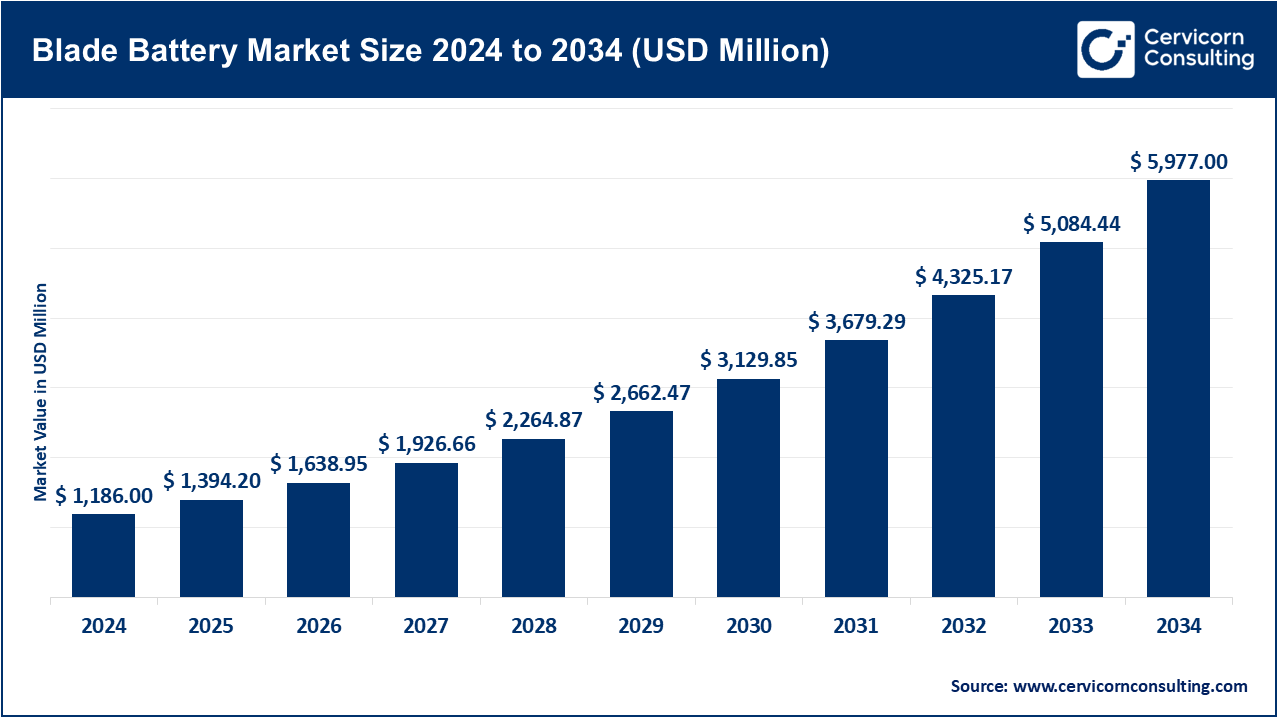
The global blade battery market size was estimated at USD 1,186 million in 2024 and is expected to hit around USD 5,977 million by 2034, exhibiting at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.69% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
The blade battery market is rapidly expanding, mainly driven by the global adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and the push for safer, more efficient battery technologies. Blade batteries, led by BYD and quickly adopted by other manufacturers, offer 50% better space utilization than traditional lithium-ion packs, while improved thermal management enhances safety by reducing fugitive risks. Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP), which depends on specific chemistry—In 2024, approximately 40% of the world's EV batteries are already installed, further increasing demand as vehicle manufacturers shift away from expensive cobalt- and nickel-based chemistries. This trend is reinforced by regulatory pressures for cleaner transportation; high EV penetration has become mandatory in regions such as Europe and China, accelerating the deployment of blade batteries in both passenger and commercial fleets.
Beyond EVS, the blade battery is gaining traction in stable energy storage systems (ESS), where its long cycle life and fire resistance are key benefits. The worldwide energy storage capacity surpassed 45 GW in 2023, and LFP-based blade designs are widely deployed to capture a large share of this growth due to their low cost and scalability. Government incentives for renewable integration, such as China's double carbon goals and the US Inflation Reduction Act, are increasing demand for grid-scale storage solutions where security is crucial. Additionally, advances in fast-charging technology enable some blade batteries to reach 80% charge in less than 30 minutes, making them more appealing to the next generation of EV platforms, thereby reinforcing their role as a disruptive force in the global battery market.
What is the Blade Battery?
Blade Battery is a next-generation lithium iron phosphate (LFP) battery introduced by BYD in 2020, designed in a thin, long "blade-like" cell format. Unlike traditional battery packs, which typically group cylindrical or pouch cells, this design allows blade cells to be arranged directly into a pack without the need for additional modules. This results in high utilization (up to 50%), better thermal management, and increased protection. One of its standout features is resistance to thermal runaway — even under nail penetration tests, the blade battery does not catch fire — making it a safe option compared to traditional lithium-ion packs. Its tall cycle life (up to 3,000+ cycles), low cost (due to cobalt- and nickel-free chemistry), and improved durability make it a transformative solution across various industries. In EVs, blade batteries extend driving range and reduce the risk of fire accidents. In grid energy storage, their safety and longevity enhance reliability for renewable integration. In consumer electronics, their slim design allows for long-lasting batteries, while in commercial transportation (buses, trucks), their robustness supports heavy-duty use with minimal decline.
Technological Roadmap of Blade Battery
| Timeline | Technology Milestone | Key Features & Developments | Impact on Market |
| 2020 | Introduction of Blade Battery (BYD) | Launch of Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) Blade Battery with ultra-slim design; Passed nail penetration test (world’s toughest battery safety test). | Established new global safety standard; Gained rapid adoption in BYD EVs (Han EV, Tang SUV). |
| 2021–2022 | Early Adoption & Expansion | Integration into BYD’s full EV lineup; Export expansion to Europe & Asia; Growing awareness of thermal stability vs. traditional Li-ion. | Blade Battery became a benchmark for safety and lower cost EV solutions. |
| 2023 | Global Partnerships & Testing | Automakers (e.g., Toyota, Tesla, Hyundai) tested/considered Blade-style LFP packs; Growing use in buses, commercial vehicles, and stationary storage. | Triggered global interest in LFP Blade architecture as a viable alternative to NMC/NCA batteries. |
| 2024–2025 (Present) | Second-Gen Blade Development | Next-gen Blade Batteries announced with fast charging (400 km in 5 mins), longer cycle life (>3,000 cycles), and higher energy density. | Pushes EV adoption forward; strengthens BYD’s global leadership; starts competing with solid-state R&D. |
| 2026–2028 (Projected) | Integration into Mass-Market EVs | Wider adoption beyond BYD into global automakers; cost per kWh reduction; potential hybrid use with solid-state electrolytes. | Expands market penetration in affordable EVs; boosts LFP dominance over NMC in mid-range EVs. |
| 2029–2032 (Projected) | Solid-State Blade Hybrid | Research convergence with solid-state and advanced materials (silicon anode, sodium-ion adaptation); enhanced thermal stability. | Blade tech evolves into hybrid solid-state architectures, ensuring longer ranges and ultra-fast charging. |
| 2033+ (Future Vision) | Next-Gen Ultra-Safe Blade | Fully solid-state Blade with >500 Wh/kg density, >10,000 cycle life, zero fire risk; integration into aerospace, defense, and grid-scale storage. | Redefines the future of energy storage across EV, aviation, and renewable grids. |
Notable Case Studies of Blade Battery Adoption:
Advancements in Fast-Charging Capability
Next-Generation Blade Battery Architectures
Material & Supply Chain Optimization (Aluminum Focus)
Infrastructure Integration: Battery Swapping Ecosystems
The blade battery market is segmented into capacity, application, chemistry, end-user, and region.
Large Capacity: Blade batteries with long-range and endurance will lead the market as they power high-performance passenger EVs and fleets that require long-range and endurance. BYD’s Han EV sedan, equipped with a 77 kWh Blade Battery, can drive up to 605 km on a single charge. Furthermore, BYD’s electric buses feature packs of 100+ kWh, enabling their deployment in cities worldwide. In China, Europe, and North America, consumer demand will drive the category's dominance in EV sales. The cost of replacing a headland battery is lower, as fewer replacements are needed, while the proven lifespan of blade batteries supports their acceptance.
Blade Battery Market Share, By Capacity, 2024 (%)
| Capacity | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Small Capacity | 14.70% |
| Medium Capacity | 33.10% |
| Large Capacity | 52.20% |
Medium Capacity: Medium capacity packs will be the most attractive option for affordable EVs, as they offer ranges of around 300-400 km, suitable for daily driving in urban areas. Automakers like Toyota (bZ3 EV) and BYD Dolphin are already targeting mid-market segments, and there's significant potential for growth in markets such as India, Southeast Asia, and Europe. Sales in the medium capacity segment are expected to surge as governments incentivise entry-level EVs with subsidies, making it the fastest-growing segment.
Passenger Cars: Global EV adoption has made passenger cars the largest mark0et segment. In 2023, worldwide EV sales crossed 14 million, with China accounting for nearly 8 million. Blade Batteries were chosen for their safety features, including no fire risk even with a puncture, and highly efficient designs that boost consumer confidence. Several Blade-powered passenger cars, such as the BYD Han, Tang, Dolphin, and Toyota’s bZ3 sedan, have found success in the passenger car market.
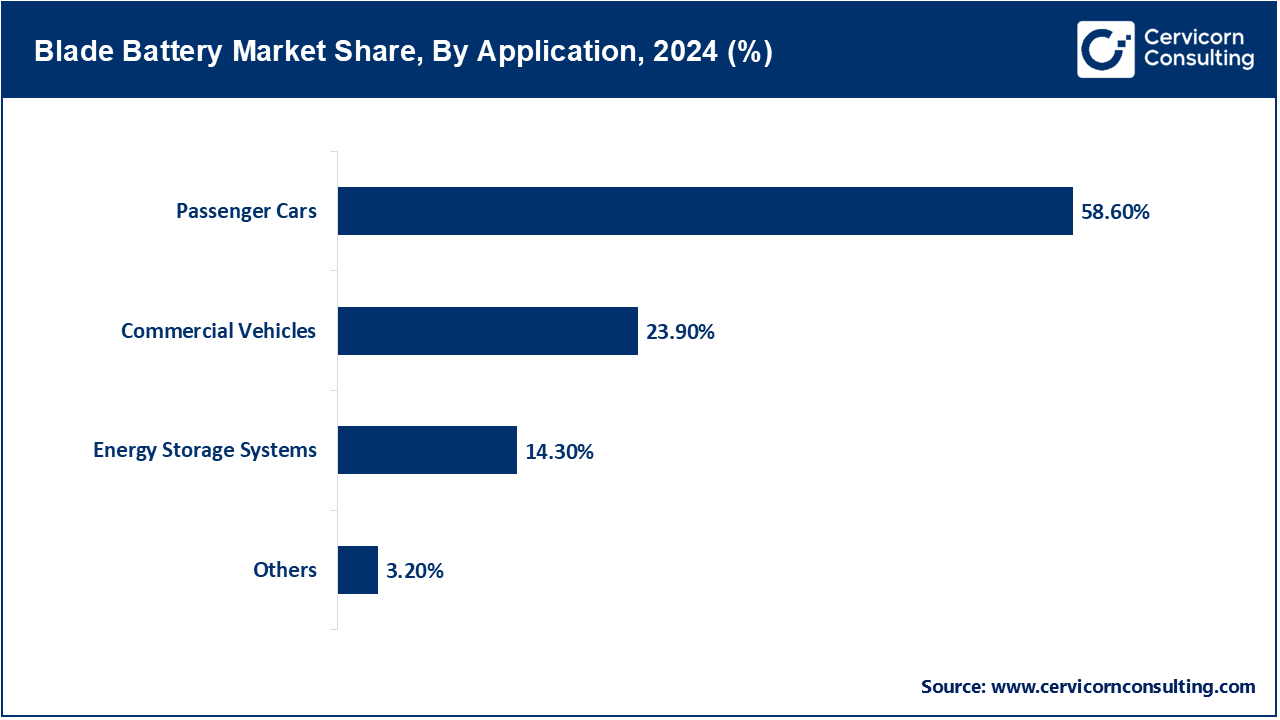
Energy Storage Systems (ESS): As solar and wind power continue to grow rapidly, ESS is the next fastest-growing application. In 2023, the worldwide installed capacity of ESS exceeded 45 GW, and is expected to grow at a rate of over 20% per year. Blade Batteries are well-suited for ESS, as they are safer to deploy in dense installations, have a life of 3,000+ cycles, and reduce the risk of thermal runaway in large grid facilities. China and Europe are currently undertaking several projects involving Blade-powered ESS, suggesting significant potential for high growth.
Li-Ion Phosphate (LFP): Leveraging its LFP chemistry, the Blade Battery offers an edge in cost, safety, and cycle life. Unlike NMC/NCA batteries, LFP chemistry doesn't rely on cobalt or nickel, reducing the risks of supply chain volatility and saving on expensive raw materials. By 2024, LFP will account for over 40% of the global demand for EV batteries, driven largely by Chinese manufacturers. Additionally, LFP performs well in applications requiring frequent charging cycles, such as grid storage and non-automotive mobile applications. The Blade design also enhances LFP's energy density, which had been one of its historical weaknesses.
Solid-State: Solid-state technology is the next big thing. While there are currently no commercially viable solid-state technologies, the potential to double energy density (400-500 Wh/kg vs 200-250 Wh/kg for LFP) and virtually eliminate fire risk makes it an attractive area for R&D investment. Reports suggest BYD and Toyota are working on solid-state concepts based on the Blade design. With pilot production lines in Japan and China, commercial solid-state EVs are expected to hit the market by 2027-2028, making it the fastest-growing area for EV innovation momentum.
Automotive: The automotive industry remains at the forefront of the company profile business, with electric vehicle acceptance and adoption gaining momentum in 2023. BYD alone sold 3 million electric vehicles in 2023, nearly all of which featured Blade Batteries. As European, Chinese, and U.S. governments implement stricter emissions targets, forcing OEMs to transition, this shift has paved the way for more eco-friendly battery technology like Blade. Advances in consumer understanding and acceptance of LFP safety have also opened the door for automotive OEMs outside of BYD, such as Toyota, Ford, and Hyundai, to explore Blade partnerships, strengthening the automotive opportunity.
Blade Battery Market Share, By End-User, 2024 (%)
| End-User | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Automotive | 58.6% |
| Renewable Energy / Power Storage | 23.9% |
| Consumer Electronics | 14.3% |
| Industrial Applications | 3.20% |
Renewable Energy / Power Storage: Power storage continues to see significant demand as the penetration of renewable energy grows. For instance, China installed 22 GW of new energy storage in 2023, with a substantial portion required to be safe and durable LFP-based packs. Blade Batteries have proven they can withstand extreme safety tests (no explosion under nail penetration) and offer a lifespan of over 15 years, making them a viable option for grid-level storage. With a substantial proportion of global renewable goals set to be achieved, this segment is expected to outpace all others by 2030.
The blade battery market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. Here is a brief overview of each region:
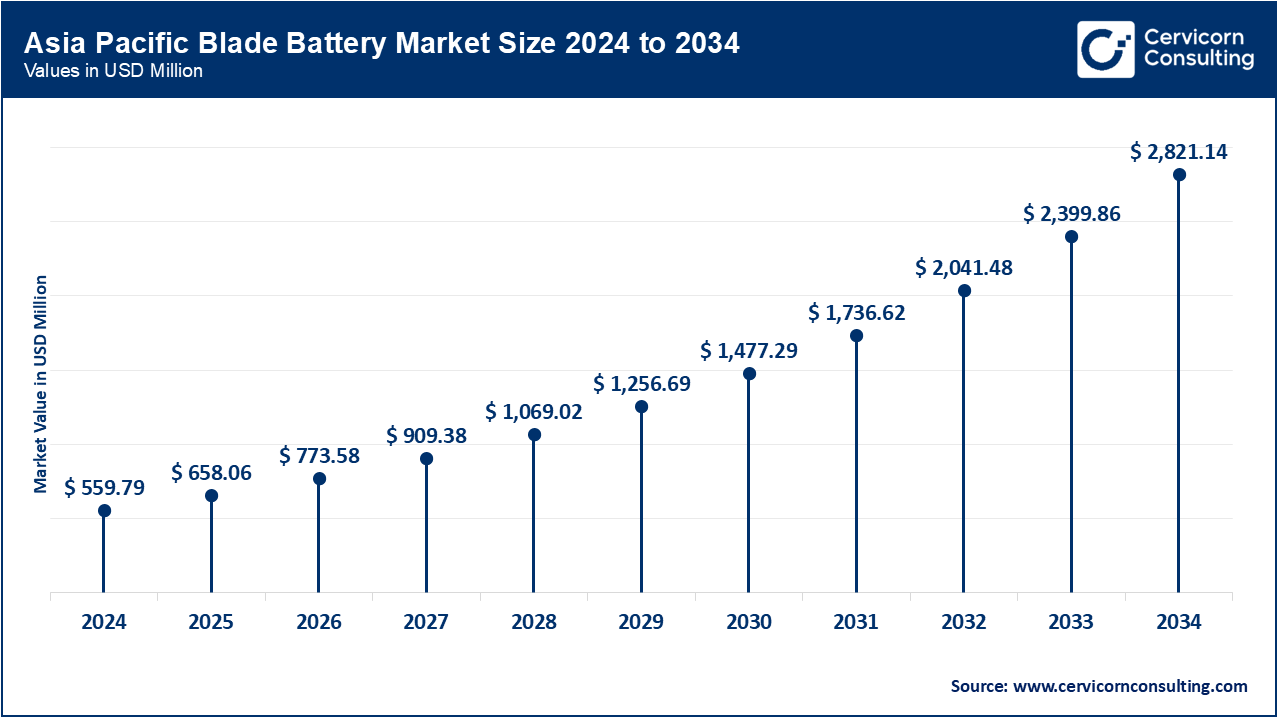
APAC is the dominant region, driven mainly by China, which was the first to pioneer and scale the technology through BYD. By 2023, China is expected to account for around 60% of global EV sales, with almost all of BYD's EV models now featuring Blade Batteries. Additionally, Japan and South Korea are investing heavily in advanced chemistries, including solid-state and improved lithium-iron phosphate (LFP). Thanks to various government mandates in the region, such as New Energy Vehicle (NEV) in China and FAME-II in India, demand for Blade Batteries is growing in APAC. With a massive manufacturing base, potential for cost advantages, and strong global exporting capabilities, APAC is not only the region with the largest demand for Blade Batteries but also the region with the greatest potential for innovation in deploying Blade Batteries in EVs, buses, and stationary storage.
EV adoption is gaining momentum rapidly across North America, driven by the United States and Canada. This growth is being fuelled by government programs that promote EVs. The U.S. government has adopted the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA, 2022), which allocates around $370 billion to clean energy development, with a significant portion going towards EVs and battery production. Major EV manufacturers like Tesla, Ford, and GM are actively exploring the development and adoption of lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries for EVs. Meanwhile, Chinese battery manufacturer BYD has expressed interest in entering the U.S. market with its Blade Battery technology. However, there are still challenges with local battery production and dependence on Asia for supply. The focus in this region is on building a local supply chain and partnering with companies in China and Korea to stabilize the adoption of Blade twelve-cell continuous, fully aqueous, lithium-ion battery technology.
Blade Battery Market Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America | 19.7% |
| Europe | 26.4% |
| Asia-Pacific | 47.2% |
| LAMEA | 6.7% |
Europe is the second-largest market, driven by the rapid adoption of electric vehicles. This is largely due to ambitious carbon neutrality targets (Net Zero by 2050) and regional bans on internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, such as the European Union’s expected ban on new petrol and diesel car sales in 2035. Leading automotive companies in Europe, including Volkswagen, Mercedes-Benz, and Stellantis, are actively adopting lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries, while forming partnerships with Chinese suppliers like BYD. Safety and sustainability are top priorities in Europe, and Blade Batteries offer thermal stability, a long lifespan, and cobalt-free chemistry – a key consideration for the European Union to adopt sustainable supply chains. Moreover, the region is seeking Blade-powered grid-scale energy storage to balance out intermittent renewable power sources, such as wind and solar.
LAMEA is still in the early adoption stage, but momentum is building, especially in Latin America with countries like Brazil and Chile driving EV adoption. As the world's largest lithium producer, Chile has a favourable location for developing local battery supply chains. In the Middle East, countries such as the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia are investing in EV infrastructure and renewable energy projects, creating an emerging opportunity for Blade Batteries' product line in energy storage systems for solar farms and smart city energy storage activities. Africa is also in the early adoption phase, but has a promising opportunity to promote adoption with affordable EVs and renewable-based microgrids, where the durability and low maintenance of Blade Batteries can provide customers with the greatest value. Although the LAMEA region is currently small, it has significant potential for long-term growth as government agencies set suitable sustainability goals and launch initiatives to explore new markets for OEMs in the region.
The blade battery industry is strongly shaped by BYD Company Ltd.'s innovation and leadership as the pioneer of the Blade Battery. BYD launched this LFP-based battery in 2020 as a safer, more durable, and cost-effective alternative to traditional lithium-ion batteries. The company quickly integrated Blade Batteries into its electric vehicles, such as the Han EV and Tang SUV, with exports expanding to Europe and other regions. BYD has established a leading position in this area, setting industry benchmarks for thermal safety and efficiency. This achievement has encouraged other automakers and battery makers to adopt similar designs, form partnerships with BYD, or pursue both strategies.
In addition to BYD, several multinational companies are now contributing to the development of Blade Batteries. Automakers such as Tesla, Volkswagen, and Toyota are either testing or preparing to adopt LFP technologies that incorporate Blade-style innovations. Battery suppliers, including CATL, LG Energy Solution, and Panasonic, are also investing heavily in LFP and solid-state chemistries to stay competitive in a changing market. Smaller players in Europe and North America are seeking to develop partnerships with their Asian battery counterparts to localise production, while numerous startup companies in energy storage systems are exploring niche applications. Together and individually, these companies represent the next phase in the evolution of the Blade Battery market, which we see as a disruptive solution aligned with the industry's aim of creating safer, greener, and more scalable energy storage technologies.
Wang Chuanfu — Chairman & CEO, BYD
Yang Hongxin — CEO, SVOLT Energy
Market Segmentation
By Capacity
By Application
By Chemistry
By End-User
By Region