The global nuclear reactors market size was valued at USD 16.59 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 23.35 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.48% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
The nuclear reactor market is expanding due to the increasing demand for sustainable and carbon-free energy. Many countries are adopting nuclear power to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and meet climate goals. Governments are investing in advanced reactors, including SMRs, which offer flexible and cost-efficient energy production. Asia-Pacific, Europe, and North America are leading in nuclear power expansion, with new projects being developed globally. Technological advancements, government policies, and the need for energy security are driving market growth. Countries like China, India, and Russia are constructing multiple reactors, while the U.S. and Europe are focusing on modernizing old reactors. The growing investment in research and development is making nuclear power more efficient and safer. Future growth is expected as innovations continue to improve nuclear technology and infrastructure.
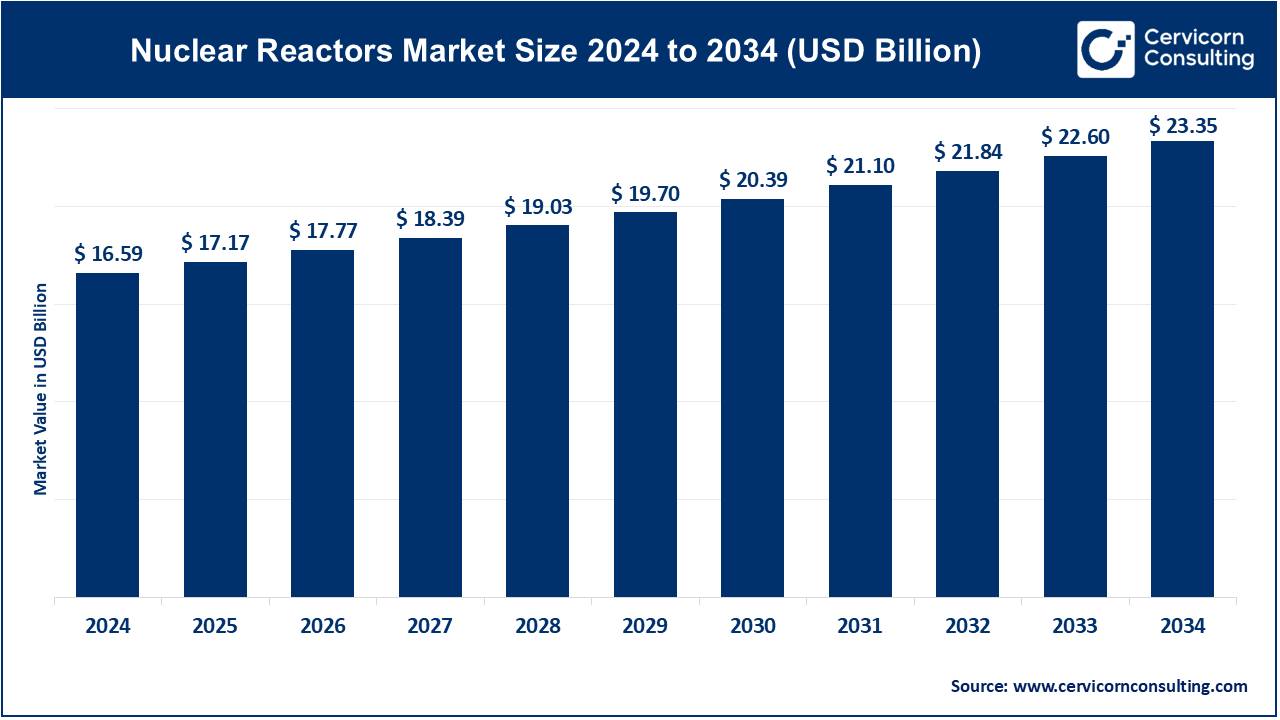
Some of the key trends driving this market include increasing demand for low-carbon energy sources, greater integration of next-generation nuclear technologies such as small modular reactors, and increased adoption of digital tools including advanced simulation and monitoring systems. There is also an intense focus on reducing construction timelines, minimizing operation risks, and improving safety standards within the industry.
Government policies and programs that support the inclusion of nuclear power in a sustainable energy mix, besides an accompanying regulatory framework that promotes innovation and investment in nuclear technology, have been major drivers for market growth.
What are Nuclear Reactors?
A nuclear reactor is a system used to generate energy by splitting atoms in a controlled process called nuclear fission. The core of a reactor contains nuclear fuel, usually uranium or plutonium, which undergoes fission to release heat. This heat is used to produce steam, which drives turbines connected to generators, producing electricity. Unlike fossil fuels, nuclear energy produces no carbon emissions, making it a cleaner energy source. Nuclear reactors are widely used for electricity generation, powering around 10% of the world's electricity. They also have applications in medical treatments, space missions, and research. Modern reactors are designed with advanced safety measures to prevent accidents. Countries are investing in small modular reactors (SMRs) for cost-effective and safer nuclear energy solutions.
The nuclear reactors market offers services and products that span from upgrading the efficiency of energy generation to making it more sustainable. This includes advanced reactor design development, implementation of innovative fuel technologies, installation, maintenance, and decommissioning services.
Key Insights Beneficial to the Nuclear Reactors Market
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 17.17 Billion |
| Projected Market Size 2034 | USD 23.35 Billion |
| Growth Rate (2025 to 2034) | 3.48% |
| Largest Revenue Holder Region | North America |
| Rapidly Growing Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Segments Covered | Reactor Type, Service, Application, End User, Region |
| Key Companies | General Electric (GE), Westinghouse Electric Company, Framatome, Rosatom, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI), Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power (KHNP), Toshiba Corporation, Hitachi, China National Nuclear Corporation (CNNC), Electricité de France (EDF), AREVA NP, Babcock & Wilcox (B&W), BWX Technologies, Inc., Doosan Heavy Industries & Construction, Holtec International and others |
Increased Funding and Investment
Energy Transition Initiatives
High Initial Costs
Public Perception and Regulatory Challenges
Emerging Markets and SMR Deployment
Advancements in Waste Management
Supply Chain and Material Sourcing
Skilled Workforce Shortages
Based on reactor types, the market is segmented into pressurized water reactors (PWRs), boiling water reactors (BWRs), small modular reactors (SMRs), fast breeder reactors (FBRs), pressurized heavy water reactors (PHWRs), light water graphite reactors (LWGRs), nuclear fusion reactors.
Pressurized Water Reactors (PWRs): PWRs are the most commonly used type of nuclear reactor globally, known for their robust safety mechanisms and efficient operation. These reactors use water as both a coolant and a neutron moderator, ensuring stability under high pressure. PWRs are favored for their ability to maintain continuous and reliable electricity generation, which is crucial for meeting large-scale energy demands. Their widespread adoption makes them a cornerstone of nuclear power in both developed and developing nations.
Boiling Water Reactors (BWRs): BWRs are another widely deployed reactor type, characterized by their simpler design compared to PWRs. They generate steam directly within the reactor vessel, which then drives the turbines to produce electricity. This direct cycle system offers certain operational efficiencies, although it operates at lower pressures than PWRs. BWRs are a popular choice for electricity generation in various countries, contributing significantly to their energy mix and providing a stable, low-carbon power source.
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs): SMRs represent an emerging segment in the nuclear market, designed for greater flexibility and scalability. These reactors are smaller in size and can be deployed in remote or smaller energy grids where traditional reactors may not be feasible. SMRs are modular, allowing for phased construction and the ability to add capacity as needed. Their enhanced safety features and potential for lower upfront costs make them a promising solution for future energy needs, particularly in regions with growing energy demand.
Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs): FBRs are designed to generate more fissile material than they consume, offering a long-term solution to nuclear fuel sustainability. These reactors are particularly important for countries looking to maximize their nuclear fuel resources and minimize waste. FBRs operate at higher temperatures and are capable of utilizing a wider range of fuel types, including depleted uranium and thorium. Their ability to breed fuel while generating power positions them as a key technology in the pursuit of sustainable nuclear energy
Based on service, the market is segmented into nuclear reactor design and engineering, construction and commissioning, operation and maintenance (O&M), decommissioning and waste management.
Nuclear Reactor Design and Engineering: This service segment involves the detailed planning, design, and engineering of nuclear reactors, ensuring they meet specific safety, performance, and regulatory standards. Companies in this sector focus on optimizing reactor designs for efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Engineering services are crucial for the successful implementation of nuclear projects, from initial concept to operational readiness, and they often involve collaboration with multiple stakeholders, including governments and regulatory bodies.
Construction and Commissioning: This segment covers the physical construction of nuclear reactors, including site preparation, installation of reactor components, and initial operational testing. Construction and commissioning are critical phases that require meticulous planning and coordination to ensure that reactors are built to the highest standards of safety and quality. Companies offering these services play a pivotal role in bringing new nuclear capacity online, contributing to the global expansion of nuclear power infrastructure.
Operation and Maintenance (O&M): O&M services are essential for the ongoing safe and efficient operation of nuclear reactors throughout their lifecycle. These services include routine maintenance, safety inspections, system upgrades, and troubleshooting. Effective O&M ensures that reactors operate at optimal performance, minimizing downtime and extending the lifespan of the reactor. Companies specializing in O&M services are integral to maintaining the reliability and safety of the global nuclear fleet.
Decommissioning and Waste Management: As nuclear reactors reach the end of their operational life, decommissioning services become critical. This involves safely shutting down the reactor, dismantling structures, and managing radioactive waste. Waste management also includes the long-term storage or disposal of spent nuclear fuel and other radioactive materials. Companies in this segment must adhere to stringent environmental and safety regulations to ensure the protection of public health and the environment
Based on application, the market is segmented into electricity generation, desalination, medical isotope production, research and development.
Electricity Generation: The primary application of nuclear reactors is in generating electricity, providing a significant share of low-carbon power to national grids worldwide. Nuclear power plants are essential in many countries' energy strategies, offering a reliable and continuous energy source that helps reduce dependence on fossil fuels. This application is particularly critical in regions aiming to meet climate goals by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, making nuclear power a key component of global energy transition efforts.
Desalination: Nuclear reactors are increasingly being used in desalination processes, particularly in arid regions where fresh water is scarce. The heat generated by nuclear reactors can be harnessed to convert seawater into potable water, addressing the growing demand for fresh water in many parts of the world. This application of nuclear technology offers a sustainable solution to water scarcity, contributing to both regional development and global water security.
Medical Isotope Production: Nuclear reactors play a vital role in producing medical isotopes, which are used in various diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, particularly in cancer treatment. This application supports the global healthcare industry by providing essential materials for nuclear medicine. The ability of reactors to produce isotopes like Technetium-99m makes them indispensable in medical diagnostics, highlighting the broader societal benefits of nuclear technology beyond power generation.
Research and Development: Nuclear reactors are used extensively in research and development (R&D) activities, particularly in advancing nuclear technology and training the next generation of nuclear engineers. Research reactors support a wide range of scientific studies, including nuclear physics, materials science, and reactor safety. These reactors are crucial for developing new nuclear technologies, enhancing safety measures, and contributing to the global knowledge base in nuclear science.
Based on end user, the market is segmented into utility companies, government and defense organizations, research institutes and universities, industrial companies.
Utility Companies: Utility companies are the primary operators of nuclear power plants, responsible for generating electricity to meet national energy demands. These companies play a crucial role in ensuring energy security and reliability, particularly in countries where nuclear power constitutes a significant portion of the energy mix. Utilities are increasingly focused on integrating nuclear power with renewable energy sources to create a more sustainable and resilient energy system.
Government and Defense Organizations: Governments and defense organizations utilize nuclear reactors for various applications, including electricity generation, naval propulsion, and research. These reactors are often part of national security strategies, providing critical capabilities for defense and strategic deterrence. Additionally, government-funded reactors are used for public research and development, contributing to advancements in nuclear technology and ensuring the safe and peaceful use of nuclear energy.
Research Institutes and Universities: Academic and research institutions operate nuclear reactors for educational and experimental purposes, contributing to scientific research and the development of nuclear technologies. These reactors are essential for training nuclear engineers and conducting research in nuclear physics, materials science, and reactor safety. The insights gained from research reactors help advance the nuclear industry and enhance global nuclear safety standards.
Industrial Companies: Certain industrial sectors, such as chemicals, mining, and manufacturing, use nuclear reactors for process heat or in combined heat and power (CHP) systems. These reactors provide a reliable and efficient energy source, helping industries reduce their carbon footprint and improve energy efficiency. The use of nuclear power in industrial applications supports the transition to a low-carbon economy and enhances the sustainability of energy-intensive industries.
The nuclear reactors market is segmented into various regions, including Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, and LAMEA. Here is a brief overview of each region:
North America is leading due to its advanced nuclear infrastructure and strong government support for nuclear energy. The U.S. and Canada are key players in the development and deployment of next-generation nuclear technologies, including small modular reactors (SMRs) and advanced reactor designs. Significant investments in modernizing existing nuclear plants and developing new nuclear projects are driving market growth. Additionally, the focus on reducing carbon emissions and achieving energy security has bolstered the adoption of nuclear energy as a sustainable power source in the region.
Europe market is characterized by a strong emphasis on innovation and sustainability in nuclear energy. Countries such as France, the UK, and Russia are at the forefront of nuclear technology development and deployment. The region's stringent environmental regulations and ambitious climate goals are driving investments in new nuclear projects and the modernization of existing reactors. Europe's leadership in the development of advanced reactor technologies and its commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions are key factors contributing to market growth.
The Asia-Pacific region is experiencing rapid growth in the nuclear reactors market, driven by the increasing demand for electricity and the need to diversify energy sources. China, India, and Japan are leading the region's nuclear expansion efforts, with significant investments in new nuclear power plants and advanced reactor technologies. Government initiatives to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, coupled with strong economic growth and urbanization, are propelling the adoption of nuclear energy. The region's focus on energy security and reducing carbon emissions further supports the market's expansion.
The LAMEA nuclear reactors market is growing due to increased interest in nuclear energy as a reliable and low-carbon energy source. In the Middle East, countries like the UAE and Saudi Arabia are investing heavily in nuclear energy to diversify their energy mix and meet rising electricity demand. Latin America is also exploring nuclear energy options, with Brazil and Argentina leading the region's nuclear initiatives. Despite challenges such as limited infrastructure and regulatory hurdles, the region is making progress through international collaborations and investments in nuclear technology.
Among the emerging players in the nuclear reactors industry, NuScale Power stands out with its small modular reactor (SMR) technology, offering a safer and more scalable nuclear energy solution. Terrestrial Energy is advancing the market with its Integral Molten Salt Reactor (IMSR), focusing on safety and efficiency improvements in nuclear power generation. Established leaders such as Westinghouse Electric Company continue to dominate with their AP1000 reactor technology, known for its passive safety features and global deployment.
Rosatom is leveraging its extensive experience and international collaborations to maintain its stronghold in the market, with recent projects expanding into new regions. Framatome remains a key player, driving innovation through partnerships and the development of next-generation nuclear technologies. These companies' innovations and strategic initiatives highlight the dynamic and competitive nature of the evolving market.
CEO Statements
Dariusz Marzec, CEO of PGE:
Dr. Carlos O. Maidana, CEO and Founder at Maidana Research:
Key players in the nuclear reactors industry are leading the charge in providing a diverse array of innovative solutions that are transforming the industry. These advancements include the use of prefabrication techniques, the integration of sustainable materials, and the deployment of advanced digital technologies. Some notable examples of key developments in this market include:
These developments highlight a significant expansion in the nuclear reactors industry through strategic acquisitions and cutting-edge projects, aimed at boosting sustainability, improving construction efficiency, and enhancing nuclear technology offerings for diverse energy applications. Companies are increasingly focusing on innovative approaches, such as advanced reactor designs, prefabrication techniques, and digital technologies, to meet the growing demand for clean and reliable energy sources.
Market Segmentation
By Reactor Type
By Service
By Application
By End User
By Region