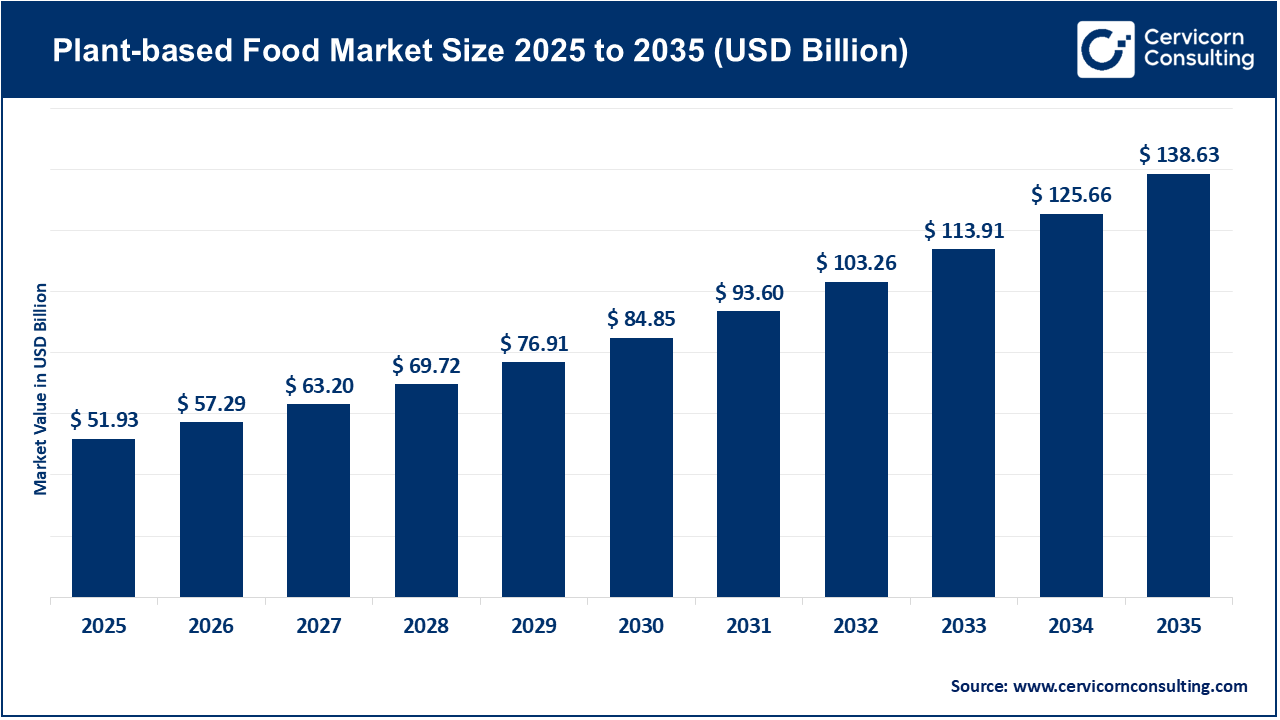
The global plant-based food market size was valued at USD 51.93 billion in 2025 and is expected to be worth around USD 138.63 billion by 2035, exhibiting at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.3% over the forecast period from 2026 to 2035. The growth of the plant-based food market is largely fueled by consumers' rising environmental consciousness. Several studies have demonstrated that traditional animal-based products, such as dairy ice cream, impose higher environmental costs in terms of land use, water consumption, and carbon emissions compared to plant-based alternatives. As sustainability shifts into mainstream values, consumers' buying decisions are increasingly guided by environmental responsibility. Many now view their dietary choices as a form of environmental activism. This trend is especially evident in developed economies, where green labels and supply chain transparency are key factors influencing purchasing decisions.
Another significant growth driver of the market is the evolving consumption patterns that are accelerating market growth, especially through the rise of the "flexitarian" movement, in which non-vegetarians are consciously reducing their meat consumption. The marketing approach has evolved to appeal to these non-vegetarian consumers by emphasising the accessibility and taste parity of plant-based meats in the food and beverage categories. The health and wellness paradigm further reinforces demand, as plant-based diets are often associated with lower risk of chronic diseases, attracting both aging consumers and younger consumers invested in health and long-term well-being. Additionally, supportive regulatory regimes that are pro-innovation and working to eliminate bureaucratic hurdles aim to increase the adoption of alternative proteins, thereby promoting economic development.
Rising Global Demand Accelerates the Plant-Based Seafood Market
The seafood market expansion is also driven by the inherent supply chain vulnerabilities in the commercial seafood industry, which make plant-based options a more sustainable and ethical choice for global food security. Commercial focus is currently directed toward high-volume items such as canned tuna and breaded fish fillets, which have lower barriers to consumer adoption. While the plant-based beef and dairy sectors have reached some stage of manufacturer saturation, plant-based seafood is likely the next frontier. Plant-based seafood is experiencing a high CAGR as consumers become more aware and conscious of the environmental and health concerns surrounding traditional fishing practices, such as overfishing, microplastic contamination, and heavy metals in seafood. Recent advancements in extrusion and 3D food printing have enabled manufacturers to recreate the delicate, flaky texture of white fish as well as the distinctive snap associated with shrimp.
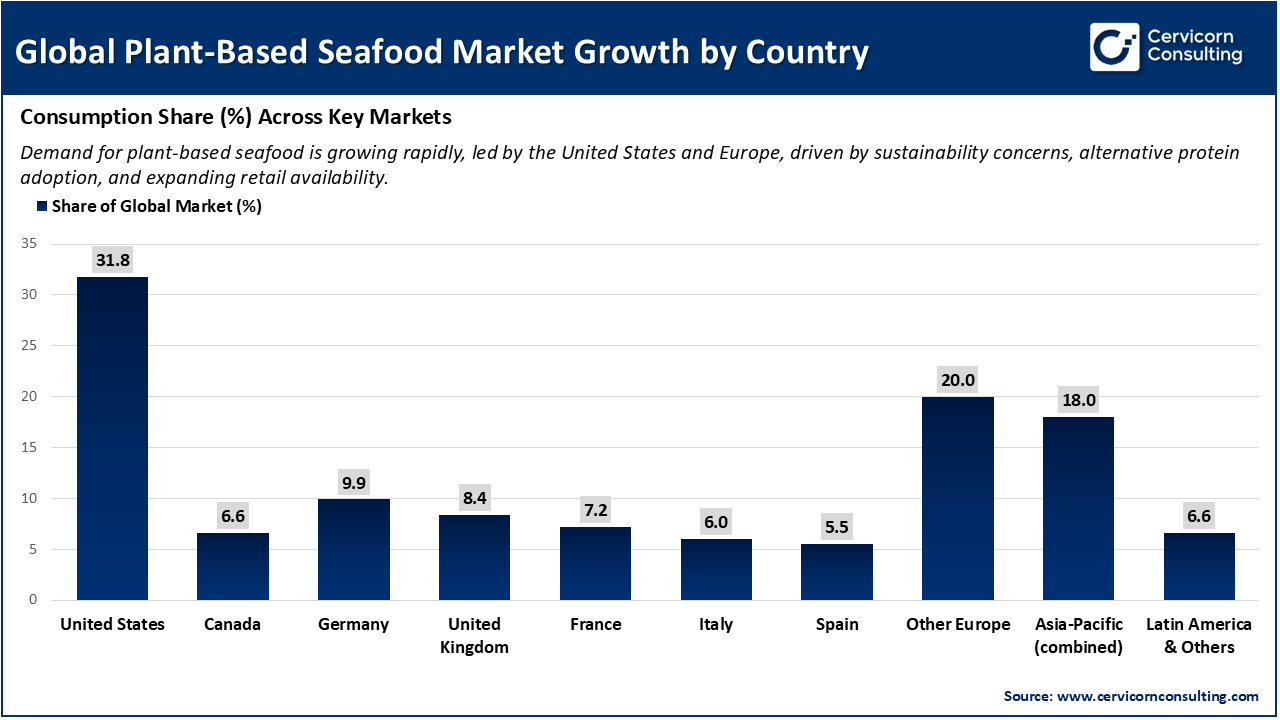
Recent data indicates that the plant-based seafood market is primarily driven by the United States, which accounts for 31.8% of the market. Europe collectively represents over 57%, with Germany at 9.9%, the UK at 8.4%, France at 7.2%, Italy at 6.0%, Spain at 5.5%, and other European countries at 20.0%. The Asia-Pacific region contributes 18.0%. This distribution demonstrates that plant-based seafood has become a significant segment within the broader plant-based food industry, particularly in regions where alternative protein consumption is already high. The increasing demand is encouraging innovation, expanding production capacity, and increasing retail availability, which is expected to reduce costs and enhance product quality. Consequently, the growth of plant-based seafood is contributing to the expansion of the overall plant-based food market by attracting a wider range of consumers, especially flexitarians, and supporting the transition toward more sustainable food choices.
1. Major Brand Portfolio Expansion
The investment by major food companies in plant-based options marks a significant milestone in stabilizing the market. Companies from Nestlé to Unilever are investing in plant-based diversification as part of their core business strategy and are implementing plant-based lines as a growth engine rather than a secondary project. These large companies have dedicated extensive R&D budgets, created private labels, and invested in existing brands to expand into new geographies. This corporate commitment ensures that plant-based options will benefit from an advanced supply chain and prime placement on grocery store shelves, which have traditionally showcased animal proteins.
2. Government Sustainability Initiatives
Government initiatives are now actively supporting plant-based food, which has remained at an all-time high, with various countries adopting protein transition as a matter of national policy. For example, in 2023-2024, Denmark announced its National Action Plan for Plant-based Foods, involving USD 100 million for the agricultural sector to transition toward plant-based production. These types of initiatives demonstrate an unprecedented shift from treating plant-based food as a mere consumer choice to considering it a national strategic asset aimed at achieving a common goal for national carbon reduction. These initiatives often include funding for research, subsidies for farmers switching to pulse crops, and support for domestic manufacturing infrastructure.
3. Major Venture Capital Influx and IPOs
While macroeconomic events continue to impact investment, the alternative protein sector remains highly attractive to institutional investors. For example, firms like BlackRock have increased the capital flow into "Alternative Protein" funds due to the belief that this sector is a core component of global food security. Although the initial "hype" of the IPO market has cooled, the market is now in a disciplined phase of capital allocation, focusing on companies’ verifiable technological benefits or path to profitability. The injection of capital is necessary to scale production and minimize the unit cost of plant-based proteins.
4. National Regulatory Approval of Novel Proteins
Regulatory approvals are increasingly facilitating the convergence of plant-based and biotechnology industries. In 2024, authorities in markets such as the United States and Israel began approving animal-free whey and other proteins produced through precision fermentation, marking a significant milestone for the industry. These approvals enable companies to develop new hybrid products, combining plant-based ingredients with bio-identical animal proteins. Establishing clear regulatory guidelines for these types of products is essential to ensure consumer safety and to promote trade in novel proteins across countries.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 57.29 Billion |
| Market Size in 2035 | USD 138.63 Billion |
| CAGR 2026 to 2035 | 10.3% |
| Dominant Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Product Type, Source, Distribution Channel, Region |
| Key Companies | Beyond Meat Inc., Impossible Foods Inc., Oatly Group AB, Danone S.A., Nestlé S.A., Kellogg Company (MorningStar Farms), The Hain Celestial Group Inc., Atlantic Natural Foods LLC, Amy’s Kitchen Inc., Quorn Foods Ltd., Lightlife Foods Inc., Vbites Food Ltd., Blue Diamond Growers, Unilever PLC (The Vegetarian Butcher), Conagra Brands Inc. (Gardein) and others |
The plant-based food market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. Here is a brief overview of each region:
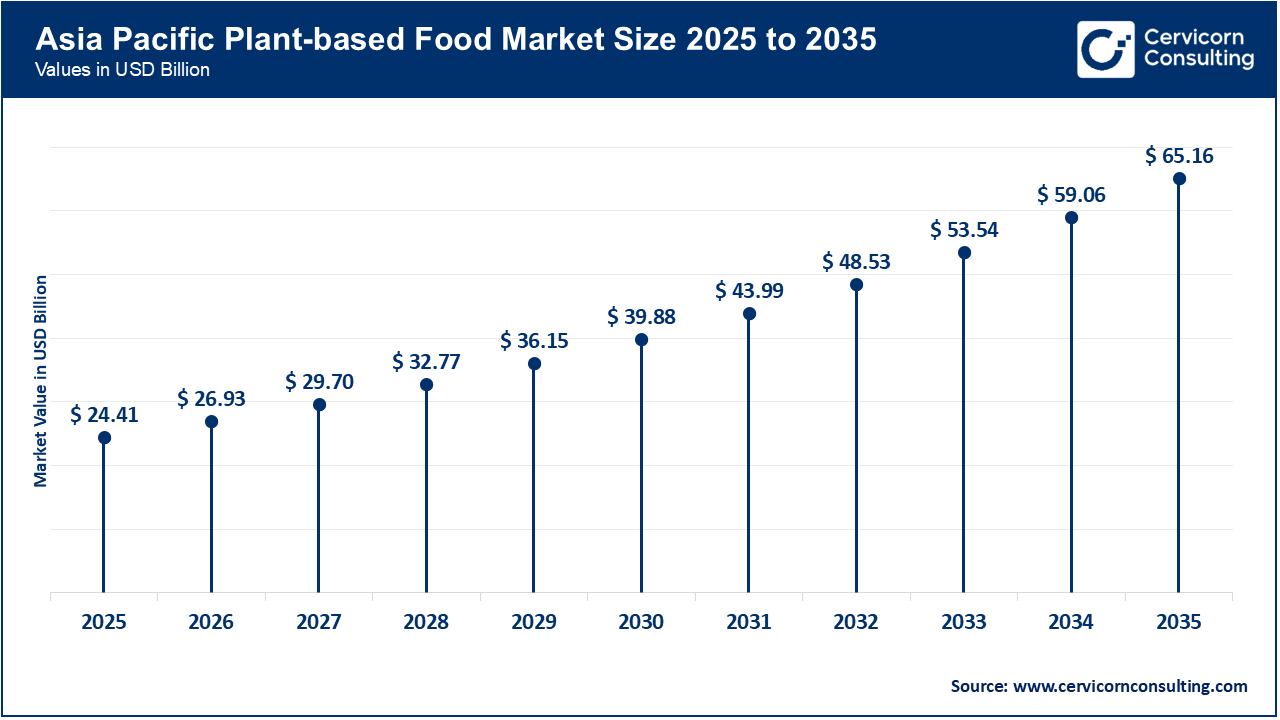
The Asia-Pacific plant-based food market size was valued at USD 24.41 billion in 2025 and is expected attain around USD 65.15 billion by 2035. The Asia Pacific (APAC) region holds the largest share, due to its large population base and longstanding consumption of plant-centric diets. For example, China accounted for over 70% of the plant-based meat market in the region, and more than 20% of the global market. The regional growth opportunity is being supported by government initiatives to decrease meat consumption to address public health and environmental sustainability. China has political milestones aimed at significantly decreasing national meat consumption. Additionally, the region has emerged as a major centre for innovation in alternative proteins, with significant industrial advancements and production milestones.
Recent Developments:
The North America plant-based food market size was estimated at USD 10.39 billion in 2025 and is forecasted to surpass around USD 27.73 billion by 2035. North America is the fastest-growing market for meat analogs. The region's strong growth is supported by a well-established research and development (R&D) environment and a high concentration of venture capital-backed food tech companies. Consumer preferences in North America increasingly show a demand for "clean label" products and high-protein, low-cholesterol alternatives to red meat. Additionally, North America is used as a test market for new product formats, such as plant-based tuna and seafood alternatives, which are gaining popularity and seem to resonate with urban populations who are health-conscious.
Recent Developments:
The Europe plant-based food market size was reached at USD 12.98 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit around USD 34.66 billion by 2035. Europe is the most mature market, driven by its strong focus on sustainability and ethical consumerism. Countries such as Germany, which has a positive growth trajectory supported by high consumer awareness of the environmental impact associated with meat consumption. In addition, the EU is actively supportive of the "green" transition with various initiatives to develop sustainable food systems. Furthermore, ethical considerations and animal welfare concerns have much greater importance in purchasing decisions in Europe compared to other regions, creating a strong demand for certified vegan and vegetarian products.
Recent Developments:
Plant-based Food Market Share, By Region, 2025 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2025 (%) |
| Asia-Pacific | 47% |
| Europe | 25% |
| North America | 20% |
| LAMEA | 8% |
The LAMEA plant-based food market was valued at USD 4.15 billion in 2025 and is anticipated to reach around USD 11.09 billion by 2035. The LAMEA region is in the early stages of development in the market but has strong market potential. Rapid urbanization and increasing discretionary incomes in certain developing economies are shifting dietary patterns and creating new opportunities for economies to be exposed to global food trends that feature a greater "modern" plant-based protein presence. Many of the consumption patterns for plant-based content are already heavily influenced by traditional cultural diets. However, "modern" plant-based analogs are resonating with low-cholesterol middle-class consumers who are searching for aspirational and healthy food. In some of the largest markets contributing to the growth of plant-based economies, global fast-food chains are either establishing their brand presence or performing well financially by advertising plant-based versions of local foods, further supporting market adoption and awareness.
Recent Developments:
The plant-based food market is segmented into product type, source, distribution channel, and region.
The dairy alternative segment accounts for the largest share of the plant-based market. This is due to the minimal level of consumer habits in the switch, since replacing cow's milk with plant-based option such as oat milk or almond milk in coffee, tea, or cereal involves little behavioral change compared to replacing a steak. However, this segment is also diversifying plant-based cheese also had an estimated 65% increase in sales in the latest comparative period, as manufacturing processes improves for plant-based dairy. Oat milk leads the plant-based milk sub-segment, being preferred for its creamy texture and a consumer perception of its environmental benefit.
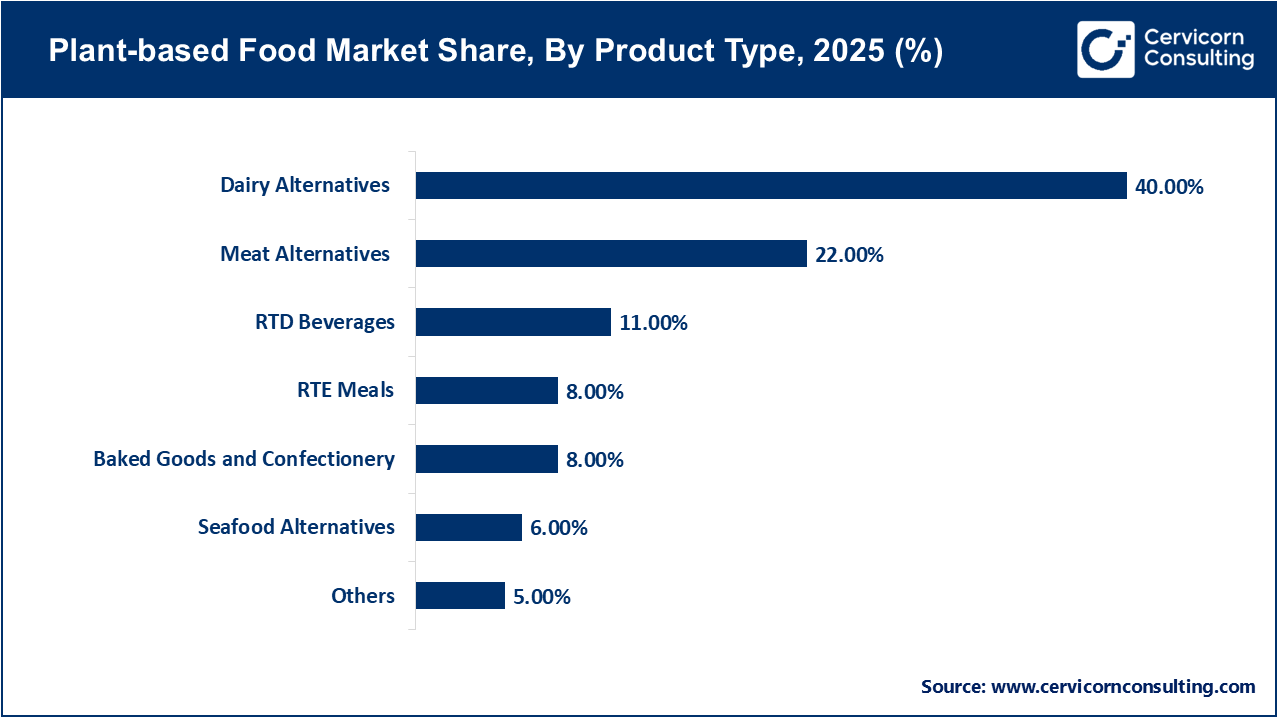
Meat alternatives are experiencing the fastest growth and most innovation of the market. The sale of plant-based meat has increased approximately one-third in the last three years, indicating a fast-moving consumer acceptance in substituting animal proteins for more "realistic" analogs. Most products within this segment mimicked traditional formats for meat, with burgers and minces long have lead the market. However, the segment is transitioning into more complicated formats, such as plant-based seafood and whole-cut meat analogs. With the entrance of major global food processing corporations into plant-based meat, it has professionalized the supply chain and created broader availability of products in business as usual retail.
Soy protein indicates the dominant source segment in the global plant-based food market, particularly across meat and dairy alternatives. Soy's dominance rests on a complete amino acid profile, protein content, and a well-established industrial processing framework. Soy-based products, such as tofu and tempeh have been common dietary staples for centuries throughout many world cultures, creating a reliable bridge between ancient food and modern food innovation. Currently, soy's flexibility allows it to be textured and flavored to mimic many animal proteins, thus making it the most desired ingredient for large scale manufacturers that would seek affordable and useful ingredient.
Plant-based Food Market Share, By Source, 2025 (%)
| Source | Revenue Share, 2025 (%) |
| Soy | 38% |
| Pea | 20% |
| Wheat | 15% |
| Canola | 10% |
| Lentil | 7% |
| Others | 10% |
Pea protein is emerging as the fastest-growing segment, due to its positioning a "next-generation" protein source. Peas are increasingly viewed as a considerably "greener" protein source compared to animal-based proteins and some traditional plant proteins. The increasing opportunity for pea protein is largely fueled by its ability to addresses consumer concerns related to allergens, and Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO's) that can sometimes be an associated with soy-based proteins. In addition, the functional advantages or pea protein such as its excellent solubility, emulsification and texture-enhancing properties serve as important plan-based food application.
Supermarkets and hypermarkets is the leading distribution segment for plant-based products because of growing consumer transition toward sustainable consumption. Retailers also have become active participants in this transition by significantly increasing shelf space for alternative proteins, and in some cases, which lowering the cost of plant-based options to compete against traditional meat and dairy products. The benefit from shopping large-scale retailers are provides plant-based brands to an opportunities to reach a broader demographic including flexitarians, who may never visit specialty health stores. The Italy serves as a strong example, where presence of plant-based brands such as Beyond Meat in mainstream supermarkets market penetration and driving broader consumer adoption.
Plant-based Food Market Share, By Distribution Channel, 2025 (%)
| Distribution Channel | Revenue Share, 2025 (%) |
| Supermarkets and Hypermarkets | 46% |
| Online Sales | 20% |
| HoReCa (Hotel, Restaurant, and Café/Catering) | 15% |
| Specialty Stores | 11% |
| Convenience Stores | 8% |
Online sales segment is the fastest-growing segment in the market. The growth of e-commerce and direct-to-consumer (DTC) models have allowed niche plant-based brands to break down traditional retail barriers. Online platforms provide a place to give all necessary education for products, which can be a critical component for new products in categories like plant based seafood or specific dietary supplements. Additionally, due to issues of packaging and subscription services, there are opportunities for other shelf stable, heavy items, such as plant-based milks to be more effective through digital sales. The e-commerce channel also gives brands the ability to collect consumer data to direct future marketing campaigns associated with dietary preferences and health goals.
By Product Type
By Source
By Distribution Channel
By Region