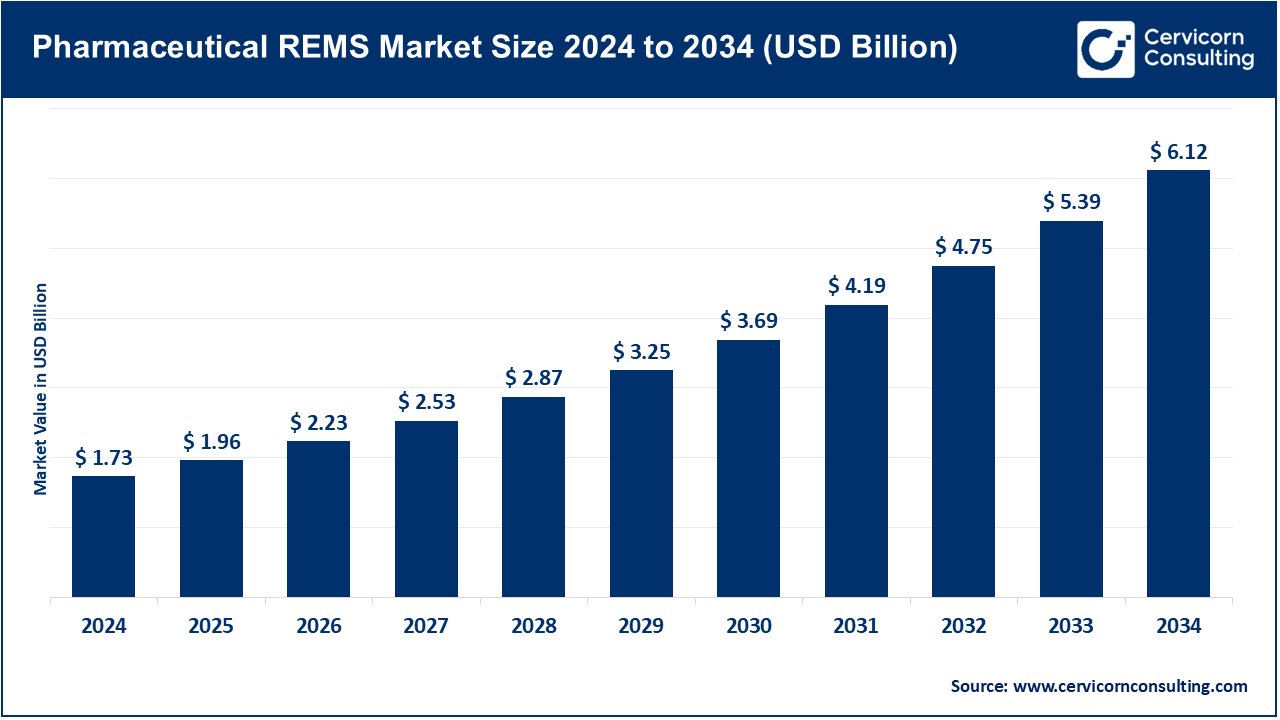
The global pharmaceutical REMS market size was valued at USD 1.73 billion in 2024 and is expected to hit around USD 6.12 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.64% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
The pharmaceutical REMS market is expected to grow significantly due to increasing regulatory focus on drug safety, rising incidence of adverse drug reactions, complex specialty drug launches, and the need for risk mitigation strategies. There is also increasing awareness about safety concerning drugs which along with the movement towards personalized medicine further drives the demand for integrated robust REMS Solutions. Guidelines strengthen with time and aim to enhance monitoring and surveillance of drug safety, thus the overall market adapts to support safer medication use while improving patient outcomes in the advanced and evolving healthcare ecosystem.
The REMS market of the pharmaceuticals sector deals specifically with risk management programs aimed at minimizing adverse effects through special monitoring, education, and compliance regarding the use of high risk and specialty drugs. Increasing global regulatory requirements as well as increasing adoption of complex therapies are factors propelling growth of the market. The use of modern digital technologies such as AI-based monitoring, analytics, and even interfacing with other EHR systems is improving the productivity and impact of REMS programs. Advances in risk and patient safety innovations developed through collaborations between pharmaceutical firms, healthcare institutions, and technology companies is changing rapidly.
Leading drugs worldwide based on projected 2025 sales
| Drug Name (Company Name) | Projected Sale, 2025 (USD Billion) |
| Zepbound (Eli Lilly) | 11.3 |
| Darzalex (J&J) | 13.2 |
| Wegovy (Novo Nordisk) | 13.4 |
| Biktarvy (Gilead) | 13.4 |
| Eliquis (BMS/Pfizer) | 13.5 |
| Skyrizi (Abbvie) | 13.7 |
| Dupixent (Sanofi) | 16.9 |
| Mounjaro (Eli Lilly) | 19.8 |
| Ozempic (Novo Nordisk) | 22.3 |
| Keytruda (Merck & Co.) | 31 |
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 1.96 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 6.12 Billion |
| Projected Market CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 13.64% |
| Dominant Region | North America |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Component, Drug Type, End User, Region |
| Key Companies | Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, AbbVie, Merck & Co., Roche, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Sanofi, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Eli Lilly and Company, Novo Nordisk, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Amgen, Gilead Sciences |
Medication Guides: These are printed Guides marked by the FDA detailing medicines that pose risks and are in turn, prescribed to patients. These guides are important in REMS since they highlight the critical steps of the side effects. The FDA for example, gives isotretinoin and its medication guides because of its teratogenic risks. The FDA also in 2023 put more attention on the fact that patients need to be clearly spoken to through guides, in order to enable patients to avoid harmful side effects. During the time of dispensing, they are given, and form a core part of patient education. The FDA does not stop working on the guides since they need to add new risk safety information.
Communication Plans: These are developed outlines to help educators including physicians tell teachers the safety measures regarding particular drugs including: their use, potential benefits, and harms. There are also letters that outline serious safety issues that need to be addressed to those who need them in resources and how to correctly write prescriptions. Like in 2024, the FDA put out more restrictions for opioids so that the overdose crisis can be relieved within the community. They primary aim is address information the prescriber need to make supportive claims towards their patients and REMS guidelines. Communication gaps between governing body and the health practitioners are filled through these documents. The FDA evaluates how these documents have been effective in the management of the risks concerning the medications.
Elements to Assure Safe Use (ETASU): ETASU are specific requirements under REMS that ensure the safe use of high-risk medications. These may include prescriber certification, patient enrollment in registries, or restricted distribution channels. For instance, the FDA mandates ETASU for clozapine due to the risk of severe neutropenia, requiring regular blood monitoring. In 2024, the FDA reviewed and updated ETASU protocols for several medications to enhance patient safety. These elements are tailored to the unique risks of each drug and are critical for preventing serious adverse events. Healthcare providers must comply with ETASU to prescribe or dispense certain medications.
Implementation Systems: Implementation Systems are the frameworks and procedures put in place by a drug manufacturer to ensure that they meet REMS obligations. These systems might include tracking systems for patient enrollment, certifying the prescriber, or dispensing records. For example, the FDA requires that manufacturers document how REMS evaluation reports are utilized to determine the effectiveness of implementation systems. Increased efficiency in the implementation of REMS programs was possible in 2023 owing to new advances in digital health technologies. Telemedicine technologies have advanced, making them easier to implement. Strong such policies are critical in enforcing control over compliance and the execution of implemented safety procedures. These comprehensive systems, known as such policy, serve the aim of REMS, which is to control specific drugs with safety risks.
Oncology Drugs: The risks associated with oncology drugs are some of the highest seen in medicine today. It is for precisely this reason that severe REMS Programs are required. These programs ensure that patients receive the appropriate treatment tailored to their condition safely. For example, the FDA approved treosulfan with fludarabine for specific leukemia patients in January 2025. Selected patients were specified safety protocols accompanying the treatment. These safety programs may incorporate training and monitoring of prescribers and patients respectively. In 2024, the FDA put more focus on the ovarian toxicity data neglect in the cancer drug trial’s data collection phase tackling long term multi generation health concerns. And such actions are essential in order to attempts to strike a balance with powerful oncology therapy mitigate their benefits and danger. REMS in Oncology is continuously modified to incorporate new emerging safety data.
CNS (Central Nervous System) Drugs: CNS disorders are those that affect behavior, emotion and cognitive abilities. REMS programs are often bring complex changes to these conditions, including psychiatric disorders. Take clozapine for example, which is prescribed for schizophrenia that resists standard treatment. It has a REMS program due to the possibility of severe and potentially fatal neutropenia, meaning that blood tests need to be performed routinely. In 2024, the FDA undertook the Clozapine REMS Program for improving overall outcome and reducing strain on healthcare workers. Aim of these programs is to highlight that reap the benefits of some CNS changes to drugs outweigh the negative impacts. This work is done as a communication between doctors, pharmacies and patients all together. With the continuous influx of new safety data the FDA works on improving and adjusting these MEMS programs.
Hormonal & Endocrine Drugs: Hormonal and endocrine drugs, such as those used for osteoporosis or hormonal therapies in cancer, may require REMS programs to manage associated risks. For example, denosumab, used for osteoporosis and cancer-related bone loss, has safety concerns related to hypocalcemia and osteonecrosis of the jaw. In 2025, the FDA approved biosimilars referencing denosumab, expanding treatment options while maintaining safety monitoring protocols. REMS programs for these drugs focus on educating healthcare providers and patients about potential risks and necessary precautions. They play a crucial role in ensuring safe and effective use of hormonal therapies.
Biologics & Gene Therapies: As advanced methods of treatment, biologics and gene therapies come with special safety considerations that may require the use of a REMS program. For example, some cancers are treated with CAR-T cell therapies that are associated with the risks of cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity. In 2024, some of these CAR-T therapies had REMS softened with the elimination of some prescriber training requirements but continued other safety measures. These changes are made to improve safety for patients while optimizing accessibility. Innovative forms of treatment have specific risks which forms the basis of tailored REMS programs for biologics and gene therapy.
Hospitals & Clinics: Hospitals and clinics manage dispensing high-risk REMS drugs and confirm the adherence to safety measures such as patient monitoring and certification by the prescribing physician. They assimilate REMS into electronic health records to monitor compliance with tracking systems. The FDA underscores the importance of their strict compliance with adverse event prevention. In 2023, there was an emphasis directed at hospitals regarding advancement in communication pertaining to the oncology and CNS drug REMS. Audits and reporting to the FDA are done routinely. Their participation in proper medication use and patient instruction is indispensable.
Retail & Specialty Pharmacies: Retail and specialty pharmacies only dispense REMS drugs after pre-ETASU diagnosis such as validating certifying and judging eligibility of the patient. Compliance is also captured for the MTMG along with Medication Guides, a requirement for more sophisticated therapies like gene therapy. Guidance to pharmacies was revised by the ADA in 2024 to enhance the protection of CNS and opioid drugs’ misuse. Pharmacies assist in the enforcement of safe use and loosed regulations. Their role is defending the patients in dispensing medications in resting conditions.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturers: Manufacturers design and manage REMS programs, submitting safety plans to the FDA and updating them as needed. For example, in 2023, Gilead enhanced lenacapavir’s REMS after safety reviews. They oversee prescriber certification, patient monitoring, and compliance tools. Manufacturers must report outcomes regularly and ensure program effectiveness. Non-compliance risks regulatory action or drug delays. Their work balances safety with drug accessibility.
Regulatory Agencies: Regulatory authorities like the FRE aim towards supervising the design, approval and REMS monitoring. Using real world data, the FDA began focusing on REMS assessments in 2024 with new guidance aimed at improving them. Stakeholder collaboration is done with agencies to update unnecessary burden and safety measures. On the other hand, they can remove or change REMS depending on the safety results. REMS oversee safeguards that have to be there for patients while supporting the REDUCE innovation standards for drugs.
The pharmaceutical REMS market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region
North America holds the highest share of the pharmaceutical REMS sector led by the U.S., Canada, and Mexico. The FDA ensures enforcement of the REMS programs and updated policies in 2023 regarding opioids and oncology drugs to enhance patient safety. The U.S. still has the most significant share of the market due to strict regulations and developed healthcare systems. Canada’s Health Canada works with agencies in the U.S. to adopt REMS-like safety protocols for Canadian biologics. Mexico is developing the regulatory frameworks to implement REMS and strengthen drug safety supervision. FDA reports indicate that more than 80% of healthcare institutions in the country use some form of digital tools to comply with policies related to REMS programs. The region continues to emphasize digital tools for REMS, driving growth in this market.
Europe’s pharmaceutical REMS industry encompasses the UK, Germany, and France, where the EMA sets the overarching guidelines for the EU, including the harmonization of risk management plans. In 2024, the EMA renewed its risk minimization guidelines, strengthening the ‘patient education and monitoring’ section for CNS and hormonal therapies. The UK's MHRA enforces strong REMS post Brexit, particularly concerning the safety of oncology drugs. Germany and France have set national policies aimed at increasing pharmacovigilance as well as REMS compliance in the country. Within Europe, cross-border cooperation facilitates the sharing of adverse drug reactions data. Regulatory focus is placed on the implementation of REMS into EHR systems for better tracking and integration. All these measures improve safety and adoption in the European market.
Asia Pacific’s key players include China, India, Japan, Australia, and South Korea, where pharmaceutical regulations are rapidly evolving. China’s NMPA has launched new drug safety guidelines within 2023 and places greater focus on risk evaluation systems like REMS. India has also started pilot REMS with increased pharmacovigilance under its National Drug Policy. Japan’s PMDA monitors biologics and oncology drugs under REMS-like scrutiny. South Korea and Australia are concerned with the management of risk through digital health records integration. Increased regional cooperation to synchronize REMS with international standards was noted after regulatory workshops in this region in 2024. Emerging opportunities are apparent in this region along with the chronic disease prevalence and modernized regulations.
Brazil’s ANVISA leadership in LAMEA, Latin America is implementing enhanced pharmacovigilance and risk mitigation strategies concerning Oncology and CNS drugs and adopting REMS from the year 2023. Argentina and Mexico are in the process of refinement of protocols concerning safety measures in alignment with REMS, which are aided by regional cooperation from PAHO. In the MEA block, The UAE, Saudi Arabia and South Africa are escalating drug safety and digital pharmacovigilance tool programs related to REMS. The UAE's Ministry of Health and SFDA of Saudi Arabia deal with controlled drugs and biologics, while with support from WHO, the MCC in South Africa increases post market surveillance. Regulatory cooperation in MEA strengthens regulatory harmonization in and between countries controlling increasing pharmaceuticals use and improving safety of patients systematically.
Recent partnerships in the pharmaceutical REMS industry highlight a strong focus on improving drug safety and regulatory compliance through technology. Pfizer has collaborated with Oracle to integrate cloud-based REMS management systems for real-time monitoring and reporting. Johnson & Johnson partnered with Veeva Systems to enhance digital REMS platforms, streamlining risk communication and prescriber training. AbbVie joined forces with IQVIA to leverage data analytics for optimizing REMS program effectiveness. Roche collaborated with Medidata to implement patient-centric digital tools supporting REMS adherence. These alliances advance automation, data transparency, and patient engagement, driving innovation in pharmaceutical risk management worldwide.
Market Segmentation
By Component
By Drug Type
By End User
By Region