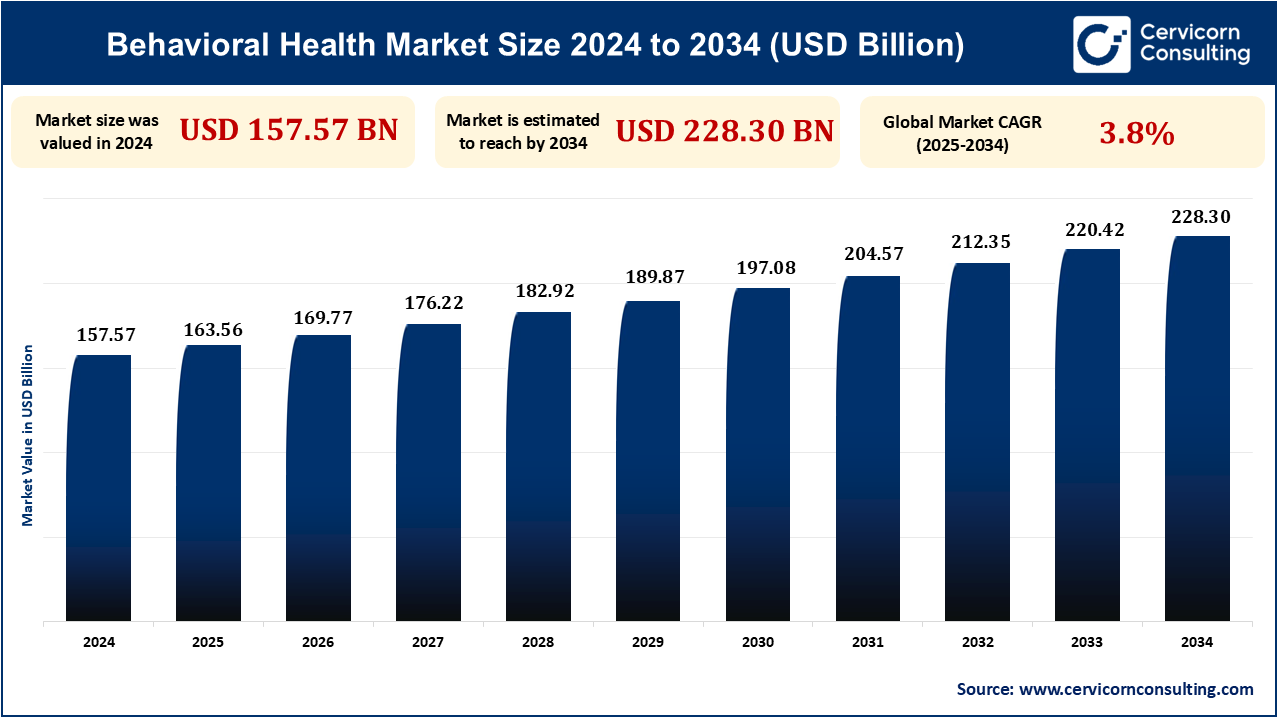
The global behavioral health market size is expected to exceed around USD 228.30 billion by 2034 from USD 157.57 billion in 2024 and is growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.8% from 2024 to 2034.
The global behavioral health market continues to grow steadily as a result of increased awareness regarding mental health and its importance as a critical component of health and well-being. Mental health programs initiated at the levels of government and healthcare providers are being expanded to include behavioral care, integrated into primary care systems. Enhanced use of telepsychiatry and digital therapeutics has increased access to services, especially in underserved areas. Demand was boosted again by the post-COVID period, as mental health disorders increased through all age groups, and healthcare systems worldwide began to respond more vigorously.
The behavioral health market comprises services, technologies, and treatments intended to manage mental health conditions and substance use disorders. Services included in this market include psychiatric care, counseling, addiction treatment, and behavioral therapy, and are provided through inpatient facilities, outpatient centers, and telehealth platforms. Other forms of conditions addressed under this market are depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, alcohol and drug abuse, and behavioral issues among children and adolescents. Stakeholders include healthcare providers, payers, digital health companies, and pharmaceutical firms.
The increase in insurance coverage for mental health services, especially for limited government-backed health programs in North America and Europe, has given a significant boost to this market. For example, in the U.S., the act titled the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act (MHPAEA) is an act that ensures that mental health treatment is treated equally with physical health treatment in the case of cases occurring against therapy, medications, and residential care. This just strengthens the demand for behavioral health services.
Prime importance is the increasing convergence of behavioral health into public and private insurance schemes. In markets such as the U.S., enrollment under the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act ensures that insurance plans cover mental conditions as physical ones. This has meant people have better access to psychiatric care, substance abuse treatment, and counseling services. Furthermore, Medicaid expansions in states and initiatives by private insurers increased the number of patients served, especially among underserved populations. With parity legislation introduced in other countries and budget allocation for mental health infrastructure, more and more patients are accessing services. There is also an increase in coverage for the use of tele-behavioral services, thus making treatment even more affordable and convenient, especially for patients living in geographically disadvantaged regions.
Digital therapeutics and AI-infused mental health apps stand at a transformative intersection in the very market of behavioral healthcare. These technologies are viable, cost-effective, scalable solutions to an ever-burdening mental health crisis, especially with access to traditional psychiatric care still being significantly impeded by vacancies in the workforce. Various startups and established companies invest actively in AI-enabled mental health technology, including virtual therapy platforms, AI chatbots, and predictive analytics for early intervention.
AI-based applications provide a variety of advanced techniques for conducting mental health care. With personalized treatment planning, the algorithms make use of machine learning techniques in order to design intervention strategies based on the history of the patient, the evolution of symptoms, and how engaged the patient has been. Continuous tracking of patients and their mental health indicators using wearables and apps can allow for real-time intervention before their condition deteriorates. Meanwhile, data-driven clinical choices can ensure optimal patient outcomes while enhancing the responsible use of resources in the health system.
Digital therapeutics come under an evolving regulatory umbrella worldwide. With FDA approvals of software therapeutics for treating mental disorders, there is confidence in the acceptability of AI-related interventions. Rejoin, a digital therapeutic approved by the FDA for major depressive disorder, helps patients rewire negative thinking through neuroplasticity-based exercises.
The dearth of trained mental health professionals, such as psychiatrists, clinical psychologists, social workers, and licensed counselors, is probably the most critical challenge that hinders market growth. World Health Organization estimates indicate that almost half of the global populace lives in areas where access to behavioral health providers is very limited. As a result, the workforce gap is very acute in rural and low-income areas since demand often outstrips available capacity. This problem leads to prolonged waits, reduced quality of care, and patient dropout. In the developed markets, high instances of burnout and turnover further constrain the delivery of services. Human resources are required for scaling up the services in behavioral health despite technological advancements. Without a proper workforce development initiative and training programs, this bottleneck will continue in accessing care.
A rapidly changing demographic scene-including a growing youth population and an aging community- has contributed to increasing incidences of anxiety, depression, and substance use disorder across the region. Furthermore, in the Asian Pacific, Latin America, and parts of Africa, some governments are beginning to take notice of mental health as a public health priority. The policies on mental health at the national level, awareness campaigns, and integration into primary care frameworks have begun to gain traction. Concurrently, global NGOs and various multinational health organizations are providing funding for capacity-building and infrastructure improvement. Stigma has remained one barrier; however, access gaps are starting to shrink with the increasing penetration of digital media and m-health technologies. With an increasing healthcare budget and due to collaboration between the public and private sectors, the behavioral health market in many developing economies shows a promising long-term opportunity for service providers, pharmaceutical companies, and digital health innovators.
| Attributes | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 157.57 Billion |
| Market CAGR | 3.8% from 2025 to 2034 |
| Key Players |
|
| By Service Type |
|
| By Disorder Type |
|
| By End-Users |
|
| By Regions |
|
India, China, and Australia have all faced increasing demands for behavioral health services due to rapid urbanization, greater educational stress, and substance abuse. Governments are continually integrating mental health services into primary care and expanding their reach through telepsychiatry.
North America is still the largest area in the behavioral health market with advanced healthcare structure, awareness levels, and extensive coverage of the insurance scheme. Most of the share in North America comes particularly from the US due to high regulatory support and the well-established network of mental health providers. The Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act provides access to behavioral health services through insurance. Also, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration is one of the critical ones in the funding and policy-making part.
Outpatient clinics are the most accessed behavioral health care form due to the affordability and increased flexible delivery methods under which it occurs. This application is open to the management of the commonest mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and substance use without spending time in a hospital. Almost every outpatient visit therapeutically can also be justified through the increasing preference for less-than-short treatment concerning insurance reimbursement models favoring outpatient treatment systems.
With the recent expansion in telehealth services, accessibility for follow-up and even consultation is done virtually; thus, continued use of outpatient clinics can only increase. Besides that, the recent COVID-19 pandemic-induced preferment for outpatient clinics has shifted service delivery to digital modes for operating and scaling services. Where early intervention and chronic condition control are needed, it positions itself sustainably and can be developed into a broader model of behavioral health service delivery.
In terms of types, depression, and anxiety disorders constitute a major segment of the behavioral health market because the high prevalence of these disorders all over the world captures a rather bigger market share. WHO reports that depression affects 300 million people, and more than 260 million people are affected by anxiety disorders. This is becoming recognized, diagnosed, and better known, as much more understanding was achieved of mental health culture, stigma was reduced, and screening initiatives were increased to include early detection. Adoption is done through technological tools such as mental wellness applications, digital therapy platforms, or AI-enabled early detection tools specifically targeting these disorders. New antidepressants and cognitive behavioral treatments among others, represent the various advances in prescription pharmaceuticals in treatment. Part of the drive in demand for such behavioral health services is provoked through work mental health initiatives and student wellness programs. Therefore, the above factors remain the major causes leading to the dominance of this segment in the world behavioral health market.
Empower your strategy with expert insights, purchase this premium research@ https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/buy-now/2335
Ask here for more details@ sales@cervicornconsulting.com