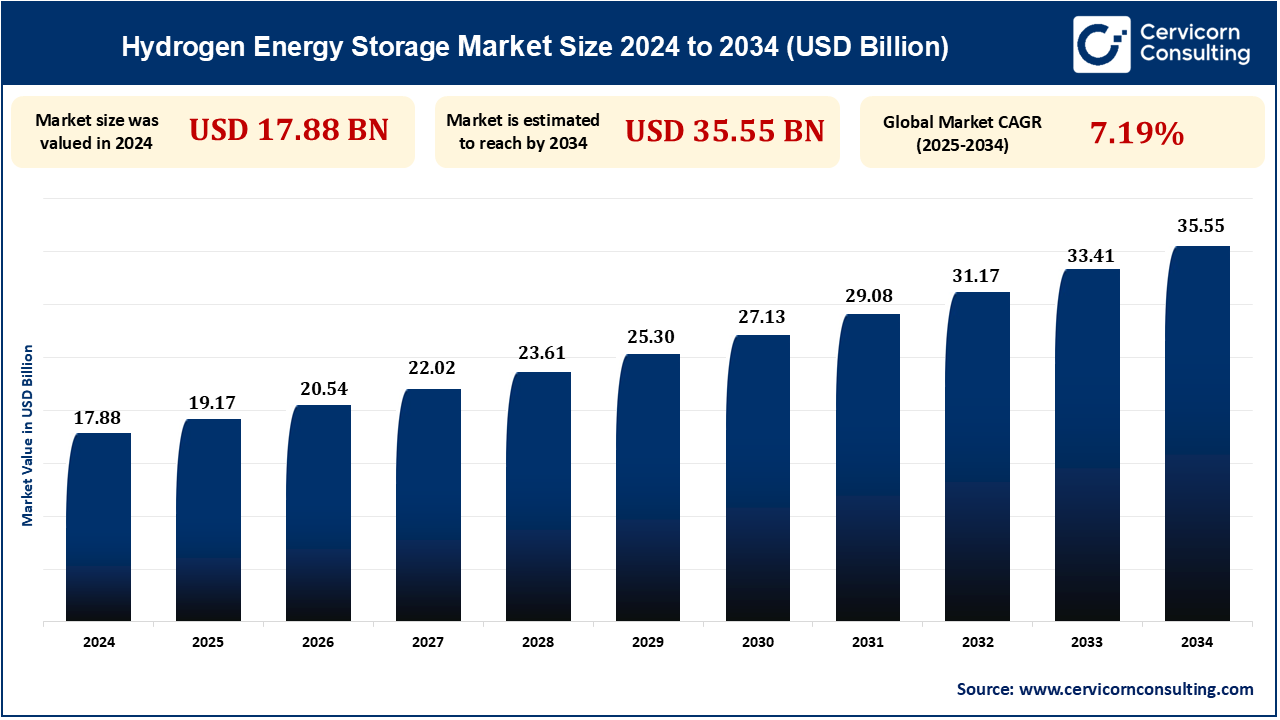
The global hydrogen energy storage market size was reached at USD 17.88 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 35.55 billion by 2034, exhibiting at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.19% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
Hydrogen energy storage is expanding quickly with the demand for efficient and sustainable energy increasing. Solar and wind power are becoming increasingly popular sources of renewable energy, and hydrogen offers a means to store surplus energy for future use. The technology provides a mechanism to convert excess renewable energy into hydrogen gas, which can be stored and utilized to produce electricity when required. Improvements in the technology of electrolysers are bringing down the costs and making production more efficient for hydrogen. Incentives, along with investment by the government, are boosting the demand for this energy storage option further. Hydrogen storage energy is stepping up to the plate in changing over to a cleaner, better energy system.
The integration of hydrogen energy storage with renewable power is gaining momentum as solar and wind generation is rising. Hydrogen enables efficient storage of surplus renewable energy and use in low-production times, thereby balancing demand and supply. Germany installed nearly 600,000 new stationary battery storage systems in 2024 with capacity increasing 50% to 19 GWh. Domestic storage rules with 0.0018 billion units (15.4 GWh), but commercial storage increased 26% to 38,000 units (1.4 GWh). Utility-scale storage doubled with 100 new facilities (0.8 GWh). Reforms and falling battery prices are driving growth, but administrative innovation needs to continue. Use of hydrogen storage would add at the leading edge of international decarbonization and push renewables even further.
The European Union introduced a major funding scheme in 2023 to accelerate hydrogen production and storage under its Green Deal. Global investment in hydrogen schemes has nearly doubled since May 2022, to USD 680 billion as of May 2024, with North America alone having USD 96 billion. While North America is projected to produce a third of the globe's hydrogen by 2030, the majority will be derived from natural gas, and green hydrogen production leadership comes from China. Ambiguity regarding U.S. regulation and incentives, and specifically the 45V tax credit, has halted renewable hydrogen projects, and fossil hydrogen enjoys support through 45Q tax credits. That Europe too experiences the same policy issues puts greater emphasis on unified global policy. These investments will also contribute to the growth of hydrogen storage technologies, driving the market growth.
Growing research and development of more efficient and affordable hydrogen production technologies are driving the expansion of hydrogen energy storage. Technological innovation, such as improved electrode materials, durable membranes, modular designs, dynamic operation on renewable energy, and artificial intelligence-based control systems, are reducing the cost of green hydrogen and making it more viable for widescale deployment. The Hydrogen Council 2023 report refers to over 500 Gigascale hydrogen projects with an investment of USD 500 billion, reducing costs even further. The projects are making green hydrogen a low-cost energy leader in the coming years. The cost of hydrogen production will be much lower, making it feasible for mass adoption of hydrogen storage in industry and household markets. It will be very important in realizing clean energy ambitions.
Hydrogen storage technology involves huge initial capital expenditure, and adoption would be difficult for smaller players and emerging economies. Most hydrogen initiatives are being put on hold or canceled as early enthusiasm is faced with reality. For example, a green hydrogen export agreement between Atlantic Canada and Germany was pushed back because of supply-demand mismatches and inflation. Fortescue Ltd. also put on hold a green hydrogen project in British Columbia because of unfavorable power prices. Experts are still skeptical of the cost-saving nature of hydrogen and its usage in various applications. Despite such constraints, the sector will also face cost constraints. Economies of scale may ultimately reduce cost over the long run, with hydrogen storage being more viable.
| Attributes | Details |
| Hydrogen Energy Storage Market Size in 2024 | USD 17.88 Billion |
| Hydrogen Energy Storage Market Size in 2034 | USD 35.55 Billion |
| Hydrogen Energy Storage Market CAGR | 7.19% from 2025 to 2034 |
| By Technology |
|
| By Physical State |
|
| By Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| Key Players |
|
North America is one of the dominant players in the hydrogen energy storage industry because of high government investment and efforts toward clean energy adoption. The United States is a leading country with initiatives like the Hydrogen Hub program, aimed at establishing hydrogen infrastructure. Canada is also contributing through its initiatives towards the production of hydrogen from renewable energy resources and its aggressive plans for hydrogen integration. Geographical proximity of Mexico to the U.S. market enhances its role as a key country for cross-border hydrogen infrastructure development. Favorable R&D and rising hydrogen fueling stations are the key drivers to drive market growth in this region.
Asia-Pacific is amongst the fastest-changing hydrogen energy storage markets, and there are notable advancements in Japan, South Korea, and China. Japan is a world leader in hydrogen technology, and their interest lies in hydrogen fuel cells for industry and transport. South Korea has vowed to be a hydrogen society with large investments made in the manufacturing of hydrogen as well as infrastructure. China is a leading adopter of electric vehicles and a major producer of hydrogen, and its demand for hydrogen storage systems is being driven. Its urbanization and industrialization at a fast pace are turning it into a popular market for hydrogen solutions in energy storage and transportation industries.
Compression: Hydrogen compression is one of the technological techniques employed for the high-pressure storage of hydrogen gas. The process requires the pressure of hydrogen gas to be raised so that its volume is reduced, making it easy to store and transport. Hydrogen filling stations and sites where high-pressure storage is required have compressors. Due to advances in compressor technology and material, the process becomes increasingly viable for commercial-scale hydrogen storage. It is used at large scale presently due to its ease of design and historic performance in industrial processes.
Solid-state hydrogen storage is one form of storage in which hydrogen is physically or chemically soaked up into solid substances such as carbon-based material or metal hydrides. Such storage accommodates high energy density and is run on comparatively low pressure. Solid-state storage systems are generally safer than the high-pressure gas storage system since it is free from the hazards provided by gaseous hydrogen. These systems are in the process of being developed for mass use but are viewed as a viable alternative for the transportation industry and mobile applications.
Residential uses of hydrogen energy storage are centered primarily on providing energy solutions for homes, particularly for heating, electricity generation, and as a backup system. Hydrogen fuel cells are used to generate heat and electricity for homes, a clean, efficient, and dependable alternative to traditional energy suppliers. Residential application will increase once hydrogen infrastructure starts to emerge, particularly in the case of a need for stability or independence on the grid in a region. The residential market also gains from the growing interest in renewable energy sources, where hydrogen storage can supplement solar or wind power systems.
Stationary applications of hydrogen energy include installing hydrogen energy storage systems to power stationary energy stations such as power plants, industrial parks, and skyscrapers. Hydrogen fuel cells are similarly applied in providing backup power, grid resilience, or as a power substitute for off-grid locations. Hydrogen is stored in the form of gas, liquid, or solid depending on the final application and requirement. The increased generation of green power from solar and wind energy contributes to the demand for hydrogen as an on-demand, clean energy source.
Empower your strategy with expert insights, purchase this premium research@ https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/buy-now/2343
Ask here for more details@ sales@cervicornconsulting.com