Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
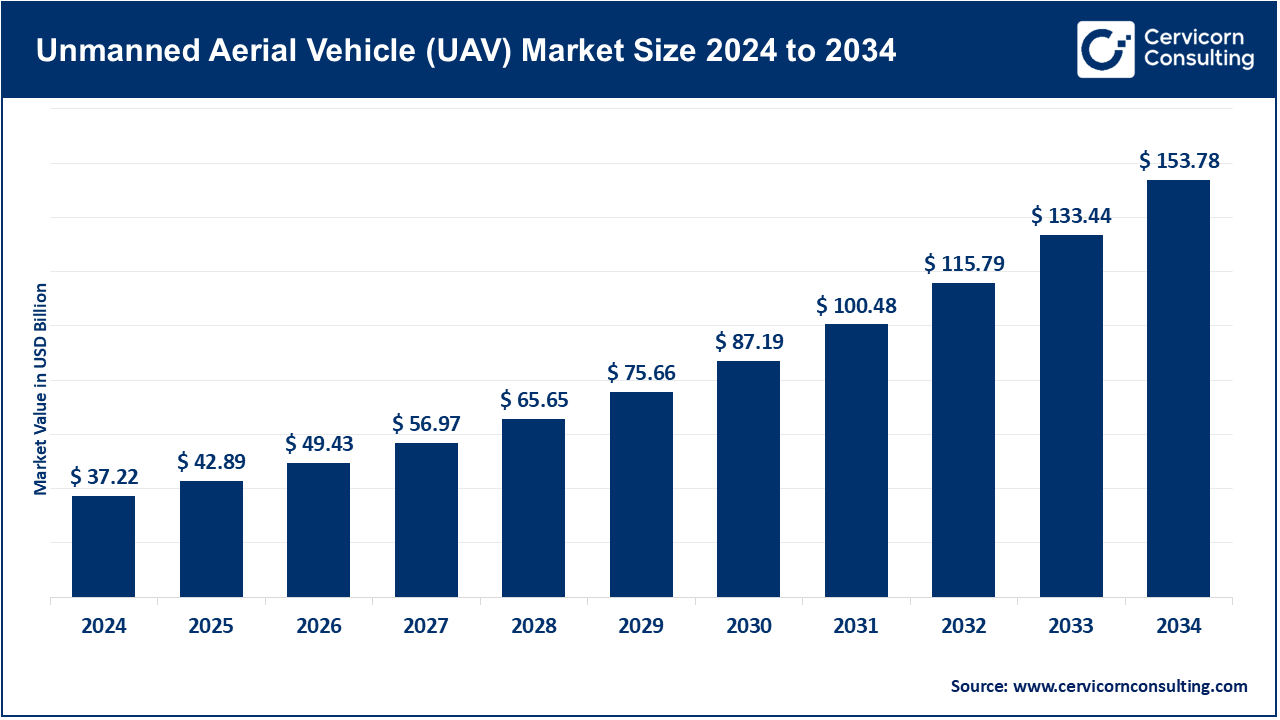
The global unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) market size was valued at USD 37.22 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 153.78 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.60% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
The unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) market is expected to grow significantly owing to rising demand across military, commercial, and civil applications. Key growth drivers include advancements in AI, sensor technologies, and autonomous flight capabilities, enabling enhanced surveillance, delivery logistics, and agricultural monitoring. Governments are increasingly investing in UAVs for border control, disaster response, and smart city infrastructure. Additionally, regulatory support and reduced hardware costs are accelerating commercial adoption, positioning UAVs as essential tools across diverse industries in the coming years.
The UAV market is evolving rapidly, with significant developments in UAV technology, including: AI, computer vision, and data analytics, to support applications with comprehensive autonomy or more complex missions across industries. The use of UAVs is increasingly being seen in defense in applications such as surveillance and operational missions, and they are informing several commercial sectors including agriculture, logistics, infrastructure inspection, and emergency response. There are several distinct drivers for UAVs development and sales, which include, battery life improvements, sensors, regulatory support, and growing demand for automation and remote operations. Innovation is accelerating in the UAV sector from collaboration between UAV manufacturers plus AI start-up companies and cloud providers, making UAVs more intelligent, reliable, and scalable. The evolution of UAVs enables a greater level of context awareness and autonomy, and it is anticipated that UAVs will play an essential role in refining operational efficiency and decision-making in a connected, data-driven ecosystem.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Market Report Highlights
- By Region, North America has accounted highest revenue share of around 39.4% in 2024.
- By class, the Small UAVs segment has recorded revenue share of around 45.6% in 2024, due to their affordability, ease of deployment, and versatility in commercial and defense applications like surveillance, agriculture, and delivery services.
- By technology, the Remotely Operated segment has recorded revenue share of around 50.2% in 2024, due to as they offer high control precision, cost efficiency, and regulatory acceptance, making them ideal for defense missions and commercial inspection tasks.
- By application, the Commercial segment has recorded revenue share of around 49.4% in 2024, due to growing use in logistics, infrastructure inspection, agriculture, and media, driven by technological advancements and increasing acceptance in civilian airspace.
- By point of sale, the OEM segment hold major share in 2024.
- By end user, the government & defense segment dominated the market in 2024.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Market Growth Factors
- Technological Advancements (AI, GPS, LiDAR, Analytics): Advances in Artificial Intelligence navigation, high-precision GPS, LiDAR payloads, and analytics in cloud computing are enabling UAVs to autonomously inspect, map, and monitor with no human intervention. These aircraft/drone systems can detect change, avoid obstacles, and communicate relevant information, all in real-time. The FAA reported over 1 million UAV registrations in the leadership of the future in early 2025, which is indicative of their wide-scale adoption across the country. Furthermore, the EU's Drone Strategy 2.0 framework implemented Remote ID directly onto drones in 2022, with Remote ID and open category regulations coming into force in early 2023 and legal approval for intelligent flights in 2024. The new laws represent confidence in investments in even expensive high-end sensors and onboard artificial intelligence systems, along with the supporting capabilities offered by the new regulations to enable a new range of UAV applications involving analytics and advanced autonomy.
- Cost Reduction in Components: Industry-wide adoption has resulted in mass production and scale capturing across UAVs, leading to massive cost reductions. All the major components, from batteries to sensors to composite airframes have been on a rapid decline for some time, opening the use of low-cost UAVs to SMEs and beginner enthusiasts. According to FAA, more than 400,000 UAV registrations exist in the U.S. alone, while the EU suggested that the drone industry is worth €28 billion in 2022, estimated to grow by ~38.6% per year. The 2023 rollout of the EU U-space frameworks, and harmonized certification requirements, further reduced barriers to manufacturing in Europe. Specifically, new laws reduced certification costs significantly and reduced certification cycles generally.
- Growing Investments and Startups: A combination of public funding and clear regulation has accelerated startup activity and investment in the UAV ecosystem. AI, autonomy, and VTOL-focused companies are drawing major grants and private capital. Between 2023–2025 the EU signaled the intention to allocate considerable funding on R&D projects in respect of VTOL systems, autonomous tools, and U-space infrastructure, while at the same time the U.S. Department of Transportation, allocated $50 million in grants to support drone investigations through to the end of 2024. Many public-private partnerships have emerged in Europe and North America, helping provide investment to support drone-as-a-service models and UAV software companies. Investors had already been buoyed by improved regulatory clarity around airspace use, and clarification in respect of remote operations had made the market easier for new entrants.
- Disaster Management & Emergency Response: UAVs (unmanned aerial vehicles) have essential capabilities in aerial mapping, search and rescue, and supply chain delivery, and have now been internationally recognized as important assets in times of emergency. Their employment in disaster-stricken areas reduces risks and promotes faster responses. Following wildfires and floods in 2023–2024, FEMA updated its drone-use guidelines, authorizing UAVs for rapid damage assessments. Both FAA and EASA approved BVLOS operations for emergency missions during that period. EU regulations effective 2024 legally integrate drones for medevac and SAR roles under the Open/Specific Category framework. These legal distinctions are now embedded in national disaster-response protocols.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Market Trends
- Integration with 5G Networks: 5G equips UAVs with low-latency HD streaming, real-time AI analysis, and reliable BVLOS control, crucial for live monitoring and logistics use. These connectivity improvements support next-gen drone services. Since 2023, U.S. and EU telecom regulators have conducted joint trials linking UAV systems with 5G networks, while the FAA sanctioned 5G-enabled drone corridors in 2024. The EU U-space documents are also supporting telecom-drone convergence. These are not only pilots, but they are also regulatory pilots, as the integration of aviation-telecom ecosystems is now seen as legal acceptance. As a result, UAVs are now moving closer to being part of smarter, connected air networks.
- Miniaturization and Portability: Drones below 250 g are becoming increasingly popular because they have less portability, regulatory burden with marginal risk, and ease of use, etc. They resonate well with hobbyists and light commercial users. As of January 2024, the EU’s C0–C3 class marks legally exempt sub-250 g UAVs from many licensing requirements. The FAA anticipates millions of recreational aircraft in the registry by mid 2025. This harmonized legal construct permits lightweight drones to operate under straightforward and accurate rules, fostering consumer adoption and small business application in industries such as mapping and inspection, and the creative sector.
- Use in Urban Air Mobility (UAM) & Flying Taxis: Urban Air Mobility would be piloted or autonomous Crewless VTOL aircraft, which is a companion to traditional UAVs, used in urban airspace. Promises on-demand passenger transport and on-demand cargo transport. Regulatory structures are being developed to support these. In April 2024 the EU established principles that define VTOL "air taxis" and medivac drones in particular categories. Later in 2024 EASA established new proposals for the pathways to certification. Furthermore, EASA's Advanced Air Mobility initiative will have draft standards anticipated to be completed in 2025. This represents an overall strengthening of legal regimes. Aviation authorities are now taking urban drone transport seriously, which supports initiatives for demonstration projects and eventual public use.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 42.89 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2025 |
USD 153.78 Billion |
| Projected Market CAGR 2025 to 2034 |
17.60% |
| Dominant Region |
North America |
| Fastest Growing Region |
Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments |
Class, Type, System, Point of Sale, Application, End-User, Region |
| Key Companies |
Aero Vironment Inc, Parrot Drones, PrecisionHawk, 3D Robotics, Airbus SAS, Boeing, General Atomics, Lockheed Martin Corporation, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Textron Inc, Thales Group |
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Market Dynamics
Market Drivers
- The Need for Real-Time Aerial Monitoring: In the area of infrastructure, border control, and environmental protection, real-time aerial monitoring is vital for industries utilizing Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). An autonomous drone will deliver better speed of detection of incidents or risk mitigation. According to FAA statistics, there were 412,505 commercial UAV registrations in the U.S. in the year 2025. More targeted funding through legislation updates in 2023 now allows UAVs to be deployed for border and infrastructure monitoring under remote-ID conditions. National security agencies are including UAVs in their area security and monitoring programs for facilities and critical assets. By providing a legal pathway, UAVs are now recognized as effective surveillance tools and can provide rapid response times.
- The Demand for Remote Monitoring in High-Risk Environments: Uncrewed platforms provide a safer method of inspecting very hazardous conditions including industrial when needed, hazardous locations, and confined space to reduce risk to humans. Regulators are recognizing and allowing this type of operation. The United States, since 2023, received guidance from OSHA, endorsing the use of UAVs for high-risk site inspections for the first time. The EASA 2024 airworthiness rules, led to guidance on UAV use under certain categories. In 2024, FEMA also issued guidance that can use UAVs to support inspections of film monitoring for chemical spills. These legal frameworks are opening up UAV controlled operations, similar to the risk-aware programs found in other industries and in many ways, provide a safer and cost-effective method to deploy remote monitoring services.
- Public Safety Applications (Firefighting, Crowd Monitoring): UAVs support public safety by aiding in firefighting, crowd control, search-and-rescue, and disaster relief, offering situational awareness while minimizing exposure. Aviation authorities are formalizing these uses with licenses and exemptions. In 2023, the FAA introduced interim rules enabling public safety agencies to operate drones under Part 107 waivers with remote-ID compliance. EU’s April 2024 package for emergency services includes UAVs for civil protection. Fire departments in California and Florida have received Certificates of Authorization since mid 2024. These legal mechanisms remedy previous uncertainties around PPE-like drone deployment.
Market Restraints
- Limited Flight Time and Battery Life: Battery life is still one of the greatest limitations for small UAVs, as they can only fly for roughly 20–30 minutes on a single charge, limiting their range and preventing mission continuity. Failures caused by the depletion of batteries and the degradation of battery battery capacity are among the highest foes of small UAV operational risks. Reliability matters in this regard. According to FAA data in 2023, battery issues accounted for around 12% of all drone incidents, and as a result, regulators have included battery endurance and emergency reserves in recent airworthiness directives and rules of the road. Insurers are now requiring proof of compliance with these mandates as a result of not just the issuance of safety bulletins. These types of regulations mean more costs in the development of small UAVs but have an overall goal of minimizing risk and providing better assurances of flight safety and performance.
- Weather Sensitivity: Weather sensitivity is a persistent limitation in the case of UAVs: drones cannot fly in windy conditions, rain, temperature extremes, or fog. Operators have practical limitations on use by restricting the use of UAVs to lighter weather conditions that limit how many times daily their UAVs can be up and flying. Research into the use of UAVs has reported the average flight window globally is 5.7 hours/day, where limited daylight reduces this number to an average of 2.8 hours. Since 2023, operators in their FAA and EASA operation manuals, have incorporated formal weather conditions, which prevent operators from operating outside of the manufacturer's thresholds. Since this recent clarification in regulations, insurers have removed coverage for any weather related claim, causing operators to increase their liability of exposure. This limits the companies operational time of their UAVs and does not allow for flexibility in when they can use them and report back to the client.
- Limited Payload Capacity: Regulatory weight caps under 2 kg (EU) and 25 kg (US) restrict UAV payloads, limiting sensors, delivery options, and operational complexity. Heavier missions require certification via the Specific Category, triggering lengthy airworthiness reviews like SORA, along with costly infrastructure and oversight. Since January 2024, EASA’s C0–C3 classification imposes strict compliance for heavier systems, while the FAA’s Part 107 reiterates weight-based limits. These restrictions constrain commercial use cases, limiting broader adoption by SMEs and impeding the integration of advanced payloads in routine operations.
Market Opportunities
- Establishing Partnerships with Telecom for 5G-Enabled UAVs: 5G compatibility also presents a high–value UAV opportunity whereby UAV pilot is capable of low-latency control, HD streaming, and long-range BVLOS delivery options. The FAA and the NTIA have offered assistance and have built a trial corridor that began in 2023, and the FAA have allowed 5G drone lanes that were established in 2024. New York’s 5G-connected drone corridor reflects the first U.S. FAA-sanctioned 5G testbed, supporting a 100+ square-mile range for BVLOS flights. EU U-Space regulations similarly promote telecom-aircraft convergence. Legally endorsed telecom partnerships now provide UAV operators with reliable communications backbones, paving the way for safer, smarter drone use in logistics, inspection, and emergency services.
- Integration into Emergency Medical Services (EMS): Medical UAVs can not only deliver AEDs, vaccines, and other supplies faster, also increase emergency response in more rural or congested regions. Between 2023-2024, multiple U.S. states received FAA waivers for drones that deliver AEDs under Part 107 and under exemptions for medical payloads that the federal government put in place. The EU's amendments to regulations in April 2024 also included drone medevac as part of its U-space/air taxi regulation framework. When Norway and Switzerland began to legally approve drones for blood-delivery operations, it represented continued regulatory progress to formalize UAVs to EMS systems and provide them legal authority to operate and legitimacy behind lifesaving operations.
- Expansion of Entertainment and Media: Drone-use for cinematography is rapidly expanding with lightweight and stable platforms offering the ability to capture high-quality aerial images at lower price points. Media drones represent about 22% of all FAA Part 107 missions in 2023. Eventually, beginning in 2024, media drones received EASA's C1/C2 class mark allowing for permission to fly above 120m without the need for EASA to pre-approve, and many U.S. states have simplified the issuance of short-term filming permits. These regulatory changes lessen red-tape, making way for increased drone-use of various creative mediums including film, events, real estate, and sports broadcasting, and broadens the legal functionality to promote creative industries efficiently and legally.
- Training and Certification Programs: Trained and certified remote pilots are required for safe UAV operations for a variety of industries and for private UAS operators. As of early 2025, the FAA has issued over 1 million remote pilot certificates, and the EU will tie pilot training to class-mark compliance beginning overshadowed by new rules expected to launch in 2024. In each of the EU countries, the national governments have begun their own drone training hubs supported by NextGenerationEU and local grants. These regulatory measures support education pathways, enhance the safety culture, and develop the professional workforce. This emphasis for remote pilot training suggests substantial legal frameworks that mandate operators be certified and capable operators to validate their credibility towards commercial and civil interests.
Market Challenges
- Battery Constraints: Even with significant improvement in battery technology, in the specific areas of Li-ion battery chemistries lower energy densities and thermal management limit drone endurance and the negative hazard implications associated with them. According to FAA analysis released in early 2023, Li-ion battery failures accounted for around 12% of all UAV incidents, and that was enough of a concern that regulators issued advisories prompting many critical infrastructure companies to assess their thermal monitoring and containment systems. The FAA has now indicated that planning to support additional regulatory structure such as procedures to contain Li-ion batteries will be part of their 2024 hazardous materials campaigns under 49CFR Part 107 - and project compliance with that regulation. It is fair to say that, with economic constraints continuing to delay useful supply chains, which raises costs by about 15% in 2023, increased regulation around how Li-ion battery systems are designed and delivered through compliance certification costs for expensive safety certifications and containment systems mandated costly compliance procedures, etc. Maintenance could be similarly complicated, operating expendables and costs could complicate numerous design trade - offs.
- Interference with Other Signals: UAVs depend on GPS and radio frequencies, making them vulnerable to signal jamming or spoofing. FAA records from 2023 reveal a 7% increase in interference-related anomalies. Though EASA class regulations enforce Remote-ID, spoofing protections remain underdeveloped. In the United States multiple states passed criminal statutes by statute in 2025 around interference with GPS related to critical infrastructure, references to airports, etc. Detection systems are deployed outside these spheres of activity and are prohibited on the basis of federal state law: very complicated to bill and deploy these systems unless the GPS interference becomes excessive and reaches level where over watch is needed. UAVs must also include GPS interference monitoring systems, compliance with new safety and security standard operating procedures.
- High Maintenance and Repair Costs: UAV's will also assume a higher slew of roles in the Specific Category, in which cases where UAVs are deployed will have mandates for airworthiness checks, sensor calibration, documents demonstrating full traceability, etc. Under EASA's proposal for airworthiness in 2024 automatic logging using a cloud based system will be required. At the same time for anyone using the FAA's part 107 and or COA the obligation is undertake a scheduled inspection and to maintain documentation. According to FAA incident reports, ~15% of operational failures in 2023 stemmed from maintenance lapses. While maintenance regimes enhance safety, they also raise operational expenditures, limiting entry for smaller operators. These legal requirements necessitate balancing cost against compliance for sustainable UAV deployment.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Market Segmental Analysis
Class Analysis
Small UAVs: The Small UAVs segment has dominated the market in 2024. Small UAVs are lightweight, small unmanned aircraft meant for civil, commercial, or recreational purposes, generally less than 20 pounds. These fall under FAA Part 107 (U.S.) or the C0–C1 class in the EASA open category. By 2025, at least 1 million commercial remote drone pilots had been certified by the FAA, which makes clear that small drone use has reached widespread use for photography, inspection and crop milling amongst other activities. In 2024, the EU and India announced that they would start a dialogue around regulatory harmonization to provide for global interoperability for commercial drones by using new operational regulations for network safety and certification model for small UAVs.
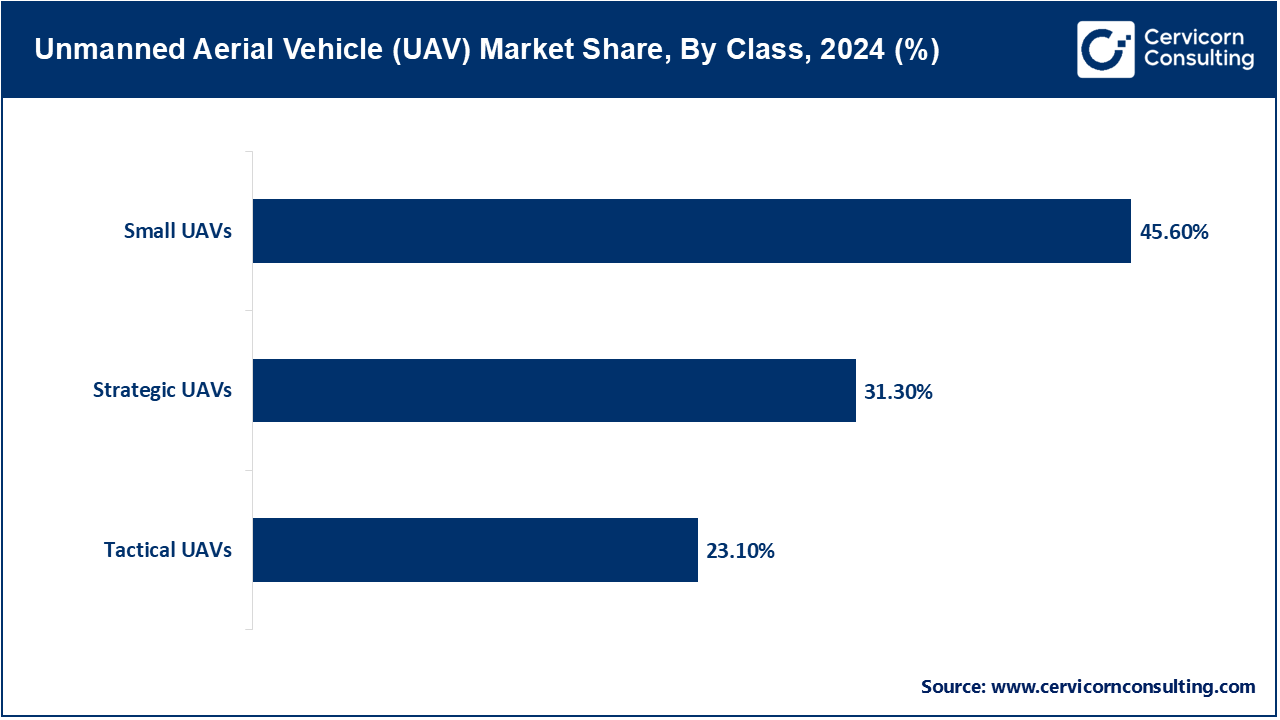
Tactical UAVs: Tactical UAVs are mid-range unmanned aircraft that enable battlefield surveillance, reconnaissance, and limited combat support. The bulk of unauthorized combat UAVs are mid-range, or Group 2 or 3 UAVs, capable of flying for multiple hours and equipped to stream real-time data feeds. In February and March of 2023 and 2024, the U.S. Department of Defense provided tactical UAVs to Ukraine and Indo-Pacific allies through security assistance programs, specifically AeroVironment's Jump 20 and RQ-20 Puma UAVs. The tactical UAVs will primarily be used to observe hostile troop movement and targeting for artillery. The regulatory input process was interrupted in January 2024, when the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) published inputs for new airworthiness regulations, specifically for mid-tier systems.
Strategic UAVs: Strategic UAVs are long endurance, high altitude drones that perform global surveillance, intelligence collection, and combat operations. Systems like the MQ-9 Reaper or RQ-4 Global Hawk are examples of drone systems relied on globally by militaries for ISR deliver and strike. The U.S. Marine Corps activated MQ-9A squadrons in Hawaii in April and August of 2023 to facilitate operations in the Pacific theater. The Marine Corps will adapt these systems to work for maritime and joint operations and the Department of Defense has upgraded their guidance for developing long range autonomy and operating within U.S. Indo-Pacific Command (INDOPACOM) planning and strategy development.
Technology Analysis
Remotely Operated UAVs: The remotely operated UAVs segment has dominated the market in 2024. Remotely Operated UAVs (RPAs) are piloted entirely by human operators using radio signals and GPS-based systems. Remote Piloted Aircraft (RPA) are developed and used in both military and commercial use cases because of their simplicity for the operator and regulatory clarity. In December 2022, the Air Force and Marine Corps RPA training programs expanded and MQ-9 squadrons gained Initial Operational Capability (IOC). By 2025, the FAA's drone registry log exceeded 1 million entries with a large portion of that in remote piloting operations. These examples show the ongoing utility of RPAs even as a higher degree of autonomy is considered.
Fully Autonomous UAVs: Fully autonomous UAVs can fly upward, navigate, perform tasks, and fly back down, all without operator intervention. Fully autonomous UAVs utilize onboard AI, LiDAR, and sensor fusion technologies, they plan and determine the actions that are necessary to autonomously perform tasks. Due to the high-risk nature of fully autonomous operations, regulation must occur before allowing their use to sufficiently mitigate risk enough to allow for 'safeness' and legality. In 2024, JARUS released the SORA v2.5 (Specific Operations Risk Assessment), which provides frameworks regarding the risk of autonomous drones. The EASA 2024 U-space regulation permits the development and deploying UAV services, using autonomous operation, in pre-determined, approved areas. The purpose of these regulatory changes is to enable AI-based drones to tackle commercial needs including logistics, infrastructure monitoring, and emergency services.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Market Revenue Share, By Technology, 2024 (%)
| Technology |
Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Fully-autonomous |
17.30% |
| Semi-autonomous |
32.50% |
| Remotely Operated |
50.20% |
Semi-Autonomous UAVs: Semi-automated UAVs have some automation, with the human operator responsible for key decisions. Building automation for semi-autonomous UAVs, such as autopilot navigation and/or obstacle detection, gives a human operator control of key operational decisions. Semi-autonomous UAVs can now be used primarily for commercial purposes including, but not limited to, inspection, logistics, and mapping / surveying. In early 2023, the FAA changed its Remote ID rule for remote pilots under Part 107 in semi-autonomous systems to include requirements to share log data for the flight objectives, and to include submitting a remote pilot log for recording the operational and visibility of the aircraft. At the same time, EASA updated its classification of drones, C2 - C3 regulations included new standards of UAV autonomy for commercial application, allowing for a smoother introduction into urban and industrial uses.
Application Analysis
Commercial UAVs: The commercial segment has leading the market in 2024. Commercial UAVs are utilized in agriculture, logistics, energy, and media. More specifically, commercial UAVs must comply with regulatory frameworks, like the FAA Part 107 or EASA’s U-space package. As of early 2025, the FAA had over 412,000 commercial drone registrations. In 2024, Europe opened up new corridors aided by 5G for drone deliveries and inspection missions. With it, legal frameworks that supported the use of drones alongside telecom companies for business purpose began to emerge. In the United States, two approved drone zone areas were formed for test flights in New York and Texas. These FAA approved test zones allowed drone operators the ability to perform advanced beyond-visual-line-of-sight (BVLOS) operations.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Market Revenue Share, By Application, 2024 (%)
| Application |
Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Commercial |
49.40% |
| Military |
37.20% |
| Recreational |
13.40% |
Military UAVs: Military UAVs are made for the purpose of surveillance on the battlefield, target acquisition, electronic warfare, and precision strikes. Examples of military drones include Group 3–5 drones, such as the MQ-9, which are flown by U.S. and NATO forces. It should be noted that in 2023, the U.S. Department of Defense stated that the rate of training of drone pilots exceeded traditional in-depth manned aircraft in training rates for pilots that can fly from the cockpit. Effective 5 July 2023, the Marine Corps published an announcement that unveiled the capability of ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance) with units to begin operating MQ-9 UAVs in support of Indo-Pacific operations. The completed MRAP with the emergency drone units flew with new MQ-9 deployments in support of CENTCOM objectives. Military UAVs must operate according to military airworthiness policies and procurement programs, such as the Army's forward test unit equipped with tactics payloads that are dangerous quality levels dependent on test objective completion as a FTUAS.
Recreational UAVs: Recreational UAVs are consumer drones used for hobby flying, photography, and racing. In the U.S., these are governed by FAA rules requiring registration for drones over 250g and compliance with Remote ID since September 2023. As of 2025, the FAA has registered more than 1 million recreational UAVs. EASA’s CE-marked C0 drones now enjoy simplified airspace access within the EU. This regulatory simplification has supported rapid consumer adoption and innovation in drone design for casual use.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Market Regional Analysis
The UAV market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region.
Why is North America leading the unmanned aerial vehicle market?
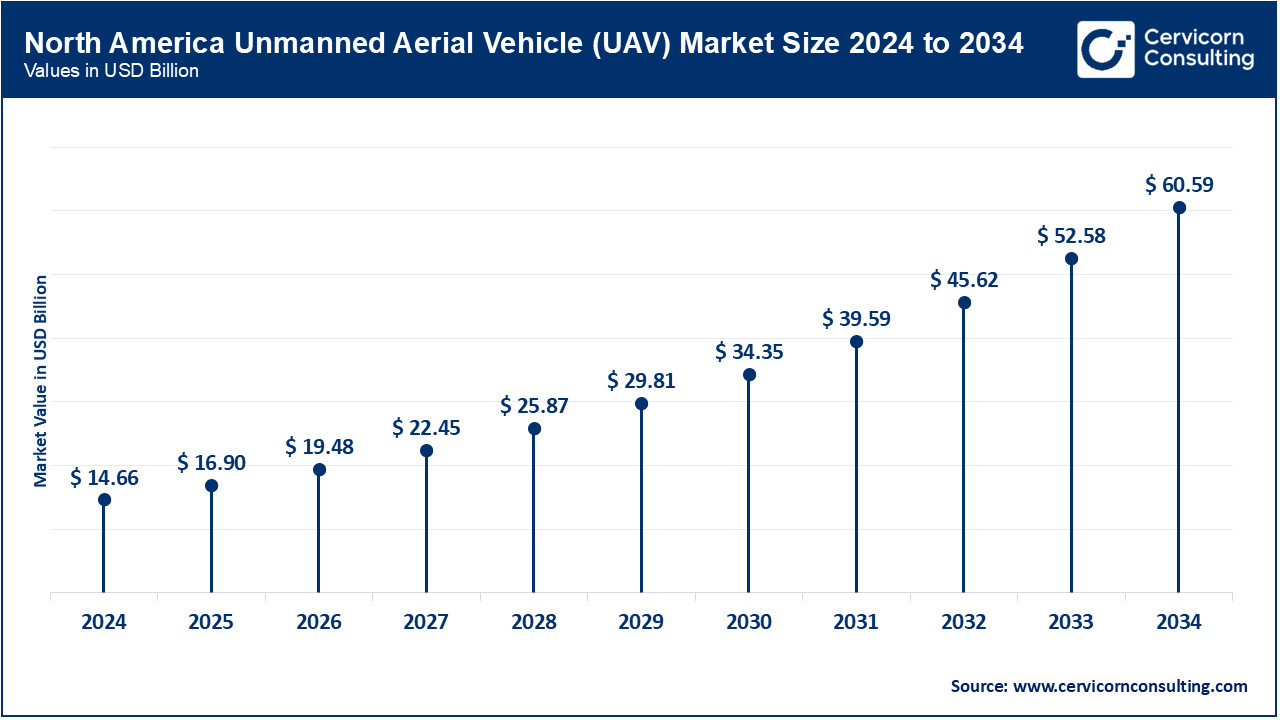
- The North America UAV market size was valued at USD 14.66 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 60.59 billion by 2034.
The United States remains the leader in drone adoption, supported by its established regulatory framework, defense budget, and public demand. The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) indicated more than 1 million registered drones and more than 400,000 certified remote pilots by 2025. The FAA issued Executive Orders promoting testing of drone corridors, and the expansion of domestic UAV manufacturers. Canada, through Transport Canada, primarily updated its RPAS regulations in 2025 to support BVLOS operations carrying a medium risk and remote ID. Mexico continues to improve its UAV-related regulatory framework, and is increasingly adopting drone usage in agri-tech and inspections of infrastructure, and benefits from increasing drone usage in smart farming applications and support for geospatial mapping. Across the region, regulatory frameworks are developing to enable the safe and scalable integration of UAVs into the civil airspace.
Why is Europe hit notable growth in the unmanned aerial vehicle market?
- The Europe UAV market size was estimated at USD 10.46 billion in 2024 and is expected to hit around USD 43.21 billion by 2034.
Europe continues to develop and integrate UAV with the use of common regulations under EASA's Drone Strategy 2.0 that outlines common rules (including digitally-enabling airspace and remote identification). The UK, post-Brexit, updated its guidance on the use of drones in 2024, and allowed trials of delivery drones using BVLOS and previous EASA options on inspectors for infrastructure. Germany has created urban drone corridors in the cities of Munich and Berlin to enable a 5G inspection service. France created an operational U-space airspace zone for integrated and harmonized airspace zones in 2024, including emergency response, and delivery of medical products by drone. A single licensing framework for pilots, and unified regulatory classes of classification of drones (C0-C4) under one category allowed safer cross border operations.
What is behind the rapid growth of the unmanned aerial vehicle market in Asia Pacific?
- The Asia-Pacific UAV market size was accounted for USD 9.38 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach around USD 38.75 billion by 2034.
Rapid UAV development is taking place in the Asia-Pacific, driven by urban automation, modernization of armed forces, and favourable regulations. China fully embraces drones in logistics through its various smart-city projects, and is testing BVLOS & autonomous flights in urban areas. India's Drone Policy 2.0 in 2023 is now allowing to dedicate drone corridors, while also encouraging domestic manufacturing with incentives. In 2024, Japan announced concrete measures to allow drones to inspect civil infrastructure and expanded its BVLOS permissions. Australia, via CASA, authorized the commercial drone delivery service for e-commerce and health supply, in 2024. In South Korea, drones had gained specific prominence in digital innovation projects with an updated policy in 2025, allowing UAV usage in smart logistics and aircraft inspection.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Market Revenue Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region |
Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America |
39.40% |
| Europe |
28.10% |
| Asia-Pacific |
25.20% |
| LAMEA |
7.30% |
What are the driving factors of LAMEA unmanned aerial vehicle market?
- The LAMEA UAV market size was valued at USD 2.72 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to grow around USD 11.23 billion by 2034.
Latin America and the Middle East & Africa region are also making noteworthy moves in the integration of UAVs, through local regulatory reform and targeted deployment. In Brazil, ANAC updated its RPAS regulatory framework in 2023, and allowed BVLOS flights specifically for agriculture use, wildfire detection and last-mile delivery, including drone logistics pilots in São Paulo that were launched in 2024. Similarly, the UAE legislated commercial BVLOS flight operations and provided BVLOS corridors to private sectors in Dubai in 2023, providing logistics and surveillance benefits. Saudi has integrated UAV taxis and inspection drones as part of its Vision2030 program. In 2023 South Africa's.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Market Top Companies
Recent Developments
Recent partnerships in the UAV market underscore a growing focus on innovation, dual-use applications, and cross-sector integration. AeroVironment has teamed up with NASA and the U.S. Department of Defense for high-altitude, long-endurance UAV projects aimed at surveillance and environmental monitoring. Airbus partnered with Swiss-based Sightec in 2024 to integrate AI-based visual navigation in its UAV platforms, boosting autonomy and precision. Northrop Grumman is working with the U.S. Navy on MQ-4C Triton enhancements for maritime ISR missions. Meanwhile, Indian drone firm ideaForge partnered with VTOL specialist SkyDrive to co-develop hybrid drones for logistics and defense. These alliances aim to advance UAV capabilities in navigation, endurance, and mission flexibility. Together, they signal a strong industry shift toward collaborative development and intelligent UAV ecosystems.
- In May 2025, AeroVironment has launched Red Dragon, a new fully autonomous, software-defined unmanned aircraft system (UAS) built for one-way attack missions in high-threat, GPS-denied, and communications-degraded environments. Red Dragon operates without continuous operator input or satellite navigation, using advanced onboard autonomy and GNSS-independent navigation. It features electronic warfare resilience, rapid mass production, and modular mission integration, making it suitable for air, land, and maritime operations. The system is designed for quick team training, easy deployment, and simplified logistics, representing a significant step forward in scalable, mission-ready autonomous warfare technology.
- In January 2024, Airbus Helicopters has agreed to acquire Aerovel, the U.S.-based maker of the Flexrotor unmanned aerial system (UAS), to strengthen its portfolio of tactical unmanned solutions. The Flexrotor is a small, vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) UAS designed for intelligence, surveillance, target acquisition, and reconnaissance (ISTAR) missions on land and at sea. It can operate for over 12–14 hours, carry various payloads such as electro-optical systems and advanced sensors, and requires only a 12 by 12 ft. area for autonomous launch and recovery, making it ideal for expeditionary operations with a minimal footprint. Flexrotor is already proven in harsh, GPS-denied environments and is used in both defense and parapublic missions, including forest fire surveillance and ice navigation. Aerovel will remain a U.S.-owned company and continue working with the U.S. Department of Defense under Airbus’ Special Security Agreement. The acquisition, pending regulatory approval, is expected to close in 2024.
Market Segmentation
By Class
- Tactical UAVs
- Small UAVs
- Strategic UAVs
By Technology
- Fully-autonomous
- Semi-autonomous
- Remotely Operated
By Type
- Fixed Wing
- Rotary Wing
- Hybrid Wing
By System
- Platform
- Airframe
- Avionics
- Propulsion System
- Payload
- Camera
- RADAR
- LIDAR
- Gimbal
- Datalink
- Ground Control Station
- Launch & Recovery System
By Point of Sale
By Application
- Commercial
- Military
- Recreational
By End-User
- Government & Defense
- Energy, Power, Oil & Gas
- Construction & Mining
- Agriculture, Forestry & Wild Life Conservation
- Public Infrastructure & Homeland Security
- Hospitals & Emergency Medical Services
- Transportation & Logistics
- Event Management
- Others
By Region
- North America
- APAC
- Europe
- LAMEA



