The global smart gas meter market size was estimated at USD 4.18 billion in 2024 and is expected to surpass around USD 6.79 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.97% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The smart gas meter market is experiencing unpredicted universal advancement due to greater needs in industrialization, energy utilization, and urbanization, and practical and reliable energy regulation in industries like manufacturing, commercial infrastructure, and utilities. Civil operations are focusing on improving operational efficiencies, performance enhancement, and carbon impairment. Automation, AI-controlled processes, and digital twins are the technologies now employed. Encouraging the deployment of cleaner energies has been supported by retained global government focus, and smart gas metering technologies are the main targets to achieve energy system regulated transition.
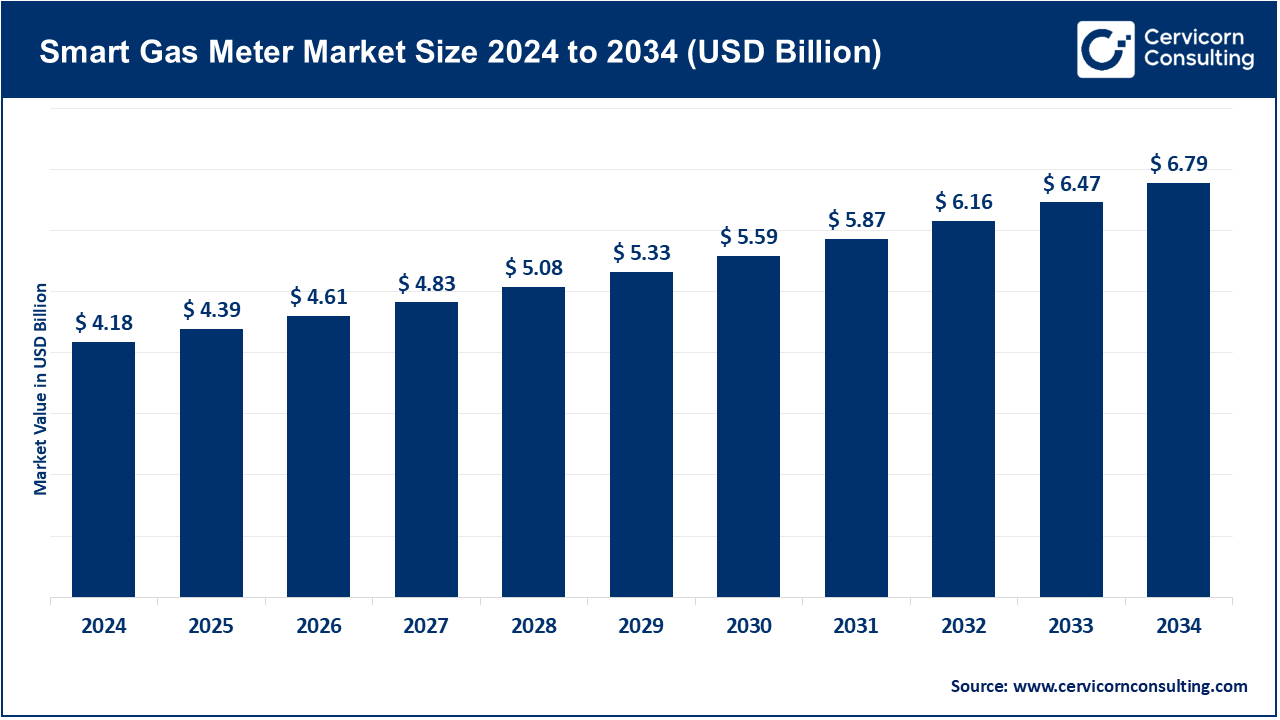
Having IoT-enabled monitoring system and smart grid interconnected energy resources control technologies the gas measures can now provide real time energy measurement and predictive calculations. Moreover, the reduction of gas emissions is now eco-friendly release goal. Hence, the gas meter devises control and calculate fuel consumption, gas release and, predictive gas measuring in commercial and industrial utilization. The gas meter devises are hybrid smart gas meters with gas meters integration with renewable gas to fulfill gas emission reduction goal. Hence, the smart gas meters are now utilized in modern ranch energy infrastructure as environment regulated and measurement enforcement devises.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 4.39 Billion |
| Estimated Market Size in 2034 | USD 6.79 Billion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 4.97% |
| Dominant Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Component, Type, Technology, Communication Type, Energy Type, End-User, Region |
| Key Companies | Itron Inc., Landis+Gyr Group AG, Elster Group GmbH (Honeywell), Sensus (Xylem Inc.), Kamstrup A/S, Siemens AG, Schneider Electric SE, Actaris, Honeywell International Inc., Aclara Technologies LLC, Diehl Metering, Zenner International GmbH & Co. KG, Arad Group, EDMI Limited, Hexing Electrical Co., Ltd. |
The smart gas meter market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region.
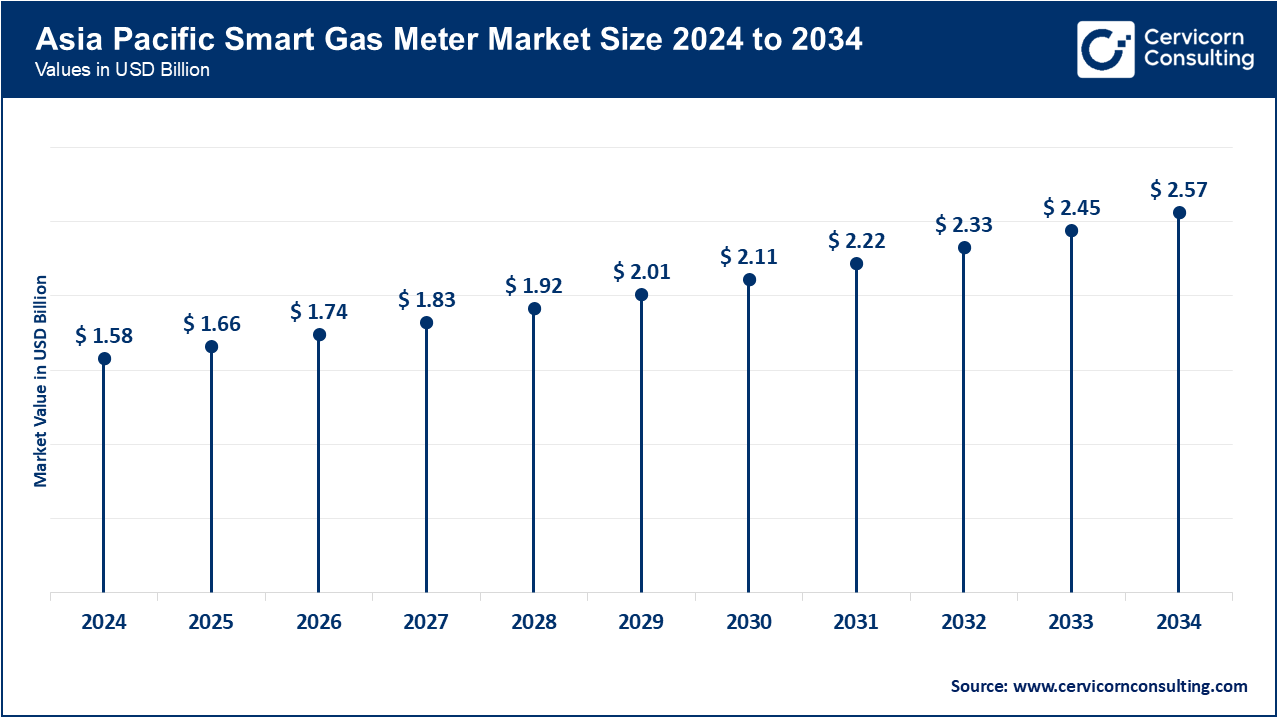
The Asia-Pacific is the leading region due to the speed of urbanization and infrastructure development, industrialization, and the modernization of infrastructure. Of the smart metering technology innovators and consumers, China, India, Japan, and South Korea are particularly important. China is focused on industrial and district energy projects while Japan and South Korea are more focused on commercial energy efficiency. India’s smart city initiatives, industrial parks, and renewable energy projects are focused on energy value improvements for energy investments. In the Southeast Asia region, countries like Vietnam, Thailand, and Indonesia are adopting traditional smart meters and smart meters with renewables as well. The region is the fastest growing globally for solar energy construction because of the availability of low cost labor and growing investments in solar energy.
The growth of North America is driven by advanced industry size, technology distribution, and regulated energy systems. In the U.S. and Canada, smart gas meters in large gas-consuming industries, commercial buildings, and utility networks are used for precise measurement, predictive maintenance, and energy tuning. Operational efficiency and emission reduction are driven by digitization, AI observation, and IoT monitoring. Encouraging and policy-positive government intervention focused on the promotion of low-carbon technology incentivizes growth in these markets. The pace of market innovation is driven by the combination of anticipated investments in renewables, utility and technology partnerships, and market-driven innovation. Investment on innovative and hydrogen-ready market systems is also innovative.
The Europe is driven by the existence of strong regulations in the region. Germany, the U.K., France, and Italy are the front runners in smart gas meter deployments across the residential, commercial, and industrial landscape. Adoption focuses on energy use, carbon decline, and the intersection of renewables and hydrogen-ready technologies. The combination of technology industry, energy partnerships, and research communities foster cross-discipline digital predictive maintenance systems. The combination of fuel cell, biogas, and IoT-enabled gas smart meters is advancing. Europe remains the global leader using smart metering technologies.
Market Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America | 24.30% |
| Europe | 29.40% |
| Asia-Pacific | 37.80% |
| LAMEA | 8.50% |
There's been great industrialization, urbanization, and infrastructure development, which drove the adoption of smart gas meter in the region. Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina are frontrunners in the installation of commercial and industrial smart gas meters. In the Middle East, the UAE and Saudi Arabia are investing in renewables integration, gas-hydrogen blended combustion, and IoT smart gas meters. From the Africa Southern, Eastern, and Western regions, African countries are rolling out localized projects for industrial, commercial, and distributed energy. International partnerships and the increase of modernization initiatives are assisting with market penetration. Poor infrastructure and regulatory enforcement are challenges, but they can work for LAMEA too. The region has long term and great projecting gas smart metering adoption potential.
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI): Systems AMI offer real-time energy data and usage analytics by giving utilities and end users two-way communication. For smart grids, residential, commercial, and industrial AMI systems are all interchangeable. Innovations include predictive maintenance, IoT-based monitoring, and digital twin integration. AMI meters provide operational efficiency and downtime reduction. More connections are being made to renewable energy and hydrogen-ready grids. AMI works best for large-scale energy distribution networks.
Automated Meter Reading (AMR): AMR systems reduce manual meter reading by automatically sending gas consumption data to utilities. For commercial and residential buildings, these systems are commonly used in urban regions. Improved customer transparency is made possible by quicker billing cycles. They are low cost and fit nicely with present systems. Functionality is being improved by technological advancements such as cloud analytics and IoT-enabled connectivity. AMR is still in widespread use in regions where energy efficiency mandates are stringent.
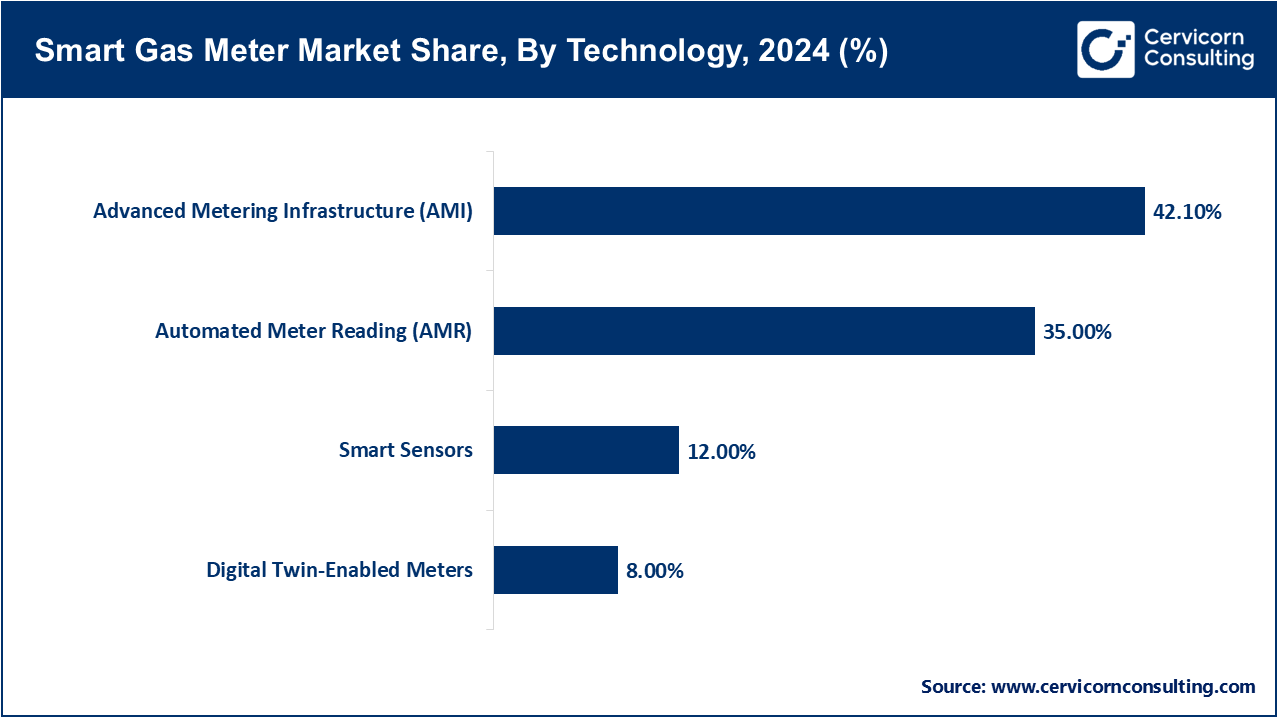
Smart Gas Meters: Smart gas meters monitor gas consumption and detect leaks or irregularities in real time. These meters integrate with AI and IoT platforms to perform predictive maintenance. Smart gas meters help to optimize and improve the safety of resource usage in both residential and commercial settings. Sensors linked to mobile apps provide real-time alerts and tools to analyze gas consumption. The combination of smart sensors and AMI technology improves operational efficiency and diminishes energy waste.
Digital Twin Gas Meters: Gas meters with digital twin technology create virtual copies of gas systems, which helps to optimize performance and usage. They provide predictive maintenance, analyze energy efficiency, and identify faults. Integrating digital twins with gas systems facilitates IoT monitoring and smart grid connections. These gas meters help utilities plan system upgrades with minimal downtime. They are mostly used in commercial and industrial energy systems. The adoption of these systems is increasing because of the need for data-driven management of energy.
Cabled Communication (PLC, RF): Data transmission via power line communication (PLC) and radio frequency (RF) wired devices remains reliable in urban networks and wired infrastructure. With wired communication, users can enjoy relatively secure data transfer with decreased cyber transfer risks. PLC meters tap into existing electrical networks for connection, while RF meters provide real time access and accurate billing. Innovations in hybrid wired systems PLC and RF systems provide improved scalability and flexibility for users.
Market Share, By Communication Type, 2024 (%)
| Communication Type | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Wired | 44.30% |
| Wireless | 55.70% |
Wireless Communication (NB-IoT, LoRaWAN, Zigbee): Meters using NB-IoT, LoRaWAN, and Zigbee for communication provide data transmission for remote monitoring and smart grid integration. These meters are used in homes, offices, and off-grid areas. With wireless systems, services predictive maintenance, fault detection, and energy optimization become possible. Integration with IoT systems provides users with real-time dashboards and notifications. Unlike wired systems, wireless communication provides greater freedom in terms of deployment, and reduces installation requirements. Emerging economies are seeing greater adoption of these systems.
Residential: Smart gas meters provide remote monitoring of household energy consumption. Meters integrated with solar PV or energy storage systems are more efficient. Users can receive usage alerts and control consumption with IoT enabled smart gas meters. There is an increase in integrated micro-CHP systems in urban areas. Smart meters contribute to low energy bills and low carbon initiatives. The European and Asian continents are leading in adoption of smart gas meters.
Commercial: Commercial meters are found in office buildings, hotels, hospitals, and shopping malls. They improve the reliability and optimization of energy usage and decrease operational costs. When coupled with smart grids and renewable energy, they predict and improve analytics. Remote monitoring is a usual practice. Predictive analytics and smart commercial meters are paired with green building certifications in developed countries, which is likely the reason for such certifications. These meters assist in large-scale emission monitoring and energy management.
Market Share, By End-User, 2024 (%)
| End-User | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Residential | 48.90% |
| Commercial | 22.70% |
| Industrial | 17.10% |
| Utilities | 11.30% |
Industrial: Industrial meters are utilized across the manufacturing, steel, chemical, and paper production industries. They assist with high-load operations and the continual process of stream heating. Predictive maintenance, alongside AI, enhances the analytics for refining energy efficiency. They also integrate with complete heating and cooling process (CHP), the internet of things (IoT), and renewables. These systems are the driving factors for emission and energy cost reductions. Adoption of these systems is particularly strong in the European, North American, and Asia-Pacific industrial hubs.
Utilities: Utilities employ smart gas meters for grid monitoring, load control, and ensuring billing accuracy. They facilitate real-time consumption depictions and two-way communication. Smart meters distribute and minimize losses. When coupled with advanced metering infrastructures (AMI), AI analytics, and IoT, utility smart meters amplify performance. Utilities predict demand and conserve energy and hence, efficiency improves over time. Market growth continues due to regulations that demand an advanced smart metering system.
Natural Gas: The Wide Use of Natural Gas Meters. Natural gas remains the most efficient and lower-emission option. All sectors and industries find uses for gas meters. Customers adapt to more sophisticated meters integrated with digital and artificial intelligence applications. Hybrid renewable and gas meter combinations are the first steps toward carbon improved initiatives. Gas meters provide load control and predictive analytics for gas distribution systems. Gas meters are the arteries of urban and industrial gas distribution systems.
Biogas: Monitoring methane production via anaerobic digestion. Agriculture, waste management, and decentralized energy systems are primary targeted markets for this technology. Optimization via the internet of things and predictive maintenance systems are the future. Microturbine and reciprocating engines will close the retaining and centering gap for flexibility. Biogas meters capture the principles of the circular economy. The integration of waste to energy projects drives the global expansion of biogas systems.
Market Share, By Energy Type, 2024 (%)
| Energy Type | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Natural Gas | 61.40% |
| Biogas | 16.70% |
| Hydrogen-Ready Systems | 13.20% |
| Renewable-Integrated Systems | 8.70% |
Hydrogen-Ready Systems: Measuring blends of hydrogen and gas to capture the no/low emission markets. Industrial and residential decarbonization is the goal. Integration of gas meters and fuel cell systems will close emission gaps for targeted industries. The internet of things will provide real-time performance and safety telemetry. Most growth will occur in Germany, India, and Japan. Hydrogen-ready gas metering systems capture the global green hydrogen infrastructure.
Hybrid Systems: BIM-integrated meters monitor gas consumption with consumption of solar, wind, or biomass systems, supporting hybrid energy solutions and low carbon burning. The combination with smart grids and the IoT provides predictive maintenance and real-time optimizations. The combination of these systems increases the efficiency of gas systems. In addition, the return on investment on these systems is very attractive. The incentives from the governments to become more sustainable, fuelled the adoption of these systems. The adoption is growing in urban and industrial environments globally.
Market Segmentation
By Component
By Type
By Technology
By Communication Type
By Energy Type
By End-User
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Smart Gas Meter
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Technology Overview
2.2.2 By Component Overview
2.2.3 By Type Overview
2.2.4 By Communication Type Overview
2.2.5 By Energy Type Overview
2.2.6 By End User Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.2 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Rising Industrial and Commercial Energy Demand
4.1.1.2 Transitioning to Low Carbon Energy
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 Significant Initial Investment and Operating Cost
4.1.2.2 Regulatory and Compliance Pressures
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
4.1.3.2 Complexity in Technology and Skills Shortage
4.1.4 Market Opportunities
4.1.4.1 Integration with Renewable Energy and IoT Platforms
4.1.4.2 Expansion in Emerging Markets
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Smart Gas Meter Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Smart Gas Meter Market, By Technology
6.1 Global Smart Gas Meter Market Snapshot, By Technology
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
6.1.1.2 Automated Meter Reading (AMR)
6.1.1.3 Digital Twin-Enabled Meters
6.1.1.4 Smart Sensors
Chapter 7. Smart Gas Meter Market, By Component
7.1 Global Smart Gas Meter Market Snapshot, By Component
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Hardware
7.1.1.2 Software
7.1.1.3 Services
Chapter 8. Smart Gas Meter Market, By Type
8.1 Global Smart Gas Meter Market Snapshot, By Type
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Smart Ultrasonic Gas Meter
8.1.1.2 Smart Diaphragm Gas Meter
Chapter 9. Smart Gas Meter Market, By Communication Type
9.1 Global Smart Gas Meter Market Snapshot, By Communication Type
9.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
9.1.1.1 Wired (PLC, RF)
9.1.1.2 Wireless (NB-IoT, LoRaWAN, Zigbee)
Chapter 10. Smart Gas Meter Market, By Energy Type
10.1 Global Smart Gas Meter Market Snapshot, By Energy Type
10.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
10.1.1.1 Natural Gas
10.1.1.2 Biogas
10.1.1.3 Hydrogen-Ready Systems
10.1.1.4 Renewable-Integrated Systems
Chapter 11. Smart Gas Meter Market, By End-User
11.1 Global Smart Gas Meter Market Snapshot, By End-User
11.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
11.1.1.1 Residential
11.1.1.2 Commercial
11.1.1.3 Industrial
11.1.1.4 Utilities
Chapter 12. Smart Gas Meter Market, By Region
12.1 Overview
12.2 Smart Gas Meter Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
12.3 Global Smart Gas Meter Market, By Region
12.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
12.4 North America
12.4.1 North America Smart Gas Meter Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.4.3 North America Smart Gas Meter Market, By Country
12.4.4 U.S.
12.4.4.1 U.S. Smart Gas Meter Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
12.4.5 Canada
12.4.5.1 Canada Smart Gas Meter Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
12.4.6 Mexico
12.4.6.1 Mexico Smart Gas Meter Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
12.5 Europe
12.5.1 Europe Smart Gas Meter Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.5.3 Europe Smart Gas Meter Market, By Country
12.5.4 UK
12.5.4.1 UK Smart Gas Meter Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
12.5.5 France
12.5.5.1 France Smart Gas Meter Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
12.5.6 Germany
12.5.6.1 Germany Smart Gas Meter Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
12.5.7 Rest of Europe
12.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Smart Gas Meter Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
12.6 Asia Pacific
12.6.1 Asia Pacific Smart Gas Meter Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.6.3 Asia Pacific Smart Gas Meter Market, By Country
12.6.4 China
12.6.4.1 China Smart Gas Meter Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
12.6.5 Japan
12.6.5.1 Japan Smart Gas Meter Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
12.6.6 India
12.6.6.1 India Smart Gas Meter Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
12.6.7 Australia
12.6.7.1 Australia Smart Gas Meter Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
12.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
12.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Smart Gas Meter Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
12.7 LAMEA
12.7.1 LAMEA Smart Gas Meter Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.7.3 LAMEA Smart Gas Meter Market, By Country
12.7.4 GCC
12.7.4.1 GCC Smart Gas Meter Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
12.7.5 Africa
12.7.5.1 Africa Smart Gas Meter Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
12.7.6 Brazil
12.7.6.1 Brazil Smart Gas Meter Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
12.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
12.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Smart Gas Meter Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
12.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 13. Competitive Landscape
13.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
13.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
13.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
13.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
13.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 14. Company Profiles
14.1 Itron Inc.
14.1.1 Company Snapshot
14.1.2 Company and Business Overview
14.1.3 Financial KPIs
14.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
14.1.5 Strategic Growth
14.1.6 Global Footprints
14.1.7 Recent Development
14.1.8 SWOT Analysis
14.2 Landis+Gyr Group AG
14.3 Elster Group GmbH (Honeywell)
14.4 Kamstrup A/S
14.5 Siemens AG
14.6 Schneider Electric SE
14.7 Actaris
14.8 Honeywell International Inc.
14.9 Aclara Technologies LLC
14.10 Diehl Metering
14.11 Zenner International GmbH & Co. KG
14.12 Arad Group
14.13 EDMI Limited
14.14 Hexing Electrical Co., Ltd.