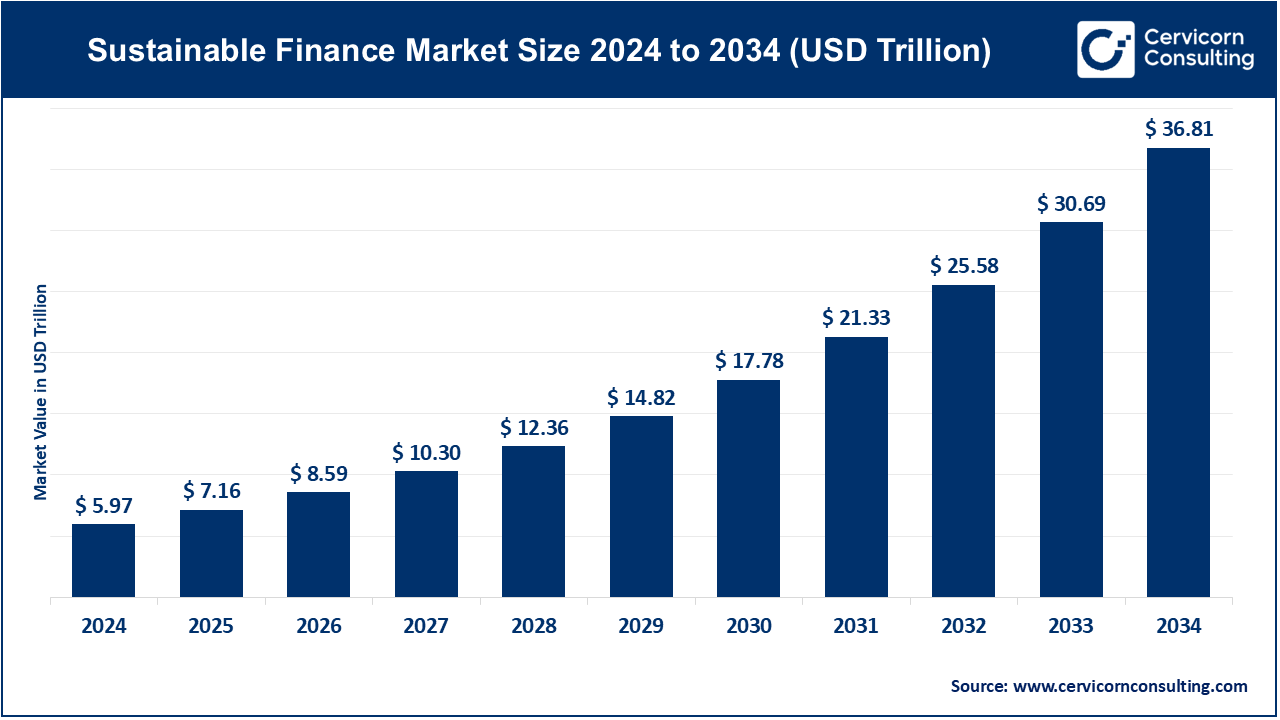
The global sustainable finance market size was reached at USD 5.97 trillion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 36.81 trillion by 2034, exhibiting at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.94% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The sustainable finance market is experiencing robust growth, driven primarily by increasing global awareness of climate change and the urgent need to transition toward a low-carbon economy. Governments and regulatory bodies are implementing stricter environmental, social, and governance (ESG) policies, compelling corporations and investors to align their financial strategies with sustainability goals. Initiatives like the European Union’s Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) and the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) are fostering transparency and accountability. Moreover, institutional investors are increasingly integrating ESG criteria into their investment decisions, recognizing the long-term financial risks and opportunities posed by environmental and social factors.
In addition to regulatory support, technological advancements and changing consumer preferences are significantly contributing to the growth of sustainable finance. Innovations in green technologies, data analytics, and fintech solutions enable better assessment and management of ESG risks and performance. At the same time, younger generations of investors and consumers are demanding more ethical and environmentally responsible financial products and services. This shift in stakeholder expectations is pushing financial institutions to develop new sustainable financial instruments, such as green bonds, sustainability-linked loans, and impact investments, which are attracting significant capital flows and further accelerating market expansion.
What is Sustainable Finance?
Sustainable finance is financial activity that takes environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into investment consideration, aiming to drive long-term economic progress and beneficial impacts on society. While conventional finance tends to only concentrate on the return on financials, sustainable finance seeks to reconcile profit and sustainability by driving capital to climate action, social equity, and responsible governance supportive projects and institutions. It is central to facilitating the shift towards a greener, more inclusive economy by financing renewable energy, sustainable infrastructure, and companies with robust ESG credentials.
There are a number of different types of sustainable finance instruments, such as green finance (green bonds and green loans for environmental initiatives), social finance (financing initiatives such as housing for affordability, healthcare, and education), and sustainability-linked finance (borrowings or bonds linked to ESG performance metrics). Uses of sustainable finance cut across industries and sectors: from investments in clean energy and climate-resilient infrastructure to financing firms that focus on diversity, good labor practices, and community development. Governments, investors, and financial institutions are increasingly employing them to achieve world sustainability objectives including the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the Paris Climate Agreement.
Growth in Sustainable Debt Issuance
Sustainable debt instruments, including green bonds, social bonds, sustainability bonds, and sustainability-linked bonds, are seeing rapid expansion. These financial instruments fund initiatives with positive environmental or social outcomes, such as renewable energy, clean transportation, or affordable housing. The surge in investor demand, coupled with supportive policies from regulators, has made these instruments a major financing vehicle.
Table: Global Sustainable Bond Issuance (USD billions)
| Year | Green Bonds | Social Bonds | Sustainability Bonds | Total |
| 2019 | 270 | 47 | 65 | 382 |
| 2020 | 304 | 163 | 93 | 560 |
| 2021 | 522 | 210 | 130 | 862 |
| 2022 | 487 | 163 | 142 | 792 |
| 2023 | 565 | 142 | 165 | 872 |
| 2024 | 523+ | 150+ | 178+ | 851+ |
Expansion of Sustainable Assets Under Management (AUM)
Over the last decade, there has been a major shift in investor behavior. Institutional investors, asset managers, and pension funds are increasingly adopting ESG integration into their portfolios. These strategies range from negative/exclusionary screening to impact investing and thematic ESG investing.
Increased Focus on Social Sustainability
While environmental issues like climate change dominate ESG discussions, the social pillar has gained prominence in recent years. Investors and regulators are focusing more on labor rights, community engagement, diversity, equity, and ethical tech development, including AI accountability.
This trend is about shifting finance toward long-term inclusive growth, where business success is aligned with societal well-being.
Resilience and Growth of Climate Finance
Despite global uncertainties like geopolitical conflicts, inflation, and supply chain issues, climate finance has remained resilient. Climate-related investment continues to grow in areas such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, sustainable agriculture, and climate adaptation projects.
Increasing Regulatory Pressure and ESG Mandates
Governments and regulatory bodies across the globe are enforcing stricter environmental, social, and governance (ESG) disclosure requirements for corporates and financial institutions. Frameworks like the EU Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR), Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), and Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) are mandating transparency in ESG performance and sustainability risks. These regulations are pushing companies and investors to adopt sustainable finance practices not only for compliance but also to attract environmentally conscious investors, reduce reputational risk, and align with long-term resilience strategies.
Rising Investor Demand for Sustainable Investment Products
Institutional and retail investors are increasingly prioritizing sustainability in their portfolios. This shift is driven by growing awareness of climate change, biodiversity loss, and social inequality, coupled with evidence that ESG-integrated funds often perform competitively or even better than traditional funds. As a result, asset managers are expanding their offerings of green bonds, ESG funds, and impact investment vehicles. According to the market report, global sustainable fund assets have more than doubled since 2019, reinforcing the influence of investor preferences on the market’s growth.
Lack of Standardization in ESG Reporting and Ratings
One of the biggest hurdles in sustainable finance is the absence of uniform ESG measurement standards. Different rating agencies use varying criteria and weightings, leading to inconsistent ESG scores for the same organization. This fragmentation creates confusion among investors, undermines comparability, and increases the risk of greenwashing. As a result, investors may hesitate to fully commit to ESG strategies without clear, reliable, and standardized frameworks to assess sustainability performance.
High Implementation Costs for Companies
Transitioning to sustainable practices often involves substantial upfront costs, especially for SMEs and developing market firms. These costs include technology upgrades, sustainable supply chain management, carbon audits, and new reporting mechanisms. Additionally, aligning with sustainability standards such as ISO certifications or third-party ESG audits can be financially burdensome. This financial strain acts as a deterrent for many businesses, particularly those with tight budgets or limited access to green financing.
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Emerging and developing economies present a major opportunity for sustainable finance as they seek funding for infrastructure, clean energy, climate adaptation, and social development projects. Institutions like the World Bank and the IFC are already facilitating sustainable investments in these regions. With the right frameworks, emerging markets could attract substantial ESG-focused capital, simultaneously boosting economic growth and sustainability. Green bonds issued by countries like India, Brazil, and Indonesia are gaining traction, indicating a shift toward responsible development financing.
Innovation in Green Financial Products
There’s a rising opportunity to innovate and expand the portfolio of sustainable financial products. Beyond traditional green bonds and ESG funds, the market is seeing the emergence of transition bonds, nature-based investing, carbon credits, and sustainability-linked insurance. Fintech and AI-driven tools are also making ESG data more accessible and actionable, enabling personalized sustainable investment options. This product diversification helps investors of all types, from individuals to pension funds, engage with sustainability according to their risk appetite and goals.
Risk of Greenwashing and Misleading Claims
Greenwashing, where companies or financial products exaggerate or misrepresent their sustainability credentials, remains a persistent challenge in the market. This not only misguides investors but also damages public trust in the entire sustainable finance movement. Without robust verification mechanisms, even well-intentioned investors may unknowingly support unsustainable businesses. Regulators are starting to crack down on greenwashing with penalties and stricter disclosure mandates, but enforcing accountability across global markets remains complex and resource-intensive.
Climate and Transition Risks Affecting Asset Values
Climate-related risks such as extreme weather, resource scarcity, or carbon taxation policies pose significant threats to the valuation of assets, especially in sectors like energy, agriculture, and real estate. Transitioning to a low-carbon economy can make certain investments (e.g., fossil fuels) obsolete or stranded, affecting returns and financial stability. For financial institutions, assessing these long-term risks is complex, as it requires scenario modeling, forward-looking data, and integration into financial decision-making, a capability that many traditional risk systems still lack.
The sustainable dinance market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA.
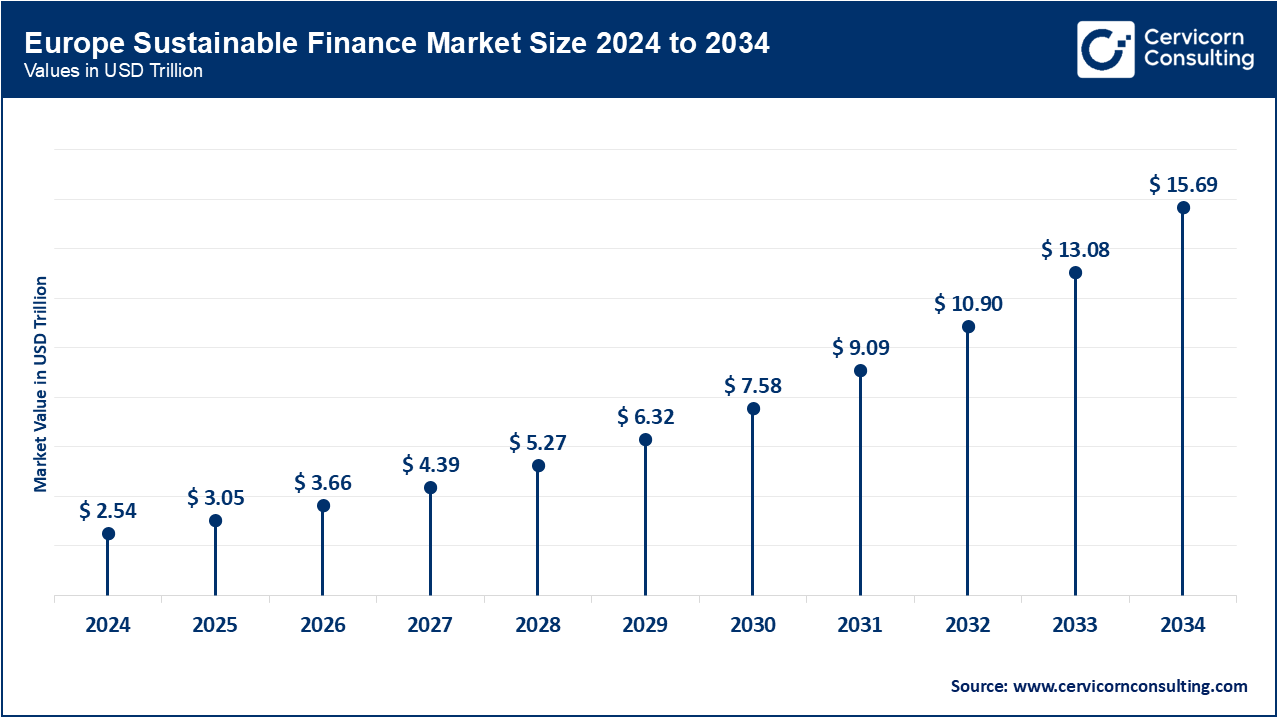
The Europe sustainable finance market size was estimated at USD 2.54 trillion in 2024 and is poised to reach around USD 15.69 trillion by 2034. Europe leads the global market, driven by regulatory frameworks, government initiatives, and growing emphasis on ESG factors in investments. The EU's Green Deal and Sustainable Finance Action Plan promote investments in sustainable projects. Clear regulations like the EU Taxonomy for sustainable activities enhance transparency and boost investor confidence. Europe’s institutional investors, including large pension funds, are increasingly prioritizing ESG factors in their portfolios. The EU’s commitment to carbon neutrality by 2050 further strengthens its market dominance, driving innovation in green financial products and ensuring Europe's continued leadership in sustainable finance.
The North America sustainable finance market size was surpassed at USD 1.67 trillion in 2024 and is forecasted to hit around USD 10.27 trillion by 2034. North America is emerging as the fastest-growing region, fueled by rising demand for ESG investments and evolving regulatory support. The U.S. is integrating ESG factors into its financial system, with the proposed climate disclosure rules by the SEC further enhancing transparency. Canada is also a key player, with its pension funds and institutional investors increasingly adopting sustainable investment strategies. This shift in regulatory frameworks and investor focus is accelerating growth in the region, and North America is expected to continue its rapid expansion as both government policies and investor demand prioritize sustainability.
Sustainable Finance Market Revenue Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America | 27.89% |
| Europe | 42.62% |
| Asia-Pacific | 20.94% |
| LAMEA | 8.55% |
The Asia-Pacific sustainable finance market size was accounted for USD 1.25 trillion in 2024 and is predicted to surpass around USD 7.71 trillion by 2034. Asia-Pacific is rapidly becoming a significant player, bolstered by government initiatives and rising investments in green projects. While the region faces challenges related to regulatory inconsistencies, countries like China, Japan, and Australia are pushing towards greater sustainability. China’s carbon neutrality goal by 2060 and Japan's focus on corporate sustainability disclosures are key drivers. Australia is also seeing growth in ESG-focused investments, spurred by institutional demand. While Asia-Pacific’s market share is smaller than Europe and North America, its fast-growing trajectory positions it as an emerging powerhouse in sustainable finance.
The LAMEA sustainable finance market size was valued at USD 0.51 trillion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 3.15 trillion by 2034. Latin America and the Middle East & Africa (LAMEA) regions offer strong growth potential. Countries like Brazil, Mexico, and Chile are increasing green bond issuances and focusing on sustainable investments as part of their climate agendas. In the Middle East, the UAE and Saudi Arabia are diversifying economies through green finance initiatives. Africa is adopting green bonds and ESG projects, particularly in renewable energy. While LAMEA currently holds a smaller market share, rising awareness, government initiatives, and international investment are creating a solid foundation for future growth, positioning these regions to play a more significant role in the global sustainable finance market.
The sustainable finance market is segmented into investment, investor, transaction, end use, and region. Based on investment, the market is classified into equity, fixed income, mixed allocation, others. Based on the investor, the market is classified into institutional investors, and retail investors. Based on transaction, the market is classified into green bond, mixed-sustainability bond, social bond, ESG integrated investment funds, and others. Based on end use, the market is classified into utilities, chemicals, transport & logistics, government, food and beverage, and others.
The equity investments segment in sustainable finance is poised for robust growth in 2024, fueled by increased investor interest in ESG-compliant companies. Investors are now prioritizing long-term value creation in industries such as renewable energy, clean technology, and sustainable agriculture. This shift is attributed to growing consumer awareness and the demand for companies that align with sustainability goals. Institutional and retail investors alike are increasing their allocation towards ESG equity funds, with assets under management expected to reach nearly USD 1 trillion by 2025. As the market matures, this trend is expected to strengthen further, with more financial products offering integrated ESG principles.
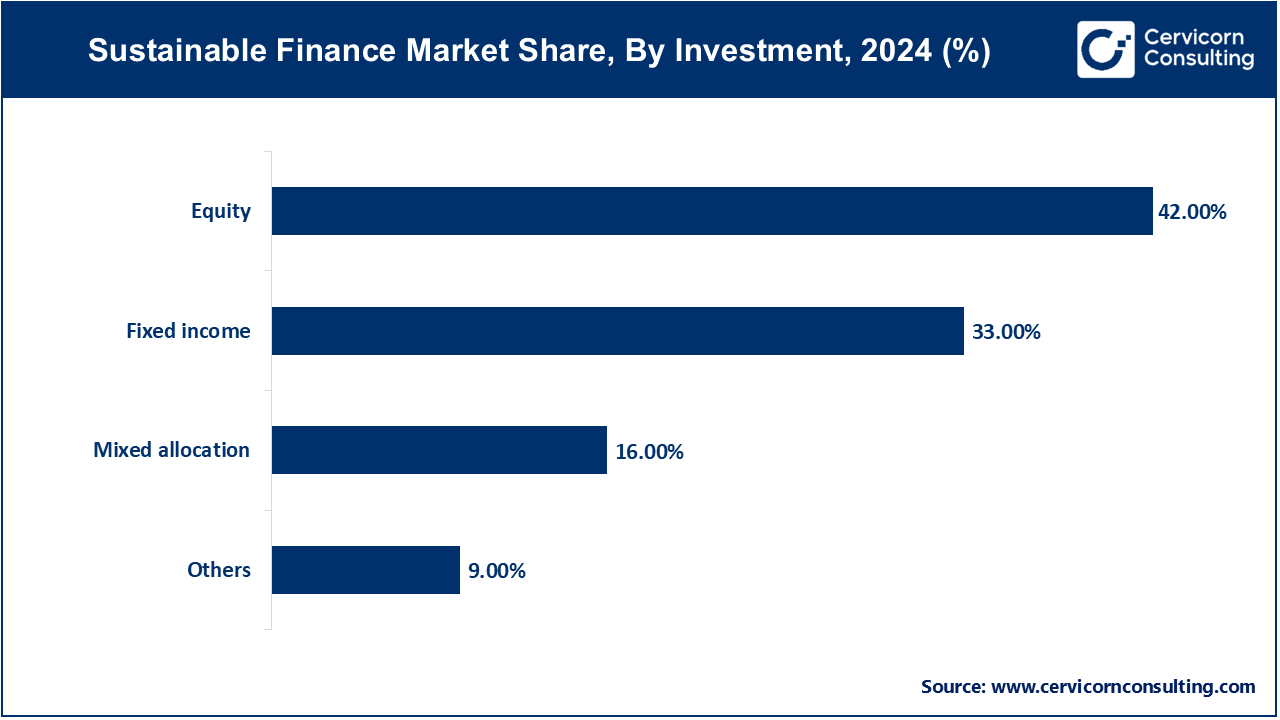
The mixed allocation funds segment is gaining substantial momentum in 2024, as investors seek diversified portfolios that balance the stability of fixed income with the growth potential of equities. These funds, which blend ESG principles across different asset classes, have seen a marked rise in demand. The flexibility of these funds allows for dynamic adjustments to market conditions, making them an attractive option for both institutional investors and retail investors. Over the past five years, the growth rate of mixed allocation sustainable funds has been approximately 20% annually, and this is expected to continue as ESG-based financial products become more widely accessible.
The institutional investors segment remains the dominant force in the sustainable finance market, with their involvement in ESG-related investments surpassing 80% of total capital inflows in 2024. This sector continues to grow as large pension funds, insurance companies, and sovereign wealth funds increase their focus on ESG-compliant assets. With their long-term investment horizons, institutional investors are pushing the needle forward in sectors such as renewable energy, green infrastructure, and utilities. Additionally, major institutional players like BlackRock and State Street are setting ambitious net-zero targets for their portfolios by 2050, further driving the momentum in sustainable finance.
Sustainable Finance Market Revenue Share, By Investor, 2024 (%)
| Investor | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Institutional investors | 78% |
| Retail investors | 22% |
Retail investors are increasingly playing a pivotal role in 2024. The growing adoption of ESG-themed exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and mutual funds has led to a significant surge in retail investments, with many consumers preferring to align their portfolios with their values. The rise of digital platforms offering personalized sustainable investment options has also fueled this trend. Younger generations, particularly millennials and Gen Z, have shown a strong preference for sustainable investing, with over half of new retail investors opting for ESG funds. This shift is supported by increased awareness and accessibility, making sustainable finance a key priority for retail investors globally.
Green bonds continue to dominate the sustainable finance market in 2024, driven by increasing investor demand for environmentally responsible investments. Green bond issuances surpassed USD 600 billion globally in 2024, as both public and private entities seek funding for renewable energy, infrastructure projects, and climate adaptation strategies. With an expanding range of issuers, including corporate players and government agencies, green bonds are becoming an essential tool for financing the global transition to a low-carbon economy. The market’s expansion is also supported by stronger regulatory frameworks, such as the EU Green Bond Standard, which enhance transparency and credibility, making green bonds a more attractive investment option.
The ESG-integrated investment funds segment has seen substantial growth in 2024, reflecting the widespread adoption of ESG principles in investment strategies. ESG-integrated funds, which incorporate environmental, social, and governance criteria alongside traditional financial metrics, have become a key focus for both institutional and retail investors. In 2024, ESG-integrated funds attracted over USD 100 billion in investments, with more traditional asset managers incorporating these strategies into their offerings. This growth is fueled by rising investor demand for holistic approaches that prioritize sustainability alongside financial returns, with ESG-integrated funds expected to account for more than half of all managed assets by 2030.
The utilities sector continues to be a major beneficiary of sustainable finance in 2024, driven by the global push for renewable energy and carbon reduction. Investments in renewable energy projects, including wind, solar, and hydroelectric power, remain strong, as governments and investors alike look to accelerate the transition to clean energy. As one of the largest recipients of sustainable finance, the utilities sector has also seen reduced financing costs due to the rising popularity of green bonds and ESG-integrated funds. This trend is expected to persist as the global energy transition progresses and more capital flows into low-carbon infrastructure projects.
The transport and logistics sector has experienced rapid growth in 2024, as companies increasingly prioritize decarbonization and efficiency. Investment in electric vehicles (EVs), charging infrastructure, and low-emission transportation systems saw a significant increase in 2024, with global investments reaching over USD 30 billion. This growth is driven by stricter emissions regulations and the growing demand for eco-friendly solutions. Furthermore, the logistics sector is focusing on creating sustainable supply chains and adopting greener technologies, positioning transport and logistics as one of the fastest-growing areas for sustainable finance in the coming years.
The sustainable finance market is highly competitive, featuring a diverse mix of global financial institutions, ESG service providers, and fintech innovators. Industry leaders like BlackRock, Inc., Goldman Sachs, BNP Paribas, HSBC Group, and Bank of America are leading the way with ESG-integrated investment strategies, green bonds, and sustainability-linked loans. Refinitiv, KPMG International, and Acuity Knowledge Partners drive the market with ESG data and analytics. Fintech companies like Aspiration Partners, Inc., Starling Bank, Tred Earth Limited, and Stripe, Inc. are building easy-to-use tools for sustainable finance. South Pole, UBS, NOMURA HOLDINGS, INC., Deutsche Bank AG, and Triodos Bank UK Ltd. are growing their green finance business. The market's momentum is driven by regulatory developments, growing investor demand, and growing corporate commitments to sustainability.
Market Segmentation
By Investment
By Investor
By Transaction
By End Use
By Region