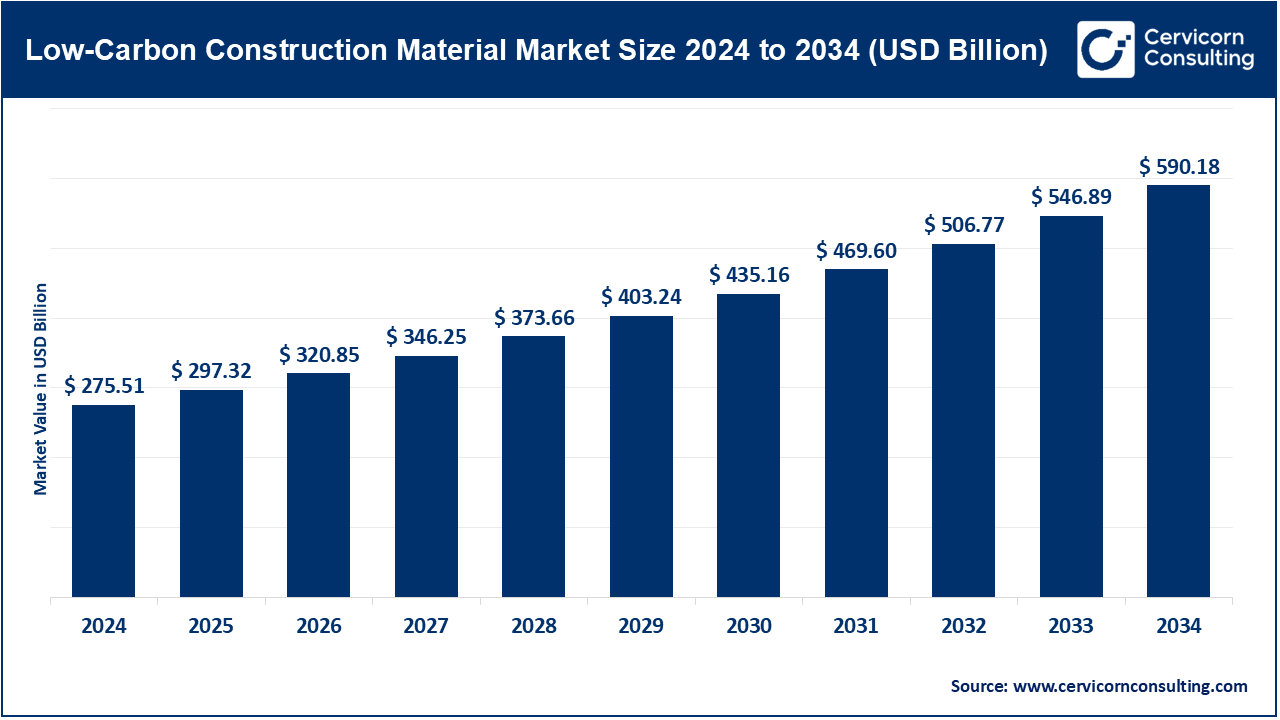
The global low-carbon construction material market size was valued at USD 275.51 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 590.18 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 8% from 2025 to 2034. The low-carbon construction material market is pace-rushing since the building industry is drifting away to the sustainable development, green certifications and net-zero pledges. The construction sector is focusing on more material that drives down embodied carbon emissions and uses fewer resources with a view to supporting greater circularity in the era of climate-conscious infrastructure. It is one of the biggest changes taking place in the construction industry today, following the tighter environmental regulation, the corporate ESG targets, and the devastating consequences of climate change that must be mitigated.
A key element of sustainable building is low-carbon construction materials which have high performance and reduces CO2 emissions throughout the life cycle. Such resolutions cover used steel, low-clinker cement, biocomposite materials, cross-laminated timber, and advanced insulating building materials that will support the global objectives to cut emissions of carbon. They support various sectors-residential, commercial, industrial and infrastructure, making projects sustainable, resource friendly, and supporting the green building trends, by minimizing impact on the environment at the ground level.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 297.32 Billion |
| Estimated Market Size in 2034 | USD 590.18 Billion |
| Expected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 8% |
| Leading Region | North America |
| Rapid Growth Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Material Type, Construction Method, Application, End User, Region |
| Key Companies | ArcelorMittal, Nucor Corporation, Steel Dynamics, CMC, NIPPON STEEL CORPORATION, CelsaGroup, HBIS GROUP, LIBERTY Steel Group, Tata Steel, Vedanta Aluminum and Power, Rio Tinto, Norsk Hydro ASA, Eco-Friendly Plastic Lumber, Naftex GmbH, Mercer Mass Timber LLC, Cemex, S.A.B. de C.V., CarbiCrete, CarbonCure Technologies Inc., HOLCIM |
Steel Recycled: Recycled steel comes in the form of scrap steel being melted and processed once more to be used in construction purposes, recycled steel uses much less energy and CO2 emissions than virgin steel by a substantially large margin. It keeps intact structural strength, and can therefore be used in beams, pillars and reinforcement. Recycled structural steel supplied 98 percent of a commercial tower in Toronto in February 2024, whereupon the embodied carbon was reduced by more than 60 percent. It saves natural resources and landfills. It is increasingly used in large scale urban projects that attempt to achieve LEED or BREEAM.
Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT): CLT is a fabricated wooden panel in which the timber boards are laid into each other cross wisely to form a composite of high strength and high stability and having lower carbon footprint as compared to concrete or steel. It has stored carbon assimilated in the growth of trees, and thus it is a sustainable source of mid- and high-rise buildings. A Berlin complex of residential buildings was built in May 2024 with the use of CLT in framing of load-carrying walls as well as floor structures. The decision cut down the time of construction and enhanced thermal performance. It is becoming increasingly popular in areas that are pushing mass timber construction codes.
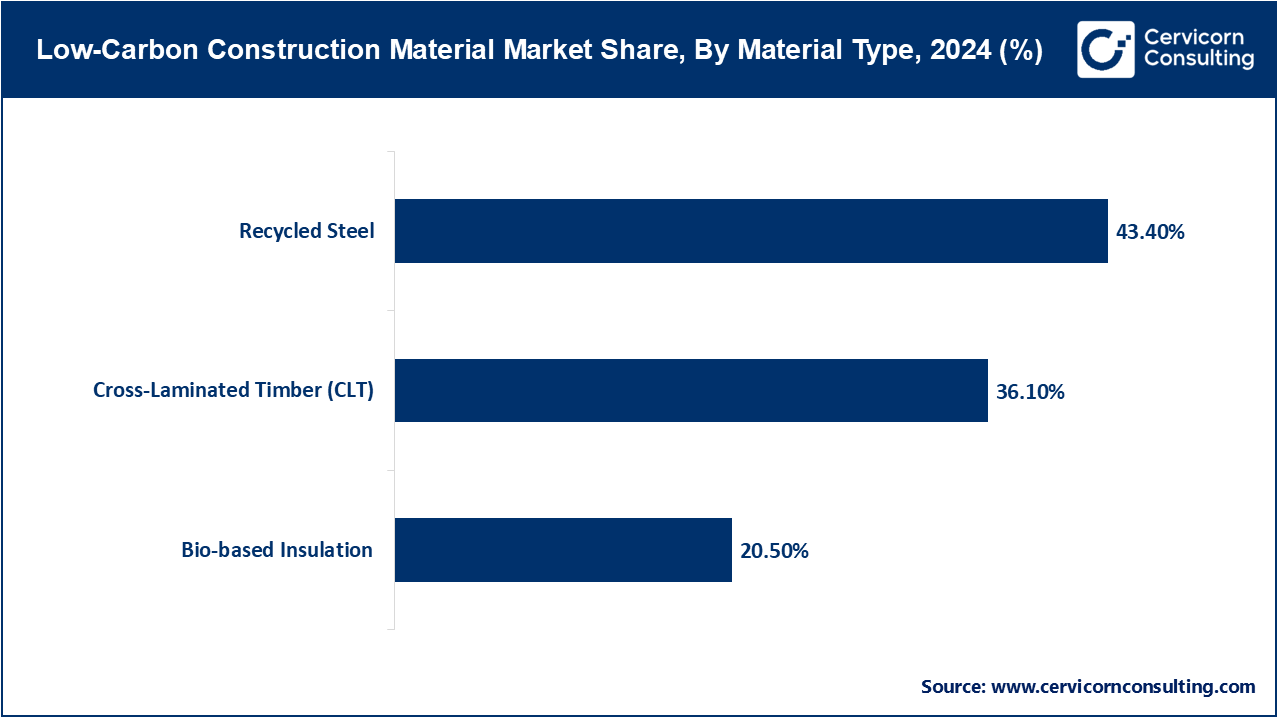
Bio-based Insulation: Bio-based insulation uses renewable plant or animal fibers (e.g. in hemp, sheep wool or cellulose) and can offer thermal and acoustic performance at low embodied carbon. It is easily worn away in a natural setting, has low toxicity and is frequently recyclable. A school renovation project in Copenhagen, in October 2023, also laid hemp fiber insulating material throughout all its classrooms in order to comply with Denmark goals in energy efficiency. This diminished the heating requirements and the design developed healthier indoor air. Green building tenders to build public infrastructure are increasingly specifying such insulation.
Floors & Interior Finishes: It constitutes the section of low-carbon material, such as bamboo floors, recycled tiles, cork, as well as reclaimed wood as interior materials. These materials limit the exploitation of resources and at the same time contribute aesthetic and practical advantages. In March 2024, a corporate Singapore-based office fitted out common areas with reclaimed teak flooring and reused ceramic tiles. Such strategy saved on wastage and embodied carbon, and fulfilled the client with wellness-oriented implementations of interior design. The hospitality and retail sectors are motivated to attain sustainable branding which encourages demand.
Insulation: The low-carbon nature of insulation materials such as mineral wool containing recycled material, aerogel, and natural fiber panels has an effect to avoid any heating of the structures and decreases lifecycle emissions. It is found that proper insulation can be used to reduce the energy demand of operations in buildings and this can surpass built in emissions over time. In July 2023, a Melbourne hospital project was involved in recycled denim insulation which enhances thermal control and minimises HVAC loads. This came with prospects of environmental and cost savings. The growth of adoption is spreading into a region that experiences high heating or cooling requirement.
Paving & Landscaping: Low-carbon paving and landscaping will consist of permeable pavers and recycled aggregates and bio-based binders, which will minimize CO2 and maximize storm water management. The resources are also urban coolers and enhancers of biodiversity. A redevelopment of a city park in Barcelona in August 2023 replaced with permeable recycled glass pavers in the park to reduce flood risk. This strategy was an addition to the native landscaping making it more ecologically valuable. The use of municipal projects is leading adoption owing to the needs of sustainability and resilience.
Residential: The residential section deals with the low-carbon of house, apartment and community housing with an emphasis on energy performance and lower embodied carbon. Such materials are CLT, recycled steel, and hempcrete. A housing cooperative in Oslo has launched, in April 2024, 120 units entirely made out of bio-based insulation and CLT planks. This was in line with tough Norwegian environmental housing requirements. Green building insurance credentials are getting even more vital among home buyers in the process of acquisition.
Commercial: Low-carbon material in commercial usage has offices, retail spaces, and hospitality facilities that consider performance and the brand. These developments tend to aim at LEED, WELL, or BREEAM certification. In January 2024, one of the hotels in Vancouver integrated recycled steel framing and flooring made of cork suited to its eco-tourism marketing. This saved emissions, besides drawing environmentally conscious visitors. Innovation in visible sustainable finish is promoted through the commercial sector.
Industrial: Low-carbon materials are used by industrial projects such as warehouses, processing plants and factories as part of corporate emissions goals, and to comply with regulations. It has to be structurally efficient and durable. In September 2023, a Mexican automotive parts factory fitted green roofing to provide bio-based insulation to cool the building down. This action served the purposes of the international carbon-cutting campaign of the company. These kinds of projects usually integrate the performance of tasks and ESG disclosures.
New Construction: The projects of new construction would incorporate the low-carbon materials into designs, which would provide a chance to maximize structural decisions and performances in the life-cycle. This is the complete way of integrating sustainability. Project Inception – In February 2024, a civic center in Helsinki was constructed with CLT, recycled steel and algae-based façade panels. This provided great embodied carbon savings on conventional builds. Such projects are fast tracked by policies adopted in Europe and North America.
Retrofit & Renovation: The approach that encompasses retrofit and building renovations is an upgrade of existing buildings, and it decreases the necessity to demolish old structures and use new raw materials. It is a major tool towards achieving Urban Emission Objectives. In May 2023, a Boston University retrofitted a dorm with hemp fiber panels instead of normal insulation. This saved on energy consumption in heating and did not interfere with the heritage character of the building. The retrofit markets are growing because of cost and sustainability advantages.
Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Share, By Construction Method, 2024 (%)
| Construction Method | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| New Construction | 40.50% |
| Retrofit & Renovation | 34.20% |
| Green Roofing Systems | 25.30% |
Green Roofing Systems: Green roofing employs vegetation stratum, recycles water resistant sheets, and low carbon layer to act as insulation, storm water management, and biodiversity. It will also minimize urban heat island effects. In November 2023, a logistical centre in Rotterdam has put in place a green roof which covers an area of 20,000 m. The recycled plastic materials used in the building up of the shower understands are the drainage layers. This not only saved on building, but also received sustainability incentives on the part of municipalities. In big commercial and industrial projects, green roofing is becoming an option.
The low-carbon construction material market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region.
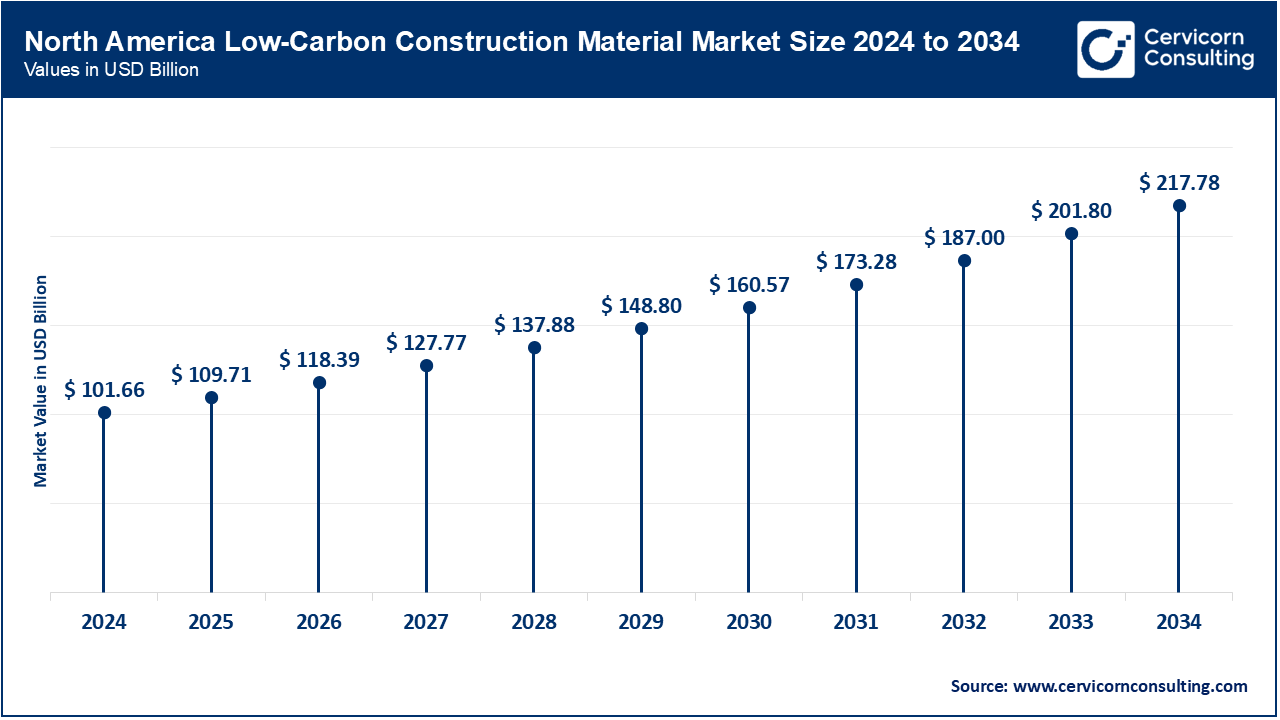
The North America is already expanding because the construction industry has implemented strict environmental building codes, developed strong green certification systems and invested heavily in sustainable real estates. In February 2025, one of the major construction companies in the United States started implementing bio-based insulation in a series of mega multi-family housing projects in California to reduce its operational emission. In August 2024, Canada announced a national program which would endorse cross-laminated timber (CLT) buildings in Ontario school systems. By April 2025, a group of commercial developers in Texas has incorporated recycled steel frame in mixed-use complexes that have embodied carbon reduced by 28%. Constant investment in retrofit projects is making sustainable items the new normal during future construction.
Due to the EU Green Deal and circular economy regulations, the construction market in Europe is evolving with low-carbon construction materials as driven by eco-innovation and an upscale of infrastructure. Germany installed a national program in January of 2025 that encourages CLT use in medium-rise city buildings. In September 2024, France retrofitted a large hospital providing near-zero energy buildings using bio-based insulation. As of May 2025, the government of the Netherlands supported the preparation of the recycled steel bridges loaded to the transport corridors in the rural region that contributed to the strengthening of the resilience and sustainability. Gradual shift in the widespread use of green roofing systems is also rampant particularly in cities that are aspiring to achieve a heat-island. Regulation further drives the builders to move to low-carbon sources.
Asia-Pacific is undergoing rapid urbanization, with government driven carbon-cutting agendas fueling the market. In March 2025, Japan has finished a high-rise construction made of recycled steel and CLT panels in the business district of Tokyo. In July 2024, an industrial park consisting of bio-based insulation was unveiled in Gujarat, India, to help increase the efficiency of energy. By June 2025, Australia installed the concept of green roofing in few commercial complexes along the coast to enhance storm water management. The reclaiming of materials is also on the increase in Southeast Asia, such as use of material reclaimed to reduce raw resource mining in paving and landscaping projects. The drive behind this region is not only on the change in the domestic policy but also worldwide investor anticipations.
Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America | 36.90% |
| Europe | 31.20% |
| Asia-Pacific | 24.60% |
| LAMEA | 7.30% |
The LAMEA market is progressing with constant progress with the help of public-private partnerships and financing that is linked with sustainability. In April 2025, the United Arab Emirates introduced a luxury housing project to be fully framed with recycled steel that would become a new green standard in the Gulf. Brazil in October 2024 opened an expansion of a public university, which is made up of CLT made of certified forests. By May 2025, South Africa completed a major commercial retrofit of high-rise building in Johannesburg with bio-based insulation, where energy reduced in cooling needs by 40%. The countries of the region are also turning towards eco-friendly paving of the public infrastructure. These undertakings match global carbon neutrality goals as well as generate regional new markets.
Market Segmentation
By Material Type
By Construction Method
By Application
By End-Use Sector
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Low-Carbon Construction Material
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Material Type Overview
2.2.2 By Construction Method Overview
2.2.3 By Application Overview
2.2.4 By End User Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.2 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Green Building Regulations Governmental
4.1.1.2 Corporate Net-zero pledges
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 Higher Upfront Costs Compared to Conventional Materials
4.1.2.2 Scarceness in New Markets
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 There exist no Standardised Carbon Measurement Frameworks
4.1.3.2 Tradition in Technical Adaptations in Building
4.1.4 Market Opportunities
4.1.4.1 Urban retrofit and upgrade projects
4.1.4.2 Carbon Negative Materials Innovation
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Low-Carbon Construction Material Market, By Material Type
6.1 Global Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Snapshot, By Material Type
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Recycled Steel
6.1.1.2 Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT)
6.1.1.3 Bio-based Insulation
Chapter 7. Low-Carbon Construction Material Market, By Construction Method
7.1 Global Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Snapshot, By Construction Method
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 New Construction
7.1.1.2 Retrofit & Renovation
7.1.1.3 Green Roofing Systems
Chapter 8. Low-Carbon Construction Material Market, By Application
8.1 Global Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Snapshot, By Application
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Flooring & Interior Finishes
8.1.1.2 Insulation
8.1.1.3 Paving & Landscaping
Chapter 9. Low-Carbon Construction Material Market, By End-User
9.1 Global Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Snapshot, By End-User
9.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
9.1.1.1 Residential
9.1.1.2 Commercial
9.1.1.3 Industrial
Chapter 10. Low-Carbon Construction Material Market, By Region
10.1 Overview
10.2 Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
10.3 Global Low-Carbon Construction Material Market, By Region
10.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
10.4 North America
10.4.1 North America Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.3 North America Low-Carbon Construction Material Market, By Country
10.4.4 U.S.
10.4.4.1 U.S. Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
10.4.5 Canada
10.4.5.1 Canada Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
10.4.6 Mexico
10.4.6.1 Mexico Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
10.5 Europe
10.5.1 Europe Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.3 Europe Low-Carbon Construction Material Market, By Country
10.5.4 UK
10.5.4.1 UK Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
10.5.5 France
10.5.5.1 France Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
10.5.6 Germany
10.5.6.1 Germany Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
10.5.7 Rest of Europe
10.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6 Asia Pacific
10.6.1 Asia Pacific Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.3 Asia Pacific Low-Carbon Construction Material Market, By Country
10.6.4 China
10.6.4.1 China Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6.5 Japan
10.6.5.1 Japan Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6.6 India
10.6.6.1 India Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6.7 Australia
10.6.7.1 Australia Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
10.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
10.7 LAMEA
10.7.1 LAMEA Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.3 LAMEA Low-Carbon Construction Material Market, By Country
10.7.4 GCC
10.7.4.1 GCC Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
10.7.5 Africa
10.7.5.1 Africa Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
10.7.6 Brazil
10.7.6.1 Brazil Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
10.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
10.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Low-Carbon Construction Material Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 11. Competitive Landscape
11.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
11.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
11.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
11.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
11.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 12. Company Profiles
12.1 ArcelorMittal
12.1.1 Company Snapshot
12.1.2 Company and Business Overview
12.1.3 Financial KPIs
12.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
12.1.5 Strategic Growth
12.1.6 Global Footprints
12.1.7 Recent Development
12.1.8 SWOT Analysis
12.2 Nucor Corporation
12.3 Steel Dynamics
12.4 CMC
12.5 NIPPON STEEL CORPORATION
12.6 CelsaGroup
12.7 HBIS GROUP
12.8 LIBERTY Steel Group
12.9 Tata Steel
12.10 Vedanta Aluminum and Power
12.11 EN+ Group
12.12 Rio Tinto
12.13 Norsk Hydro ASA
12.14 Eco-Friendly Plastic Lumber
12.15 Naftex GmbH
12.16 Mercer Mass Timber LLC
12.17 Cemex, S.A.B. de C.V.
12.18 CarbiCrete
12.19 CarbonCure Technologies Inc.
12.20 HOLCIM