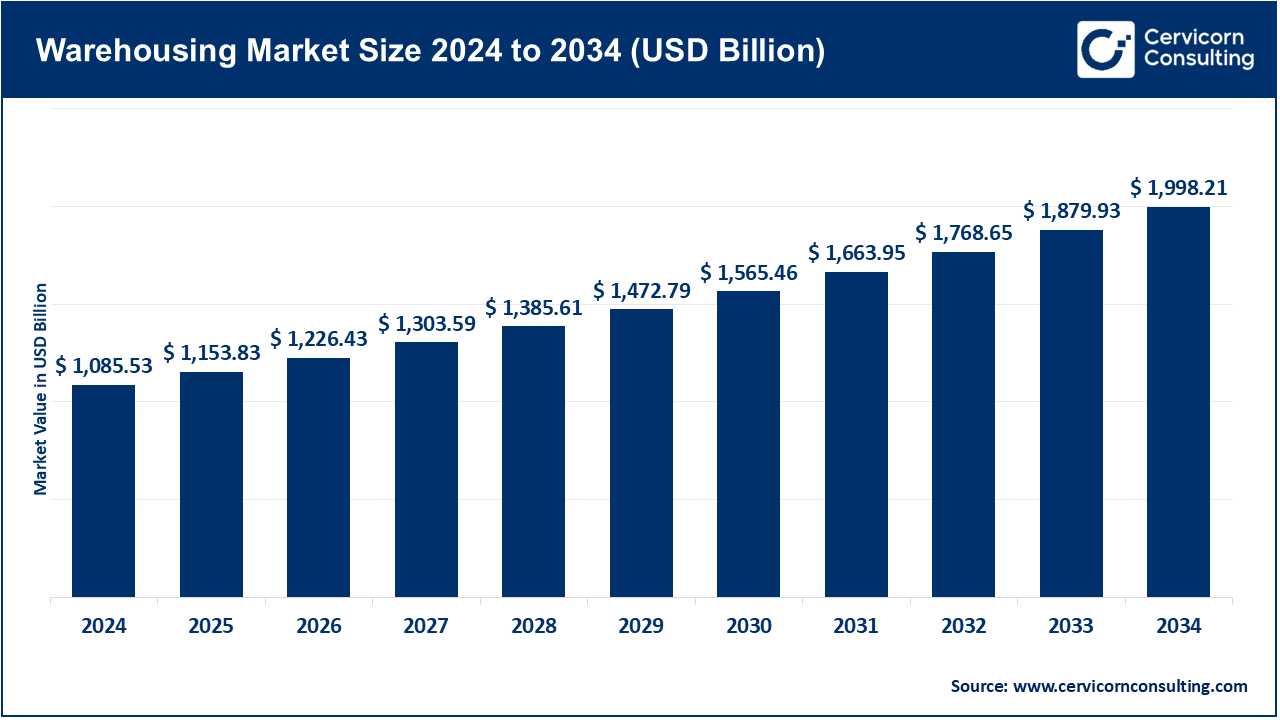
The global warehousing market size was valued at USD 1085.53 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 1998.21 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.0% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
The warehousing is the current trend of the businesses and industries that are transforming in response to the fast-pacing e-commerce, the shifted consumer demands, and more effective activities in the chain of supply. With the growing knowledge of the efficiency in logistics the temptation to find facilities that can process orders quicker, store specialized items and provide value services is growing. With the help of the advanced warehousing solutions that incorporate the utilization of automation, robotization, and smart storage systems, companies become able to manage their stock in real-time scenarios, minimize the delivery timing, and cut the operational investment required. Such a transition is changing warehousing not to be a static storage system, but a vibrant technology-based service to assist with everything to same-day deliveries to worldwide distribution programs.
The warehousing is provided as the part of the logistics and supply chain industry providing facilities of storage, handling and distribution, and also integrated technologies that provide the speed, accuracy, and flexibility. It also has dedicated warehouses like cold storage facilities, fully automated distribution facilities and cross-docking outspan, in addition to value-added operations like packages, labeling services and returns. With the help of such innovations as IoT-enabled tracking, AI-based demand forecasting and the warehouse management systems, this industry offers enterprises opportunities to optimize business practices, enhance customer satisfaction and stay competitive in a rapidly changing global environment. With the increase in the need to deliver goods more speedily and reliably, warehousing will be one of the key elements of efficiency and resilience in supply chain.
Materials handling systems in use
| Systems | Uses in % |
| Forklifts | 83% |
| Pushcarts | 55% |
| Conveyors | 37% |
| Vertical Lift Modules | 25% |
| Palletiezer | 19% |
| Sorter | 12% |
| Robotics | 12% |
| Carousels | 9% |
| AGVs/AMRs | 9% |
| Others | 6% |
General Storage: General warehouses propose a flexible and scalable warehouse with a wide offering of non-perishable products. These facilities are crucial in the handling of bulk goods and provision of supply chain advocacy. Amazon led an outbreak of warehousing development in the United States in December of 2024 driving demand in favor of such multi-purpose storage. This highlights the fact that general storage is still the building block of logistics infrastructures.
Cold Storage: Cold storage warehouses are specifically refrigerated or frozen product conditions that are necessary for perishables, pharmaceuticals and temperature sensitive products. This division requires a high-end HVAC, monitoring and backup systems, because it is important to guarantee product integrity. ColdStar Logistics has since grown by establishing another temperature-controlled hub in Visakhapatnam in August 2025 to provide temperature-controlled last-mile delivery to the FMCG, marine, and pharma industries.
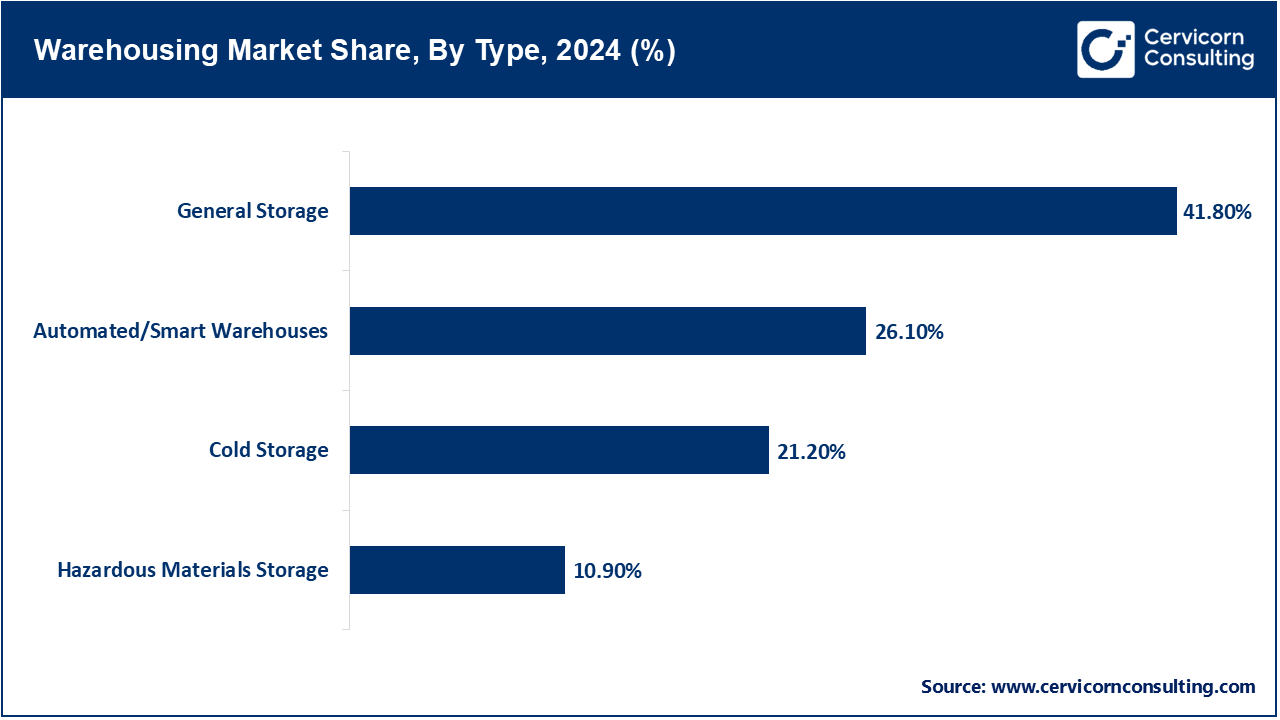
Posts of Hazardous Materials Storage: Hazardous storage warehouses are constructed specifically to store safely flammable, toxic, or corrosive materials. They have distinct safety features such as ventilation, compartmentalization, spill control, and they are vital to industrial use. These facilities proved that even though no recent news could be found, they are still vital in controlled supply chains that deal with dangerous materials.
Automated/ Smart Warehouses: As a part of automation, robotics and AI are in use in these warehouses to maximize storage, access and order fulfilment, enhancing speed and accuracy. This is the segment that is increasing at a high rate in the e-commerce and large-volume logistics. Amazon In December 2024, Amazon opened a 3-million-square-foot facility in Shreveport, Louisiana, which is its most advanced facility in term of automation and combines robotics and human labor, to efficiently process orders.
Private Warehouses: The entire control and customization of warehousing through privately owned warehouses keeps the logistics operation of one company in full control and de-centralized with the location in manufacturing or retailing hubs. Amazon began a large new facility in Cleburne, Texas, in November 2024 (1.7 million square feet), some signatures of strategic investment in private fortune warehousing to increase regional distribution.
Public Warehouses: 3PL warehouses are flexible and commitment free and usually leasing storage space to a number of clients in the 3PL warehouse. They are perfect in firms that prefer scalable activity to capital investment. In December 2024, Amazon transiently ended up facing labor locks across United States warehouses amid seasonal demand, spotlighting dependence on 3PL infrastructure that needs abridged placidness amid seasonal demand.
Warehousing Market Share, By Ownership, 2024 (%)
| Ownership | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Private Warehouses | 35.90% |
| Public Warehouses | 28.40% |
| Bonded Warehouses | 16.80% |
| Cooperative Warehouses | 18.90% |
Bonded Warehouses: The imported goods in these facilities are kept under the supervision of customs and duty paid at a later stage only after clearance, which aids the trade flow. This sub-segment has not had any topical headline captured but it has been in the center of world logistics and international trade facilitation.
Cooperative Warehouses: These warehouses, which are owned and used by the producer cooperatives, such as the farming groups, save expenditures and increase the bargaining power of the individual members. The Indian government (Uttar Pradesh) declared in May 2025 that it would open more than 20 farmer cooperative warehouses in 16 districts to reduce post-harvest loss and facilitate storage by farmers.
Distribution Warehouses: The distribution warehouses segment has dominated the market. The sorting and delivery of goods is effective because a distribution center delivers faster to retailers or regional centers. The warehousing rush in Amazon in December 2024 demonstrates how essential facilitative nodes become in the current supply chains.
Fulfillment Centers: Fulfillment centers accept, process and deliver orders placed by individual customers either through a relatively high level of automation to fast track the delivery. This technological advancement of the sub-segment is heightened by the fact that Amazon opened one of its automated facilities in Shreveport in December 2024.
Cross-Docking Facilities: Transfers In cross-docking hubs, inbound shipments are passed directly to outbound transport, by reducing the storage of shipment and accelerating throughput. The expanding facility of ColdStar in Visakhapatnam in August 2025 will have cross-docking to smoothen out the last-mile logistics.
Consolidation Warehouses: These posts receive small consignments of different suppliers and combine them into larger loads so as to reduce freight expenses as well as enhance transport routing. No recent advances were noted although they are very imperative to the efficient management of freights.
Conventional Warehousing: Depends on human work and simple shelving--generally applied on an industry-wide basis. The fact that warehouse openings will increase in December 2024 underlines the persistence of traditional setups, especially against the backdrop of a quick growth in ecommerce.
Semi-Automated Warehousing: The semi-automated warehousing segment has registered highest revenue share in the market. Contains a mixture of more traditional tasks and mechanized elements such as conveyors or sorter systems to increase productivity. Although explicit reports were not located, lots of current facilities are increasingly becoming integrated with such type of systems.
Automated Warehousing to the Fullest: Also, fully automated warehouses are run through robotics and AI with minimal human interaction. Amazon is an ideal illustration of this advancement as seen in its Shreveport, December 2024 facility where huge volumes of orders are processed via automation but with human supervision.
AI and associated robotics-enabled warehousing: This sub-segment involves mobile robots (AMRs), AI-enabled picking, and predictive analytics to streamline operations. Though recent news lacks a direct mention of this, it significantly indicates an escalated usage of the fulfillment technology across the sector.
E-commerce & Retail: The e-commerce & retail segment has dominated the market. It involves fast fulfillment and scalability that is required by the e-commerce and retail industries to respond and fulfill the varying needs of the consumers. Close location to urban centers would allow quicker movement, and the business would have to manage huge SKUs variety, and reverse logistics would have to be efficient. Automation is a solution that is central to order accuracy and speed. It was quite evident where the industry relies heavily on this agile infrastructure when the December 2024 warehousing expansion Amazon spearheaded came into the scene.
Food & Beverage: The industries necessitate the cold and frozen storage, to store perishable products that must deal with hygiene and temperature controls as nonnegotiables. These facilities shall also be expected to deal with the peak periods during seasons like festivals. They are coupled with a just in time delivery package to guarantee freshness on arrival. A great example of this particular specialised sub-segment in practice is the August 2025 operation of the hub in Visakhapatnam, which is run by ColdStar.
Pharmaceutical & Healthcare: This industry requires warehousing that is secure with controlled climate to store sensitive drugs, vaccines among other medical devices. Strict rules also apply in the area of storage and handling and regulatory compliance must be observed. In a bid to provide visibility and safety, real-time tracking systems are usually integrated. The facility is located in August 2025, and it does not only help to store goods; it also contributes to the pharmaceutical supply chain resilience portrayed by ColdStar.
Automotive & Industrial: Cars and industrial industries need huge warehouses to store machines, parts, and raw materials which are bulky. Such warehouses are usually situated in and around manufacturing centres in order to facilitate just-in-sequence production systems. This equipment is necessary to transport heavyweight and oversized parts. The explosion in warehousing construction in the month of December 2024 highlighted the expanding logistic requirements of the industry.
Consumer Goods: Consumer goods industry requires a flexible warehousing in which a variety of product lines like electronics and home essentials can be stored. According to the high turnover rates and seasonal peaks, the balance between the manual and automated processes is required. Such plants need to be responsive in meeting the peaks in promotions and mass purchase tendencies. The pressure on this sub-segment was manifested by increased rents and highly demanded late 2024 and early 2025.
The warehousing market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region.
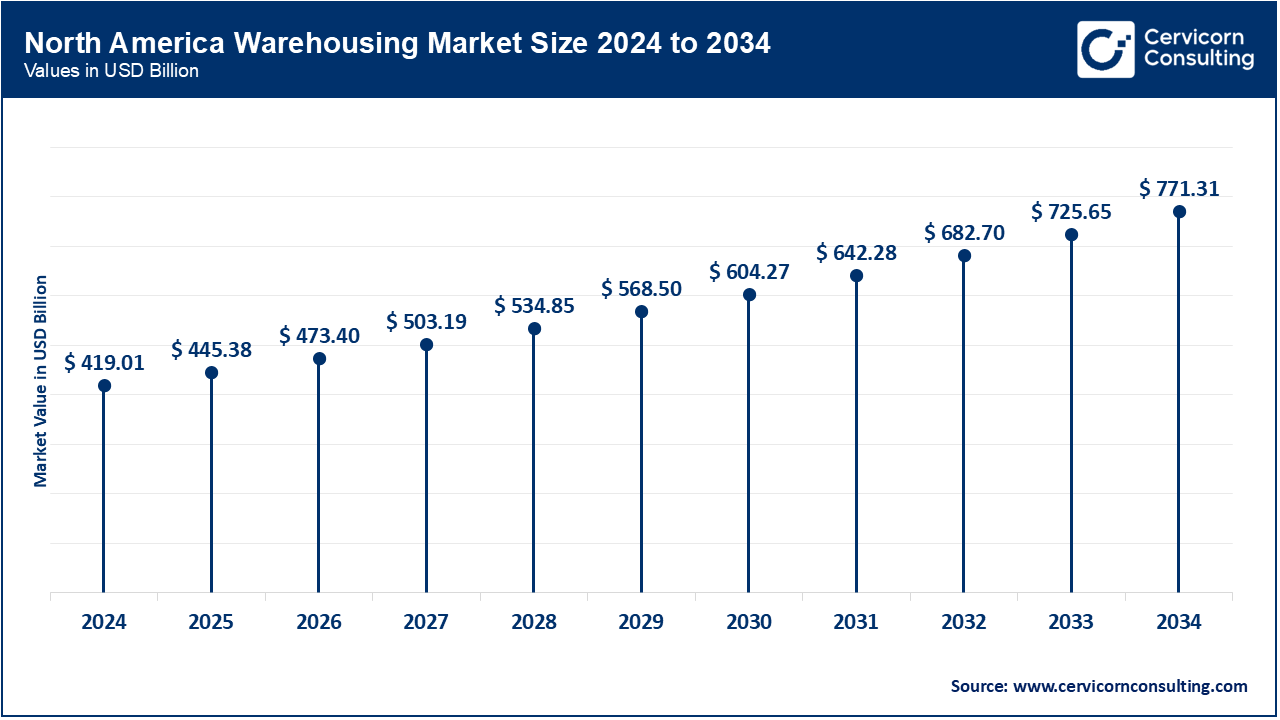
North America has been a global giant in terms of a contribution, because of the high level of automation, robust e-commerce and integrated supply chains. At the beginning of February 2025, one of the largest logistics companies in the U.S. launched a multi-state implementation of AI-enabled inventory tracking in its facilities. Canada opened a cold storage hub in Ontario in August 2024 with an intention to assist domestic distribution and export foodstuff. In April of 2025, a strategic alliance between two retail giants and one robotics company was closed aimed at retrofitting fulfillment centers with autonomous mobile robots, which will increase the efficiency of operations throughout the region.
The European warehousing business is booming as the region has sustainability-oriented infrastructure and modernisation efforts by the government and a dense transport system. In January 2025, France put their first zero-carbon distribution center in operation, which is fully supplied with solar-generated and wind energy. In September 2024, Germany initiated the granting of SMEs to take up the practice of automating their intended warehouse in the export led manufacturing sectors. In May 2025, the UK finished an enlargement of all the way of the Midlands in logistics, with cutting-edge sorting frames to take care of the development of the omnichannel trade. Cross-border logistics is becoming homogenized as EU-wide cooperation in the form of smart logistics corridors facilitates the passing of freight and use of warehouses between countries.
The Asia-Pacific region is also increasing its warehousing capabilities due to mega logistics parks, production of high production, and bulk e-commerce. In March 2025, a super-modern bonded warehouse inaugurated in Shenzhen, to service high-tech exports. In June 2024, an automated fulfillment center that serves the domestic and regional market was opened in Japan that provides next-generation picking systems. In July 2025, South Korea started to build a specialized cold storage every ounce to integrate the robot technology specifically to support the seas and the pharmaceutical industries. India is also gaining pace in skill development programmes in warehouse operation keeping up the pace with the fast digitalization of the sector.
Warehousing Market Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America | 38.60% |
| Europe | 24.50% |
| Asia-Pacific | 29.10% |
| LAMEA | 7.80% |
The LAMEA is slowly picking up with strategic investment, trade facilitation project and regional infrastructural development. In April 2025, Brazil started the construction of a logistics hub in the state of Sao Paulo to act as an agricultural exporting gateway. In October 2024, the UAE opened a smart warehousing zone as part of its free trade hub to welcome foreign-based distribution businesses. In May 2025, South Africa commissioned the first high-density automated warehouse to serve the local manufacturing industries as well as cross border trade in the SADC region. Such efforts are indicative of the increased competitive nature of LAMEA in the global supply chains.
Market Segmentation
By Type
By Ownership
By Function
By Technology Adoption
By End-Use Industry
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Warehousing
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Type Overview
2.2.2 By Ownership Overview
2.2.3 By Function Overview
2.2.4 By Technology Adoption Overview
2.2.5 By End User Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.2 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Gold Rush in E-commerce & Space
4.1.1.2 Smart warehousing adoption
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 Huge upfront Capital Requirement and Long ROI
4.1.2.2 Shortages & Increasing prices
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 Labor Displacement Workforce Adjustment
4.1.3.2 Cross compatibility with Legacy Systems
4.1.4 Market Opportunities
4.1.4.1 AMRs to Cover Uninvolved Labor
4.1.4.2 Expansion in Warehousing Policy-Driven
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Warehousing Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Warehousing Market, By Type
6.1 Global Warehousing Market Snapshot, By Type
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 General Storage
6.1.1.2 Cold Storage
6.1.1.3 Hazardous Materials Storage
6.1.1.4 Automated/Smart Warehouses
Chapter 7. Warehousing Market, By Ownership
7.1 Global Warehousing Market Snapshot, By Ownership
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Private Warehouses
7.1.1.2 Public Warehouses
7.1.1.3 Cooperative Warehouses
Chapter 8. Warehousing Market, By Function
8.1 Global Warehousing Market Snapshot, By Function
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Distribution Warehouses
8.1.1.2 Fulfillment Centers
8.1.1.3 Cross-Docking Facilities
8.1.1.4 Consolidation Warehouses
Chapter 9. Warehousing Market, By Technology Adoption
9.1 Global Warehousing Market Snapshot, By Technology Adoption
9.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
9.1.1.1 Conventional Warehousing
9.1.1.2 Semi-Automated Warehousing
9.1.1.3 Fully Automated Warehousing
9.1.1.4 Robotics & AI-Driven Warehousing
Chapter 10. Warehousing Market, By End-User
10.1 Global Warehousing Market Snapshot, By End-User
10.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
10.1.1.1 E-commerce & Retail
10.1.1.2 Food & Beverage
10.1.1.3 Pharmaceutical & Healthcare
10.1.1.4 Automotive & Industrial
10.1.1.5 Consumer Goods
Chapter 11. Warehousing Market, By Region
11.1 Overview
11.2 Warehousing Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
11.3 Global Warehousing Market, By Region
11.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
11.4 North America
11.4.1 North America Warehousing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.3 North America Warehousing Market, By Country
11.4.4 U.S.
11.4.4.1 U.S. Warehousing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
11.4.5 Canada
11.4.5.1 Canada Warehousing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
11.4.6 Mexico
11.4.6.1 Mexico Warehousing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
11.5 Europe
11.5.1 Europe Warehousing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.3 Europe Warehousing Market, By Country
11.5.4 UK
11.5.4.1 UK Warehousing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
11.5.5 France
11.5.5.1 France Warehousing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
11.5.6 Germany
11.5.6.1 Germany Warehousing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
11.5.7 Rest of Europe
11.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Warehousing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6 Asia Pacific
11.6.1 Asia Pacific Warehousing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.3 Asia Pacific Warehousing Market, By Country
11.6.4 China
11.6.4.1 China Warehousing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.5 Japan
11.6.5.1 Japan Warehousing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.6 India
11.6.6.1 India Warehousing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.7 Australia
11.6.7.1 Australia Warehousing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
11.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Warehousing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7 LAMEA
11.7.1 LAMEA Warehousing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.3 LAMEA Warehousing Market, By Country
11.7.4 GCC
11.7.4.1 GCC Warehousing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7.5 Africa
11.7.5.1 Africa Warehousing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7.6 Brazil
11.7.6.1 Brazil Warehousing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
11.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Warehousing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 12. Competitive Landscape
12.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
12.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
12.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
12.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
12.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 13. Company Profiles
13.1 Deutsche Post AG
13.1.1 Company Snapshot
13.1.2 Company and Business Overview
13.1.3 Financial KPIs
13.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
13.1.5 Strategic Growth
13.1.6 Global Footprints
13.1.7 Recent Development
13.1.8 SWOT Analysis
13.2 BrightKey, Inc.
13.3 GEODIS
13.4 NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS, INC.
13.5 FedEx
13.6 RXO Inc.
13.7 XPO, Inc.
13.8 Ryder System, Inc.
13.9 Mitsubishi Logistics Corporation
13.10 C.H. Robinson Worldwide, Inc.
13.11 Americold Logistics, Inc.
13.12 Lineage, Inc.
13.13 Kuehne+Nagel
13.14 A.P. Moller – Maersk
13.15 NewCold