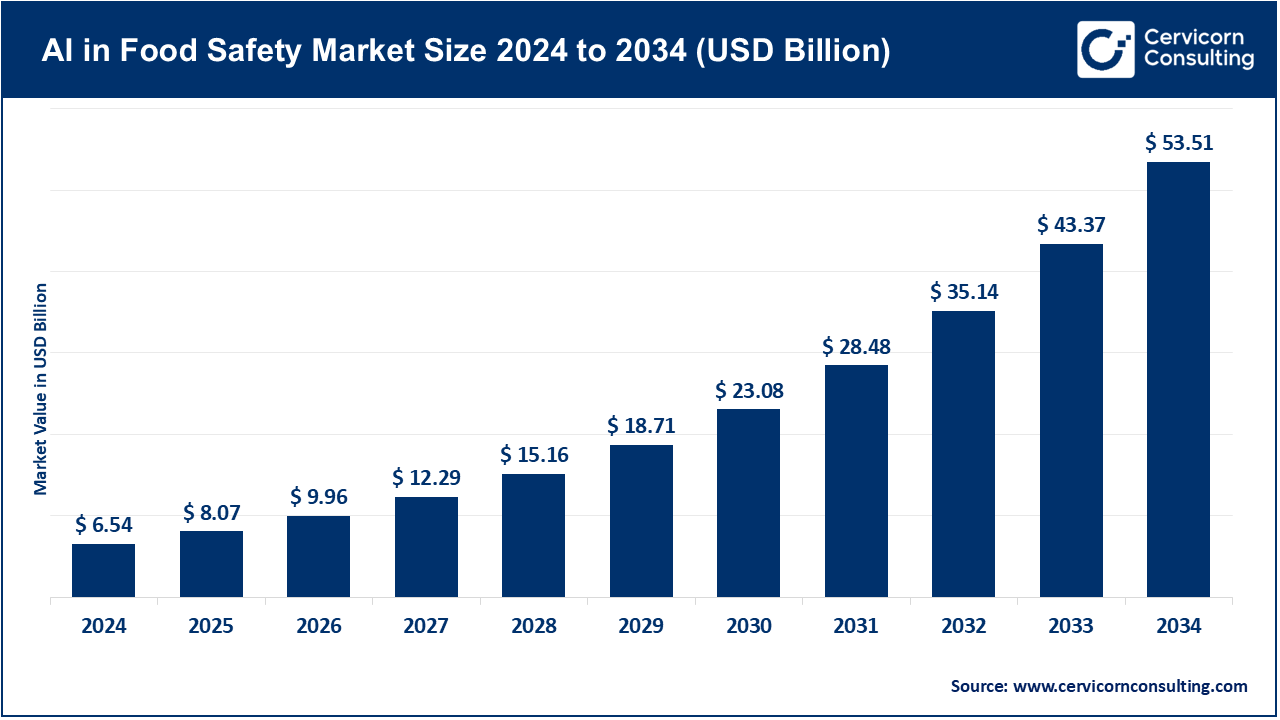
The global AI in food safety market size was valued at USD 7.20 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 53.51 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 25.1% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The food safety market growth has continued to rise, especially due to its proliferating role in food processing, retail, agricultural sectors, and regulatory environments. Amid growing fears about foodborne illness, contamination and strict international safety regulations, industries, technology providers and research organisations are seeking use of artificial intelligence on its far-reaching capability in order to assure that various lawful, efficiencies and consumer level trusts are met. Artificial intelligence is turning the food safety management industry on its head; spanning control of supply chains to quality inspection, predictive analytics to real time contamination. Rising regulatory pressure, ESG-related promises and consumer-driven demand to see a clean supply chain and safety are also catalyzing the movement towards adopting AI solutions, and are a source of strategic investment to stakeholders up and down the value chain.
What is AI in food safety?
Applied to food safety, artificial intelligence (AI) in food safety includes all artificial intelligence technologies (including machine learning, computer vision, natural language processing, and predictive analytics) to identify risks, process data, and enhance decisions made throughout the food value chain. It allows automating inspection procedures, live tracking of contamination, and effective predictions of possible risks. Being non-intrusive and scalable, with AI in Food Safety, the existing food safety frameworks can be smoothly integrated, serving as a guarantee of the identification of risks at an early stage and the maintaining of the quality. Its flexibility in application that it can do either in precision farming, compliance in the retail industry or food production in industrial proportion has been a revolutionizing tool both in 1st and 3rd world markets. AI in Food Safety is starting to become a pillar technology in the global food ecosystem following increased efficiency levels, decreased human error, and environmental footprint.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 8.07 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 53.51 Billion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 25.10% |
| Leading Region | North America |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Technology, Application, Deployment, Risk Type, Region |
| Key Companies | IBM Corporation, Microsoft Corporation, Google LLC (Alphabet Inc.), Amazon Web Services (AWS), SAP SE, Siemens AG, ABB Ltd., Cisco Systems, Inc., Schneider Electric SE, Rockwell Automation, Inc., Tata Consultancy Services (TCS), Infosys Limited, Bosch GmbH, Neogen Corporation, Kellton Tech Solutions Ltd. |
Machine and Deep Learning: The machine and deep learning segment has accounted for a highest revenue share. AI-based methods that can use quite big data and learn patterns to classify or predict food safety risks include machine learning and deep learning. The models find wide application in detection of contamination and food quality monitoring. The University of South Australia researchers in August 2025 revealed how deep learning combined with hyperspectral imaging can identify mycotoxin contamination in grains and nuts with greater than 90 % accuracy exemplifying the essential part they play in the safeguarding of food.
Computer Vision: With Computer Vision, AI-based models can analyze images and videos to automate the checks on the quality and better the quality, hygiene and contamination of food. It eliminates coding optically part. In the month of August 2025, the University of South Australia used the combination of computer vision with hyperspectral imaging to detect non-invasively the presence of the aflatoxin B1 contamination in nuts and grains and provided real-time solutions to contamination threats throughout the food industry.
Predictive Analytics: Predictive Analytics can be described as using past and current data to predict potential food safety risks before they can take place. It assists in prevention of active outbreaks and contamination. A study published in March 2023 in Science Advances demonstrated how AI-driven predictive analytics might be able to predict food insecurity crises through analysis of millions of news articles, demonstrating its possibility in predicting early warning signs of global food system failures.
Robotics & Automation: Robotics and Automation use AI to combine machine functionality to perform the tasks of food handling, preparation, and inspection, with precision and particularly high standards of hygiene. They enhance efficiency through a reduction of a human presence in the sensitive processes. Burgerbots, a restaurant in Los Gatos, California, displayed the effectiveness of the AI-driven automation in the food industry that opened its doors in May 2025, offering the robotic arms produced by ABB that managed to make a single burger within 27 seconds.
Contamination Detection: Contamination Detection is the application of AI in detecting biological, chemical, or physical contamination in food products within the shortest possible time with precision. It makes food safe because it decreases the use of manual sampling. In August 2025, South Australian researchers demonstrated the application of hyperspectral imaging equipped with AI having the potential to detect mycotoxin-contaminated grains at industrial levels, a revolution in industrial-scale non-invasive and on-the-fly contamination diagnosis.
Quality Control & Inspection: The quality control and inspection segment has accounted for a highest revenue share. Quality control and Inspection uses AI to verify the presence of defects in foods, freshness of food, and quality conformance to the processing lines. It automates an otherwise manual and error-prone exercise. In January 2021, scientists trained support vector machines and YOLO v3 on bananas to classify bananas on a conveyor belt and achieved 96 percent accuracy, proving the potential of AI applied on the automation of food inspection.
Supply chain monitoring: Supply Chain Monitoring is another application of AI that is used to monitor a food item that is being manufactured to the distribution levels in retail and store to meet criteria of being traceable, fresh, and safe during each step in the supply chain. It aids in preventing risks of spoilage and fraud. By June 2025, the industry publications indeed noted the first steps in the implementation of the AI-powered supervision tools being employed by the global food processors that aimed at maintaining the control over the temperature-based safety of the logistics processes and negating the threats of the contamination throughout the distribution chains.
Food Fraud Detecting: Food Fraud Detection is an AI-based method to reveal false labelling, contamination or replacement of food items. It creates trust because of being non-phony and regulatory. In July 2025, the U.S. FDA released its AI bot called Elsa aimed at detecting labeling inconsistencies and fraudulent packing of foods, so that regulators can move much quicker in relation to fraud threats
On-Premises: On-Premises deployment The on-premises deployment implies that the AI systems are put on a local server and within the company infrastructure, and thus control over data and faster reaction times are ensured. The model is appropriate in sensitive operations that need privacy. By January 2021, a study has been performed which showed an on-premises mobile inspection system grading bananas on a conveyor belt where 96% accuracy could be realized without resorting to external cloud servers.
Cloud-Based: The cloud-based segment has accounted for a highest revenue share. Cloud-Based deployment is the use of AI platforms via remote servers to enable scale up, and remote control with the ability to tie to IoT systems. It facilitates the cooperation in large food networks. As an example of the benefits of cloud computing, in July 2025, the FDA deployed what it calls an AI tool called “Elsa”, which is cloud-based and assists regulators in evaluating safety reports, to flag inconsistencies and accelerate recalls.
Hybrid: Hybrid deployment involves an on-premises infrastructure along with cloud capabilities to provide services that offer both control and scalability to food safety applications. This strategy can be applicable particularly when a company deals with sensitive information that requires remote tracking. AMD has contributed more personalities that consistently orchestrate the goals of internal control and cloud-powered analytics-based supply chain monitoring by adopting hybrid AI systems among some European food processors in 2024.
Biological Hazards (Bacteria, Viruses): The biological hazards segment has generated highest revenue share. Biological Hazards These are microorganisms such as Salmonella and E. coli, viruses that cause illness and infection in food. It is in discovering these threats before conventional testings that the assistance of AI comes in. In September 2024, scientists in Japan developed an AI program that might be used to analyze food samples to identify the presence of E. coli contamination in several minutes, which is much quicker than the standard laboratory test.
Pesticides, Allergens (Chemical Hazards): Chemical Hazards manifest in the form of toxic substances such as pesticide residues, toxins and allergens that can be found in food. Chemical safety management is observed and forecasted by using AI systems. In October 2024, a European Union funded initiative involved AI-based sensors to identify residue of pesticides in fresh products to raise food safety compliance levels in agricultural exports.
Foreign Objects (Physical Hazards): Foreign materials found in food produced accidentally are known as Physical Hazards and they include glass, plastic, or metal pieces. AI systems, which have been used in the vision system, aid in the detection of such contaminants in the processing phase. In March 2025, scientists created a kind of Vision Transformer (ViT) model with the aid of hyperspectral imaging, able to detect a foreign object in pork belly samples with the accuracy of an industrial apparatus.
Fraudulent Practices (Mislabeling, Adulteration): Fraudulent Practices involve the deliberate misrepresentations to food products, e.g. through mislabeling and addition of non-declared ingredients. Such fraud is increasingly being detected on scale with the aid of AI. The FDA launched its AI system called “Elsa” (launched in July 2025) to identify discrepancies in the labelling of packaged foods and thus act more promptly to prevent labeling inaccuracies and fraud.
The AI in food safety market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region.
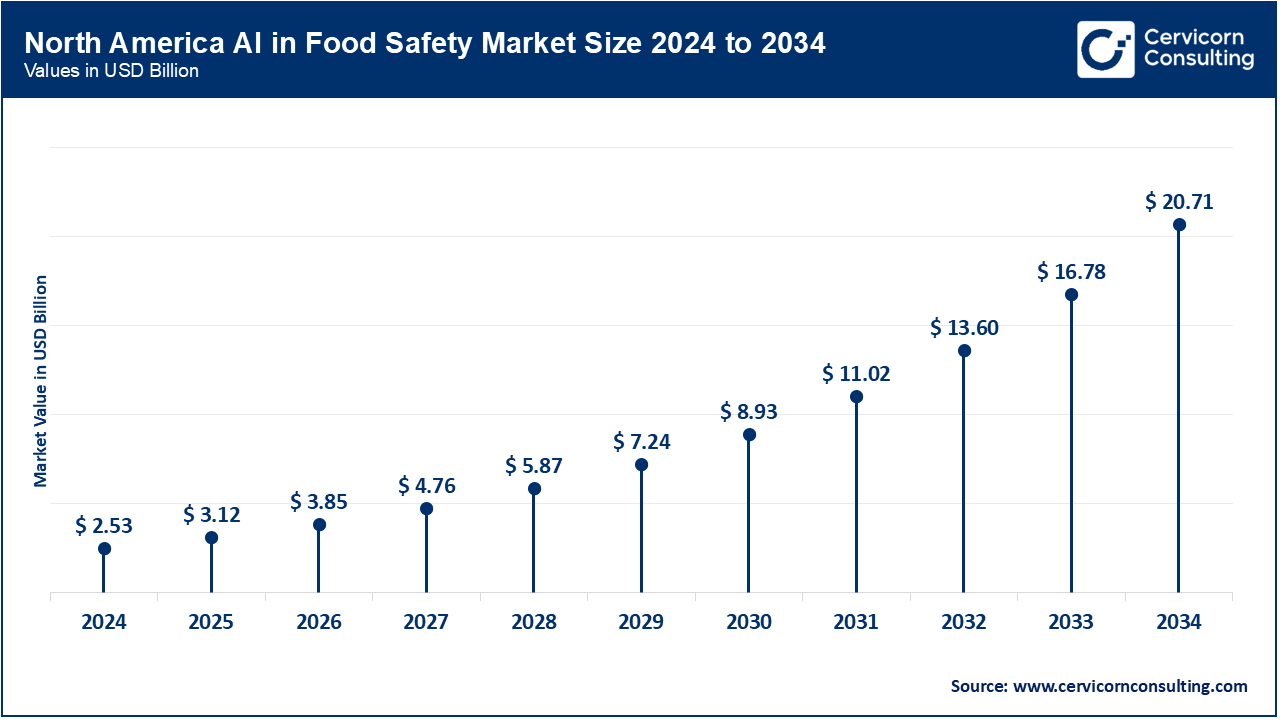
Strict food safety regulations and high rate of automation in the food processing sector are factors leading to mushrooming of the market in North America. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) of the U.S. has been promoting AI-based systems of traceability and monitoring to enhance transparency in the supply chain. In February 2024, IBM and Tyson Foods teamed up to implement AI-powered predictive food safety solutions at their locations across the United States. Canada also has plans to invest in the idea of contamination detection technologies based on AI in the use of meat and dairy. The trend in recalls within the U.S. is propelling the increase in the adoption of AI by industries. The sourcing based on ESG is further boosting the implementation of AI in safe and sustainable food management.
The Europe has been growing due to the effective implementation of food safety legislation including the ones like EFSA standards and the Farm-to-Fork approach in EU. Nations such as Germany, France, and the UK are embracing AI in food production for the detection of contamination in foods and predictive analytics of food. In March 2024, Nestle reported a Switzerland-based collaborative where it would commercialize AI-powered quality control of food and beverages. France and Italy are making investments in allergen detection consumer health through AI. Transnational cooperation in Europe is promoting the harmonisation of AI standards in terms of food safety. There are startups that are being sponsored by EU research programs working on the basis of AI-based monitoring and risk prevention.
In food safety, Asia-Pacific region is experiencing a considerable mount of AI demand all because of an increasing urban population, escalating consumption of packaged food and high cases of contamination. Executing food testing and traceability with the use of AI seems to be heading China, India, and Japan. The Japanese Ministry of Agriculture initiated funding on the AI-based detection systems to detect pathogens in seafood to be exported in May 2024. One of the Chinese initiatives has been to expand on smart food inspection programs involving AI so that international trade standards can be met. Startups in India are developing AI-infused cold chain tracking system that can avoid wastage. Governments in the region are facilitating the trainings of SMEs to implement solutions of AI in food safety.
The LAMEA is rising slowly as a result of increased food exports and governmental investments, as well as cooperations with international technology suppliers. In April 2024, Brazil, one of the epicenters of food exporting, announced AI-powered surveillance in meatpacking plants as part of the measures to comply with the U.S. and EU regulators. In the Middle East, Saudi Arabia is implementing AI in the identification of food contamination as a vision 2030 solution. South Africa and Kenya are using AI-powered technologies in dairy and agriculture to decrease foodborne illnesses. The Gulf nations are placing investments in the transparency of its food supply chain through Artificial intelligence. In the food and beverage sector, local-global partnerships are aiding the increased pace of AI use.
Market Segmentation
By Technology
By Application
By Deployment
By Risk Type
By Region