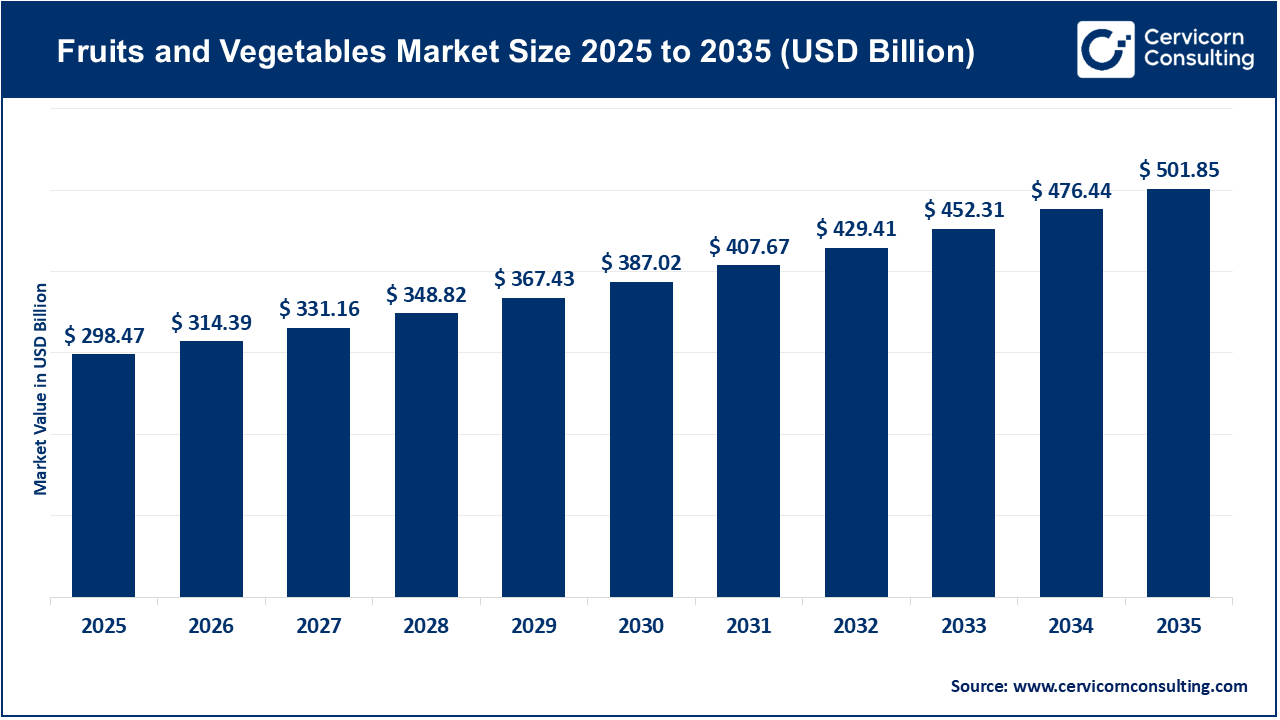
The global fruits and vegetables market size was valued at USD 298.47 billion in 2025 and is expected to be worth around USD 501.85 billion by 2035, exhibiting at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.4% over the forecast period 2026 to 2035. The growth of the global fruits and vegetable market is primarily driven by a fundamental shift in consumer dietary behavior, commonly referred to as the "Preventative Health" movement. As more scientific evidence supports that a diet high in fruits and vegetables lowers the risk of cardiovascular diseases and some cancers, encouraging consumers to replace processed carbohydrates with fresh produce, demand increases. Urbanization also pushes the market forward, as populations migrate from lower-nutrient diets toward nutrient-rich produce, which drives market growth along with a shift toward more structured and integrated commercial agri-food value chains. This transition fosters a new market relationship between urban consumers and their understanding of the value of convenient access to quality whole fruits and vegetables per capita.
From a statistical perspective, in the United States, the vegetable sector is expected to see a slight increase in fresh market vegetable production in 2023, supporting healthy volume growth in 2024. Globally, in certain crop categories, aggregate production often dominates smaller or sustainable commodity segments. For example, Turkey accounted for 55.9% of the total 375 thousand tons of global fig production as of 2024. Additionally, growth in frozen produce and e-commerce segments signals a market pivot toward convenience and waste reduction. This analysis further explores the roles of adopting precision agriculture, government infrastructure improvement schemes, and evolving trade regulations in shaping the future market outlook.
Technology Integration into Operations of Precision Agriculture
The rapid expansion of precision agriculture is a pillar of growth across the horticultural production sector. Precision Agriculture integrates Industry 4.0 technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI) applications, and remote sensors to improve production methods throughout each stage of the growing cycle. By utilizing GPS technology, seeders can now use equipment that enhances plant establishment in the soil, while remote sensors can estimate yields of horticultural crops in real-time, thereby increasing efficiency and reducing environmental impacts. The development of autonomous agricultural robots for specialty crops has the potential to significantly improve the precision of harvests by 2025, providing immediate solutions to labor shortages in labor-intensive crops and bringing the industry closer to a steady supply of high-value crops.
1. Corporate Investments in Infrastructure Are Expanding
The growth of corporate investment into increased production capacity and technology infrastructure expanded its market in 2024. For example, significant corporate investments have gone into large-scale automated greenhouses and vertical farms, particularly in regions facing extreme weather conditions. These advanced farming models enable climate-resilient production capabilities, producing 10-20 times more than traditional open-air farming. In Ukraine, there has been development and investment in strawberry vertical farms paired with shared freezing and storage warehousing. This helps stabilize supply and create price stability in a volatile market. These capabilities allow companies to overcome seasonal limitations of traditional growing practices and deliver high-quality produce to their retail partners every day.
2. Government Resilience Programs, National Security and Controlled Environment Production
Around the globe, there is increasing recognition of the horticulture sector as an important aspect of national economic security and export growth. In early 2024, the Government of Uzbekistan launched a significant initiative to expand agricultural precision across an additional 500,000 hectares, focusing on local supply chain optimization and resilience efforts. Meanwhile, in Botswana, a SWOT analysis of the horticultural sector has led to government policies aimed at broadening opportunities in wildlife and horticulture to address production and distribution constraints. Both of these countries will need government-led initiatives to attract capital and meet regulatory requirements for smallholders and large-scale producers to adopt modern, resilient agricultural practices.
3. New Cold Chain Innovations
Preservation of perishable foods remains a long-standing challenge; however, major advancements in the preservation of agri-food products occurred in 2024-2025. The integration of blockchain technology into cold chain logistics marks a new milestone for food safety and traceability, enabling real-time monitoring of temperature and humidity from farm to consumer. Organizations can also monitor that their "cold chain" is maintained from the farm gate or production facility until the consumer. The commercialized innovations in advanced freezing technologies, such as Individual Quick Freezing (IQF), will dramatically change this segment of frozen produce. IQF allows fruits and vegetables to be quickly frozen while better preserving cellular structure than frozen bulk products. Frozen produce has now become a highly viable high-quality substitute for fresh produce, especially when consumed out of season.
4. Global Trade Policy and Export Milestones
A significant milestone for the overall trade of fruits and vegetables continues to be trade liberalization and strategic agreements. In 2024, a major milestone was the implementation of the Serbia-China Free Trade Agreement (FTA), targeting the agri-food sector to improve export strategies and market access. This is an important agreement for many countries, as it creates pressure demand, expands their markets, and reduces their overall dependence on traditional regional partners. Additionally, the global market continues to adjust to stricter regulatory environments, such as the EU's reduction targets for pesticide residues. As a result, exporting countries have destinations that demand cleaner production methods to continue accessing markets that pay more for produce. These types of process regulations will serve as a beneficial change for adopting sustainable agricultural practices globally.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 314.39 Billion |
| Market Size in 2035 | USD 501.85 Billion |
| CAGR 2026 to 2035 | 5.40% |
| Dominant Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Product, Type, Distribution Channel, Region |
| Key Companies | Dole Food Company, Fresh Del Monte Produce, Chiquita Brands International, Total Produce plc, Greenyard NV, Driscoll’s, Bonduelle Group, General Mills, Taylor Farms, SunOpta, Sunkist Growers, Calavo Growers, Mission Produce, Zespri International, Naturipe Farms |
The fruits and vegetables market is segmented by region into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. Here is a brief overview of each region:
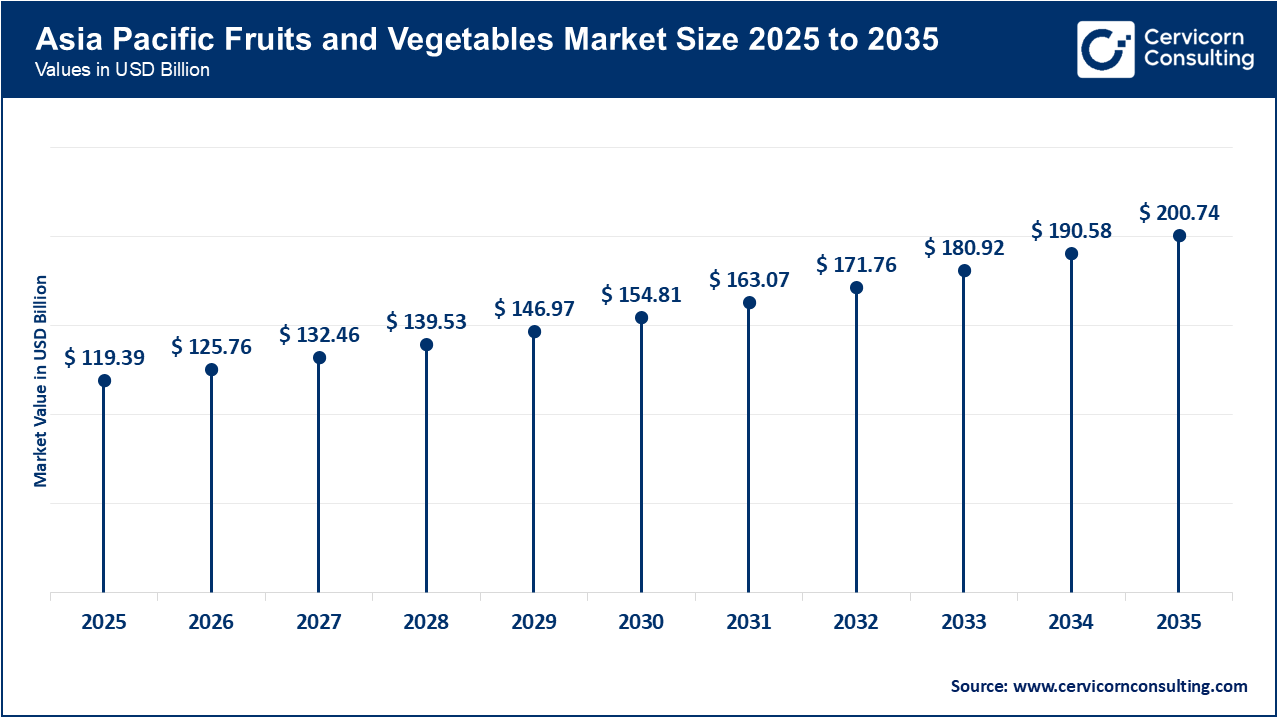
The Asia-Pacific fruits and vegetables market size was valued at USD 119.39 billion in 2025 and is predicted to grow around USD 200.74 billion by 2035. The Asia Pacific region is the largest share of the market, mainly driven by the explosion of urbanisation and the growing middle class in China and India. Rapid urbanization is decreasing wet markets in favour of organized retail and supermarkets to ensure quality control and access to global verities. The increasing economic growth in disposable incomes in the APAC region has created a high demand market for premium and "exotic" fruit integrations into the gift-giving culture of the market. Efficient e-commerce platforms connecting smallholder farmers to the national supply chain will increase their market access, reduce waste, and engage them.
Recent Developments:
The North America fruits and vegetables market size was estimated at USD 83.57 billion in 2025 and is forecasted to surpass around USD 140.52 billion by 2035. The North American market has shown very strong demand for premiumization and health-centric functional consumption. United States and Canadian consumer trends are leading the "clean label" and organic-certified high-value market segments. An exclusive driver in North America has been the integration of "Produce Prescriptions" together with the health insurance plans to subsidize fruits and vegetables to prevent long-term health and reduced diet-related chronic disease. The convenience model of fruit and vegetable purchases is driving major expansion in the pre-packaged salad kit and ready-to-eat fruit snack segments.
Recent Developments:
The Europe fruits and vegetables market size was reached at USD 68.65 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit around USD 115.43 billion by 2035. In the European market, the EU Green Deal and the "Farm to Fork" strategy represent strong species mandates that reduce pesticide usage and increase organic farming. European consumers have the highest levels of sustainability, prioritize local, and in-season produce to minimize their carbon footprint. These mandates boost demand in sustainable packaging innovation and transparency along the supply chain. Several of the larger European countries have already committed to banning plastic packaging for small-count fruits and vegetables by the years 2024-2025.
Recent Developments:
Fruits and Vegetables Market Share, By Region, 2025 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2025 (%) |
| Asia Pacific | 40% |
| North America | 28% |
| Europe | 23% |
| LAMEA | 9% |
The LAMEA fruits and vegetables market was valued at USD 26.86 billion in 2025 and is anticipated to reach around USD 45.17 billion by 2035. The LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa) region, a significant driver of the market, is driven by the professionalisation of agriculture and the expansion of export corridors. Countries such as Peru, Chile, and Kenya are focused on high-value products such as avocados, blueberries, and citrus to meet the Northern Hemisphere's year-round demand. Development of value chains and agro-processing facilities is needed to improve competitiveness in the international market, while investment in port infrastructure and development of "Green Corridors" are help these regions to overcome geographic and transit challenges.
Recent Developments:
The fruits and vegetables market is segmented into product, type, distribution channel, and region.
Vegetable segment leads the global product market due to its universal consumption across cultures, serving as a fundamental dietary component for billions of people. Major vegetables such as potatoes, onions, and tomatoes are core items consumed by billions of people as part of their daily caloric intake. In the United States, fresh market vegetable production has remained steady, with modest sales volume growth in 2023 despite rising input costs. The vegetable segment remain stable, as significant share of production is directed beyond fresh consumption into processed formats such as canning, freezing, and juice-making, to fulfill different consumer needs.
Fruits and Vegetables Market Share, By Product, 2025 (%)
| Product | Revenue Share, 2025 (%) |
| Vegetables | 54% |
| Fruits | 46% |
The fruit segment is the fastest growing in the market, supported by increasing revenue and strong consumer demand for daily consumption. Rising preference for convenient snack foods and exotic nutrient-rich items such as avocados, blueberries, and mangoes are creating demand in the fruit industry that is becoming an increasingly critical segment of the global trade. Advancements in genetic engineering and breeding programs focused on improving flavor composition, shelf life, and functional benefits, such as antioxidants. As consumer continue to reach for more natural sweetness, along with convenience to ease the demands of health and well-being.
Fresh type is the largest portion of the global vegetables and fruit market, primarily driven by sensory experience of taste, texture, and aroma, which processed alternatives struggle to replicate. Consumers also feel that fresh produce is more "natural" and healthier than other alternatives. Retailers actively support this segment by positioning fresh produce to locating their fresh departments at the entrance of any retail establishment. However, fresh produce itself is known for high perishability, meaning the supply chain must handle high amounts of waste, which researchers are trying to resolve through improved supply chain efficiency and innovation solutions such as edible coatings to extend shelf life and reduce waste.
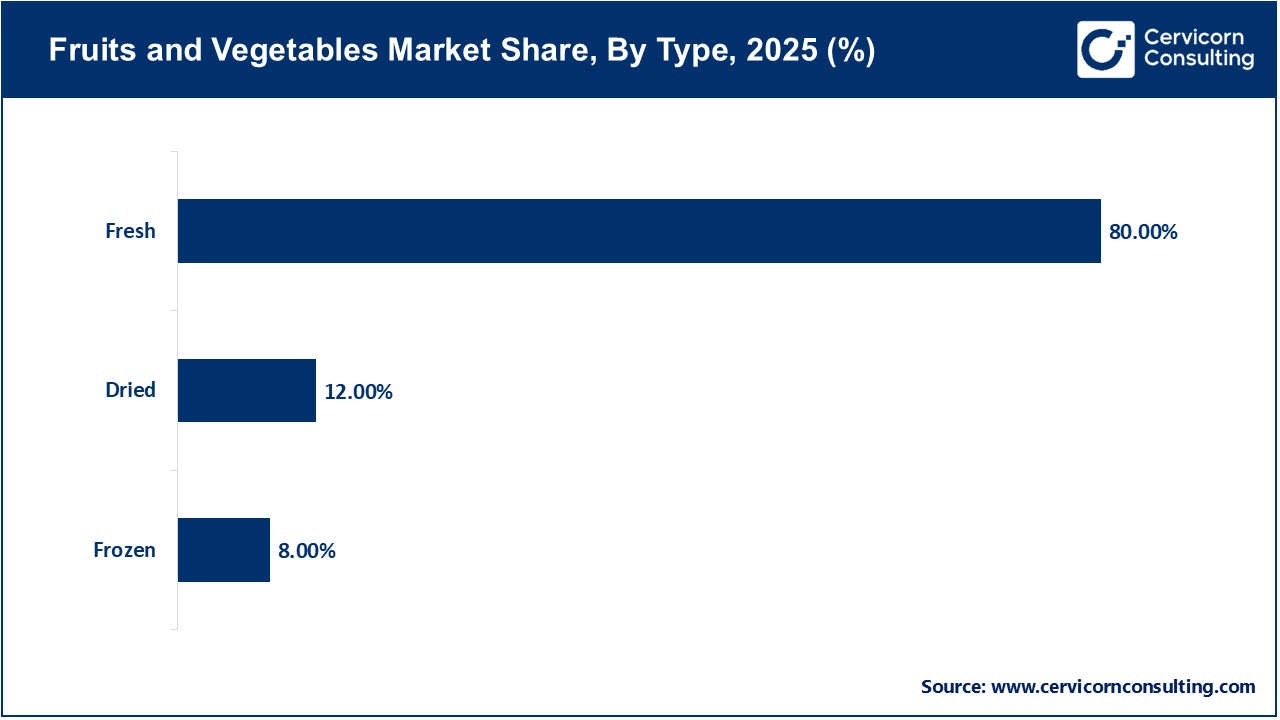
Frozen segment is the fastest-growing segment in the market because of advanced in preservation technology and changing consumer perceptions. The adoption of IQF (Individually Quick Frozen) technology enables produce is frozen at the optimal level of ripeness, helping retain essential vitamins and minerals. In addition, it is important to consider the "freshness paradox," in which the carbon footprint of air-freighting fresh berries, such as blueberries, and other crops is more problematic. Frozen produce reduces food waste, supports year-round consumption of seasonal items, and manages food costs.
Supermarkets and hypermarkets represent the primary distribution channel for the fruit and vegetable market, due to their ability to provide "sensory verification" through touch and smell, and to assess freshness while purchasing. These Large grocery stores can also take advantage of advance logistics networks for fruit and vegetables, allowing them to offer a wide variety of domestically-sourced and imported produce at a competitive price point. Additionally, many supermarkets are focused on adopting "urban agriculture" concepts, such as in-store hydroponics farming, to promote a heightened focus on freshness and sustainability, and quality, further strengthening their dominance in the market.
Fruits and Vegetables Market Share, By Distribution Channel, 2025 (%)
| Distribution Channel | Revenue Share, 2025 (%) |
| Supermarkets/Hypermarkets | 63% |
| Grocery Stores | 22% |
| Online | 10% |
| Others | 5% |
Online is the fastest growing distribution segment in the market because of the digital transformation of the grocery sector. The rise of quick commerce, where produce can be delivered in less than 30 minutes, has possibly removed the "immediate need" barrier that made online sales of produce challenging. Consumers continue to become more comfortable using a mobile app and digital finance to purchase perishables items. Curbside pickup and home delivery have now become standard, with the online segment continuing to take market share away from classic brick and mortar stores right through 2025.
By Product
By Type
By Distribution Channel
By Region