmatic older adults frequently experience reduced lung function alongside other chronic diseases and polypharmacy. In 2023, Medicare RPM coverage extended to over 16,000 patients, improving medication adherence and reducing hospitalizations. Pulse oximetry devices which allow self-monitoring of breathing and were approved in 2023, assist geriatric patients. Remote patient monitoring (RPM) systems put in place during the pandemic continued through 2025, enabling physicians to monitor respiratory metrics during non-contact visits. The acceptance of Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) is driven by the newly created billing codes for RPM services from Medicare. The outcome of RPM is particularly beneficial for older patients. These changes demonstrate the evolution of policy regarding patients with asthma in the geriatric population towards promoting self-sufficiency and lessening hospital admissions.
Technology Integration Analysis
AI & Bluetooth Integrated Devices: Smart inhalers equipped with Bluetooth and artificial intelligence technologies monitor patient adherence to inhalation and medication protocols in real time. They improve adherence by notifying patients and caregivers, thus minimizing hospital admissions. ProAir Digihaler by Teva was integrated into remote asthma management systems in U.S. hospitals in 20203, which operated on a data driven system. An NIH study showed users of smart inhalers reported over 30% reduction in monitored ER visits. Other systems, like NHS in the UK, are also pilot testing these technologies. The initiative was further extended in 2024 with digital inhalers from Propeller Health and AstraZeneca. By 2025, smart inhalers are anticipated to be incorporated into a fully integrated chronic precision medicine framework.
Connected Nebulizers: Connected nebulizers are portable, internet-connected devices for aerosol delivery systems, which stream data about use and techniques to the prescribing physician in real time. The continuous use of these devices during the pandemic has supported the management of chronic asthma, including telehealth supported rural clinic connected nebulizer programs Philips launched in India in 2023. According to ATS in its 2024 whitepaper, connected nebulizers are expected to reduce the tendency to over-prescribe steroids in pediatric asthma patients. Connected nebulizers come with automated caregiver alerts and reminder systems. Clinicians are able to view real-time dashboards providing data to make proactive changes. In 2025, some Medicaid programs in underserved areas began reimbursing connected nebulizer therapy. These advances improve clinical responsibility and access in the management of severe asthma.
Digital Adherence Monitors: Digital adherence monitors are small electronic sensors embedded into or affixed on the inhalers which track the temporal aspects of doses taken by the patient. Through mobile apps, data is uploaded and processed which track specific behaviors by the clinician and enables proactive intervention where necessary. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services published a study in 2023 stating that patients with adherence monitors showed 26% improvement in regular asthma medication use. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has recently issued reimbursement codes as of 2024 covering remote therapeutic monitoring (RTM) of adherence. Major firms like Cohero Health and Hailie have launched updated devices equipped with AI-based reminder systems and real-time alerts for caregivers. These tools have become commonplace as of 2025 in pediatric and geriatric asthma care programs. The technology curtails healthcare spending by reducing preventable exacerbations.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Platforms: These platforms enable healthcare professionals to monitor vital patient data remotely, including spirometry, oxygen saturation, and adherence to medications. Between 2023 and 2024, CMS expanded coverage for RPM under CPT codes 99453 and 99454 for both device provision and monitoring. In 2024, the AMA eliminated the 16-day transmission requirement, broadening access and boosting patient enrollment. In the U.S., Mount Sinai Health System incorporated RPM into asthma care pathways and reported lower high-risk readmission rates. More than 30 state Medicaid programs began reimbursing RPM in 2025, accelerating adoption in community health clinics. RPM tools are now equipped with AI-powered dashboards that predict the occurrence of asthma attacks several minutes—or hours—before symptoms manifest. These platforms turn the management of asthma into a data-driven, proactive process.
Asthma Treatment Market Regional Analysis
The asthma treatment market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region:
What factors contribute to North America's leadership in the asthma treatment market?
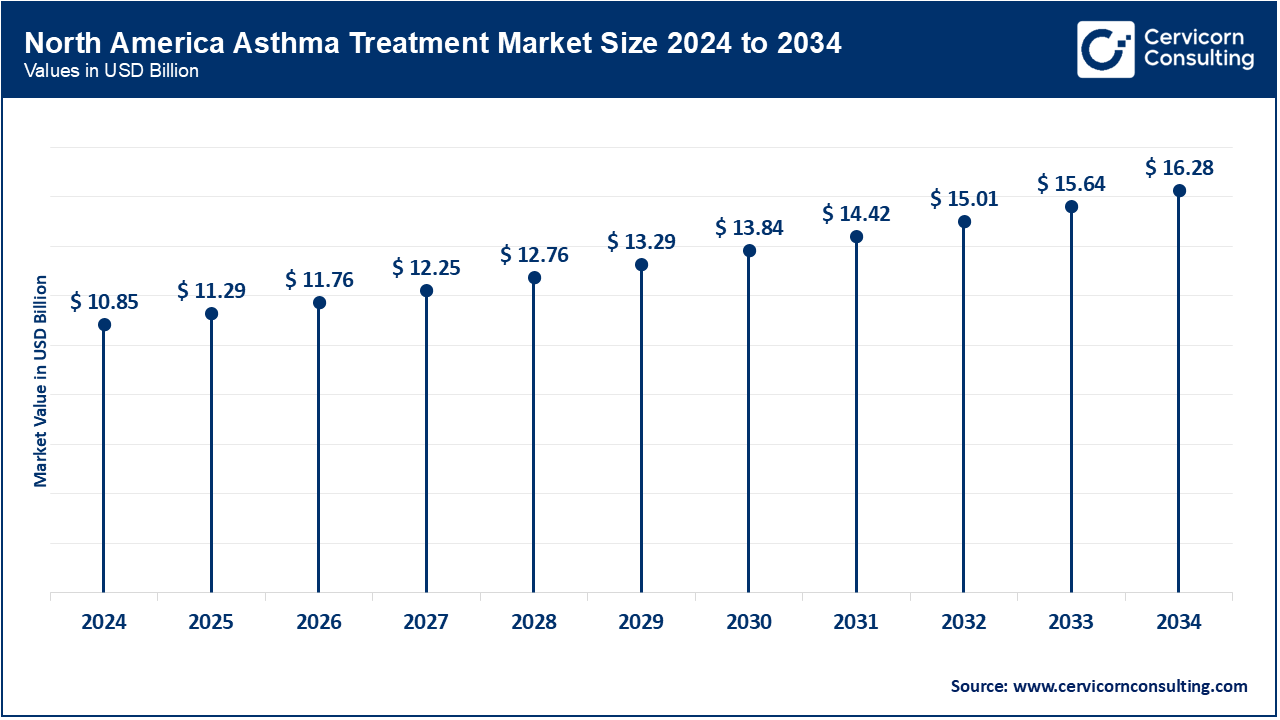
- North America Market Size in 2024: USD 10.85 Billion
- North America Market Expected Size in 2034: USD 16.28 Billion
North America maintains its position as a global leader in asthma management because of the newer biologics and inhalers accessible to patients. The CDC reported approximately 25 million Americans with asthma in 2023, resulting in 1.6 million emergency room visits annually. The self-administered Tezepelumab biologics seemed to have greatly benefited rural Americans by around 2024 regionally controlling their severe asthma. Canada's progress is notable too; some provincial public health insurances have started to cover more recent therapies. After the 2023 public campaigns, Mexico's Ministry of Health has also expanded issuing inhaled corticosteroids to rural clinics. Throughout the region, digital monitoring of patients and air quality alert systems are being integrated with clinical guidance. These programs are redefining the personalization and access paradigm for asthma management.
Europe Asthma Treatment Market Trends
- Europe Market Size in 2024: USD 5.44 Billion
- Europe Market Expected Size in 2034: USD 8.16 Billion
Addressing sustainability and access to biologics remains a focus for Europe’s asthma strategy. The NHS England launched a respiratory program in the UK which favored prescribing ICS inhalers instead of SABA inhalers due to their positive outcomes and for SABA's environmental impact. Germany set out a goal to improve medication adherence by 2024 by expanding reimbursement policies to include smart inhalers and mobile health apps. France's national guideline for asthma updated by late 2024 included monoclonal antibodies for children aged 6 and above with severe asthma. Propellant free inhalers are now granted by all regulatory bodies in Europe which fulfill climate as well as health care goals. Outpatient integration for asthma biologics is now commonplace in hospital settings. Europe is refining the accessibility and precision of asthma care through integrated clinical pathways alongside digital frameworks.
Why is the Asia-Pacific region driving faster growth in the asthma treatment market?
- Asia-Pacific Market Size in 2024: USD 7.32 Billion
- Asia-Pacific Market Expected Size in 2034: USD 10.99 Billion
Despite the rapid developments, the Asia-Pacific region still suffers from the disproportionate burden of asthma. Australia's AIHW telemedicine rollout and the funding for biologic therapies came after identifying 2.8 million asthma cases in 2023. In 2024, the National Health Mission of India facilitated access to ICS/LABA through procurement in the rural public sector. China diagnosed a rise in urban asthma cases which led to the implementation of diagnostic phenotypic therapeutic approaches in public hospitals in 2025. Japan revised treatment guidelines with an emphasis on biologic prescription for eosinophilic asthma. South Korea rolled out nation-wide spirometry screening for early diagnosis as of 2023. The region is now shifting from reactive treatment approaches to predictive, comprehensive-data care models alongside widened inhaler provision.
Asthma Treatment Market Revenue Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region |
Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America |
39.70% |
| Europe |
19.90% |
| Asia-Pacific |
26.80% |
| LAMEA |
13.60% |
LAMEA Asthma Treatment Market Trends
The LAMEA regions are now addressing a chronic lack of treatment with systematic changes. Brazil's Health Ministry ICSs released clinical protocols and subsidized ICSs after recognizing approximately 20,000 asthma-related deaths over the last decade spanning from 2020 to 2030. Saudi Arabia and UAE in 2023 sponsored access to combination inhalers and issued standardized asthma management protocols. South Africa started providing ICS and long-acting bronchodilator inhalers through its rural clinics in 2024 as part of its essential medicines policy. LAMEA regulatory authorities approved dupilumab and tezepelumab between 2023 and 2025. Train the Trainer campaigns for general practitioners are being implemented in parallel to the national awareness campaigns. There is emerging systematic emphasis on equitable asthma care.
Asthma Treatment Market Top Companies
Recent Developments
Recent partnerships in the asthma treatment market highlight innovation in drug delivery, biologics, and digital integration. AstraZeneca and Amgen continue their alliance on Tezspire, focusing on expanding global access and home-use options approved in 2024. Teva Pharmaceuticals partnered with MedinCell in 2023 to co-develop long-acting injectables for respiratory care. Boehringer Ingelheim collaborates with Click Therapeutics to develop digital therapeutics for asthma symptom tracking. GSK has teamed up with Propeller Health to integrate smart inhaler technology with patient adherence platforms. These collaborations enhance personalized care, improve adherence, and expand biologic accessibility. Together, they drive the market toward smarter, patient-centered asthma solutions.
- In May 2025, AstraZeneca will showcase new research from its comprehensive respiratory portfolio at the ATS 2025 conference, highlighting significant advances in asthma and COPD care. The company will present over 75 abstracts, including late-breaking data on inhaled therapies like Airsupra and Breztri, as well as biologics such as Fasenra and Tezspire. These studies focus on improving treatment outcomes, reducing exacerbations, and targeting underlying disease mechanisms. AstraZeneca’s pipeline also features early-stage assets and the use of AI to better understand and predict respiratory disease progression. The company’s efforts aim to address unmet needs across all severities of respiratory diseases and move towards disease modification and potential cures. This research underscores AstraZeneca’s commitment to transforming respiratory care for millions of patients worldwide.
- In May 2025, GSK announced it will present over 40 abstracts at the 2025 American Thoracic Society Congress, showcasing advances across its respiratory medicine portfolio, including inhaled therapies and biologics for asthma and COPD. Key highlights include new analyses from the MATINEE trial demonstrating mepolizumab’s ability to reduce COPD exacerbations and hospital visits, and updated data on the twice-yearly biologic depemokimab for asthma. Additional studies address treatment goals for severe asthma, refractory chronic cough, and the environmental impact of inhaler devices. GSK’s research aims to improve patient outcomes, prevent disease progression, and advance clinical remission in respiratory diseases. The company is committed to setting new standards in respiratory care through innovative science and technology.
Market Segmentation
By Treatment
- Long-Term Control Medications
- Quick-Relief Medications
By Route of Administration
By Patient Type
- Pediatric Patients (0–17 years)
- Adult Patients (18–64 years)
- Geriatric Patients (65+ years)
By Technology Integration
- Smart Inhalers (with Bluetooth/AI)
- Connected Nebulizers
- Digital Adherence Monitors
- Remote Patient Monitoring Platforms
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies & Drug Stores
- Online Pharmacies
By Region
- North America
- APAC
- Europe
- LAMEA




