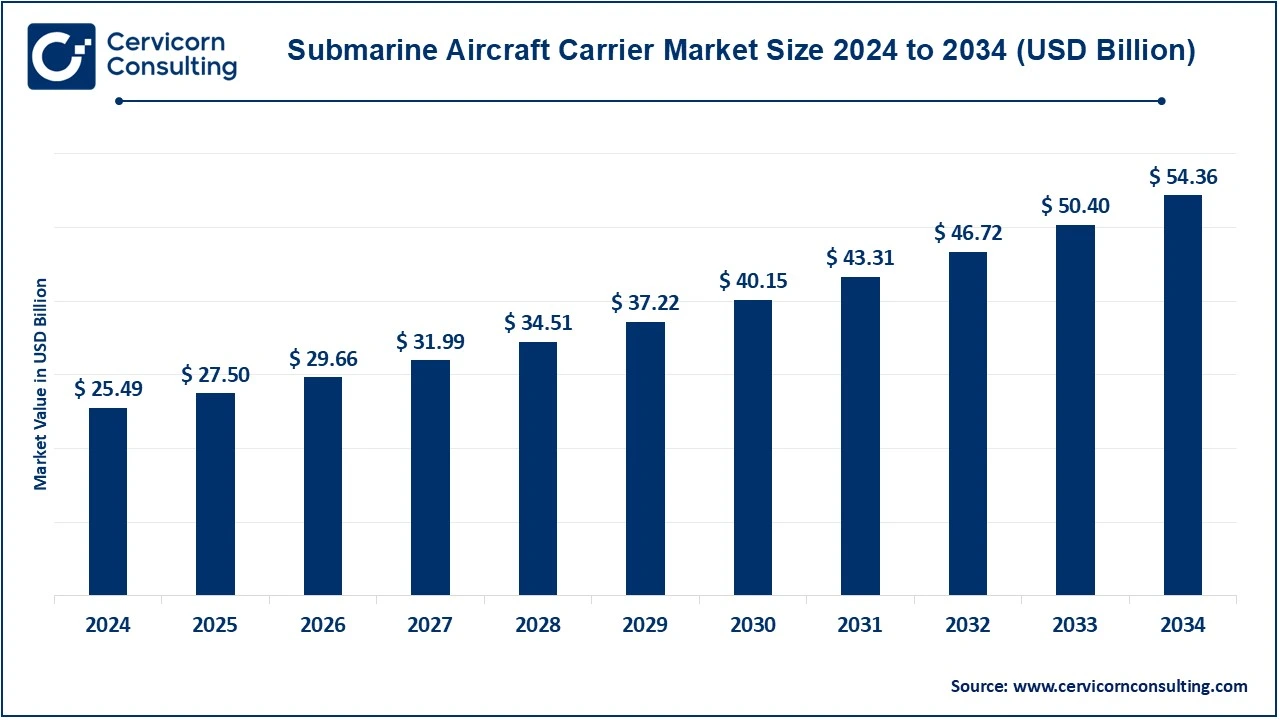
The global submarine aircraft carrier market size was valued at USD 25.49 billion in 2024 and is expected to surpass around USD 54.36 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.86% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
A submarine aircraft carrier is a hypothetical or conceptual combination of a submarine and an aircraft carrier that combines the stealth and diving capabilities of a submarine with the air engagement capabilities of an aircraft carrier. Although there is currently no such vessel in operational military fleets, the idea offers interesting possibilities, particularly for increasing the strategic advantages of naval operations. Although a fully operational submarine aircraft carrier is primarily a concept rather than a reality, it symbolizes a potential path for the future of naval warfare, combining the stealth features and versatility of submarines with the operational agility of aircraft carriers.
The submarine aircraft carriers market is anticipated to be shaped by a combination of technological progress, geopolitical dynamics, and evolving military strategies. As nations seek more covert, versatile, and efficient means to strengthen their naval dominance, this hybrid craft might provide a strategic advantage in displaying might, tackling security concerns, and managing complex global issues such as terrorism, maritime piracy, and international conflicts. Though the concept is mainly theoretical, it holds considerable potential to change naval warfare in the future.
The global defense sector is investing heavily in next-generation naval technologies, driving the potential growth of submarine aircraft carriers. With increasing geopolitical tensions and the demand for stealth-based warfare, naval forces are looking for advanced capabilities. The rise of UAVs has further accelerated research in this area, making unmanned submarine-launched aircraft a promising military innovation. Countries like the U.S., China, and Russia are investing in underwater drone technology, which could evolve into submarine aircraft carrier concepts. Additionally, advancements in artificial intelligence, underwater navigation, and drone miniaturization are supporting the development of submarine-launched aircraft systems. As military strategies shift towards unmanned and stealth-based operations, the market for submarine aircraft carriers is expected to witness increased research funding and development projects in the coming years.
What is a Submarine Aircraft Carrier?
A submarine aircraft carrier is a type of naval vessel that combines the stealth of a submarine with the capability to launch and recover aircraft. These specialized submarines are designed to carry, deploy, and retrieve small aircraft, usually for reconnaissance, attack, or strategic missions. Historically, Japan's I-400 class submarines in World War II were among the first to incorporate this technology, capable of launching seaplanes for surprise attacks. Modern developments in military technology are reviving interest in submarine aircraft carriers, with advancements in drone technology making them more viable. Instead of traditional manned aircraft, modern submarine aircraft carriers could deploy unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for surveillance, electronic warfare, and strategic strikes. These vessels provide a stealth advantage, making them useful for deep-sea missions and covert operations.
Key Insights Beneficial to the Submarine Aircraft Carrier Market
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 27.50 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 54.36 Billion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 7.86% |
| Dominant Region | North America |
| Rapidly Expanding Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Type, Aircraft Type, Application, Technology, End User, Region |
| Key Companies | General Dynamics Electric Boat, Huntington Ingalls Industries, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, BAE Systems, Thales Group, DCN (Direction des Constructions Navales), Naval Group, Rosatomflot, Rubin Design Bureau, JSC United Shipbuilding Corporation, Hyundai Heavy Industries, Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Saab AB, Leonardo S.p.A, Fincantieri, Rolls-Royce, Textron Systems, Boeing, Raytheon Technologies, L3 Technologies, General Atomics, China Shipbuilding Industry Corporation |
Growing Demand for Submarine-Based UAVs
Increase in geopolitical issues between countries
Ethical and Legal Considerations
High costs for development, maintenance and repair
Investments in submarines
Increasing Maritime Power in Global Waters
Geopolitical Tensions
Terrorist Adaptation
The submarine aircraft carrier market is segmented into type, aircraft type, application, technology, end user and region. Based on type, the market is classified into manned, and autonomous. Based on aircraft type, the market is classified into aircraft, fixed wing, rotary wing aircraft, and UAVs. Based on application, the market is classified into naval defense, maritime surveillance & reconnaissance, search and rescue & humanitarian operations. Based on technology, the market is classified into submersible technologies, and aircraft deployment systems. Based on end-user, the market is classified into military & defense agencies, private defense contractors, security & intelligence agencies.
Manned Submarine Aircraft Carriers: They would consist of fully crewed, functioning vessels that could carry submarines and aircraft. It is likely that they would be designed for strategic military purposes including defense, attack, and surveillance. For instance, submarines with nuclear or diesel-electric engines that can transport different UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles) or VTOL (Vertical Take-Off and Landing) planes.
Autonomous Submarine Aircraft Carriers: Unmanned aircraft systems, like drones, are being used for reconnaissance, surveillance, and striking missions from submerged platforms. This includes autonomous submarines equipped with drones or smaller VTOLs.
Naval Defense: These submarine aircraft carriers would act as a mobile base for nuclear or conventional deterrence, allowing a country to uphold a covert yet powerful military stance in critical maritime areas. Submarine aircraft carriers might be dispatched to hot spots for rapid tactical attacks, providing aircraft to participate in reconnaissance, surveillance, and air strikes.
Maritime Surveillance & Reconnaissance: With drones or specialized aircraft, submarine aircraft carriers could be used to support maritime patrol, early warning systems, and intelligence collection without risking the presence of larger carriers.
Search and Rescue & Humanitarian Operations: The submarine aircraft carriers could be used for non-combat purposes, such as humanitarian missions, search and rescue operations, or disaster relief in areas where airstrips or large vessels cannot operate.
Submersible Technologies: These include submarines powered by nuclear energy and those that are diesel-electric. The submarines powered by nuclear energy would use nuclear reactors to provide almost infinite underwater endurance. The market for these would primarily be restricted to countries with advanced nuclear capabilities. Diesel-electric submarines offer a more cost-effective option for nations without access to nuclear technology while still desiring the stealth and endurance of submersible aircraft carriers.
Aircraft Deployment Systems: These systems include VTOL aircraft and drone or UAV systems. The VTOL aircraft have the capability for vertical take-off and landing, comprising drones, helicopters, or specialized fighter jets, which would be crucial for launching from a submerged platform. The drone or UAV systems signify unmanned aircraft that would improve the practicality of a submarine aircraft carrier. Drones are projected to be a crucial component of this market segment.
Military & Defense Agencies: Nations with sophisticated naval capabilities like the United States, Russia, China, and others may lead in the development or acquisition of such vessels, particularly for strategic military benefit. Allied countries and NATO member states would also commit resources to advanced naval technologies to sustain a competitive advantage in defense, especially in air-sea operations.
Private Defense Contractors: Companies involved in building or designing specialized vessels for naval forces would be part of this market, either in providing prototypes, systems integration, or maintenance services.
Security & Intelligence Agencies: Countries focusing on maritime reconnaissance and surveillance may allocate resources to unmanned or autonomous submarine aircraft carriers for non-combat purposes like espionage, reconnaissance, and border monitoring.
The submarine aircraft carrier market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. Here is a brief overview of each region:
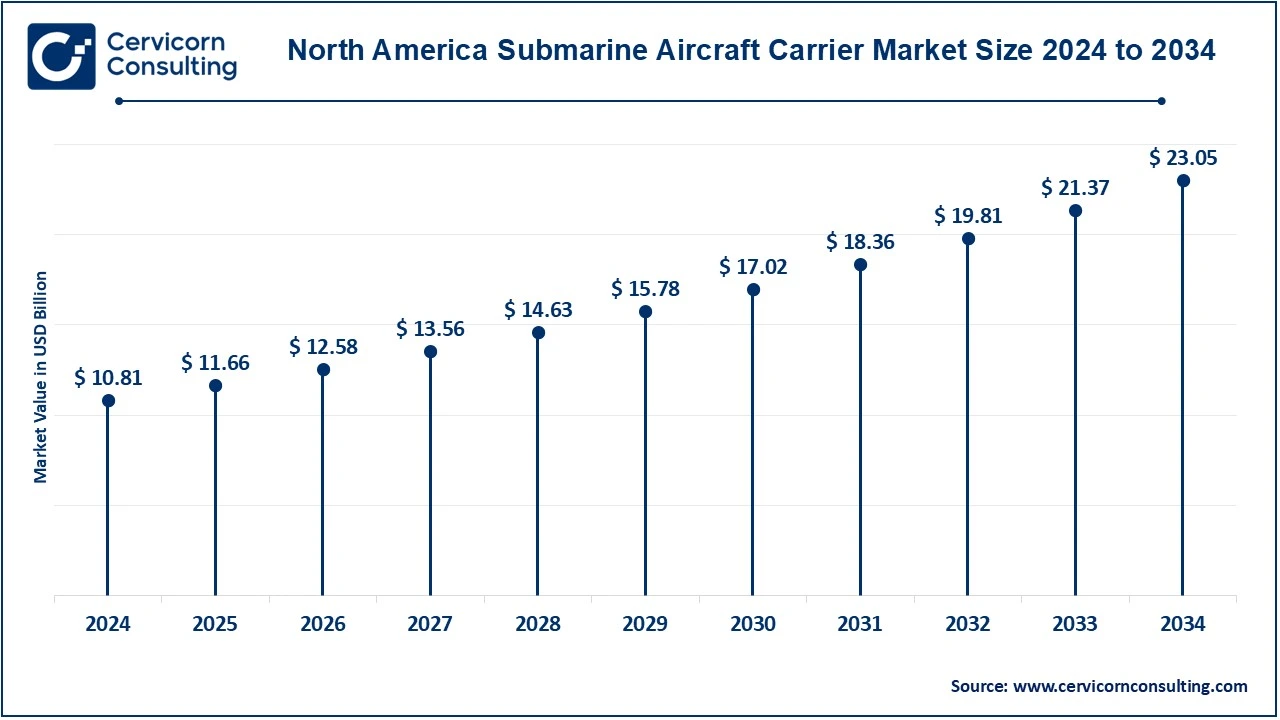
The North America submarine aircraft carrier market size was valued at USD 10.81 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 23.05 billion by 2034. North America is anticipated to witness robust growth in defense investments and advancements, especially in the U. S. Navy’s effort to grow its fleet to 355 ships by 2030. This growth entails the acquisition of sophisticated warships such as the Gerald R. Ford-class aircraft carriers, emphasizing state-of-the-art technologies for combat preparedness and operational effectiveness. This significant defense expenditure in North America fosters regional growth through procurement, research, and development projects.
The Europe submarine aircraft carrier market size was estimated at USD 7.44 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to hit around USD 15.86 billion by 2034. European nations such as France, Italy and the United Kingdom are investing heavily in advanced naval technology, with a focus on submarines and unmanned aerial systems. The EU and NATO are driving forward the development of next generation defense systems, with leading companies such as Naval Group, Fincantieri and BAE Systems at the forefront of naval defense and shipbuilding. France, Britain and Russia have expertise in nuclear-powered submarines, essential for ships with long-range and stealth capabilities, including potential anti-submarine aircraft carriers. These countries may have positioned themselves as pioneers in advanced naval technology by leveraging their knowledge in nuclear-powered submarines for the development of innovative hybrid systems.
The Asia-Pacific submarine aircraft carrier market size was accounted for USD 5.53 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 11.80 billion by 2034. With crucial shipping routes such as the South China Sea and the Strait of Malacca facing threats from terrorism and piracy, the Asia-Pacific region is crucial to global maritime trade. Japan, China, and India are enhancing their naval forces, concentrating on aircraft carriers and underwater warfare. China is increasing its number of ships and carriers, while India is bolstering its naval strength and maritime capabilities. These actions signify strategic objectives and modernization initiatives in the area, backed by collaborations and developments in avionics, propulsion technology, and unmanned aerial systems.
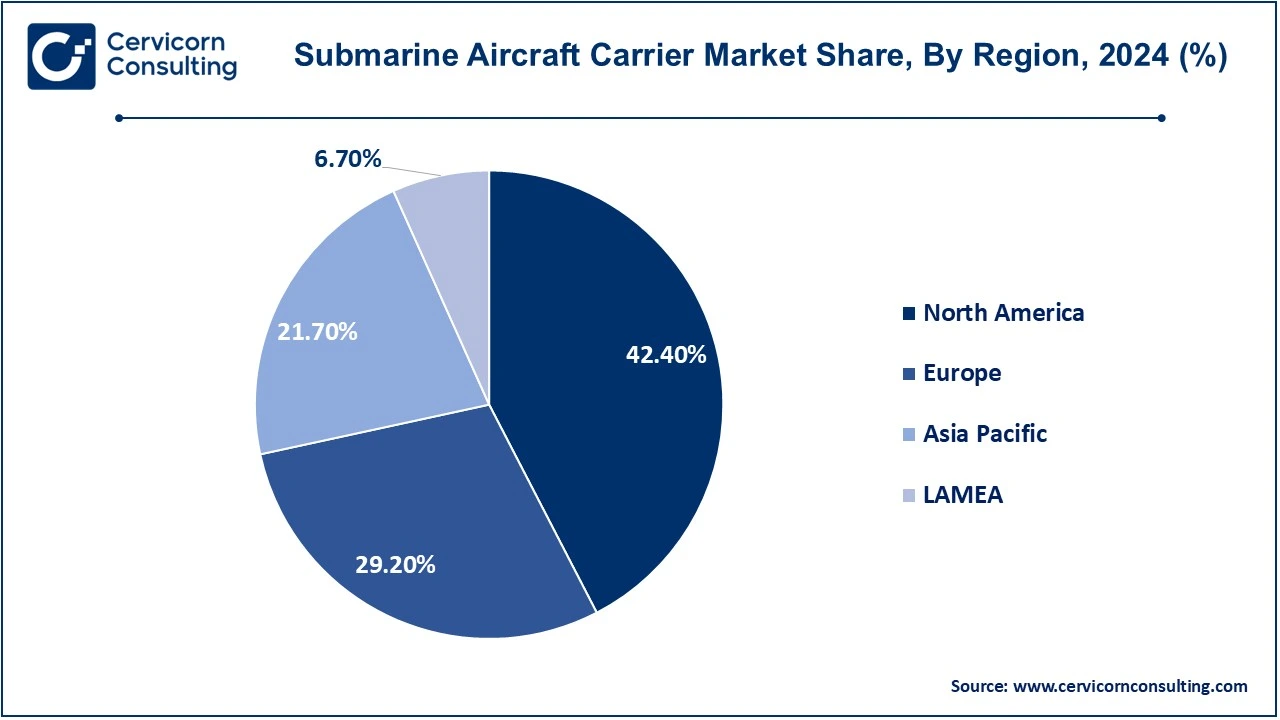
The LAMEA submarine aircraft carrier market size was valued at USD 1.71 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 3.64 billion by 2034. Because of growing worries about border security, terrorism, and maritime safety in vital waterways, the market for submarine aircraft carriers is expanding in the LAMEA area. With the development of nuclear-powered submarines and the possibility of hybrid ships like submarine aircraft carriers, Brazil is well-positioned to join the market. Piracy and maritime terrorism are major problems in areas like the Strait of Malacca, the Gulf of Guinea, and the Somali coast, which increases demand for cutting-edge military technology. Given its increasing interest in forming alliances with foreign armed forces, the LAMEA area is well-positioned to contribute significantly to the development of the rising market.
CEO Statements
Michael Peter, CEO of Siemens Mobility
Tracy Robinson became president and CEO of the Canadian National Railway Company (CN Rail)
Market Segmentation
By Type
By Aircraft Type
By Application
By Technology
By End-User
By Region