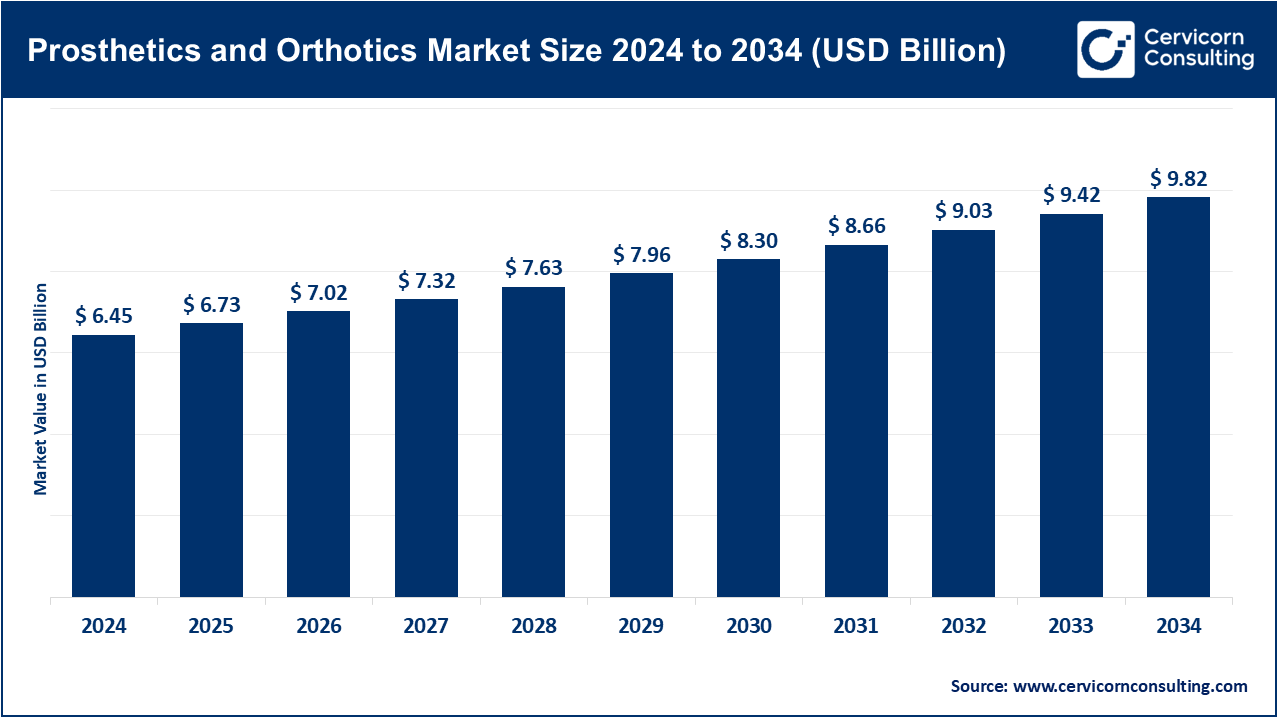
The global prosthetics and orthotics market size was reached at USD 6.45 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 9.82 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.7% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
The prosthetics and orthotics market focuses on the design and production of advanced medical devices that restore mobility and function for individuals with limb loss or musculoskeletal conditions. Driven by rising incidences of diabetes, trauma, and vascular diseases, the market benefits from innovations like 3D printing, smart sensors, and AI-powered adaptive prosthetics that offer improved comfort and functionality. Collaborations between device manufacturers and tech companies are accelerating the development of personalized, lightweight, and intelligent solutions, while regulatory support and increasing awareness boost adoption. Integration with digital health and tele-rehabilitation platforms is further enhancing patient care, making prosthetics and orthotics more accessible, responsive, and effective in improving quality of life.
Electric-powered Prosthetics: Electric-powered prosthetics, also called myoelectric limbs, identify muscle signals through sensors to turn them into motorized movement, vastly benefiting function because you can reconcile activities of daily life far, far better than without it. In 2024, the FDA approved BionicM's motorized knee system for use in the U.S.A. This marks a movement away from traditional prosthetics, to a growing approval of robotic prosthetics. By seamlessly providing motion onto rough surfaces, and potentially independence, these devices are typically considered desirable. The U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs used these advanced prosthetics in their rehabilitation process. WHO's assistive technology reports have also referred to electric-powered limbs as assistive devices with the singular purpose of improving offer to restore mobility, particularly in high-income environments. Public/private investments will be a driver of innovation; to date, DARPA's investment in an AI-powdered limb is still shown on its website. In part to embedded AI and intuitive control mechanisms, these types of technologies are accruing interest around the world, especially in the services of assisting mobility.
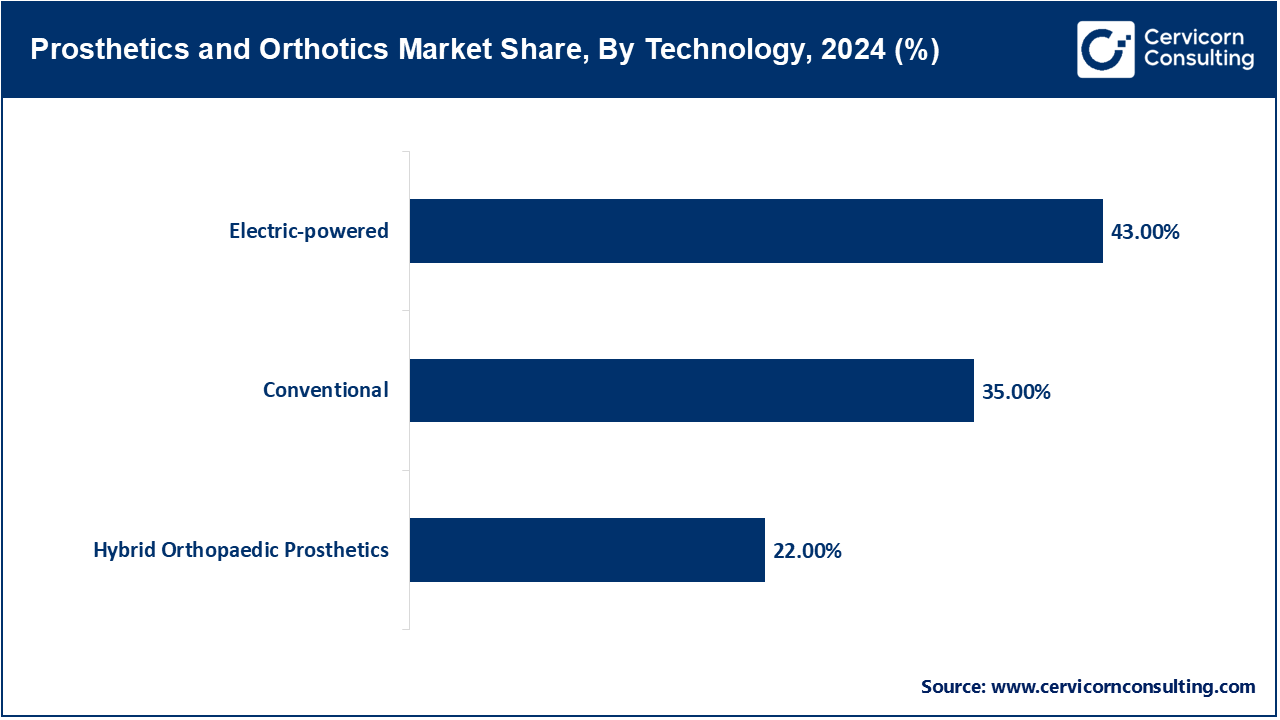
Conventional Prosthetics: Conventional prosthetics remain widely used due to affordability, durability, and simplicity, especially in low-resource settings. According to reports from WHO in 2024, most people in lower-income countries who use prosthetics have conventional designs fitted with metal rods, rubber or wood. It provides basic function without powered components, yet it is still essential to mobility. Recently, WHO and ISPO released guidelines on local production and distribution protocols to ensure a better pathway to achieving these products through local workshops. Technology changes in 3D-printing enabled them to reduce manufacturing costs with less compromise to customization. Countries such as Bangladesh and Kenya have found the means to distribute government subsidized conventional prosthetics throughout public health missions. These devices should still be able to provide the necessary support to people with disabilities as part of inclusive and accessible healthcare systems.
Hybrid Orthopedic Prosthetics: Hybrid prosthetics combine mechanical structures with select powered or sensor-driven elements, aiming to balance functionality and cost. They typically offer powered knees or wrists with passive feet or sockets, making them appealing to middle-income regions. In 2023, hybrid knee-ankle systems were introduced in pilot projects funded by the WHO in Southeast Asia and Eastern Europe. Clinical trials in public hospitals showed improved gait and balance when using hybrid systems. The FDA has recognized hybrid designs under emerging tech frameworks for partial automation. Their modular nature allows upgrades over time, which is attractive for patients with evolving physical needs. These devices represent a middle ground between cost-effective conventional limbs and high-tech electric systems.
Orthotic Devices: Orthotics, such as a brace or a support structure, help to stabilize or correct that deformity of the musculoskeletal, and is particularly important in recovery from traumatic injuries and in chronic conditions like scoliosis. According to WHO’s 2024 data, one-third of the global population could benefit from rehabilitation interventions like orthotics. Assistive devices can also be extremely valuable for patients with congenital disabilities, or with acquired disabilities from strokes or spinal injuries. Countries with national health care plans in Africa and Asia that were supported by WHO have recently begun to include coverage for orthotics for low income populations. Furthermore, there have been advances such as 3D-printed orthoses that shorten time to produce and lower cost, while allowing for a number of customizations. In Uzbekistan, WHO supported orthotic programming has included government structural or funded facilities for more accessible pediatric services for orthotics. These products are among the core health products identified by global health governance.
Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Revenue Share, By Type, 2024 (%)
| Type | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Orthotics | 60% |
| Prosthetics | 40% |
Prosthetic Devices: Prosthetic limbs are designed to restore mobility in those who have experienced trauma, disease, or defects causing loss of limb(s). While prosthetic limbs can range from simple designs to state-of-the-art devices, the most widely available are basic to mid-level limb prosthetics. In 2023, DEKA's LUKE Arm was approved by the FDA, which lets users perform multiple joint movements with enhanced dexterity. The World Health Organization (WHO) has promoted prosthetic devices as a human rights issue that must be considered under the approach to universal health coverage. Pilot programs targeted at rural communities have been funded by WHO and local governments in several Southeast Asian countries to expand access to prosthetic care. U.S. veterans' hospitals indicated a 35% improvement in quality-of-life measures with next-gen devices compared to standard fittings. Modular, appropriate technology solutions, or low-cost building block designs for amputees are gaining use in many developing countries and low- and middle-income nations. Growing prosthetic devices are incorporating artificial intelligence, adaptive control, and lighter-weight materials.
Prosthetic Clinics: Prosthetic clinics are the main entry, or access point for, prosthetic device fitting, adjustment, and patient-training. Many clinics make up a significant portion of prosthetic device sales, and are crucial in getting new technologies like AI-enabled limbs or robotic limbs into the hands of customers. Many clinics in the U.S. have added FDA-cleared electric-powered systems in discovered in 2023. and offer advanced mobility solutions. Clinics in developing countries are usually public-private partnerships with the support of WHO, and often deliver prosthetics care under partnership with WHO's assistive technology progam. Clinics in developing countries often provide training courses for prosthetists, to enhance local availability of services. New reimbursement models have helped clinics in developing countries in Europe and Asia gain viability and provide better access to care. Clinics will remain essential to the supply of ongoing prosthetic device care, adjustments to prosthetic devices after use, and education to devise users for their continued journey with their devices.
Hospitals: Hospitals play a central role in the prosthetics and orthotics ecosystem, especially in surgical preparation, rehabilitation, and integrated device fitting. Many major hospitals in the U.S. and Europe are incorporating smart prosthetics as part of orthopedic and trauma care. The FDA's approvals like the DEKA arm were clinical trials led by hospitals. The WHO's Rehabilitation 2030 recommended a"hospital committee" to assist with integrating the provision of orthotic and prosthetic services into routine hospital care. Following the WHO support and recommendation, hospitals in south-east Asia are developing and expanding their prosthetic departments to address growing demand. Hospitals are increasingly taking the lead in a variety of innovations, including AI-powered diagnostics for limbs, as well as using pressure-mapping technology to improve accurate lens fittings. Hospitals are critical to both high-tech and community-based prosthetic solutions.
The prosthetics and orthotics market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region
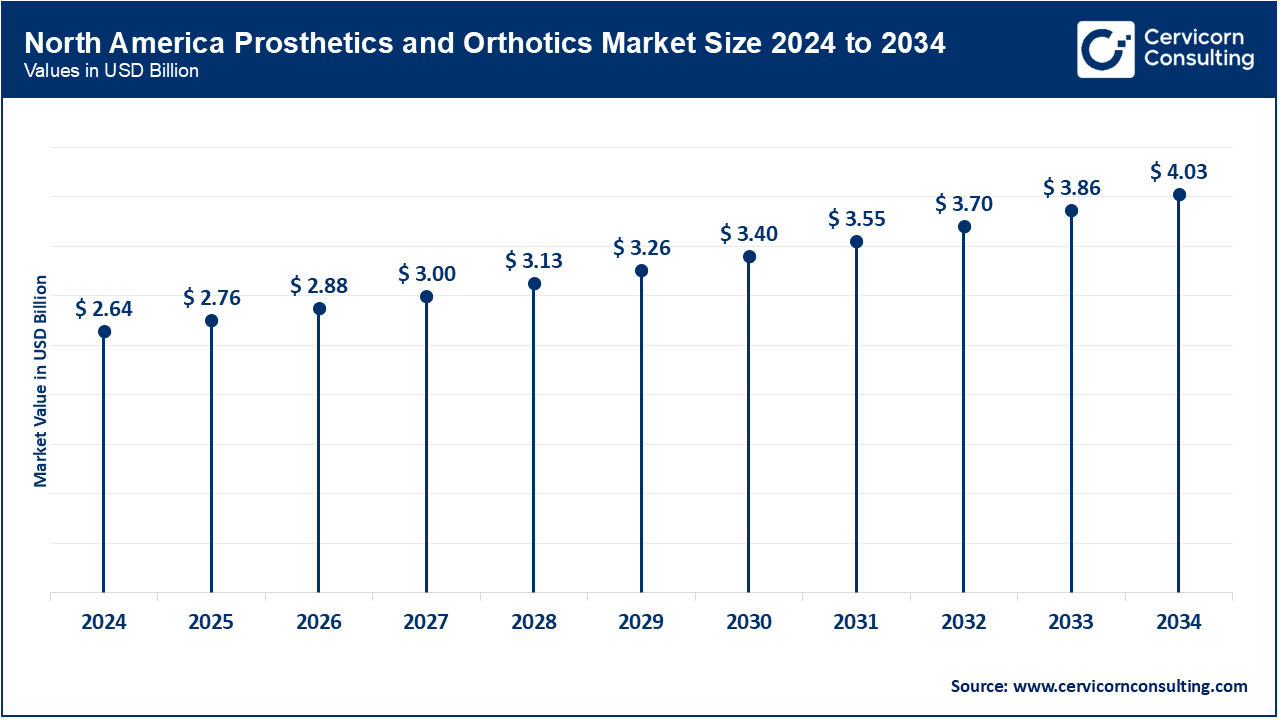
North America is led by the U.S. in advanced prosthetic technologies; in 2024, the FDA approved additional prosthetics with AI-enabled/robotic features - BionicM’s motorized knee and the DEKA LUKE Arm - along with strong regulatory approval/popularity. Canadian provincial governments fund prosthetics through government policies, referring to plans in provinces such as Ontario, which funds microprocessor knees (~USD 15,000) for eligible clients and Saskatchewan which covers similar plans and the recent Canada Disability Benefit legislation of USD 6.1 B over six years for assistive technology in 2024 funding. Mexico's path for regulating prosthetic devices includes COFEPRIS and standards for NOM devices, ensuring these prosthetic devices are safe for consumers, government generated safety protocols and can rely on the national quality infrastructure, all of which also help provide consumer protection. In summary, across North America, sources of public funding, developing regulations around prosthetic and orthotic devices and disability benefit plans are all seeds of improvement of accessing prosthetic and orthotic care.
In Europe, the UK has budgeted USD 0.017 B (2023-24) into 17 prosthetic/orthotic R&D's through NIHR and UKRI via the National Health Service, including smart limbs and AR sensory tools for patients; NHS England now pays for (the manufacturer provides) bionic arms with natural grip for eligible patients. We assume Germany will or is still funding or supporting same research for their continued reliance on sensor orthotic and digital rehabilitation as prosthetics and orthotics that remain under the provision of care under federal healthcare standards and guidelines. France’s national health authority (HAS) has expanded coverage for advanced orthotic devices in 2023, ensuring broader access under universal health coverage. EU-wide regulations harmonize safety standards for smart prostheses and AI medical devices, supported by public hospital rollout of next-gen limbs. These coordinated initiatives reflect strong state commitment to innovation and equitable service delivery across Europe.
Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Revenue Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America | 41% |
| Europe | 22% |
| Asia-Pacific | 28% |
| LAMEA | 8% |
In Asia-Pacific, China’s National Health Commission in 2024 issued directives to bolster prosthetic clinics equipped with smart diagnostic tools in rural and urban centers. India’s Ministry of Social Justice supports institutes like SVNIRTAR in Odisha (~900 students) to train orthotists and expand AI-based socket use; local manufacturing and NGO collaborations are growing. Japan’s Ministry of Health continues to fund research into lightweight carbon-fiber limbs, while Australia’s Department of Health reformed the Prostheses List in 2023–25, reducing private health gaps and allocating USD 0.014 billion for list modernization. South Korea’s KIMM unveiled an AI-based adaptive prosthetic socket in 2023, responsive to residual limb volume changes in real time via smartphone integration. These developments underscore APAC’s blend of regulation, training, and innovation across countries.
In LAMEA, Brazil’s SUS health system (USD 7.3 billion budget, ~100% population coverage) provides free dental prosthetics and is expanding limb prosthesis through specialized centers, recovering from pandemic delays. The UAE’s Ministry of Health has included prosthetic services in national disability policy since 2023, enhancing access to robotic limbs in Abu Dhabi hospitals. Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 targets expanded rehabilitation and prosthetic centers, with pilot exoskeleton programs reported in Riyadh in 2024. South Africa’s provincial health departments, including Eastern Cape, partnered with universities like Walter Sisulu to provide pediatric prosthetic legs in 2024, improving rural access. UAE and Saudi regulatory agencies (e.g., SFDA) are working to harmonize standardization with international norms to ensure safety and quality.
Recent partnerships in the prosthetics and orthotics industry emphasize innovation, rehabilitation access, and smart device integration. In 2023, Össur partnered with the Alfred Mann Foundation to accelerate neuro-controlled prosthetic limb research using implanted myoelectric sensors. Blatchford collaborated with the UK NHS to expand access to energy-efficient microprocessor knees for post-amputation patients. Aether Biomedical teamed up with Polish rehabilitation hospitals to trial AI-powered bionic hand technology under clinical supervision. Fillauer LLC signed an agreement with Liberating Technologies, Inc. to co-develop upper-limb prosthetics using multi-electrode signal processing. Meanwhile, Bauerfeind worked with German sports medicine institutes to refine dynamic orthoses for injury prevention. These alliances highlight the industry’s commitment to merging clinical care with biomechatronics and adaptive technologies.
Market Segmentation
By Technology
By Type
By End-User
By Region
Chapter 1 Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Prosthetics and Orthotics
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Technology Overview
2.2.2 By Type Overview
2.2.3 By End-User Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3 Global Impact Analysis
3.1 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.2 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4 Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Customization and Personalization
4.1.1.2 Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
4.1.1.3 Growing Awareness and Acceptance
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 High Costs
4.1.2.2 Limited Access to Healthcare Services
4.1.2.3 Regulatory challenges
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 Limited Availability of Skilled Practitioners
4.1.3.2 Complexity of Technology Integration
4.1.3.3 Societal and Psychological Barriers
4.1.4 Market Opportunities
4.1.4.1 Technological advancements
4.1.4.2 Growth in Emerging Markets
4.1.4.3 Increase in Pediatric Prosthetics
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5 Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6 Prosthetics and Orthotics Market, By Technology
6.1 Global Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Snapshot, By Technology
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Electric-powered
6.1.1.2 Conventional
6.1.1.3 Hybrid Orthopaedic Prosthetics
Chapter 7 Prosthetics and Orthotics Market, By Type
7.1 Global Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Snapshot, By Type
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Orthotics
7.1.1.2 Prosthetics
Chapter 8 Prosthetics and Orthotics Market, By End-User
8.1 Global Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Snapshot, By End-User
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Prosthetics Clinics
8.1.1.2 Hospitals
8.1.1.3 Rehabilitation Centre
Chapter 9 Prosthetics and Orthotics Market, By End-User
9.1 Global Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Snapshot, By End-User
9.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
9.1.1.1 Utility Companies
9.1.1.2 Commercial Maritime Operators
9.1.1.3 Governments and Municipalities
9.1.1.4 Energy Providers
9.1.1.5 Private Users
Chapter 10 Prosthetics and Orthotics Market, By Region
10.1 Overview
10.2 Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
10.3 Global Prosthetics and Orthotics Market, By Region
10.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
10.4 North America
10.4.1 North America Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.3 North America Prosthetics and Orthotics Market, By Country
10.4.4 U.S.
10.4.4.1 U.S. Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
10.4.5 Canada
10.4.5.1 Canada Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
10.4.6 Mexico
10.4.6.1 Mexico Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
10.5 Europe
10.5.1 Europe Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.3 Europe Prosthetics and Orthotics Market, By Country
10.5.4 UK
10.5.4.1 UK Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.4.3 UK Market Segmental Analysis
10.5.5 France
10.5.5.1 France Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.5.3 France Market Segmental Analysis
10.5.6 Germany
10.5.6.1 Germany Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.6.3 Germany Market Segmental Analysis
10.5.7 Rest of Europe
10.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.7.3 Rest of Europe Market Segmental Analysis
10.6 Asia Pacific
10.6.1 Asia Pacific Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.3 Asia Pacific Prosthetics and Orthotics Market, By Country
10.6.4 China
10.6.4.1 China Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.4.3 China Market Segmental Analysis
10.6.5 Japan
10.6.5.1 Japan Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.5.3 Japan Market Segmental Analysis
10.6.6 India
10.6.6.1 India Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.6.3 India Market Segmental Analysis
10.6.7 Australia
10.6.7.1 Australia Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.7.3 Australia Market Segmental Analysis
10.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
10.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.8.3 Rest of Asia Pacific Market Segmental Analysis
10.7 LAMEA
10.7.1 LAMEA Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.3 LAMEA Prosthetics and Orthotics Market, By Country
10.7.4 GCC
10.7.4.1 GCC Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
10.7.5 Africa
10.7.5.1 Africa Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.5.3 Africa Market Segmental Analysis
10.7.6 Brazil
10.7.6.1 Brazil Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.6.3 Brazil Market Segmental Analysis
10.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
10.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Prosthetics and Orthotics Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEA Market Segmental Analysis
Chapter 11 Competitive Landscape
11.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
11.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
11.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
11.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
11.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 12 Company Profiles
12.1 Ossur
12.1.1 Company Snapshot
12.1.2 Company and Business Overview
12.1.3 Financial KPIs
12.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
12.1.5 Strategic Growth
12.1.6 Global Footprints
12.1.7 Recent Development
12.1.8 SWOT Analysis
12.2 Blatchford Limited
12.3 Fillauer LLC
12.4 Bauerfeind
12.5 Aether Biomedical
12.6 Mobius Bionics
12.7 Ultraflex Systems Inc.
12.8 Steeper Group
12.9 Ottobock
12.10 WillowWood Global LLC.
12.11 Hanger, Inc.