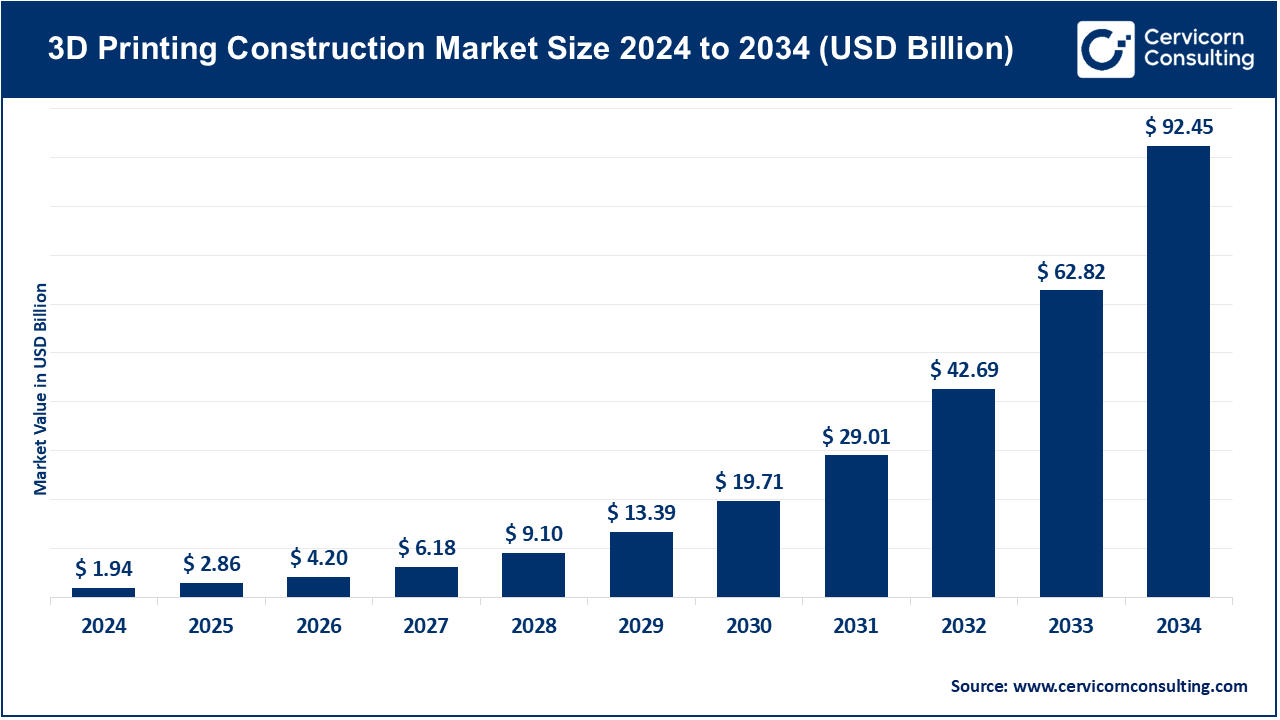
The global 3D printing construction market size was valued at USD 1.94 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 92.45 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 102.5% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The 3D printing construction market is in the phase of fast global expansion due to the growing requirements in industrialization, urbanization, and efficient infrastructure in terms of energy use. The construction activities are converging towards better performance in terms of efficiency and minimization of carbon gases and other performance related aspects. Automation, AI-assisted procedures, and digital twins are getting extensively implemented, and government programs that encourage the use of cleaner energy sources have fueled the adoption of 3D printing solutions to commercial, industrial, and urban activities.
The 3D printed constructions of the modern world are getting more combined with the monitoring systems based on the IoT and providing the opportunity to track the real-time situation, predictive analytics, and optimize resource use. Hybrid systems that integrate 3D printing with renewable energy technologies and gas measurement systems allow the accurate use of fuel, decrease in emissions, and sustainable processes. Consequently, the construction of 3D printing is becoming a multifunctional, environmentally controlled, and energy saving option to the built environment of the next generation.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 2.86 Billion |
| Estimated Market Size in 2034 | USD 92.45 Billion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 102.50% |
| Dominant Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Method, Material Type, Application, Region |
| Key Companies | ICON, Apis Cor, COBOD International, Mighty Buildings, CyBe Construction, SQ4D, Peri 3D Construction, WASP, Nidus 3D, Alquist 3D |
The 3D printing construction market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region.
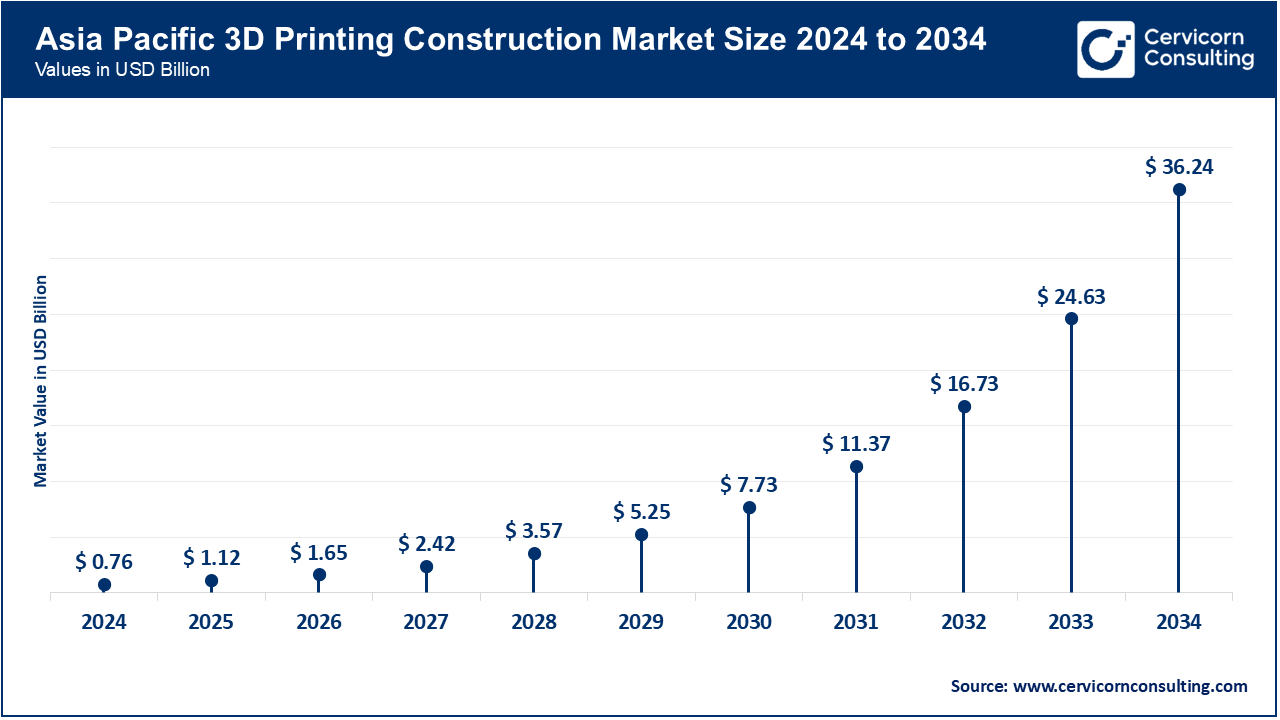
Asia-Pacific is the most promising area in terms of growth because of the high rates of urbanization, industrialization, and modernization of the infrastructure. China, India, Japan and South Korea are the major markets and China concentrates on the industrial and urban infrastructure whereas Japan and South Korea focus on commercial and energy-efficient projects. The smart city initiatives, industrial parks and investment in renewable energy, in India are facilitating the use of 3D printing. There is an emerging trend in the adoption of modular 3D printing solutions to both residential and commercial uses in Southeast Asian countries such as Vietnam, Thailand, and Indonesia. Affordability of cheap labor as well as governmental assistance and rising renewable energy investments also contribute to market growth. The region is projected to spearhead development of the world in the advanced and low-carbon construction solutions.
North America is the largest market because of the progressive industrial base, high technological usage and controlled energy and building standards. In the United States and Canada, 3D Printing Constructions are utilized in the industrial, commercial, and utility fields to construct a design quickly, develop a modular structure, predictive maintenance. AI, IoT monitoring, and digital twins are efficient in improving operational efficiency and minimising carbon emissions. The government is also encouraging the use of low-carbon and energy-saving technologies through incentives and policies. Technological partnerships between utilities and industrial players with technology service providers quicken the innovation in the market. The market leadership of the North American region is still being consolidated by investments in renewable-integrated and sustainable construction systems and hybrid.
The Europe is rising due to strict regulations, sustainability requirements, and emphasis on low-carbon infrastructure. The residential, commercial and industrial deployments are ahead in Germany, the U.K, France and Italy. The European market focuses more on energy efficiency, reduction of emissions and incorporation with renewable and hydrogen-ready technologies. Provision of smart construction and predictive maintenance solutions is improved by cooperation between research institutions, building companies, and technological suppliers. The integration of AI, IoT, and digital twins enhances optimization of operations and lessening waste of materials. Europe is still an international reference point in developed and controlled 3D printing constructions applications.
Market Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America | 28.70% |
| Europe | 23.80% |
| Asia-Pacific | 39.20% |
| LAMEA | 8.30% |
Infrastructure development, urbanization, and industrialization are the factors that led to the adoption of 3D printing construction in LAMEA. Installations of commercial and industrial projects in Latin America are dominated by Brazil, Mexico and Argentina. UAE and Saudi Arabia are concerned with renewable integration, hydrogen-capable and intelligent modular constructions in the Middle East. The Southern, Eastern, and Western Africa region are executing the projects of industrial, commercial, and distributed power infrastructure on a local level. The market penetration is enabled by international relationships and modernization projects despite the regulatory enforcement barriers and infrastructure differences. LAMEA is an area with real potential in 3D printing construction technology and low carbon infrastructure solutions in the long term.
Concrete: Concrete is applied in structural elements, walls, and foundations, tough, robust and economical. Favors building on a modular basis and sustainability. IoT and AI improve performance and forecasting maintenance. Can be used with hybrid methods of construction. Being used extensively in residential, commercial and infrastructure developments.
Plastic/Polymer: Light and can be designed to suit interior and non-structural purposes. Minimizes wastage of materials and promotes environmental conservation. Works with IoT-compatible monitoring and AI-compatible analysis. Increases design flexibility and architecture. Hybrid constructions are often used, where concrete or metal are mixed. There is an increased adoption of commercial and residential outlooks.
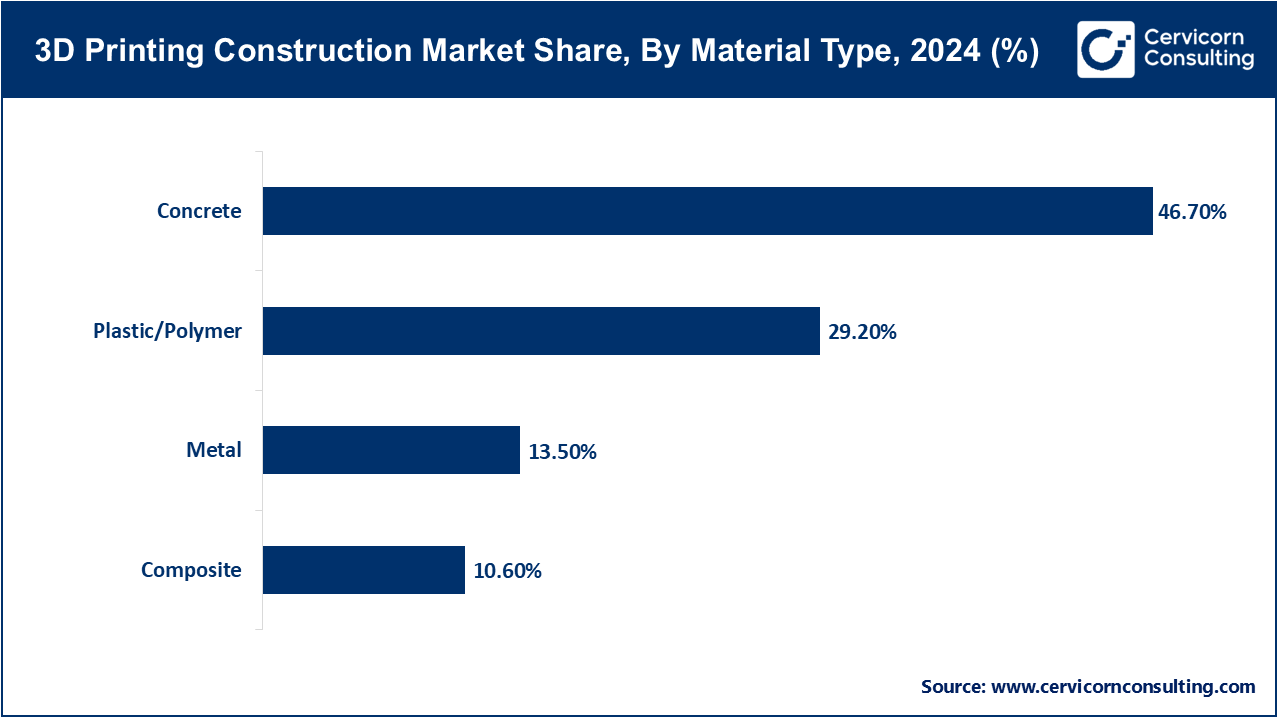
Metal: It is employed in the precision and high-strength elements of industrial and infrastructural application. Provides complicated geometries and longevity. Combinations with intelligent surveillance, artificial intelligence, and predictive maintenance. Minimizes the operational costs and improves the building efficiency. Frequently applies in hybrid 3D printing. There is an increase in industrial and high-value infrastructure development adoption.
Composite: It is a mixture of concrete, polymers and metals that can be used in various functions. Increases strength, durability and sustainability. Sustains AI predictive maintenance and Internet of Things surveillance. Commercial and industrial projects Modular, scalable. Less usage of resources and time in construction. There is a growth in adoption of advanced construction and hybrid infrastructure solutions.
Residential: 3D printing can allow homes to be built in a cost-efficient manner and quickly. Promotes flexibility of design and environmentally friendly use of materials. It can be integrated with smart home monitoring of energy. Predictive maintenance that is powered by AI enhances the safety of buildings. Minimizes building materials and work force needs. Urban and emerging markets are becoming more adopted.
Commercial: Commercial applications. Favors fast implementation and flexible plans. Combined with smart energy systems to make it operational. Amplifies sustainability using low-carbon materials. Predictive maintenance and digital twins streamline the performance. In developed countries, there is an increase in adoption with smart city programs.
Market Share, By Application, 2024 (%)
| Application | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Residential | 28.30% |
| Commercial | 38.20% |
| Industrial | 14.50% |
| Infrastructure | 19% |
Industrial: Used in warehouses, factories and other large-scale manufacturing. Enhances strong building structures and expansions. In AI and IoT, predictive maintenance and energy efficiency are enhanced. Combinations with renewable energy and smart grids. Lowers the cost of operation and construction. Asia-Pacific, North America and Europe have high levels of adoption.
Infrastructure: 3D printing is benefiting infrastructure in form of bridges, tunnels, and public utilities. Allows sophisticated and tailored designs. IoT and energy monitoring can be integrated to improve operational performance. Saves time and material wastage on construction. Favors low-carbon and green building. Government and other projects of the world are adopting.
Concrete 3D Printing: This has found extensive application in constructing walls, foundations, and structural elements. The construction is fast and cost-effective in terms of labor. Predictive maintenance and quality monitoring are possible due to the integration of AI and IoT. Modular construction improves residential and commercial designs. Embedding of low-carbon materials helps in achieving the sustainability. The adoption is high in the advanced countries that specialize in industrial and urban construction.
Polymer 3D Printing: It operates with non-structural items and interior parts as well as lightweight building. Allows complicated geometries and customization. It helps to monitor performance and predictive maintenance with the help of IoT sensors. Minimizes wastes and consumption of materials, which is in favor of environmental friendly practices. Usually used in architectural and interior designs. Increasing popularity of concrete and metal constructions.
Metal 3D Printing: Used in industrial, commercial and infrastructure projects in high-strength components. Facilitates accurate manufacture and sophisticated forms. Technologies of AI and digital twins can be used to improve efficiency and predictive maintenance. Cuts down on construction time and cost of operation. Combined more and more with intelligent monitoring to maximize energy efficiency. The high-value industrial and infrastructure projects are the drivers of adoption.
Hybrid 3D Printing: An amalgamation of concrete, polymer and metal technology to use in multifunctional applications. Favors modular building and optimization of mixed materials. AI, IoT, and smart energy monitoring will be incorporated to make sure that the operations are efficient. Makes it possible to predict maintenance and performance. Minimizes the carbon footprint and use of resources. Increasing application in high industrial, commercial and urban development.
Market Segmentation
By Method
By Material Type
By Application
By Region