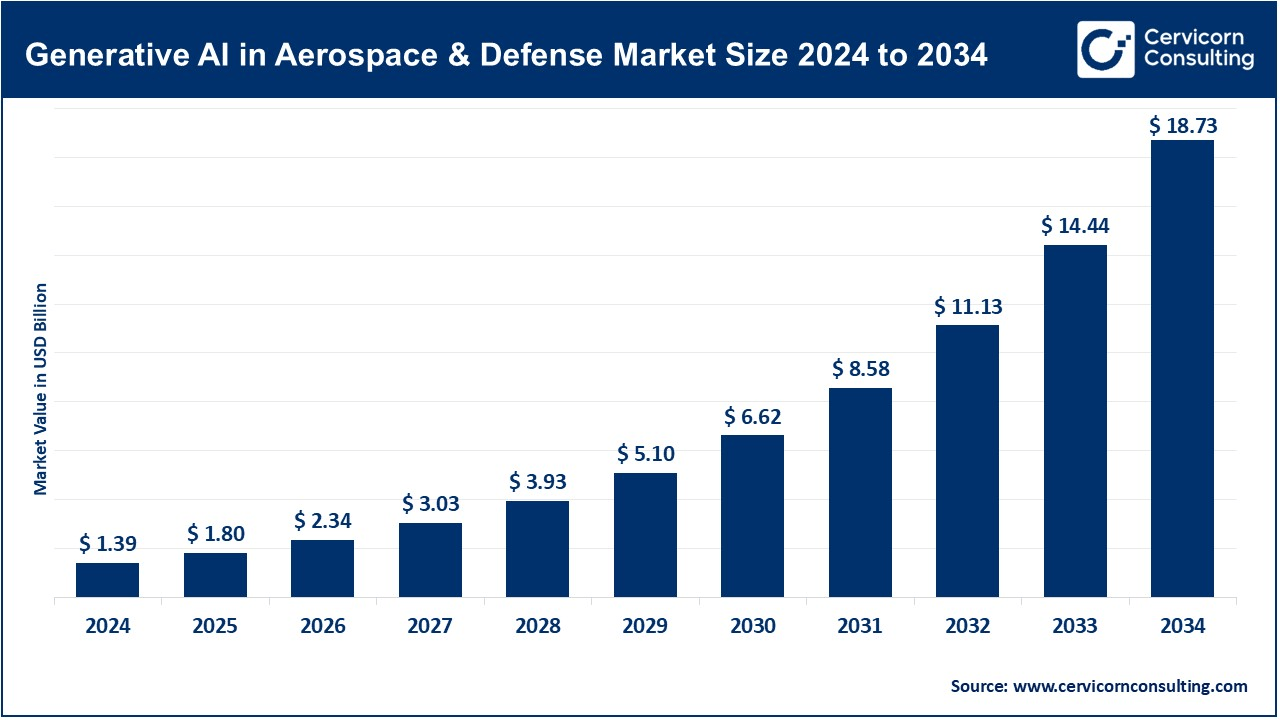
The global generative AI in aerospace and defense market size was reached at USD 1.39 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 18.73 billion by 2034, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 29.7% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The generative AI in aerospace and defense market is being driven by the rising demand for autonomous systems, real-time threat analysis, and mission-specific simulations. Government and defense contractors are adopting AI to make fast decisions, improve strategic schemes, and reduce operating costs. The generative AI enhances the ability to simulate war scenarios, design aircraft components, and generate synthetic data for training and testing systems without real-world risks. The future also promises reduced downtime, increased application in logistics, and enhanced fleet readiness, making it a crucial asset in modern defense infrastructure.
A major growth factor is the integration of AI with monitoring and reconnaissance systems, capable of rapidly detecting threats through real-time image and signal processing. For example, in 2024, Northrop Grumman collaborated with the US Department of Defense to deploy an AI-capable autonomous drone that uses generic models to track enemy behavior and adapt missions accordingly. Such progress demonstrates not only the strategic advantage provided by generative AI but also strengthens investments by global defense agencies striving for technical superiority in high-stakes environments.
What is a Generative AI in Aerospace and Defense?
The generative AI in aerospace and defense refers to the use of advanced artificial intelligence techniques, such as generative adversarial networks (GANs), transformer models, and reinforcement learning, to adapt to the construction, simulation, or military operations involving systems, data, and decision-making. This technique enhances the design of aircraft and weapons, generates synthetic training data for simulation, improves mission plans, and supports real-time threat detection and response. Applications include predictive maintenance, autonomous drones, cyber defense, satellite image enhancement, and creating a virtual environment for training soldiers or pilots.
Key Statistics and Insights on Generative AI Adoption in Aerospace and Defense:
| Insight Area | Details |
| Adoption in Defense Agencies | 67% of NATO member countries plan to deploy AI for mission simulation by 2026 |
| Synthetic Training Data Usage | Reduces real-world data collection time by 60% |
| AI-Enabled Drone Missions | Increase mission adaptability by 45% over traditional drones |
| Predictive Maintenance Efficiency | Improves aircraft uptime by 30–40% |
| Cyber Defense Enhancement | AI systems detect 50% more threats than rule-based legacy systems |
| Simulation Training Cost Savings | Cuts costs by up to 35% compared to physical simulations |
| R&D Investment Growth | 3x increase in AI-related defense R&D budgets since 2020 |
AI-Powered Design and Engineering Automation
The generative AI is bringing a revolution in aerospace design by enabling the automatic construction of optimal aircraft and component structures. The AI models can detect thousands of design variations compared to traditional CAD systems, reducing development time and improving efficiency.
In 2024, Airbus announced the use of generative AI to redesign internal cabin components, resulting in a 10% reduction in weight and fuel consumption. AI detected countless lightweight material configurations in days instead of months.
Synthetic Data Generation for Training and Simulation
The generative AI model is being used to produce synthetic data such as imagery, landscapes, and environments for training defense personnel, AI systems, and autonomous vehicles. It reduces dependence on sensitive or rare real-world data.
DARPA is funding projects that use GANs to envision the battleground and generate sensor data; the simulation of the environment is classified for very dangerous or live training.
AI-Enhanced Autonomous Mission Systems
The generative AI is improving decision-making in autonomous systems such as UAVs and underwater drones by imitating real-time enemy behavior and mission paths. These systems are dynamically adapted during missions without human intervention.
In late 2023, Northrop Grumman tested the A-Nhansed UAV, which is able to generate an alternative flight path when faced with threats to increase the success rate of the mission.
AI in Cyber Defense and Threat Modeling
Generic AIs are employed to predict, simulate, and prevent cyber threats. AI can simulate adverse attacks and automatically generate defense protocols, making it an essential part of digital defense infrastructure.
Palantir Technologies and the U.S. Air Force participated in 2024 to deploy the generative AI model, which simulates cyber attacks on critical systems and generates defensive strategies in real time.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 1.80 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 18.73 Billion |
| Projected Market CAGR from 2025 to 2034 | 29.70% |
| Dominant Region | North America |
| Growing Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Component, Technology, Deployment Mode, Application, End-User, Region |
| Key Companies | Lockheed Martin Corporation, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Raytheon Technologies Corporation (RTX), BAE Systems plc, General Dynamics Information Technology Inc., Thales Group, L3Harris Technologies, Boeing Company, Airbus SE, Palantir Technologies Inc., IBM Corporation, Microsoft Corporation |
The generative AI in aerospace and defense market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA.
The North America generative AI in aerospace and defense market size was valued at USD 0.61 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 8.24 billion by 2034. North America currently leads the market, largely due to significant investments by major aerospace firms such as the United States Department of Defense (DOD), NASA, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, and Boeing. The sector benefits from AI startups, advanced R&D infrastructure, and a strong ecosystem of strategic cooperation between tech companies and defense agencies. Generative AI is widely applied in the analysis of future maintenance, mission simulation, unmanned vehicles, and threats. The emphasis of the US government on AI modernization and battlefield superiority continues to sustain this dominance.

The Asia-Pacific generative AI in aerospace and defense market size was estimated at USD 0.38 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 5.06 billion by 2034. The APAC region is witnessing the fastest growth in this market, fueled by increasing geopolitical tensions in countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea, rising military expenditure, and expanding digital transformation efforts. Governments across the region are rapidly integrating AI into their defense modernization programs, focusing on autonomous systems, satellite imagery analysis, and applications in cyber defense. China, in particular, is investing heavily in liberal AI to strengthen its military edge and aerospace ambitions. Private players and defense technology startups are also contributing to the rapid AI capacity expansion in the region.
The Europe generative AI in aerospace and defense market size was accounted for USD 0.28 billion in 2024 and is predicted to surpass around USD 3.75 billion by 2034. Europe is emerging as a significant player, with countries such as the United Kingdom, France, and Germany advancing AI adoption through joint defense initiatives, NATO programs, and public-private partnerships. European Defense Funds and Horizon Europe are investing in research and technology development in AI for military and aerospace use cases. Major areas of focus include simulation-based training, cybersecurity, and AI-operated aircraft designs. Despite regulatory complications, Europe's commitment to AI and its push for defense autonomy is intensifying innovation in this sphere.
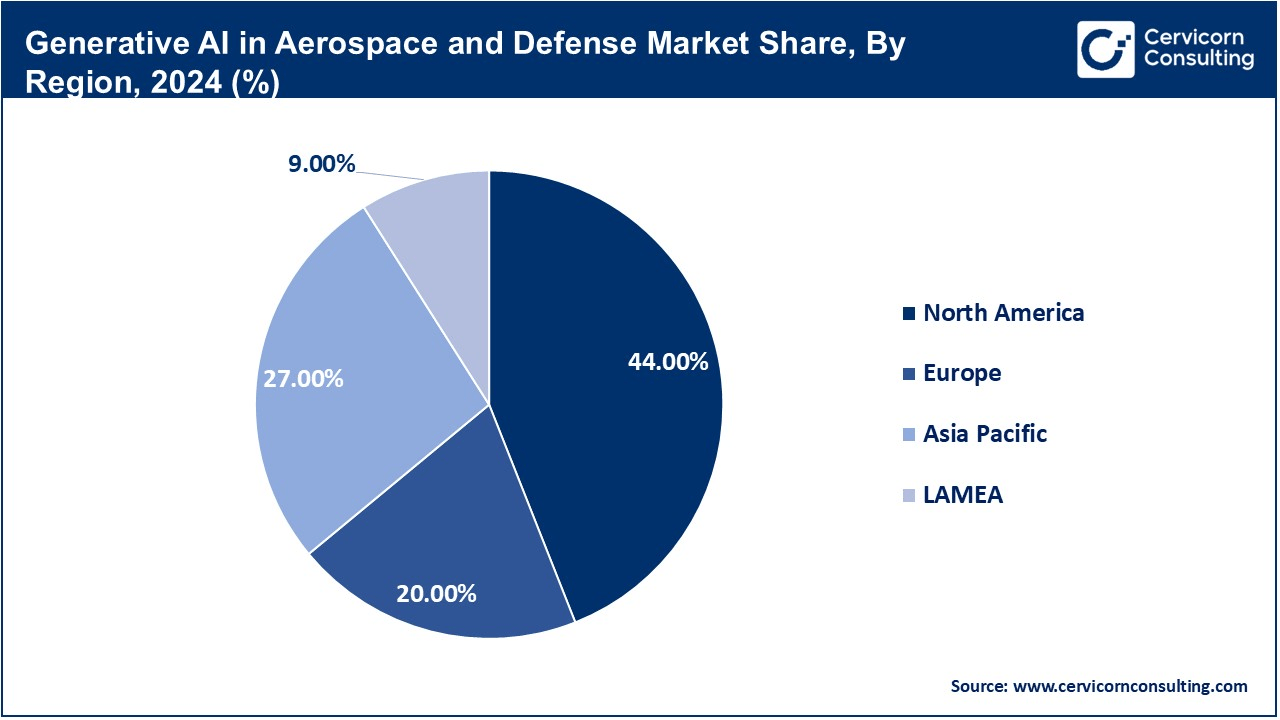
The LAMEA generative AI in aerospace and defense market size was valued at USD 0.13 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 1.69 billion by 2034. The LAMEA region is showing steady growth in generative AI adoption, although it lags behind other regions in terms of maturity. The Middle East—especially the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Israel—is leading the charge with strategic investments in defense and aerospace monitoring, threat assessment, and drone technology. Africa and Latin America are beginning to adopt AI for border security, logistics, and satellite-based applications, driven by an increasing awareness of AI's potential in international cooperation and defense modernization.
The generative AI in aerospace and defense market is segmented into components, technology, deployment mode, application, end-user, and regions. Based on component, the market is classified into software, and services. Based on the technology, the market is categorised into machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, reinforcement learning, deep learning, and generative adversarial networks (GANs). Based on deployment mode, the market is categorised into on-premises, and cloud-based. Based on application, the market is classified into autonomous vehicles and drones, simulation and training, predictive maintenance, mission planning, cybersecurity, surveillance and reconnaissance, weapon system design, satellite image analysis, and threat detection and analysis. Based on end-user, the market is categorised into defense sector (army, navy, and air force) and aerospace sector (aircraft manufacturers, space agencies and commercial space companies, and airport and airline operators).
Software: The software segment currently holds the largest market share in the generative AI in aerospace and defense market. This dominance stems from the widespread use of AI-operated platforms and modeling tools for mission planning, simulation, arms design, and autonomous systems. These software solutions enable organizations to streamline operations, enhance decision-making, and adapt to emerging hazards and requirements in real time.
Services: The services segment is projected to experience the fastest growth in the coming years. These services include consultation, integration, maintenance, and training, which are crucial for operating complex AI systems. As aerospace and defense organizations face increasing pressure for modernization, they are turning to service providers for expert deployment, adaptation, and support, fueling the section's developmental trajectory.
Generative AI in Aerospace and Defense Market Revenue Share, By Component, 2024 (%)
| Component | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Software | 65% |
| Services | 35% |
Machine Learning: The machine learning (ML) subsegment currently dominates the market due to its significant role in decision-making for both defense and aerospace operations. ML algorithms are used in everything from flight adaptation and threat detection to equipment maintenance, providing actionable insights into the supply chain.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by their ability to create high-fidelity synthetic data, simulate training environments, and test weapon systems without real-world trials. These capabilities are particularly useful in security-sensitive or data-classified landscapes, making GANs an important tool in next-generation defense strategies.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP enables AI to process and interpret human language. It is used in command systems, intelligence gathering, and threat analysis, where rapid and accurate interpretation of text and speech can affect mission outcomes. It also supports multilingual communication between concerned forces.
Computer Vision: Important in monitoring and reconnaissance, computer vision enables AI to process visual input from drones, satellites, and sensors to identify patterns, detect threats, or track targets. It plays a critical role in real-time monitoring and decision automation.
Reinforcement Learning: This type of AI learns from experience, making it suitable for dynamic military environments. It is used in unmanned systems and simulations, where AI must adapt strategies based on trial and error, such as in air combat or robotics in challenging terrains.
Deep Learning: Deep learning underpins many advanced AI systems by mimicking the human neural network. It enables complex tasks such as voice control, target identification, and radar signature analysis, which supports high-stakes missions with deep insights.
On-Premises: The on-premises segment holds the largest share due to security concerns and the need to protect classified or sensitive military data. Defense and government agencies prefer on-premises solutions that offer better control, compliance with defense protocols, and minimal delays in critical systems.
Cloud-Based: The cloud-based segment is projected to grow at the highest rate. Cloud infrastructure allows for rapid deployment of AI tools, easy collaboration among departments, and the scalability necessary to handle large datasets from drones, satellites, and autonomous systems. Commercial aerospace firms and non-classified defense operations are leading the adoption of cloud-based AI models.
Generative AI in Aerospace and Defense Market Revenue Share, By Deployment Mode, 2024 (%)
| Deployment Mode | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| On-Premises | 40% |
| Cloud-Based | 60% |
Autonomous Vehicles and Drones: The application of autonomous vehicles and drones leads the market, driven by the military's increasing dependence on unmanned systems for monitoring, logistics, and combat missions. AI enhances their operational autonomy, real-time decision-making, and situational awareness, making them indispensable in modern warfare and defense logistics.
Simulation and Training: The simulation and training subsegment is anticipated to grow the fastest. The generative AI revolution is transforming how armed forces and aerospace professionals are trained, creating hyper-ethical, adaptive training environments. This leads to more effective skill development, better preparation, and reduced training costs.
Predictive Maintenance: AI-powered maintenance forecasts failures before they occur, increasing equipment uptime and reducing lifecycle costs. This has become a priority as the age and operational readiness of the fleet grow increasingly important in modern warfare.
Mission Planning: AI simulates numerous scenarios and outcomes, helping commanders develop strategic plans with greater speed and accuracy. It improves mission success rates by accounting for real-time variables such as weather, enemy movements, and terrain.
Cybersecurity: AI protects critical systems by analyzing traffic patterns, detecting anomalies, and identifying cyber threats in real-time. In aerospace and defense, where digital systems operate on fast networks, AI-powered cybersecurity is essential.
Surveillance and Reconnaissance: Generative AI facilitates automatic monitoring, object detection, and situational awareness in real-time. It is extensively used in aerial drones and satellite systems to identify targets or suspicious activity across vast areas.
Weapon System Design: AI aids in designing and simulating weapon systems, from aerodynamics to ballistics, optimizing functionality before prototyping. Generative design reduces development cycles and enables rapid testing of multiple configurations.
Defense: The defense sector, particularly the army, dominates the end-user landscape due to its heavy investment in AI-capable technologies such as unmanned ground vehicles, battlefield analytics, and real-time mission planning. Generative AI tools enhance intelligence processing and operational efficiency.
Aerospace: The aerospace sector, specifically space agencies and commercial space companies, is expected to be the fastest-growing end-user group. As the space race intensifies, AI plays a crucial role in automating space missions, optimizing satellite communications, and enhancing spacecraft design, driven by agencies such as NASA, SpaceX, and Blue Origin.
The competitive landscape of the generic AI in aerospace and defense market is characterized by a blend of established aerospace and defense contractors, emerging AI-focused startups, and major technology firms. Key players like Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, Raytheon Technologies, and Boeing are integrating generic AI into advanced defense systems, simulation platforms, and autonomous vehicles to maintain technical superiority. Meanwhile, tech giants such as Nvidia, IBM, and Palantir are providing robust AI infrastructure and analytics solutions to enable rapid growth and deployment. Startups specializing in AI algorithms, generic advertiser networks (GANs), and simulation are also gaining traction through defense innovation programs and strategic partnerships. The market is highly dynamic, with frequent collaborations, government-backed initiatives, and an increasing focus on real-time intelligence and mission-support applications driving competition and innovation.
Market Segmentation
By Component
By Technology
By Deployment Mode
By Application
By End-User
By Region