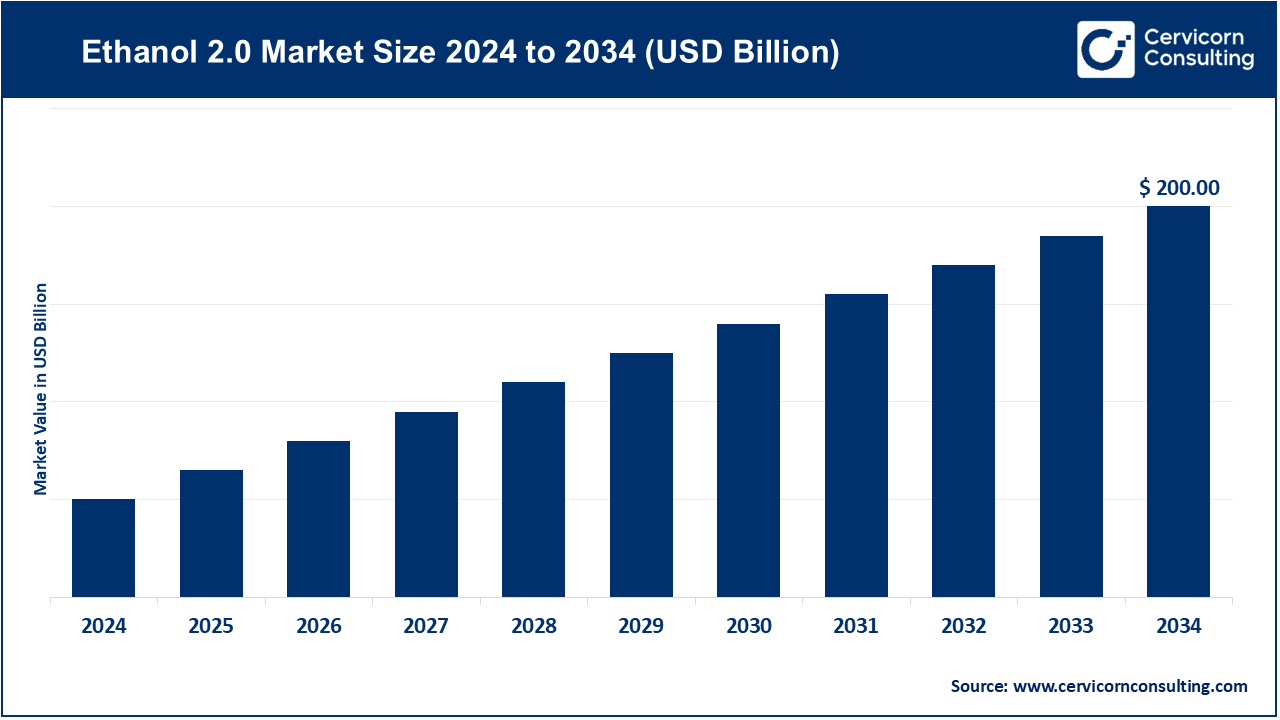
The global ethanol 2.0 market size is anticipated to reach around USD 200 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 6% from 2025 to 2034. The ethanol 2.0 market is diversifying across different regions due to changes in industrialization, urbanization, and energy management. Each manufacturing, utility, and commercial and industrial infrastructure sectors are adopting Ethanol 2.0 to improve operational efficiencies, enhance effectiveness, and shrink carbon footprints. AI automation, digital twins, and other automation energy advanced systems technologies are incorporated as more Ethanol 2.0 is implemented. Ethanol 2.0 adoption is also influenced by government initiatives to adopt cleaner energy technologies.
Ethanol 2.0 technologies provide predictive analytics and real time energy measurement and analytics through IoT integrated monitoring systems and smart grid interconnected energy resources. Commercial and industrial versatile gas meters monitor emissions, track gas usage, and predict gas consumption. Software integrated with renewable energy handler in gas meters emissions and energy management systems and management encourages energy regulatory compliance. Environmental monitoring, emissions reductions, and Ethanol 2.0 increasingly deployed advanced energy infrastructures regulatory compliance in and enforcement to modern systems in energy made Ethanol 2.0 pivotal.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Estimated Market Size in 2034 | USD 200 Billion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 6% |
| Dominant Region | North America |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Solution Type, Technology, End-User, Region |
| Key Companies | Archer Daniels Midland Company (ADM), POET LLC, Valero Energy Corporation, Cargill, Green Plains Inc., Alto Ingredients, Raízen, BP, Koch Industries, Andersons Inc., Cardinal Ethanol LLC, Tereos, BlueFire Renewables, LanzaJet, Godavari Biorefineries Limited |
The ethanol 2.0 market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region.
The North America has well established industrial infrastructure, high levels of technology usage and stringent energy regulations, which makes it a market leader. In the U.S. and Canada, software applications are popular in predictive maintenance, energy optimization, and emission monitoring of major industrial plants, commercial buildings and utility networks. The use of AI analytics, IoT based monitoring and digital twins improve efficiency in operations. The market growth is also facilitated by the government policies that favor the low-carbon and renewable energy technologies. Intimate co-operation among utilities, industrial players and technology suppliers encourages innovation. The area is also developing the hydrogen-ready and renewable-integrated energy systems.
Europe is the place that is propelling the use of Ethanol 2.0 because of the strict regulatory structures and sustainability objectives. The residential, commercial and industrial deployments are at the forefront in Germany, the U.K., France, and Italy. Its major areas of focus are energy efficiency, carbon reduction, and connection to renewable and hydrogen-ready. The smart energy solutions and predictive maintenance are being developed through collaborations between the technology firms, energy corporations, and research centers. AI, IoT, fuel cells, and biogas tracking improve performance and operation efficiency. Europe remains on the forefront of implementing smart meters and low-carbon energy software across the world.
Ethanol 2.0 Market Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America | 43.80% |
| Europe | 22.60% |
| Asia-Pacific | 25.10% |
| LAMEA | 8.50% |
Asia-Pacific is the most expanding market because of the rapid urbanization, industrialization, and modernization of the infrastructure. China, India, Japan and South Korea are all contributing factors to increase in the market. In China, the emphasis is on the industrial and district energy projects, whereas in Japan and South Korea, the emphasis lies in the commercial energy efficiency. In India, the big optimization of energy is backed by smart city, industrial park, and renewable energy programs. The countries in Southeast Asia including Vietnam, Thailand and Indonesia are linking renewable systems with smart meters. The cheap labor and the rising investments on solar and renewable energy infrastructure also fuel regional development.
There is a driving force behind ethanol 2.0 in LAMEA; industrialization, urbanization and infrastructure development. Latin America is a leader in commercial and industrial rollouts which are spearheaded by Brazil, Mexico and Argentina. The UAE and Saudi Arabia pay attention to the integration of renewable energy, the systems that use hydrogen and the systems that work with the IoT and energy. In Africa, localized industrial, commercial and distributed energy initiatives are taking place in the southern, eastern and western parts. International partnerships and modernization efforts facilitate market penetration. The region has the potential of being a smart metering and energy management solution despite the gaps in the infrastructure and the challenges in regulations.
Predictive Maintenance Software: These systems foresee maintenance and likely failures of industrial equipment and energy infrastructure. Operational efficiency is enhanced and unplanned downtimes minimized because of AI analytics. Integration of IoT-enabled smart sensors provides continuous data streaming and predictive scenario simulations. Digital twins and simulators extend predictive capabilities toward optimizing processes. These systems are prevalent in manufacturing and logistics in smart cities. They extend the useful life of systems while predictive maintenance and system level energy unbalance encourage low carbon initiatives. Considering the low downtime and life cycle cost of systems, operational cost efficiency is a major driving factor. Predictive insights also fuel cross sector low carbon initiatives and energy efficiency programs.
Energy Management Software: These solutions provide monitoring, evaluation, and ontrol of energy consumption strateigies for systems in industrial, commercial, and urban contexts. They also provide system integration for smart grid technologies. They contribute real time control and balance of energy load for IoT connected systems. Predictive analytics assist in control of peak load and hybrid energy systems. Centralized control for monitoring and operational systems are provided through cloud technologies. These solutions help balance hybrid programmable systems and assist in achieving carbon reduction goals set through integrated renewable energy systems.
Emission Control Software: These solutions monitor and control emissions from industries, utilities, and transportation. Adopting AI and IoT allows for the real-time identification of anomalies and detects compliance to the requirements of emission limits. Automated emissions control allows for adherence to regulations and control of processes to not exceed the limits. Predictive analytics enable the proactive planning of initiatives aimed at carbon reduction and improving the efficiency of energy use. Adoption of these solutions is greatest in the areas with robust environmental regulations and hybrid energy systems. Increasing interest in sustainability is leading to wider use everywhere.
Digital Twin & Process Automation Software: AI driven digital twins provide real-time virtual replicas of energy and industrial systems for elements of process optimization. The incorporation of AI and IoT makes predictive maintenance, hazard identification, and operational efficiency enhancement more advanced. They run simulations, pinpoint inefficiencies, and assist in smart grid incorporation. Common in manufacture, utilities and smart cities, they reduce waste and operational downtime. Adoption of these systems enhances digitalization and sustainable industrial process. They are essential for operational excellence and energy optimization.
IoT-Enabled Systems: Predictive AI models designed for the identification and optimization of operational and energy performance capture real-time data. IoT powered devices and sensors track equipment, emissions and energy use. The integration to smart grids allows for energy load and resources optimization. Widely used in the industrial, commercial and urban infrastructures, they improve operational efficiency. IoT systems reinforce initiatives aimed at decarbonization and renewable energy.
AI-Driven Analytics: AI analyzes extensive datasets from integrated systems, detecting trends and forecasting potential system failures. Operational and energy efficiencies are gained through the automation of systems. AI integrates with Internet of Things (IoT) devices and cloud computing platforms to perform real-time analytics. Predictive analytics improve safety by lowering downtime and maintenance expenditures. AI analytics aligned with organizational Objectives supports carbon footprint reduction and sustainability. The global industry adoption trend of AI analytics is witnessed across industrial and commercial use cases, and smart city initiatives.
Cloud-Based Platforms: The consolidation of cloud systems into centralized platforms delivers energy and industrial system control, monitoring, and management functionalities. Predictive analytics on real-time data enables maintenance and energy use efficiencies. Operational efficiency is enhanced through the use of IoT, AI, and digital twin technologies. (Cloud systems) Meet regulatory needs for secure remote user access with multi-site control and system management. There is an adoption trend for advanced integrated cloud solutions for industrial parks, smart cities, and energy-intensive industries. These cloud systems and platforms provide seamless infrastructure scalability and lower operational costs associated with IT management systems.
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI): AMI supports two-way communication for real-time dynamic energy data recording and collection. AMI functionality, when integrated with IoT, digital twin technologies, and AI models focused on predictive maintenance, energy distribution systems optimization and roughly real-time energy systems metric monitoring become possible. AMI systems enhance operational systems that support the integration of renewable energy resources and smart grid technologies. AMI reduces operational downtime and inefficiencies in commercial and industrial systems. The adoption of AMIs is prevalent in large-scale energy infrastructure and the automotive industry. AMI enhances energy transparency, monitoring, and reporting for regulatory compliance.
Blockchain Integration: Users will seamlessly monitor their energy consumption and costs because of blockchain's guarantee of safe and transparent tracking. It also assists in determining the use of renewable energy and helps in tracking the use of carbon credits. It accurately integrates and consolidates records along with the cloud systems with IoT and AI. It provides decentral energy systems to the users and assists in peer-to-peer energy trading. It accounts for and manages urban commercial and industrial energy systems. Adoption of the technology increases with the expansion of digital energy ecosystems worldwide.
Manufacturing and Industrial Facilities: Predictive maintenance powered by the IoT lowers business downtime and boosts continuous production. AI-integrated energy management streamlines business operations and energy use. The smart grid system provides demand response and sustains system integration. Emission monitoring systems provide operational efficiency and seamless tracking of carbon and other emissions. These systems are to a large extent adopted across the globe in regions like North America, Europe and Asia-Pacific, posing advancement in the low-carbon and renewable energy sectors in multiple industries.
Commercial Infrastructure: Offices, hotels, hospitals and shopping malls are utilizing the IoT for management of energy and tracking of emissions. The integration of smart grids and renewable energy sources result to operational efficiency. Compliance to green building standards is achieved through predictive and real-time analytic provisions. The systems facilitate fault detection which in turn aids in the reduction of energy wastage and operational costs. These systems are readily adopted in urban centers of developed regions to aid in the sustainable management of energy.
Utilities & Energy Companies: The uses of Ethanol 2.0 is being used by utilities for real-time system monitoring, load balancing, and optimizing billing. Energy saving smart meters combined with AI algorithms in energy distribution perform better and cut distribution line losses. The IoT enabled systems for emission tracking and operational monitoring aid in compliance. More companies are modernizing and adopting these systems because of regulatory compliance. These systems manage low carbon energy, renewables coupled with energy transitions, and are used extensively in developed and emerging markets.
Smart Cities & Urban Infrastructure: Predictive analytics are being used by cities for system management and tracking of energy, emissions and other urban atmospheric elem. AI and other IoT devices for emission monitoring aid real-time management and enhancement of energy of other systems. Renewable energy and smart grid integration offer more to urban centers. Predictive emission analytics aid urban planning and facilitate compliance. Enhanced systems are being used more in Europe and Asia pacific for urban systems and North America.
Market Segmentation
By Solution Type
By Technology
By End-User
By Region